Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Abstract
Abstract
Uploaded by
7d8qbbzktqCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Abstract
Abstract
Uploaded by
7d8qbbzktqCopyright:
Available Formats
Abstract – Blood truths and myths
Blood is essential for maintaining the health and life of the human being. Therefore,
it has many functions, which are: - transporting oxygen, CO2, nutrients, hormones, heat and
wastes; - helps regulate the pH of the body by interacting with acids and bases and also
regulates the water balance by transferring water to and from tissues; - Protects against
diseases through phagocytic white blood cells and antibodies and against blood loss through
clotting.
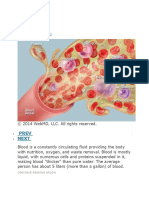
The main constituents of the blood are: the plasma which occupies about 55% of the
blood and it is 92% constituted by water and 7% by proteins; the red blood cells, or
erythrocytes are the most abundant in the blood and give it its bright red color, Red cells
contain a special protein called hemoglobin, which helps carry oxygen from the lungs to the
rest of the body;- the white blood cells or leukocytes protect the body from infections. They
are much fewer in number than red blood cells, accounting for about 1 percent of your
blood; - the last ones are the platelets that help the blood clotting process (or coagulation)
by gathering at the site of an injury, sticking to the lining of the injured blood vessel.
There are some problems related to the blood caused by the deficit or excess of
these elements. The lack of red blood cells can lead to anemia and the excess can to
Polycythemia vera, a fatal decease if not diagnosed and treated. In the white blood cells the
excess of them can cause leukocytosis which can also be caused by leukemia, on the
contrary the lack of white blood cells can lead to leukopenia. The excess of platelets can
lead to thrombocytopenia and the lack of platelets, thrombocythemia.
The decease that we chose to talk about is the venous and arterial thrombosis.
Venous thrombosis is characterized by the presence of a large clot attached to the inner wall
of a vein (thrombus). The clot can break free and cause an embolism in an organ such as the
lungs or brain. The symptoms are pain, felling of heaviness and swelling of the limb and it
has some complications like pulmonary embolism and venous gangrene, which can lead to
limb amputation. To prevent this situation there are some simple things we can do like:
Exercise the muscles, get up and walk at least every half hour; take anticoagulant
medications and wear compression stockings (if prescribed).
You might also like
- Red Blood CellsDocument10 pagesRed Blood CellsReyl EspirituosoNo ratings yet
- Blood BasicsDocument24 pagesBlood BasicsMusallam M. AbukhalilNo ratings yet
- Blood Clinical CorellaionsDocument12 pagesBlood Clinical Corellaionssinte beyuNo ratings yet
- Blood Is A Body Fluid in Human and Other Animals That Delivers Necessary Substances Such AsDocument24 pagesBlood Is A Body Fluid in Human and Other Animals That Delivers Necessary Substances Such AsPaulo DanielNo ratings yet
- Anemia: Our Lady of Fatima University College of NursingDocument21 pagesAnemia: Our Lady of Fatima University College of NursingPOTENCIANA MAROMANo ratings yet
- Blood and CirculationDocument5 pagesBlood and CirculationSatyam RoyNo ratings yet
- HematologyDocument57 pagesHematologyNurhidayahNo ratings yet
- 1 HaematologyDocument6 pages1 HaematologyEma FröhlichováNo ratings yet
- Introduction To HaematologyDocument27 pagesIntroduction To HaematologyKesha NjobvuNo ratings yet
- Año de La Lucha Contra La Corrupción y La ImpunidadDocument5 pagesAño de La Lucha Contra La Corrupción y La ImpunidadHelen Salazar SagasteguiNo ratings yet
- Components of BloodDocument3 pagesComponents of BloodWild RoseNo ratings yet
- HematologyDocument2 pagesHematologyMohammed Al-RahmaweeNo ratings yet
- Modul6 Lbm2-Aulia SifanaDocument41 pagesModul6 Lbm2-Aulia SifanapademotNo ratings yet
- HDL CholesterolDocument3 pagesHDL CholesterolBrylle GamotinNo ratings yet
- Acute Myelogenous Leukemia - Patho, Anatomy, and Diagnostic TestDocument66 pagesAcute Myelogenous Leukemia - Patho, Anatomy, and Diagnostic TestCharles Kevin L. Bataga33% (3)
- Heart: Right Heart Left Heart. Fish in Contrast Have Two Chambers, An Atrium and A Ventricle, WhileDocument5 pagesHeart: Right Heart Left Heart. Fish in Contrast Have Two Chambers, An Atrium and A Ventricle, WhileMiguel PatrickNo ratings yet
- Shock Overview: How The Body WorksDocument9 pagesShock Overview: How The Body WorksZubairAwan00No ratings yet
- Red Blood Cells: The Human Heart Is About The Size of A Clenched FistDocument5 pagesRed Blood Cells: The Human Heart Is About The Size of A Clenched FistPrince JenovaNo ratings yet
- How Does Blood WorkDocument10 pagesHow Does Blood WorkFunnylyn CruzNo ratings yet
- Bone Marrow Is The Soft, Flexible, Vascular Tissue Found in The Hollow InteriorDocument6 pagesBone Marrow Is The Soft, Flexible, Vascular Tissue Found in The Hollow InteriorIanne Sandra SorrosaNo ratings yet
- Health Assessment of The Hematologic SystemDocument28 pagesHealth Assessment of The Hematologic Systemjuanlungu94No ratings yet
- Anemia Anemia Describes The Condition in Which The Number of Red Blood Cells in The Blood Is Low. Probability & StatisticsDocument7 pagesAnemia Anemia Describes The Condition in Which The Number of Red Blood Cells in The Blood Is Low. Probability & StatisticsSahara GalayNo ratings yet
- Blood ComponentsDocument20 pagesBlood Componentsreannevangelista25No ratings yet
- Blood & HematologyDocument6 pagesBlood & HematologyAymen OmerNo ratings yet
- Blood Conditions: BleedingDocument3 pagesBlood Conditions: BleedingAngelo ReyesNo ratings yet
- Cells : Further InformationDocument7 pagesCells : Further InformationMica SaeronNo ratings yet
- BloodDocument2 pagesBloodErica RosislifeNo ratings yet
- Erythrocytes: The erythrocyte is a biconcave disk between 5 and 7.5 μm inDocument7 pagesErythrocytes: The erythrocyte is a biconcave disk between 5 and 7.5 μm inJoselyn Vilcherrez CruzNo ratings yet
- Anatomy: Blood Is A Specialized Bodily Fluid in Animals That Delivers Necessary Substances SuchDocument5 pagesAnatomy: Blood Is A Specialized Bodily Fluid in Animals That Delivers Necessary Substances Suchjeoffrey_castroNo ratings yet
- Polycythemia Vera: What Are The Symptoms of Polycythemia?Document10 pagesPolycythemia Vera: What Are The Symptoms of Polycythemia?Dimpal ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Introduction To HematologyDocument30 pagesLecture 1 - Introduction To Hematologyimam100% (1)
- Components of BloodDocument10 pagesComponents of BloodDJ GAMARINo ratings yet
- Polycythemia Vera - Blood Disorders - MSD Manual Family Health VersionDocument4 pagesPolycythemia Vera - Blood Disorders - MSD Manual Family Health VersionShoaib BajwaNo ratings yet
- Blood ReviewDocument35 pagesBlood ReviewCharli ParachinniNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Fisiologi Manusia: HematologiDocument54 pagesAnatomi Fisiologi Manusia: HematologiARUMNo ratings yet
- Assignment in Science 6 Arianne S. de Guzman 6-Samar 1. What Are The Functions of The Blood?Document3 pagesAssignment in Science 6 Arianne S. de Guzman 6-Samar 1. What Are The Functions of The Blood?Allana PonceNo ratings yet
- Blood CirculatoryDocument5 pagesBlood CirculatoryRekesh SaeedNo ratings yet
- Blood Composition PowerpointDocument40 pagesBlood Composition PowerpointJeremy Wallace100% (3)
- PBL Blood DonationDocument5 pagesPBL Blood DonationSamuel GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Hematology SystemDocument15 pagesHematology SystemayuNo ratings yet
- Blood Questions ReviewDocument8 pagesBlood Questions ReviewJohn Rey AbadNo ratings yet
- Composition of BloodDocument5 pagesComposition of BloodMeghaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Iii - Discussion of The DiseaseDocument13 pagesChapter Iii - Discussion of The DiseaseJemima LaigoNo ratings yet
- Blood DisordersDocument12 pagesBlood DisordersDebby Love GoodluckNo ratings yet
- Human PhysiologyDocument34 pagesHuman PhysiologyMuhammad AliNo ratings yet
- Blood Cells 2Document4 pagesBlood Cells 2Jo Louis CamiguingNo ratings yet
- Assignment in Science 6 John Marvin V. Sarile 6-Samar 1. What Are The Functions of The Blood?Document2 pagesAssignment in Science 6 John Marvin V. Sarile 6-Samar 1. What Are The Functions of The Blood?Allana PonceNo ratings yet
- The Transport SystemDocument29 pagesThe Transport SystemMatthew RamnauthNo ratings yet
- Leukemia Case StudyDocument10 pagesLeukemia Case StudyQueennieMarelRamos100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology Summary Body Fluids and BloodDocument22 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Summary Body Fluids and BloodKelly Anne BrandNo ratings yet
- Picture of Blood: Prev NextDocument4 pagesPicture of Blood: Prev NextArcie NograNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System (Blood)Document57 pagesCirculatory System (Blood)Trisha NideaNo ratings yet
- CH 15 BloodDocument6 pagesCH 15 Bloodsann1992No ratings yet
- BLOODDocument10 pagesBLOODChrisjohn Aster OsioNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System2Document9 pagesCirculatory System2Wajeeha AsifNo ratings yet
- Blood ReadingDocument2 pagesBlood Readingapi-383564780No ratings yet
- Animal Physiology Theory Lec3Document20 pagesAnimal Physiology Theory Lec3ao868598No ratings yet
- Functions of BloodDocument10 pagesFunctions of BloodKert trocioNo ratings yet
- Presenting Problems in Blood Disease and Clinical Examination of PatientsDocument31 pagesPresenting Problems in Blood Disease and Clinical Examination of Patientsساره عدي مصطفىNo ratings yet