Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 viewsChapter 3 Part 2
Chapter 3 Part 2
Uploaded by
joysteven88This document contains the results of a plagiarism check on a content sample that found 0% plagiarized content. It also includes survey results from 137 students about parental involvement in their education. The results show that most students were between 13-15 years old, more were boys than girls, most had parents who were self-employed, and most agreed that parental control positively impacts student achievement.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- General PsychologyDocument4 pagesGeneral PsychologyDaniel C. Dequiña100% (1)
- Chapter 4-5 RemedialDocument19 pagesChapter 4-5 RemedialTata Duero Lachica100% (4)
- PCS-921 - X - Instruction Manual - EN - Overseas General - X - R1.02 - (EN - FZBH5101.0086.0003) PDFDocument276 pagesPCS-921 - X - Instruction Manual - EN - Overseas General - X - R1.02 - (EN - FZBH5101.0086.0003) PDFLeister Carneiro TheodoroNo ratings yet
- 3 IS Module 5Document11 pages3 IS Module 5Hiezeyl Ymana GuntangNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three Research Methodology 3.1 Research DesignDocument14 pagesChapter Three Research Methodology 3.1 Research DesignepocyberNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Background Information On RespondentsDocument6 pages4.1 Background Information On RespondentsManfred GithinjiNo ratings yet
- Analysis & Interpretation of DataDocument42 pagesAnalysis & Interpretation of DataSaili SarmalkarNo ratings yet
- A Study To Assess The Knowledge and Educate Regarding Immunization in Children Amongst Mother in A Community SettingDocument20 pagesA Study To Assess The Knowledge and Educate Regarding Immunization in Children Amongst Mother in A Community SettingAbhishek Rajoria100% (2)
- Chapter - 4 Data Analysis and InterpretationDocument36 pagesChapter - 4 Data Analysis and InterpretationNagireddy KalluriNo ratings yet
- Statement of The ProblemDocument15 pagesStatement of The ProblemJoel Mangallay100% (1)
- Chapter 5Document4 pagesChapter 5joysteven88No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Finale - 071349Document8 pagesChapter 4 Finale - 071349Amman GuntingNo ratings yet
- Empowering Potencial Leaders: Effects On Building Leadership CapacityDocument41 pagesEmpowering Potencial Leaders: Effects On Building Leadership CapacityRochelle May CanlasNo ratings yet
- Chapter IIIDocument7 pagesChapter IIIGrey SonNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 4 and 5Document20 pagesCHAPTER 4 and 5Miziey ZainieNo ratings yet
- Data Gathereddiscussion Areis Divided Presented, Which Are The Following Artroblem - Artroblem ArtroblemDocument13 pagesData Gathereddiscussion Areis Divided Presented, Which Are The Following Artroblem - Artroblem ArtroblemDoneva Lyn MedinaNo ratings yet
- ResultsDocument18 pagesResultsJohn Elton PilarNo ratings yet
- Table ParametricDocument15 pagesTable ParametricDanniella GalleroNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three Research Methodology 3.1Document27 pagesChapter Three Research Methodology 3.1Joseph JboyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document8 pagesChapter 4hamidahmkhalid44No ratings yet
- CopyeditDocument13 pagesCopyeditNisa ShabrinafiNo ratings yet
- Non TeachingDocument30 pagesNon TeachingEdwin Okoampa BoaduNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document17 pagesChapter 4Rico Jon Hilario GarciaNo ratings yet
- EDITED Chapter 3 and 4Document47 pagesEDITED Chapter 3 and 4Raymond AbanesNo ratings yet
- Demographic Profile of Pe Teachers and Their Motivational Approaches Across Secondary Schools in SurallahDocument38 pagesDemographic Profile of Pe Teachers and Their Motivational Approaches Across Secondary Schools in SurallahMericel Dela Rosa EstorninosNo ratings yet
- Data AnalysisDocument6 pagesData Analysisapi-250134758No ratings yet
- Chapter II ThesisDocument5 pagesChapter II ThesisJheiczhietoot KibasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document3 pagesChapter 5hamidahmkhalid44No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Method of ResearchDocument28 pagesChapter 2 Method of ResearchChristian Mendoza MusicNo ratings yet
- Presentation, Analysis, and Interpretation of Data: 1. Respondent's ProfileDocument5 pagesPresentation, Analysis, and Interpretation of Data: 1. Respondent's ProfilefgfgfNo ratings yet
- Kabanata 3Document18 pagesKabanata 3Mark CastroNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER-5Document3 pagesCHAPTER-5jonnahmaemaurNo ratings yet
- Amoni and Final Chapter 4 Results and Discussion RecoverDocument12 pagesAmoni and Final Chapter 4 Results and Discussion Recovergoldenskydrive1No ratings yet
- Running Head: SPSS Research ReportDocument23 pagesRunning Head: SPSS Research ReportJacoby23No ratings yet
- Descriptive Analysis: Respondent Demographic ProfileDocument22 pagesDescriptive Analysis: Respondent Demographic ProfileAbygail ManaloNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four AnnethDocument15 pagesChapter Four AnnethRaytone Tonnie MainaNo ratings yet
- 103690S15Document49 pages103690S15steveparker123No ratings yet
- Competency 3 Table 1 5Document7 pagesCompetency 3 Table 1 5roshell IbusNo ratings yet
- Kaylon Nelson 5T1 Prefect SbaDocument6 pagesKaylon Nelson 5T1 Prefect SbaKaylon NelsonNo ratings yet
- 271 Assign 1 - Jan2013Document3 pages271 Assign 1 - Jan2013Mark LeonardNo ratings yet
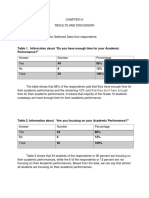
- Table 1. Information About "Do You Have Enough Time For Your Academic Performance? "Document5 pagesTable 1. Information About "Do You Have Enough Time For Your Academic Performance? "Katrina CyberNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 (RDM)Document8 pagesChapter 3 (RDM)Julliana BabilaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument11 pagesUntitledMark Rhyan AguantaNo ratings yet
- Sample AnalysisDocument23 pagesSample AnalysisGopaul UshaNo ratings yet
- J. L. Depaynos, MA AS Math 100Document18 pagesJ. L. Depaynos, MA AS Math 100Jane PadillaNo ratings yet
- Fully Corrected Chapters 4 & 5Document21 pagesFully Corrected Chapters 4 & 5Iyobosa OmoregieNo ratings yet
- Draft in Educ 12Document11 pagesDraft in Educ 12Gracy PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Age 16 Child Behavior Checklist External Site MM FinalDocument6 pagesAge 16 Child Behavior Checklist External Site MM FinalSammy FilipeNo ratings yet
- INPUT-effectiveness of Virtual LaboratoryDocument21 pagesINPUT-effectiveness of Virtual Laboratorynena marie evalaroza100% (1)
- Hypertension Elder Based On Self Care Orem Theory Perspective in RW 03 Wonokromo SurabayaDocument7 pagesHypertension Elder Based On Self Care Orem Theory Perspective in RW 03 Wonokromo Surabayaliga afseliaNo ratings yet
- Presentation, Analysis and Interpretation of DataDocument9 pagesPresentation, Analysis and Interpretation of DataCorin Ahmed CorinNo ratings yet
- Ma-Sampletest-Gr4 2010-13-2Document16 pagesMa-Sampletest-Gr4 2010-13-2api-302146189No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 ProfileDocument9 pagesChapter 4 ProfileRon Magno100% (1)
- Data Analysis and Interpretation Media Preferences of StudentsDocument67 pagesData Analysis and Interpretation Media Preferences of Studentssakthikumar22No ratings yet
- 6th PT Sample Results and Discussion QuantitativeDocument25 pages6th PT Sample Results and Discussion QuantitativeAvinejNo ratings yet
- Final Thesis Chapter 4Document12 pagesFinal Thesis Chapter 4Rena AlauyaNo ratings yet
- Chapters 4 & 5 of Impact of Parental InvolvementDocument11 pagesChapters 4 & 5 of Impact of Parental InvolvementPauline MaranonNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Statistics - Quintos, Isnain, Majaba - Word FileDocument3 pagesDescriptive Statistics - Quintos, Isnain, Majaba - Word FileIsabella QuintosNo ratings yet
- School and Community ProfileDocument31 pagesSchool and Community Profileapi-253260591No ratings yet
- Revilla - Nomerto Jr. M 19 4767 933Document14 pagesRevilla - Nomerto Jr. M 19 4767 933Maestro MertzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - The Relationship Between Peer Groups and Student MotivationDocument8 pagesChapter 4 - The Relationship Between Peer Groups and Student MotivationBrent ChristerNo ratings yet
- Top 10 Machine Learning AlgorithmsDocument12 pagesTop 10 Machine Learning AlgorithmsUmang SoniNo ratings yet
- Old Age HomeDocument24 pagesOld Age HomeAnkit Tiwari100% (2)
- Kneehigh TheaterDocument2 pagesKneehigh Theaterapi-706488422No ratings yet
- SC TRDocument15 pagesSC TRNishat SinghNo ratings yet
- CA Final Law Amendments by CA Swapnil Patni PDFDocument56 pagesCA Final Law Amendments by CA Swapnil Patni PDFUjju100% (1)
- Tugas Arsitektur Komputer Paralel4Document9 pagesTugas Arsitektur Komputer Paralel4Grasiadi HersantoNo ratings yet
- The Travels of Macarius, Patriarch of Antioch: Written by his Attendant Archdeacon, Paul of Aleppo, In Arabic. Volume I and II. Translated By F. C. Belfour London: Printed for the Oriental Translation Fund, 1837Document8 pagesThe Travels of Macarius, Patriarch of Antioch: Written by his Attendant Archdeacon, Paul of Aleppo, In Arabic. Volume I and II. Translated By F. C. Belfour London: Printed for the Oriental Translation Fund, 1837Nicholas PappasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Auditing IT Governance Controls: True/FalseDocument9 pagesChapter 2 - Auditing IT Governance Controls: True/FalseShanygane Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- FM302 Financial Management in The Pacific Region: Week 4: Lecture 7 - Major Assignment Some Discussions and DirectionsDocument15 pagesFM302 Financial Management in The Pacific Region: Week 4: Lecture 7 - Major Assignment Some Discussions and DirectionsHitesh MaharajNo ratings yet
- Whitehead Et Al. 2009Document11 pagesWhitehead Et Al. 2009Benedikt EngelNo ratings yet
- Ria Anggraini A2 - 20131061Document2 pagesRia Anggraini A2 - 20131061Riaa AnggrainiNo ratings yet
- Module 7 Week 7 Dyadic Relationshp Followershp Delegation L SHIP 7 PDFDocument67 pagesModule 7 Week 7 Dyadic Relationshp Followershp Delegation L SHIP 7 PDFHarshithaNo ratings yet
- Outline and Notes - Biography of The Dollar-KarminDocument7 pagesOutline and Notes - Biography of The Dollar-KarminBankingLinguisticCheckmatesNo ratings yet
- Parricide and Violence Against Parents Throughout History: (De) Constructing Family and Authority? 1st Edition Marianna MuravyevaDocument54 pagesParricide and Violence Against Parents Throughout History: (De) Constructing Family and Authority? 1st Edition Marianna Muravyevasherry.minor170100% (10)
- Corruption & Insecurity PDFDocument8 pagesCorruption & Insecurity PDFterry odisuNo ratings yet
- Cotización Criba 50Document2 pagesCotización Criba 50Grace MartinezNo ratings yet
- CSC315 System Analysis and DesingDocument4 pagesCSC315 System Analysis and DesingMag CreationNo ratings yet
- Making Sense of MethodsDocument2 pagesMaking Sense of MethodsRinda nurulNo ratings yet
- The New Elliot Wave RuleDocument40 pagesThe New Elliot Wave RuleUlisses76100% (3)
- 06 Reported SpeechDocument12 pages06 Reported SpeechGuadalupe Meza MartinezNo ratings yet
- Best Books For IIT JEE Preparation - AskIITiansDocument5 pagesBest Books For IIT JEE Preparation - AskIITiansskluxNo ratings yet
- AutodeskCertifiedUserAutoCADExamOverview PDFDocument5 pagesAutodeskCertifiedUserAutoCADExamOverview PDFAyman KandeelNo ratings yet
- Bacarro Vs CastanoDocument2 pagesBacarro Vs CastanoMaiti LagosNo ratings yet
- ID Kerjasama United Nations World Tourism Organization Unwto Dengan Indonesia DalamDocument15 pagesID Kerjasama United Nations World Tourism Organization Unwto Dengan Indonesia DalamRollindevasaNo ratings yet
- BrainstormingDocument194 pagesBrainstormingArvind Ranganathan100% (3)
- UE18EE325 - Unit1 - Class4 - Performance Characteristics-StaticDocument16 pagesUE18EE325 - Unit1 - Class4 - Performance Characteristics-StaticGAYATHRI DEVI BNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces of Attraction Quiz AnswersDocument1 pageIntermolecular Forces of Attraction Quiz AnswersKaye ConejosNo ratings yet
- Sonny Lo vs. KJS Eco-Formwork System Phil, Inc, GR No. 149420 (2003)Document2 pagesSonny Lo vs. KJS Eco-Formwork System Phil, Inc, GR No. 149420 (2003)Je S BeNo ratings yet
Chapter 3 Part 2
Chapter 3 Part 2
Uploaded by
joysteven880 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views3 pagesThis document contains the results of a plagiarism check on a content sample that found 0% plagiarized content. It also includes survey results from 137 students about parental involvement in their education. The results show that most students were between 13-15 years old, more were boys than girls, most had parents who were self-employed, and most agreed that parental control positively impacts student achievement.
Original Description:
Tetsyhhsya
Original Title
chapter 3 part 2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document contains the results of a plagiarism check on a content sample that found 0% plagiarized content. It also includes survey results from 137 students about parental involvement in their education. The results show that most students were between 13-15 years old, more were boys than girls, most had parents who were self-employed, and most agreed that parental control positively impacts student achievement.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views3 pagesChapter 3 Part 2
Chapter 3 Part 2
Uploaded by
joysteven88This document contains the results of a plagiarism check on a content sample that found 0% plagiarized content. It also includes survey results from 137 students about parental involvement in their education. The results show that most students were between 13-15 years old, more were boys than girls, most had parents who were self-employed, and most agreed that parental control positively impacts student achievement.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 3
Date: Sun, Jan 14, 2024
Exclude Url: No Rocords Found 0
100% 0% 0%
Unique ContentPlagiarized ContentParaphras
Content Checked For Plagiarism:
Item total statistics Scale mean if item deleted
Scale variance if item deleted Corrected- item total
correlation Cronbach’s alpha if item deleted my
parents’ job does not give them enough time to
get involved in my studies 8.50 7.355 .781 .757
Lack of formal education doesn’t allow my parents
get involved in my education 8.92 7.076 .809 .746
Lack of knowledge of the school curriculum makes
my parents not to get involved in my studies 8.31
8.349 .479 .843 Language barriers doesn’t allow
my parents get fully involved in my studies 8.69
9.290 .450 .844 My parents financial capability to
provide for my educational materials makes my
parents not to be involved in my education 8.36
7.248 .675 .788 3.7 PROCEDURE FOR DATA
ANALYSIS The questionnaire will be personally
shared by hand to the respondents.The
questionnaire was allowed for answering for (15)
minutes with the respondents before submitting
of the questionnaire for further computing. 3.8
Method of Data analysis Data collection will be
properly analyzed in next chapter (chapter 4)
using statistical analysis chart and simple
percentage In the statistical chart, all the table
would show a display of each respondent based
on the questions provided.DATA ANALYSIS AND
D1SCUSSION OF FINDINGS 4.1 INTRODUCTION In
this chapter, collected data from the
questionnaires were compiled interpreted, and
analyzed in an appropriate manner.Deductions
were made from the necessary information
collected and relevant chart was contrasted.a
necessary information collected from the
questionnaire is appropriately out in tabulated
form in the sequence and statistical manner in
order to relate respondent's answers with
certain identifiable characteristics.This is derived
by construction of statistical tables that involves
the responses, number of responses and
percentage with brief comments.Part two has to
do with the main analysis by using simple
percentages to ascertain the correlation of
variables stated under research questions in first
chapter one. 4.1.1 ANALYSIS OF RESPONDENTS’
CHARACTERISTICS A sum total of one hundred
and fifty (150) questionnaires were given out of
which only one hundred and thirty-seven (137)
that represent 91.
3% respondents (consisting of 137 students) were
considered more viable and reliable for this study.
Thirteen (13) questionnaires that represent 8.7%
were rejected due to inadequate and improper
filling of information on the questionnaire.One
hundred and thirty-seven (137) questionnaires
considered properly useful for this study and
these represent 91.3% positive responses. TABLE
4.1.1 Distribution of respondents according to
their age Responses No of responses Percentage
(%) 8-12 years 43 31.4 13-15 years 85 62.0 16
years and above 9 6.6 Total 137 100 The table
above shows distribution of respondents
according to their age distribution. Total of 43 (31.
4%) of the total sample size with respondents
were between 8-12 years while 85 respondents (6.
6%) were 16 years and above.The above table
shows chart and distribution of the students
according to their ages. Total of 43 (31.4%) of the
total sample size with students were between
8-12 years while 85 students (6.6%) were 16 years
and above. TABLE 4.1.2 Sex Distribution Sex No of
responses Percentage (%) Boys 81 59.1 Girls 56
40.
9 Total 137 100 The one above shows distribution
of the students according to their sex 81
respondents that covered 59.1% are Girls, 56
respondents that covered 40.9% are boys Class
distribution 4.1.3 Class No of Responses
Percentage (%) JSS1 -SS1 41 29.9 JSS2-SS2 47 34.3
JSS3-SS3 49 35.8 Total 137 100 The table above
shows distribution of Students according to their
classes Total of 41 (29.9%) of the total sample size
with Students were JSS1 to SS1 Students While 47
Students representing 34.3% where JSS2 to SS2
students and 49 Students representing 35.
8%were JSS3 to SS3 Students. TABLE 4.1.4 Parent
Employment Distribution Responses No of
Responses Percentage (%) Employed by self 75
54.7 Employed 49 35.8 Unemployed 13 9.5 Total
137 100 The table above shows the distribution of
Students according to the job done by their
parents Total of 75 (54.7%) of the total sample size
with students’ parents that are self-employed
while 49(35.8% respondents’ parents were
employed 13 respondents representing 9.5%
were not employed.Bar charts showing Parental
control and students’ educational achievement
Frequency Percent Valid Percent Cumulative
Percent Valid strongly agreed 151 22.1 22.1 22.1
agreed 366 53.6 53.6 75.
7 disagreed 101 14.8 14.8 90.5 strongly disagreed
39 5.7 5.7 96.2 undecided 26 3.8 3.8 100.0 Total
683 100.0 100.0 TABLE 4.1.5 Chi square
distribution showing the relationship between
parental control and students’ educational
achievement S/N STATEMENT SA A D SD U 1 My
parents often monitor my movement with and
outside the home which doesn’t allow me
misbehave 34 25.0% 63 46.0% 24 17.5% 11 8.0% 5
3.6% 2 My parents often censor what I watch on
television 24 17.5% 73 53.3% 26 19.0% 8 5.8% 6 4.
4% 3 My parents often scold me each time I
misbehave 21 15.363.010.2.0.6% 4 My parents
often censor the kind of friends I keep at home
and in school 40 29.1% 80 58.4% 19 6.6% 5 3.6% 3
2.2% 5 My parents often censor the parties I
attend to keep me from bad occurrences 36 26.3%
62 45.3% 28 20.4% 7 5.1% 4 3.0% Mean total 31.0
72.8 20.2 7.8 5.2
Matched Sources
Report Generated: Sun, Jan 14, 2024 by plagiarismremo
You might also like
- General PsychologyDocument4 pagesGeneral PsychologyDaniel C. Dequiña100% (1)
- Chapter 4-5 RemedialDocument19 pagesChapter 4-5 RemedialTata Duero Lachica100% (4)
- PCS-921 - X - Instruction Manual - EN - Overseas General - X - R1.02 - (EN - FZBH5101.0086.0003) PDFDocument276 pagesPCS-921 - X - Instruction Manual - EN - Overseas General - X - R1.02 - (EN - FZBH5101.0086.0003) PDFLeister Carneiro TheodoroNo ratings yet
- 3 IS Module 5Document11 pages3 IS Module 5Hiezeyl Ymana GuntangNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three Research Methodology 3.1 Research DesignDocument14 pagesChapter Three Research Methodology 3.1 Research DesignepocyberNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Background Information On RespondentsDocument6 pages4.1 Background Information On RespondentsManfred GithinjiNo ratings yet
- Analysis & Interpretation of DataDocument42 pagesAnalysis & Interpretation of DataSaili SarmalkarNo ratings yet
- A Study To Assess The Knowledge and Educate Regarding Immunization in Children Amongst Mother in A Community SettingDocument20 pagesA Study To Assess The Knowledge and Educate Regarding Immunization in Children Amongst Mother in A Community SettingAbhishek Rajoria100% (2)
- Chapter - 4 Data Analysis and InterpretationDocument36 pagesChapter - 4 Data Analysis and InterpretationNagireddy KalluriNo ratings yet
- Statement of The ProblemDocument15 pagesStatement of The ProblemJoel Mangallay100% (1)
- Chapter 5Document4 pagesChapter 5joysteven88No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Finale - 071349Document8 pagesChapter 4 Finale - 071349Amman GuntingNo ratings yet
- Empowering Potencial Leaders: Effects On Building Leadership CapacityDocument41 pagesEmpowering Potencial Leaders: Effects On Building Leadership CapacityRochelle May CanlasNo ratings yet
- Chapter IIIDocument7 pagesChapter IIIGrey SonNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 4 and 5Document20 pagesCHAPTER 4 and 5Miziey ZainieNo ratings yet
- Data Gathereddiscussion Areis Divided Presented, Which Are The Following Artroblem - Artroblem ArtroblemDocument13 pagesData Gathereddiscussion Areis Divided Presented, Which Are The Following Artroblem - Artroblem ArtroblemDoneva Lyn MedinaNo ratings yet
- ResultsDocument18 pagesResultsJohn Elton PilarNo ratings yet
- Table ParametricDocument15 pagesTable ParametricDanniella GalleroNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three Research Methodology 3.1Document27 pagesChapter Three Research Methodology 3.1Joseph JboyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document8 pagesChapter 4hamidahmkhalid44No ratings yet
- CopyeditDocument13 pagesCopyeditNisa ShabrinafiNo ratings yet
- Non TeachingDocument30 pagesNon TeachingEdwin Okoampa BoaduNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document17 pagesChapter 4Rico Jon Hilario GarciaNo ratings yet
- EDITED Chapter 3 and 4Document47 pagesEDITED Chapter 3 and 4Raymond AbanesNo ratings yet
- Demographic Profile of Pe Teachers and Their Motivational Approaches Across Secondary Schools in SurallahDocument38 pagesDemographic Profile of Pe Teachers and Their Motivational Approaches Across Secondary Schools in SurallahMericel Dela Rosa EstorninosNo ratings yet
- Data AnalysisDocument6 pagesData Analysisapi-250134758No ratings yet
- Chapter II ThesisDocument5 pagesChapter II ThesisJheiczhietoot KibasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document3 pagesChapter 5hamidahmkhalid44No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Method of ResearchDocument28 pagesChapter 2 Method of ResearchChristian Mendoza MusicNo ratings yet
- Presentation, Analysis, and Interpretation of Data: 1. Respondent's ProfileDocument5 pagesPresentation, Analysis, and Interpretation of Data: 1. Respondent's ProfilefgfgfNo ratings yet
- Kabanata 3Document18 pagesKabanata 3Mark CastroNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER-5Document3 pagesCHAPTER-5jonnahmaemaurNo ratings yet
- Amoni and Final Chapter 4 Results and Discussion RecoverDocument12 pagesAmoni and Final Chapter 4 Results and Discussion Recovergoldenskydrive1No ratings yet
- Running Head: SPSS Research ReportDocument23 pagesRunning Head: SPSS Research ReportJacoby23No ratings yet
- Descriptive Analysis: Respondent Demographic ProfileDocument22 pagesDescriptive Analysis: Respondent Demographic ProfileAbygail ManaloNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four AnnethDocument15 pagesChapter Four AnnethRaytone Tonnie MainaNo ratings yet
- 103690S15Document49 pages103690S15steveparker123No ratings yet
- Competency 3 Table 1 5Document7 pagesCompetency 3 Table 1 5roshell IbusNo ratings yet
- Kaylon Nelson 5T1 Prefect SbaDocument6 pagesKaylon Nelson 5T1 Prefect SbaKaylon NelsonNo ratings yet
- 271 Assign 1 - Jan2013Document3 pages271 Assign 1 - Jan2013Mark LeonardNo ratings yet
- Table 1. Information About "Do You Have Enough Time For Your Academic Performance? "Document5 pagesTable 1. Information About "Do You Have Enough Time For Your Academic Performance? "Katrina CyberNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 (RDM)Document8 pagesChapter 3 (RDM)Julliana BabilaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument11 pagesUntitledMark Rhyan AguantaNo ratings yet
- Sample AnalysisDocument23 pagesSample AnalysisGopaul UshaNo ratings yet
- J. L. Depaynos, MA AS Math 100Document18 pagesJ. L. Depaynos, MA AS Math 100Jane PadillaNo ratings yet
- Fully Corrected Chapters 4 & 5Document21 pagesFully Corrected Chapters 4 & 5Iyobosa OmoregieNo ratings yet
- Draft in Educ 12Document11 pagesDraft in Educ 12Gracy PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Age 16 Child Behavior Checklist External Site MM FinalDocument6 pagesAge 16 Child Behavior Checklist External Site MM FinalSammy FilipeNo ratings yet
- INPUT-effectiveness of Virtual LaboratoryDocument21 pagesINPUT-effectiveness of Virtual Laboratorynena marie evalaroza100% (1)
- Hypertension Elder Based On Self Care Orem Theory Perspective in RW 03 Wonokromo SurabayaDocument7 pagesHypertension Elder Based On Self Care Orem Theory Perspective in RW 03 Wonokromo Surabayaliga afseliaNo ratings yet
- Presentation, Analysis and Interpretation of DataDocument9 pagesPresentation, Analysis and Interpretation of DataCorin Ahmed CorinNo ratings yet
- Ma-Sampletest-Gr4 2010-13-2Document16 pagesMa-Sampletest-Gr4 2010-13-2api-302146189No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 ProfileDocument9 pagesChapter 4 ProfileRon Magno100% (1)
- Data Analysis and Interpretation Media Preferences of StudentsDocument67 pagesData Analysis and Interpretation Media Preferences of Studentssakthikumar22No ratings yet
- 6th PT Sample Results and Discussion QuantitativeDocument25 pages6th PT Sample Results and Discussion QuantitativeAvinejNo ratings yet
- Final Thesis Chapter 4Document12 pagesFinal Thesis Chapter 4Rena AlauyaNo ratings yet
- Chapters 4 & 5 of Impact of Parental InvolvementDocument11 pagesChapters 4 & 5 of Impact of Parental InvolvementPauline MaranonNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Statistics - Quintos, Isnain, Majaba - Word FileDocument3 pagesDescriptive Statistics - Quintos, Isnain, Majaba - Word FileIsabella QuintosNo ratings yet
- School and Community ProfileDocument31 pagesSchool and Community Profileapi-253260591No ratings yet
- Revilla - Nomerto Jr. M 19 4767 933Document14 pagesRevilla - Nomerto Jr. M 19 4767 933Maestro MertzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - The Relationship Between Peer Groups and Student MotivationDocument8 pagesChapter 4 - The Relationship Between Peer Groups and Student MotivationBrent ChristerNo ratings yet
- Top 10 Machine Learning AlgorithmsDocument12 pagesTop 10 Machine Learning AlgorithmsUmang SoniNo ratings yet
- Old Age HomeDocument24 pagesOld Age HomeAnkit Tiwari100% (2)
- Kneehigh TheaterDocument2 pagesKneehigh Theaterapi-706488422No ratings yet
- SC TRDocument15 pagesSC TRNishat SinghNo ratings yet
- CA Final Law Amendments by CA Swapnil Patni PDFDocument56 pagesCA Final Law Amendments by CA Swapnil Patni PDFUjju100% (1)
- Tugas Arsitektur Komputer Paralel4Document9 pagesTugas Arsitektur Komputer Paralel4Grasiadi HersantoNo ratings yet
- The Travels of Macarius, Patriarch of Antioch: Written by his Attendant Archdeacon, Paul of Aleppo, In Arabic. Volume I and II. Translated By F. C. Belfour London: Printed for the Oriental Translation Fund, 1837Document8 pagesThe Travels of Macarius, Patriarch of Antioch: Written by his Attendant Archdeacon, Paul of Aleppo, In Arabic. Volume I and II. Translated By F. C. Belfour London: Printed for the Oriental Translation Fund, 1837Nicholas PappasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Auditing IT Governance Controls: True/FalseDocument9 pagesChapter 2 - Auditing IT Governance Controls: True/FalseShanygane Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- FM302 Financial Management in The Pacific Region: Week 4: Lecture 7 - Major Assignment Some Discussions and DirectionsDocument15 pagesFM302 Financial Management in The Pacific Region: Week 4: Lecture 7 - Major Assignment Some Discussions and DirectionsHitesh MaharajNo ratings yet
- Whitehead Et Al. 2009Document11 pagesWhitehead Et Al. 2009Benedikt EngelNo ratings yet
- Ria Anggraini A2 - 20131061Document2 pagesRia Anggraini A2 - 20131061Riaa AnggrainiNo ratings yet
- Module 7 Week 7 Dyadic Relationshp Followershp Delegation L SHIP 7 PDFDocument67 pagesModule 7 Week 7 Dyadic Relationshp Followershp Delegation L SHIP 7 PDFHarshithaNo ratings yet
- Outline and Notes - Biography of The Dollar-KarminDocument7 pagesOutline and Notes - Biography of The Dollar-KarminBankingLinguisticCheckmatesNo ratings yet
- Parricide and Violence Against Parents Throughout History: (De) Constructing Family and Authority? 1st Edition Marianna MuravyevaDocument54 pagesParricide and Violence Against Parents Throughout History: (De) Constructing Family and Authority? 1st Edition Marianna Muravyevasherry.minor170100% (10)
- Corruption & Insecurity PDFDocument8 pagesCorruption & Insecurity PDFterry odisuNo ratings yet
- Cotización Criba 50Document2 pagesCotización Criba 50Grace MartinezNo ratings yet
- CSC315 System Analysis and DesingDocument4 pagesCSC315 System Analysis and DesingMag CreationNo ratings yet
- Making Sense of MethodsDocument2 pagesMaking Sense of MethodsRinda nurulNo ratings yet
- The New Elliot Wave RuleDocument40 pagesThe New Elliot Wave RuleUlisses76100% (3)
- 06 Reported SpeechDocument12 pages06 Reported SpeechGuadalupe Meza MartinezNo ratings yet
- Best Books For IIT JEE Preparation - AskIITiansDocument5 pagesBest Books For IIT JEE Preparation - AskIITiansskluxNo ratings yet
- AutodeskCertifiedUserAutoCADExamOverview PDFDocument5 pagesAutodeskCertifiedUserAutoCADExamOverview PDFAyman KandeelNo ratings yet
- Bacarro Vs CastanoDocument2 pagesBacarro Vs CastanoMaiti LagosNo ratings yet
- ID Kerjasama United Nations World Tourism Organization Unwto Dengan Indonesia DalamDocument15 pagesID Kerjasama United Nations World Tourism Organization Unwto Dengan Indonesia DalamRollindevasaNo ratings yet
- BrainstormingDocument194 pagesBrainstormingArvind Ranganathan100% (3)
- UE18EE325 - Unit1 - Class4 - Performance Characteristics-StaticDocument16 pagesUE18EE325 - Unit1 - Class4 - Performance Characteristics-StaticGAYATHRI DEVI BNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces of Attraction Quiz AnswersDocument1 pageIntermolecular Forces of Attraction Quiz AnswersKaye ConejosNo ratings yet
- Sonny Lo vs. KJS Eco-Formwork System Phil, Inc, GR No. 149420 (2003)Document2 pagesSonny Lo vs. KJS Eco-Formwork System Phil, Inc, GR No. 149420 (2003)Je S BeNo ratings yet