Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Structural Components of Cell Membrane
Structural Components of Cell Membrane
Uploaded by
Erich Mae Laviste0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views18 pagesThe cell membrane is composed of a phospholipid bilayer with integral and peripheral proteins embedded. It selectively controls what enters and exits the cell, allowing the passage of some substances like water, oxygen, and other molecules through transport proteins. The fluid mosaic model describes the cell membrane as a fluid structure containing phospholipids, cholesterol, and carbohydrates that gives the membrane flexibility and semi-permeability.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe cell membrane is composed of a phospholipid bilayer with integral and peripheral proteins embedded. It selectively controls what enters and exits the cell, allowing the passage of some substances like water, oxygen, and other molecules through transport proteins. The fluid mosaic model describes the cell membrane as a fluid structure containing phospholipids, cholesterol, and carbohydrates that gives the membrane flexibility and semi-permeability.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views18 pagesStructural Components of Cell Membrane
Structural Components of Cell Membrane
Uploaded by
Erich Mae LavisteThe cell membrane is composed of a phospholipid bilayer with integral and peripheral proteins embedded. It selectively controls what enters and exits the cell, allowing the passage of some substances like water, oxygen, and other molecules through transport proteins. The fluid mosaic model describes the cell membrane as a fluid structure containing phospholipids, cholesterol, and carbohydrates that gives the membrane flexibility and semi-permeability.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 18
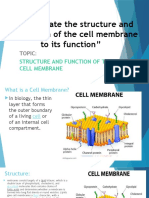
CELL MEMBRANE
▪ the boundary that
separates the living cell
from its surroundings
▪ controls traffic into and
out of the cell
▪ exhibits selective
permeability - it allows
some substances to cross
it more easily than others
STRUCTURAL
COMPONENTS
OF THE CELL
MEMBRANE
CELL MEMBRANE
properties
(1) Fluidity
(2) Semi-permeability
(3) Rigidity
▪ The cell membrane
is mainly composed
of lipids and
proteins.
▪ Its framework
consists of a
phospholipid bilayer
LIPIDS
▪ A group of organic compounds that are insoluble
in water
▪ Its examples include fats, oils, waxes and hormones
Amphipathic molecule
- Having both
hydrophilic and
hydrophobic parts
Semi-permeable
- Allows some materials
to pass through but
not all
Pliable
- Easily bent
Fluid
- Able to flow freely
PROTEINS
▪ Are biomolecules
made up of
amino acids and
joined together
by peptide bonds
Types of Proteins
▪ Integral - inserted
into the membrane and
most pass through the
membrane
▪ Peripheral - are
exterior to and
connected to the
membrane by
interactions with other
proteins
1. Structural proteins help to give the cell support and
shape.
2. Cell membrane receptor proteins help cells communicate
with their external environment through the use of
hormones, neurotransmitters, and other signaling
molecules.
3. Transport proteins, such as globular proteins, transport
molecules across cell membranes through facilitated
diffusion.
4. Glycoproteins have a carbohydrate chain attached to
them. They are embedded in the cell membrane and help
in cell to cell communications and molecule transport
across the membrane
CARBOHYDRATES
▪ Are biomolecules
made of C, H and
O
▪ Sugar, starches
and fiber are
some examples
CARBOHYDRATES
▪ They are mostly
found in the
external surface
Types:
- Glycoproteins
- Glycolipids
Functions:
▪ Forms distinctive
cellular markers
▪ Cell-cell
recognition
▪ Cell-pathogen
interaction
CHOLESTEROL
▪ A type of lipid found in cells
▪ Essential in the production of other
biomolecules like steroids, hormones and
Vitamin D
Functions:
▪ Regulates the fluidity of the cell membrane as
temperature varies
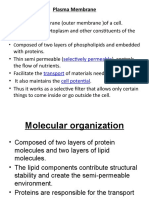
▪ The fluid mosaic
model describes the
structure of the
plasma membrane as
a mosaic of
components – such
as phospholipids,
cholesterol, proteins,
and carbohydrates—
that gives the
membrane a fluid
character.
▪ The fluid mosaic
model was
formulated by Singer
and Nicolson in 1972
FUNCTIONS OF THE CELL MEMBRANE
1. PROTECTION – Cell membrane acts like a
barrier that separates the contents of the cell
from the external environment
2. MATERIAL TRANSPORT – It is a semi-
permeable membrane that regulates the
transport of materials in and out of the cell
3. CELL SHAPE – It is where the cytoskeleton
attaches that helps in maintaining the shape
of the cell
4. COMPARTMENTALIZATION – It separates the
organelles from each other and from the
cytoplasm providing their own environment
and functional individuality.
5. CELL RECOGNITION – Enables cells to
identify other cells and foreign substances
6. CELL FUNCTION – It plays an important role
in the performance of cell function such as
locomotion, absorption and transmission.
You might also like
- Study Guide Percent Yield WS 2 2021Document1 pageStudy Guide Percent Yield WS 2 2021conorskate 1705No ratings yet
- The BIG BOOK of Solid Edge FundamentalsDocument1,539 pagesThe BIG BOOK of Solid Edge FundamentalsJocaNo ratings yet
- Molecular Organization of The Plasma MembraneDocument53 pagesMolecular Organization of The Plasma MembraneJD100% (1)
- A Method To The MadnessDocument20 pagesA Method To The Madnessmadhukarshukla100% (1)
- 1 ST InterviewDocument5 pages1 ST Interviewshaliesh0% (2)
- Membrane PhysiologyDocument223 pagesMembrane PhysiologyteklayNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane in Transport MechanismsDocument29 pagesCell Membrane in Transport MechanismsAnnie LouNo ratings yet
- The Cell and CytoplasmDocument70 pagesThe Cell and Cytoplasmbunniecaronan113003No ratings yet
- Structure of Cell Membrane: Surabhi Roll No. - 39Document24 pagesStructure of Cell Membrane: Surabhi Roll No. - 39Kumar AbhishekNo ratings yet
- 2 - kh201295 kh201295Document11 pages2 - kh201295 kh201295murtada gubaNo ratings yet
- The Cell: Prof. Bond AnyaehieDocument32 pagesThe Cell: Prof. Bond AnyaehieOkwor SundayNo ratings yet
- CMT 2021-22 by Mr. Adeel AhmadDocument24 pagesCMT 2021-22 by Mr. Adeel AhmadADEEL AHMADNo ratings yet
- 2.1. Cellular Physiology Organization Structure and Functions of The CellDocument77 pages2.1. Cellular Physiology Organization Structure and Functions of The CellalfonsoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Notes Cellular Basis of LifeDocument11 pagesLecture 3 Notes Cellular Basis of Lifeochienganthony001No ratings yet
- Cell MembraneDocument44 pagesCell MembraneTere CantikkNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane 2024, DPT (JSMU) Semester-I, 12.02.2024, 12.00-01.00Document16 pagesCell Membrane 2024, DPT (JSMU) Semester-I, 12.02.2024, 12.00-01.00Sheeraz jan BalouchNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane Structure and FunctionDocument31 pagesCell Membrane Structure and FunctionXembergNo ratings yet
- q1 Genbio1 Slkweek6 EditDocument13 pagesq1 Genbio1 Slkweek6 EditInele Ellia AgReNo ratings yet
- Cellular-Organization Part1Document7 pagesCellular-Organization Part1Nina IlaganNo ratings yet
- Transport Mechanism 1Document15 pagesTransport Mechanism 1tlmargullanoNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of CellsDocument93 pagesStructure and Function of CellsRonald BakangNo ratings yet
- Cell StrucutreDocument40 pagesCell StrucutreJeevitha VanithaNo ratings yet
- Transport MechanismDocument2 pagesTransport MechanismStephanie Cyrelle Jane BacaniNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 - Cell MembraneDocument26 pagesLesson 8 - Cell MembraneArvin Jay LamberteNo ratings yet
- Cell StructureDocument5 pagesCell StructureTortelliniNo ratings yet
- Cellular Level of OrganizationDocument76 pagesCellular Level of OrganizationCherub DaramanNo ratings yet
- 2a-Membranes and Transport 2Document67 pages2a-Membranes and Transport 2kfy8vr7wtwNo ratings yet
- Cell MembranesDocument5 pagesCell MembranesJANET ANNE BORROMEONo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles 1Document17 pagesCell Organelles 1James IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure & MembraneDocument24 pagesCell Structure & MembraneAbhishek Singh ChandelNo ratings yet
- Structure and Functions of The Plasma MembraneDocument19 pagesStructure and Functions of The Plasma MembraneDanessa Mina BalboaNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane Flow of MaterialsDocument13 pagesCell Membrane Flow of Materialsnorhain4.aNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Cell Membrane and Lesson 3 HomeostasisDocument14 pagesLesson 2 Cell Membrane and Lesson 3 HomeostasisAj MirandaNo ratings yet
- The Cell: Department of PhysiologyDocument40 pagesThe Cell: Department of PhysiologyonijinoNo ratings yet
- Biology NotesDocument20 pagesBiology Noteshopekingbwalya23No ratings yet
- Physiology Chapter 2 Part 1Document21 pagesPhysiology Chapter 2 Part 1prabokrishna02No ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument39 pagesCell Structure and Functiondoubleyouem2003No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Cell Membranes and TransportDocument33 pagesChapter 4 Cell Membranes and TransportChia Hon LamNo ratings yet
- Cell OrganellesDocument63 pagesCell Organellessyafi zulNo ratings yet
- Cell Bio Assignment 2Document2 pagesCell Bio Assignment 2Toga BrandonNo ratings yet
- The Cell Day 1Document50 pagesThe Cell Day 1Abegail Ashley PenoniaNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure FunctionDocument43 pagesCell Structure Functioneishawajid75No ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument2 pagesCell Structure and FunctionRoseNo ratings yet
- General Medical Biology: Lecture 3: Cell Structure and FunctionDocument24 pagesGeneral Medical Biology: Lecture 3: Cell Structure and FunctionRasan QadrNo ratings yet
- The Cell Structure, Functions of The CellDocument76 pagesThe Cell Structure, Functions of The CellCharles Ssekawu100% (1)
- 2 4 Plasma MembraneDocument22 pages2 4 Plasma Membraneıamnıkolaı 4No ratings yet
- General Medical Biology: Lecture 3: Cell Structure and FunctionDocument23 pagesGeneral Medical Biology: Lecture 3: Cell Structure and FunctionRasan QadrNo ratings yet
- 2 Cell Structure - A 2019Document88 pages2 Cell Structure - A 2019Isworo RukmiNo ratings yet
- Cell ConstituentsDocument39 pagesCell ConstituentsMilky YadavNo ratings yet
- Cell Final 2Document100 pagesCell Final 2Dell E6430No ratings yet
- 03 - Chapter 3 Plasma Membrane Transport 20222023 (S)Document77 pages03 - Chapter 3 Plasma Membrane Transport 20222023 (S)Nurul Farahin MokhtarNo ratings yet
- Structure of CellDocument42 pagesStructure of CellJeevitha VanithaNo ratings yet
- Hist of Cell-Organelles 2022Document45 pagesHist of Cell-Organelles 2022betelhema71No ratings yet
- General Biology 1: Quarter 1 - Module 5Document5 pagesGeneral Biology 1: Quarter 1 - Module 5karyo eseymNo ratings yet
- Additional Notes in Histology LecDocument8 pagesAdditional Notes in Histology LecJISOO KimNo ratings yet
- B2.1, 2, 3Document13 pagesB2.1, 2, 3Taleen YounisNo ratings yet
- Basic Unit of All Living Things: 3 Main RegionsDocument18 pagesBasic Unit of All Living Things: 3 Main RegionsRikki Mae BuenoNo ratings yet
- Genbio Plasma Membrane ReviewerDocument3 pagesGenbio Plasma Membrane ReviewerEleah MelchorNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 4: Chapter 2: Cell Structure and Cell OrganisationDocument4 pagesBiology Form 4: Chapter 2: Cell Structure and Cell OrganisationSera ChanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To BiochemistryDocument32 pagesIntroduction To BiochemistryArbaan HashmiNo ratings yet
- Plasma Membrane: Selectively Permeable Transport Cell PotentialDocument10 pagesPlasma Membrane: Selectively Permeable Transport Cell PotentialSujan maharjanNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane TransportDocument3 pagesCell Membrane TransportHarry TeasdaleNo ratings yet
- Biyoloji IngilizceDocument21 pagesBiyoloji Ingilizced46smsfpwcNo ratings yet
- Variabel Random Dan Distribusi ProbabilitasDocument4 pagesVariabel Random Dan Distribusi ProbabilitasromyNo ratings yet
- Solar Bloc DatasheetDocument2 pagesSolar Bloc DatasheetAyman Al-YafeaiNo ratings yet
- PriDocument8 pagesPritubNo ratings yet
- Verilog ExercisesheetDocument6 pagesVerilog ExercisesheetFionna ImmaculateNo ratings yet
- Dce 1Document21 pagesDce 1Jay MehtaNo ratings yet
- Pneumatic Water Pumping SystemDocument46 pagesPneumatic Water Pumping SystemAjithNo ratings yet
- A3: Veda Vyasa - (Correct Alternative)Document28 pagesA3: Veda Vyasa - (Correct Alternative)Priyank PatelNo ratings yet
- Slide PPT Seminar InternasionalDocument6 pagesSlide PPT Seminar InternasionalFandi AfandiNo ratings yet
- Subnetting Assignment #1: Instructions For All ProblemsDocument3 pagesSubnetting Assignment #1: Instructions For All ProblemssugapriyaNo ratings yet
- TCP/IP Protocol Suite and IP AddressingDocument31 pagesTCP/IP Protocol Suite and IP AddressingHungry LadyNo ratings yet
- Math Las - q2-w1Document10 pagesMath Las - q2-w1jam ananggoNo ratings yet
- Course 2 Unit 4Document90 pagesCourse 2 Unit 4amit aryaNo ratings yet
- Atoms Molecules and IonsDocument46 pagesAtoms Molecules and Ionschandro57No ratings yet
- Sequence of TensesDocument6 pagesSequence of TensesLucanezulNo ratings yet
- Science 8 PPT W3Q1Document32 pagesScience 8 PPT W3Q1charlie cubacubNo ratings yet
- 2n3906 DatasheetDocument3 pages2n3906 DatasheetZain AliNo ratings yet
- Control Systems - State Space ModelDocument8 pagesControl Systems - State Space ModelVivek PatilNo ratings yet
- 02 Hobas Jacking PipesDocument20 pages02 Hobas Jacking Pipesdliu88100% (1)
- Chapter 2 Software Development Life Cycle ModelsDocument48 pagesChapter 2 Software Development Life Cycle ModelsGurteg SinghNo ratings yet
- PP 303 To 312 Jordan Peng Horng Tan Final Paper EditedDocument10 pagesPP 303 To 312 Jordan Peng Horng Tan Final Paper EditedjaywarvenNo ratings yet
- Reference Manual: Updated For Version 2.7 of Capture PolarDocument33 pagesReference Manual: Updated For Version 2.7 of Capture PolarGangaNo ratings yet
- Data Structures LightHall ClassDocument43 pagesData Structures LightHall ClassIwuchukwu ChiomaNo ratings yet
- Class III Stress Strain ProblemsDocument13 pagesClass III Stress Strain ProblemsMadhan kumarNo ratings yet
- ServiceManual en E-Series V 1.1.6Document201 pagesServiceManual en E-Series V 1.1.6Nghia PhanNo ratings yet
- Stress Control: Equipotential Lines 20% 40% 60% 80%Document4 pagesStress Control: Equipotential Lines 20% 40% 60% 80%Jalal AlbadriNo ratings yet