Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Rohini 74049417647
Rohini 74049417647
Uploaded by
Aakash SharmaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Rohini 74049417647
Rohini 74049417647
Uploaded by
Aakash SharmaCopyright:
Available Formats
ROHINI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY
1.9 TRANSISTOR-TRANSISTOR LOGIC (TTL)
Transistor-Transistor Logic belongs to the digital logic family. It consists of transistors
at both input and output side, diodes and few resistors. Unlike Resistor-transistor
logic and Diode transistor logic, both the logic function and amplifying function are
performed by the transistors.
The TTL integrated circuits are very popular in different applications including computer
controls, consumer electronics, industrial control systems, etc.
There are various subfamilies in transistor-transistor logic, which includes standard TTL,
Low power TTL, Schottky TTL, Advanced Schottky TTL, High power TTL, fast TTL,
etc. In this section, you will learn about the circuit and operation of standard TTL and
different output configurations of TTL.
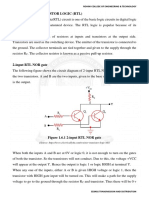
The following figure shows the circuit diagram of the 2-input TTL NAND gate. It has
four transistors Q1, Q2, Q3 and Q4. Transistor Q1 has 2-inputs on the emitter side.
Transistor Q3 and Q4 form the output side, called Totem pole output.
Figure 1.9.1 2-input TTL NAND gate
[Source: https://www.electrically4u.com/transistor-transistor-logic/]
EE8402 TRANSMISSION AND DISTRIBUTION
ROHINI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY
When both inputs A and B are low, both the diodes are forward biased. So the current
due to the supply voltage +VCC = 5 V will go to the ground through R1 and the two diodes
DA and DB.
The supply voltage gets dropped in the resistor R1 and it will not be sufficient to turn ON
the transistor Q2. With Q2 open, the transistor Q4 will also cut off. But the transistor Q3 is
pulled high. Since Q3 is an emitter follower, the output at the terminal will also be HIGH,
which is at logic 1.
When any one input, either A or B is low, the diode with low input will be forward biased.
The same operation will take place as explained above. In this case, the output will be
HIGH.
When both the inputs A and B are high, both the diodes at the emitter-base junction will
be reverse biased. The diode DC at the collector-base junction is forward biased. It will
turn on the transistor Q2. With Q2 turned ON, transistor Q4 will also be turned ON.
Both the transistors at the output side will conduct and so the output at terminal will have
LOW value, which is considered as logic 0.
1.9.1 Output configuration of TTL
There are three different output configurations in transistor-transistor logic
1. Totem-pole output
2. open collector output
3. Tri-state gate output
Totem-pole output
In the circuit shown below, the shaded portion shows the totem-pole output. Transistor
Q3, Q4, diode D and current limiting resistor R3 form the totem-pole output configuration
of TTL.
There are a few advantages of using this configuration. When the output switches from
LOW to a HIGH state, the output transistor Q4 goes from saturation to cut off. During
this transition, the load capacitance across Q3 charges exponentially from low to a high
voltage level.
EE8402 TRANSMISSION AND DISTRIBUTION
ROHINI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY
Figure 1.9.2 Totem-pole output configuration in Transistor-Transistor Logic
[Source: https://www.electrically4u.com/transistor-transistor-logic/]
Due to the low output impedance of both transistors Q3 and Q4, the output voltage can
change quickly from LOW to HIGH value as the capacitance charge and discharge
quickly.
Open collector output
The open-collector output configuration of Transistor-Transistor Logic is shown in the
below figure. In this configuration, the transistor Q3 and pull-up resistor is eliminated.
Instead, external pull up resistor for proper operation as shown in the figure.
The output is taken from the open collector terminal of Q4. When transistor Q4 is OFF,
the output Y will be HIGH and when Q4 is ON, the output will be LOW.
EE8402 TRANSMISSION AND DISTRIBUTION
ROHINI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY
Figure 1.9.3 Open-Collector Output Configuration Of Transistor-Transistor Logic
[Source: https://www.electrically4u.com/transistor-transistor-logic/]
Tri-state gate output
While operating the transistor in this output configuration, it is possible to attain high
speed. Three output state is possible: HIGH, LOW and high impedance.
When the transistor Q3 is ON, the output at terminal Y is HIGH. The output is LOW
when the transistor Q4 is turned ON. The first and second states are the normal operation
of TTL. In the third state, both the transistors Q3 and Q4 are turned OFF, which results
in neither LOW nor HIGH output.
EE8402 TRANSMISSION AND DISTRIBUTION
ROHINI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY
Figure 1.9.4 Tri-state gate output
[Source: http://users.cecs.anu.edu.au/]
Advantages
High-speed operation. The propagation delay is around 10 ms, which is fast compared to
DTL and RTL logic devices.
Less power dissipation compared to DTL and RTL.
Low cost
Better fan-out
Reliable operation for noise.
EE8402 TRANSMISSION AND DISTRIBUTION
You might also like
- Open Ended 1Document12 pagesOpen Ended 1AneeshaNo ratings yet
- SD WanDocument53 pagesSD WanAlisamiir100% (1)
- Indian Mass Media: A Critical Analysis Based On PopularityDocument3 pagesIndian Mass Media: A Critical Analysis Based On Popularityrajv88100% (1)
- Rohini 57301694152Document3 pagesRohini 57301694152Tsiky RavalisonNo ratings yet
- Ade Unit 2 XcvbgfreDocument21 pagesAde Unit 2 XcvbgfreRishabh Singh RajputNo ratings yet
- UNIT-5: Realization of Logic Gates and Sampling GatesDocument11 pagesUNIT-5: Realization of Logic Gates and Sampling GatesSanjana PulapaNo ratings yet
- Unit V Sampling Gates and Logic Gates: IC FamiliesDocument11 pagesUnit V Sampling Gates and Logic Gates: IC FamiliesAlapati RajasekharNo ratings yet
- TTL LOGIC Family - Hariram-1Document16 pagesTTL LOGIC Family - Hariram-1Hari RamNo ratings yet
- Digital Electronics: Logic Gates: Using TTLDocument10 pagesDigital Electronics: Logic Gates: Using TTLfarukNo ratings yet
- Digital FamiliesDocument20 pagesDigital FamiliesRajni ShingalaNo ratings yet
- TTL - Ecl - CmosDocument5 pagesTTL - Ecl - CmosAli AsgerovNo ratings yet
- Logic FamiliesDocument9 pagesLogic FamiliesJNo ratings yet
- Unit-2 DE TOTALDocument35 pagesUnit-2 DE TOTALParameshwar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Nand TTLDocument8 pagesNand TTLAnas SadiqNo ratings yet
- 1587289957digital Logic FamiliesDocument6 pages1587289957digital Logic Familiesjunry2017No ratings yet
- Experiment No: DateDocument24 pagesExperiment No: DateChaitanya ShahNo ratings yet
- All About Logic Families PDFDocument32 pagesAll About Logic Families PDFSaiKanthG100% (1)
- ThristerDocument63 pagesThristerPitchandi ArumugamNo ratings yet
- LIC Mod 2Document15 pagesLIC Mod 2Sona PrakashNo ratings yet
- Dec Exp 2 Student Manual PDFDocument4 pagesDec Exp 2 Student Manual PDFS M AkashNo ratings yet
- Uvufigigigi 747858 UfuDocument4 pagesUvufigigigi 747858 UfuHussein A. AlsameeNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1Document7 pagesExperiment 1Clement RajNo ratings yet
- L12 - BJT - Logic GatesDocument28 pagesL12 - BJT - Logic GatesamonNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes For Logic Family: (Electronics: PHYS4008)Document20 pagesLecture Notes For Logic Family: (Electronics: PHYS4008)Tanvir kabirNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Logic FamiliesDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Logic FamiliesASHURA HAMISINo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - TTL Family Part 1Document22 pagesLecture 2 - TTL Family Part 1GhostNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document46 pagesUnit 3jana kNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document16 pagesUnit 2Kavitha SelvarajNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 (2020)Document15 pagesLecture 6 (2020)زياد عبدالله عبدالحميدNo ratings yet
- DE ManualDocument37 pagesDE ManualKishore ReddyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document85 pagesChapter 8edward solomonNo ratings yet
- Mini Project FinalDocument11 pagesMini Project FinalShreyas BhandareNo ratings yet
- Over-Under Voltage Cut-Off With On-Time Delay PROJECT REPORTDocument35 pagesOver-Under Voltage Cut-Off With On-Time Delay PROJECT REPORTSumit Agarwal75% (4)
- De Unit5 SlidesDocument162 pagesDe Unit5 SlidesAravind RaoNo ratings yet
- Transistor Transistor LogicDocument33 pagesTransistor Transistor LogicCaranto Lois CarantoNo ratings yet
- And, NorDocument5 pagesAnd, NorAnoud AlkabodiNo ratings yet
- Diode Transistor LogicDocument14 pagesDiode Transistor LogicheissenriyadhovicNo ratings yet
- Digital Logic FamiliesDocument7 pagesDigital Logic FamiliesYousif ElsayedNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument13 pagesIntroductionnokia58No ratings yet
- Logic Family - Logic FamilyDocument4 pagesLogic Family - Logic FamilyCDAC VLSINo ratings yet
- Transistor-Transistor LogicDocument22 pagesTransistor-Transistor LogicSameeha AkramNo ratings yet
- TTL-Transistor - Transistor Logic Transistor-Transistor Logic, or TTL, Refers To The Technology For Designing and FabricatingDocument3 pagesTTL-Transistor - Transistor Logic Transistor-Transistor Logic, or TTL, Refers To The Technology For Designing and FabricatingAbhishek VermaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Logic FamiliesDocument10 pagesUnit 4 Logic FamiliesJagat SinghNo ratings yet
- Current-Mode Logic (CML) : Logic Family BJT Saturation RegionDocument5 pagesCurrent-Mode Logic (CML) : Logic Family BJT Saturation Regionnik2955No ratings yet
- Micro Controller Based System Design1Document188 pagesMicro Controller Based System Design1Indumathi ElayarajaNo ratings yet
- Digital Electronics - Contd.: Rijil RamchandDocument19 pagesDigital Electronics - Contd.: Rijil RamchandAshna JoseNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Introduction TTLcpe313Document10 pagesModule 2 Introduction TTLcpe313Jessie Tess TolentinoNo ratings yet
- An11001-Rev03 3l NPC TNPC TopologyDocument12 pagesAn11001-Rev03 3l NPC TNPC Topologyrambabu potluriNo ratings yet
- EC304Document22 pagesEC304api-3853441No ratings yet
- Ade Ca2Document9 pagesAde Ca2Pratiksha IngoleNo ratings yet
- Running Head: OSCILLATORSDocument11 pagesRunning Head: OSCILLATORSAhmer FarooqNo ratings yet
- Silicon Controlled Rectifier SCR - Two Transistor Model - Operating PrincipleDocument24 pagesSilicon Controlled Rectifier SCR - Two Transistor Model - Operating PrinciplesixfacerajNo ratings yet
- LAB 1b PracticalDocument4 pagesLAB 1b PracticalguntadiNo ratings yet
- DSD LogicFamiliesDocument32 pagesDSD LogicFamiliesibiiuoujNo ratings yet
- Stuart1 150Document6 pagesStuart1 150Rafael PiccoNo ratings yet
- EE 120 - Integrated Circuit FamiliesDocument15 pagesEE 120 - Integrated Circuit FamiliesAids SumaldeNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Lab Manual-withoutreadingsandprepostlab-EE0314Document69 pagesPower Electronics Lab Manual-withoutreadingsandprepostlab-EE0314Sankaran Nampoothiri KrishnanNo ratings yet
- An Independently Regulated Multiple Output Forward Converter TopologyDocument11 pagesAn Independently Regulated Multiple Output Forward Converter TopologyDavidMaighlNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Digital Circuit 6-6: Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument33 pagesChapter 6 Digital Circuit 6-6: Department of Mechanical EngineeringGoitom TeclaiNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Power Supply Projects: A Collection of Innovative and Practical Design ProjectsFrom EverandPower Supply Projects: A Collection of Innovative and Practical Design ProjectsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Btech Cse 6 Sem Mobile Computing 36115 May 2019Document2 pagesBtech Cse 6 Sem Mobile Computing 36115 May 2019Aakash SharmaNo ratings yet
- Henna ShowdownDocument1 pageHenna ShowdownAakash SharmaNo ratings yet
- FirewallsDocument20 pagesFirewallsAakash SharmaNo ratings yet
- Interfacing of Stepper Motor To Intel 8086 Microprocessor Through 8255 PPIDocument6 pagesInterfacing of Stepper Motor To Intel 8086 Microprocessor Through 8255 PPIAakash SharmaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 20Document6 pagesLecture 20Aakash SharmaNo ratings yet
- Training ReportDocument50 pagesTraining ReportAakash SharmaNo ratings yet
- General Business ReportDocument15 pagesGeneral Business ReportAakash SharmaNo ratings yet
- 3rd Year SyllabusDocument30 pages3rd Year SyllabusAakash SharmaNo ratings yet
- Ramdump Modem 2021-06-26 00-06-27 PropsDocument15 pagesRamdump Modem 2021-06-26 00-06-27 PropsKoikoiNo ratings yet
- How To Hide PCDocument1 pageHow To Hide PCSuiko22No ratings yet
- SWOT 4 CountriesDocument4 pagesSWOT 4 CountriesPrateek VyasNo ratings yet
- DLink Product GuideDocument44 pagesDLink Product GuideKPP SPUTNo ratings yet
- Dec 2019 EC370 - Digital Image Processing (S) - Ktu QbankDocument2 pagesDec 2019 EC370 - Digital Image Processing (S) - Ktu QbankSharmin SathiNo ratings yet
- Network Lab NewDocument64 pagesNetwork Lab NewAnonymous sTUtKBbz67% (3)
- Department of Education: 2020 Inset On Ict Literacy and InstructionDocument4 pagesDepartment of Education: 2020 Inset On Ict Literacy and InstructionRainiel Victor M. CrisologoNo ratings yet
- An Internet Service ProviderDocument23 pagesAn Internet Service ProviderGlocer BartolabaNo ratings yet
- LTE BTS HW Introduction To Ogero PDFDocument44 pagesLTE BTS HW Introduction To Ogero PDFOlivier RachoinNo ratings yet
- Job Description - Audio TechnicianDocument3 pagesJob Description - Audio TechnicianIkar GubelkijanNo ratings yet
- Philips Universal Remote Control SBC RU 644 English ManualDocument20 pagesPhilips Universal Remote Control SBC RU 644 English ManualCarlos VieitesNo ratings yet
- TWIX-2 PLC - Compact Series: FeaturesDocument2 pagesTWIX-2 PLC - Compact Series: FeaturesAmeya KoushikNo ratings yet
- Starlink BookletDocument8 pagesStarlink BookletHulio EagleNo ratings yet
- Sony HT-CT370 Startup GuideDocument16 pagesSony HT-CT370 Startup GuideclpiauNo ratings yet
- Script Writing and Radio Broadcasting E.D. BibalDocument22 pagesScript Writing and Radio Broadcasting E.D. Biballovelymae.madaliNo ratings yet
- Breadboard Power Supply v10Document5 pagesBreadboard Power Supply v10pierdonneNo ratings yet
- AV Receiver: Discover The Benefits of Registering Your Product Online atDocument31 pagesAV Receiver: Discover The Benefits of Registering Your Product Online atdacamajxxxNo ratings yet
- TSSR MW Istana PlazaDocument14 pagesTSSR MW Istana PlazaSuprapto ToNo ratings yet
- Acharya Motibhai Patel Institute of Computer StudiesDocument4 pagesAcharya Motibhai Patel Institute of Computer StudiesAyush SahNo ratings yet
- Ap F508RDocument1 pageAp F508RRamtelNo ratings yet
- Sibas Computer (Traction Control Unit (Tcu) ) : ApplicationDocument59 pagesSibas Computer (Traction Control Unit (Tcu) ) : ApplicationTiagohowpy RamosNo ratings yet
- 10 1108 - Bij 11 2020 0583Document31 pages10 1108 - Bij 11 2020 0583selorm7tettehNo ratings yet
- AN TA001 enDocument1 pageAN TA001 enjohnNo ratings yet
- Aoc Monitor E2270SWNDocument1 pageAoc Monitor E2270SWNRichard Henry Sutter RosendoNo ratings yet
- Tronsmart Element t6 Max Bluetooth Speaker Manual OptimizedDocument10 pagesTronsmart Element t6 Max Bluetooth Speaker Manual OptimizedMircea CatalinNo ratings yet
- Wms Req 05Document2 pagesWms Req 05j srisai sekharNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2&3 Imp MeowDocument10 pagesUNIT 2&3 Imp MeowNani tomNo ratings yet