Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electricity 1
Electricity 1
Uploaded by
krichenkyandex.ruOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Electricity 1
Electricity 1
Uploaded by
krichenkyandex.ruCopyright:
Available Formats
ELECTRICITY - 1
ELECTRICROSTATICS
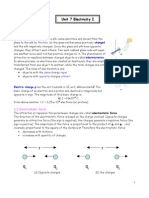
Electric Charge: Q [Coulombs]
(electrons, protons, charge carriers – ions, particles)
Electrostatics – interaction between stationary electric charges
=>> like charges repel / opposite charges attract
Coulomb’s Law (interaction between stationary charged particles)
Electrostatic (Coulomb) Force:
q1 q 2
⃗
F =k 2 [N],
r
Coulomb constant k ≈ 9.0 ×10
N m2
9
C2
;
[ ]
Electrostatic Field: (produced by a charge / set of charges)
⃗
F
⃗
E = [N/C = V/m]
q0
force per unit charge exerted on a small positive test charge (q0) placed at a test point.
E-filed lines start on positive charge and terminate on negative charge
Transfer and storage of charge: charging / discharging
Common conductors: metals; Insulators (plastics, distilled water, air…)
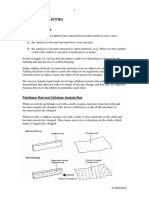
Charging by friction
rubbing different insulators:
loss / gain of electrons
building up of total (+ / - ) electrostatic charge
Electrostatic phenomena: transfer of electrons by friction
ELECTRICITY - 1
Insulator material with weaker electron bonds loses electrons
Uses of electrostatic charges, Potential dangers of electrostatic charges
e.g. in photocopiers and inkjet printers Aircraft flying through the air =>> friction causes buildup of static
electricity.
After landing => risk of discharge to
earth as a spark or flash of electricity
Can cause an explosion during
refueling.
The plane has to be earthed
(grounded) with a conductor as soon
as it lands.
FLOW OF CHARGE
Electric current is the rate of flow of charge I = Q / t [C/sec = Amp]
Solid metallic conductors =>> Net flow of electrons (negatively charged)
Voltage (Potential difference) drives the current
Power = VI [Watts]
Energy = Power * time [Joules]
=>> Energy = Q V
=>> Volt = Joule / Coulomb
Voltage is the energy transferred per unit charge passed
ELECTRICITY - 1
Test Problem #7 (4PH1_January 2020 (R) QP1):
(b) When the van der Graaff generator is fully charged,
it stores 2.9 × 10–8 C of charge.
(i) State the formula linking charge, current and time. (1)
(ii) The charge on the generator discharges through the air as a spark.
The charge takes a time of 0.68 ms to leave the generator.
Calculate the mean (average) current in the air. (3)
(ii) State the formula linking energy transferred, voltage and charge. (1)
(iii) Calculate the energy transferred to an electron when it passes through a
voltage of 150 kV. [charge of electron = 1.6 × 10–19 C]
(3)
ELECTRICITY - 1
Test Problem #4 (4PH1_January 2020 QP2):
ELECTRICITY - 1
You might also like
- Chapter 8 - Properties of Electric Charges-LatestDocument16 pagesChapter 8 - Properties of Electric Charges-Latestsameery86No ratings yet
- Ams6419 Rev JDocument10 pagesAms6419 Rev JJonicus-DextoreNo ratings yet
- Test Series 15 Dec 2023Document8 pagesTest Series 15 Dec 2023sachin724787No ratings yet
- Electric ChargeDocument3 pagesElectric ChargeAnn Margarette MoralesNo ratings yet
- ELECTRICAL Quantities: Friction and ChargeDocument11 pagesELECTRICAL Quantities: Friction and ChargeNick MillerNo ratings yet
- Ch-1 Basic Elctrical Enginnering Paramters RevisedDocument39 pagesCh-1 Basic Elctrical Enginnering Paramters Revisedtemesgen adugnaNo ratings yet
- Intro To Electrical EngineeringDocument52 pagesIntro To Electrical EngineeringAerdia100% (1)
- PTE - 02 Sejarah ProfesiDocument56 pagesPTE - 02 Sejarah ProfesiHema SaputraNo ratings yet
- JNTUA JNTUH JNTBasic Electrical and Electronics Engineering BEEE NoteDocument93 pagesJNTUA JNTUH JNTBasic Electrical and Electronics Engineering BEEE Notejiyija2465No ratings yet
- Document 11Document5 pagesDocument 11Rishi Prakash MohapatraNo ratings yet
- 2nd Year Short Question Answers From Within ChaptersDocument40 pages2nd Year Short Question Answers From Within ChaptersZain ZuhabNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Static Electricity and Conduction (24 Slides)Document24 pagesTopic 2 Static Electricity and Conduction (24 Slides)crye shotNo ratings yet
- Ec1semi2223 Chapter1 NurmizapdfDocument61 pagesEc1semi2223 Chapter1 NurmizapdfYathavan A/l KalaichlvanNo ratings yet
- Bej10303 Electric Circuit I: Dr. Nur Anida Binti JumadiDocument61 pagesBej10303 Electric Circuit I: Dr. Nur Anida Binti JumadiDaneshSathaNo ratings yet
- Static Electricity ConductionDocument21 pagesStatic Electricity ConductionMirza ImanNo ratings yet
- Circuits 1Document13 pagesCircuits 1Larios, Miguel Angelo S. -CEANo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Atoms, Charge, Voltage and CurrentDocument51 pagesLecture 2 - Atoms, Charge, Voltage and CurrentRa JallowNo ratings yet
- 1 - Electrostatics - Theory - PDF Module-4Document28 pages1 - Electrostatics - Theory - PDF Module-4Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- SP1402 Exam1 NotesDocument17 pagesSP1402 Exam1 NotesKamaraman TVeNo ratings yet
- Electricity NotesDocument34 pagesElectricity Noteskavin shahNo ratings yet
- Electric FieldsDocument21 pagesElectric FieldsMark Lorenz BertulfoNo ratings yet
- Physics IIDocument2 pagesPhysics IIbagongstorageNo ratings yet
- Electric ChargeDocument34 pagesElectric Chargeglaizamaeodinario5No ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument1 pageElectricityShajeena Abdul NasarNo ratings yet
- Electric Charge, Coulomb's Law, and Electric Fields: Mr. Joseph de Mata General Physics 2Document68 pagesElectric Charge, Coulomb's Law, and Electric Fields: Mr. Joseph de Mata General Physics 2Nathalia MeiNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuit Fundamentals: Essential QuestionDocument15 pagesElectric Circuit Fundamentals: Essential QuestionMOBILEE CANCERERNo ratings yet
- Electrical Interaction IDocument7 pagesElectrical Interaction Iapi-19505025No ratings yet
- ElectroDocument28 pagesElectronishant kumarNo ratings yet
- 14 - 15 - H2 - COE - Notes Final PDFDocument18 pages14 - 15 - H2 - COE - Notes Final PDFeltytanNo ratings yet
- 3rd Quarter Examination ReviewerDocument4 pages3rd Quarter Examination ReviewerBruhNo ratings yet
- 01 Chapter-12Document21 pages01 Chapter-12royalcamp2005No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electrical CircuitDocument19 pagesFundamentals of Electrical CircuitSamuel TafereNo ratings yet
- NMAT - Electricity and MagnetismDocument56 pagesNMAT - Electricity and MagnetismPauleen Trisha SamparaniNo ratings yet
- EST 130 BEE Module 1Document94 pagesEST 130 BEE Module 1Gayathri VijayachandranNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Electric Charge PDFDocument21 pagesChapter 1 Electric Charge PDFRessyl Mae PantiloNo ratings yet
- Electric Forces and Electric FieldsDocument23 pagesElectric Forces and Electric FieldsbrianhguyNo ratings yet
- Charge and Electrical VariableDocument44 pagesCharge and Electrical VariableNeverson RusipinNo ratings yet
- Unit: Electricity: Chapter: ElectrostaticsDocument81 pagesUnit: Electricity: Chapter: Electrostaticsshivanshsagar2No ratings yet
- Electric Charge and Electric FieldDocument76 pagesElectric Charge and Electric FieldGladys Lambayong100% (1)
- DVS PhysChem 6 2011Document35 pagesDVS PhysChem 6 2011Jake GaynonNo ratings yet
- Electric Charges & Fields. Full Notes21Document15 pagesElectric Charges & Fields. Full Notes21DHANUSH PATEL .MNo ratings yet
- Electricity and MagnetismDocument22 pagesElectricity and Magnetismkhrisannmiller12No ratings yet
- HSSRPTR - Splash +2 Physics 2022 FinalDocument52 pagesHSSRPTR - Splash +2 Physics 2022 Finalbijijiju8129No ratings yet
- IIPUC Physics - Passing PackageDocument59 pagesIIPUC Physics - Passing PackagelikhithNo ratings yet
- KDU - EE1102 - 2a - DC - Circuit - Calculations - SlidesFeb2021-Verbal 1Document30 pagesKDU - EE1102 - 2a - DC - Circuit - Calculations - SlidesFeb2021-Verbal 1HimayaNo ratings yet
- TextDocument15 pagesTextafiqhzzhrNo ratings yet
- ABE 112 ReviewerDocument2 pagesABE 112 ReviewermikotaktNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuit Lec1Document12 pagesElectric Circuit Lec1Mohammed EmadNo ratings yet
- Hssreporter - Com - +2 Physics Full Chapters 2024Document169 pagesHssreporter - Com - +2 Physics Full Chapters 2024presannamNo ratings yet
- Physics 12th Full NOTESDocument170 pagesPhysics 12th Full NOTESKiranshreeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Electrical EngineeringDocument55 pagesIntroduction To Electrical Engineeringksreddy2002No ratings yet
- Electrostatics Summary Term 1Document21 pagesElectrostatics Summary Term 1Vigneshwaran K-1121No ratings yet
- Unit 7 Electricity IDocument9 pagesUnit 7 Electricity Itwy113No ratings yet
- Electric Charges and Fields Class 12 Notes Chapter 1Document6 pagesElectric Charges and Fields Class 12 Notes Chapter 1RajakumaranNo ratings yet
- AP10006 Physics II: ElectricityDocument38 pagesAP10006 Physics II: Electricity白卡持有人No ratings yet
- EC CH 1-3Document7 pagesEC CH 1-3Stephanie M. BernasNo ratings yet
- Mid 02 IEC Charge V I R PDocument34 pagesMid 02 IEC Charge V I R Pshawanashimu09No ratings yet
- +2 Physics Full Chapters 2024-2025 - Hssreporterâ ComDocument176 pages+2 Physics Full Chapters 2024-2025 - Hssreporterâ ComNeethaNo ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterNo ratings yet
- Waves 3Document6 pagesWaves 3krichenkyandex.ruNo ratings yet
- Astrophysics 2Document7 pagesAstrophysics 2krichenkyandex.ruNo ratings yet
- Astrophysics 3Document4 pagesAstrophysics 3krichenkyandex.ruNo ratings yet
- Electricity 2Document5 pagesElectricity 2krichenkyandex.ruNo ratings yet
- Forces and Motion 1Document4 pagesForces and Motion 1krichenkyandex.ruNo ratings yet
- The Oriental Chemical Works PVTDocument3 pagesThe Oriental Chemical Works PVTAgniva DuttaNo ratings yet
- BoB FinalDocument34 pagesBoB FinalBob AndrewsNo ratings yet
- Sucrose GradientsDocument1 pageSucrose GradientsSusan ZhouNo ratings yet
- DioriteDocument13 pagesDioriteGantang NugrahaNo ratings yet
- Computers and Geotechnics 2017 PDFDocument24 pagesComputers and Geotechnics 2017 PDFAyman ABEDNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Chapter 3Document32 pagesChemistry Chapter 3amit_idea1No ratings yet
- MMUP Exam QuastionsDocument2 pagesMMUP Exam QuastionsBalaji NaikNo ratings yet
- Lab 9 - Fluid Properties (Viscosity)Document22 pagesLab 9 - Fluid Properties (Viscosity)Amanda AmaniNo ratings yet
- Deformable - Chapter 5Document21 pagesDeformable - Chapter 5Charlotte FerriolNo ratings yet
- FREEMIUM - 11th JEE - Hinglish - Valence Bond Theory - 53Document35 pagesFREEMIUM - 11th JEE - Hinglish - Valence Bond Theory - 53Rathana sabpathyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Mechanical Properties of SolidsDocument49 pagesChapter 9 Mechanical Properties of SolidsNitish MehraNo ratings yet
- Combined Footing Design To BS8110: SolutionDocument6 pagesCombined Footing Design To BS8110: SolutionMAGED MOHMMED AHMED QASEMNo ratings yet
- Veetagrout V71 Information Sheet v1Document1 pageVeetagrout V71 Information Sheet v1Alirio Ramirez VelasquezNo ratings yet
- Disain Kolom-Segui PDFDocument4 pagesDisain Kolom-Segui PDFulalaNo ratings yet
- Folha de Dados - VDM Metals - Magnifer 7904Document16 pagesFolha de Dados - VDM Metals - Magnifer 7904LowanNo ratings yet
- IFEM Ch14Document14 pagesIFEM Ch14Othman BouazizNo ratings yet
- 반도체소자 기말 (2022)Document8 pages반도체소자 기말 (2022)지눈No ratings yet
- Effect of PolypropyleneDocument18 pagesEffect of PolypropyleneBenharzallah KrobbaNo ratings yet
- Quantum Confinement III Quantum Wires An PDFDocument383 pagesQuantum Confinement III Quantum Wires An PDFpuceiroaleNo ratings yet
- Shape Memory AlloysDocument20 pagesShape Memory Alloysaqsa imranNo ratings yet
- Bend Test and Ductility Test 1Document25 pagesBend Test and Ductility Test 1Novie Dave EstremaduraNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of An Electronic On-Load Tap Changer Distribution Transformer For Automatic Voltage RegulationDocument12 pagesAnalysis and Design of An Electronic On-Load Tap Changer Distribution Transformer For Automatic Voltage RegulationRaphael NgenyiNo ratings yet
- Brochure 10 FINALDocument2 pagesBrochure 10 FINALRodel PelimianoNo ratings yet
- Department of ChemistryDocument15 pagesDepartment of ChemistryWorcPrimerNo ratings yet
- BD 90/05Document25 pagesBD 90/05ferasalkamNo ratings yet
- Las Interacciones Entre Las Proteínas de La Leche y Goma de Gelano en Geles AcidificadasDocument10 pagesLas Interacciones Entre Las Proteínas de La Leche y Goma de Gelano en Geles AcidificadasJoel PeñaNo ratings yet
- Yield Line TheoryDocument18 pagesYield Line TheoryKartika PurwitasariNo ratings yet