Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bank Job Math Lec 14
Bank Job Math Lec 14
Uploaded by
MusaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- G8 Term+3 AnglesDocument20 pagesG8 Term+3 AnglesRam AthreyapurapuNo ratings yet
- Plane and Solid Geometry Module Bsed Math1Document50 pagesPlane and Solid Geometry Module Bsed Math1Ces Sy100% (3)
- Geometry EOC Review PacketDocument39 pagesGeometry EOC Review PacketVale Mejia100% (1)
- Group 1 Solid MensurationDocument71 pagesGroup 1 Solid MensurationEjay Abante83% (6)
- MathematicsDocument9 pagesMathematicsRachel AmairaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Key Points: y F (X) + C y F (X) - C y F (X + C) y F (X - C)Document18 pagesChapter 1 Key Points: y F (X) + C y F (X) - C y F (X + C) y F (X - C)Angel Angel100% (1)
- Maths NotesDocument21 pagesMaths NotesSRIKY CHANNELNo ratings yet
- Untitled-document-2024-05-21T120045.065Document9 pagesUntitled-document-2024-05-21T120045.065Jagveer SinghNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry Revision NotesDocument27 pagesCBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry Revision NotesArpita SharmaNo ratings yet
- Class 8 NotesDocument40 pagesClass 8 NotesAvantika SNo ratings yet
- Revcards SSMDocument12 pagesRevcards SSMapi-200177496No ratings yet
- Class IXLines and AnglesDocument40 pagesClass IXLines and AnglesManoj Pandey100% (1)
- Angles: (180°) and Go Full (360°)Document10 pagesAngles: (180°) and Go Full (360°)Fons Roxas-ChuaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Grade 10 Weeks 1-5 - Term 3Document63 pagesMathematics Grade 10 Weeks 1-5 - Term 3Daniel Dowding100% (1)
- Basic TechDocument35 pagesBasic TechOluwagbeminiyi Gabriel OrisunmibareNo ratings yet
- 6th - Maths - Basic Geometrical IdeasDocument20 pages6th - Maths - Basic Geometrical Ideasvaibhav singhNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Geometry - Formulas PDFDocument31 pages2.1 Geometry - Formulas PDFManju JNo ratings yet
- Parallel Lines Cut by A Tranversal 1 AutosavedDocument56 pagesParallel Lines Cut by A Tranversal 1 Autosavedfreid jaredNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Notes PDFDocument24 pagesMathematics Notes PDFIftikhar AhmedNo ratings yet
- GeometryDocument44 pagesGeometryMickey Mouse100% (1)
- Circle GeometryDocument65 pagesCircle GeometrygideonmknNo ratings yet
- DLP g10 Math 2nd QTR Week 7 FinalDocument13 pagesDLP g10 Math 2nd QTR Week 7 FinalCei-Cei100% (1)
- Short Notes For Geometry - PrintDocument8 pagesShort Notes For Geometry - PrintAvinash GudainiyanNo ratings yet
- A Math Plane Geometry PracticesDocument7 pagesA Math Plane Geometry PracticesgraisetaoNo ratings yet
- Geometry Review by Peaceminusone: CHAPTER 1: Points, Lines, Planes, and AnglesDocument15 pagesGeometry Review by Peaceminusone: CHAPTER 1: Points, Lines, Planes, and AnglesHuzaifa MureedNo ratings yet
- Quadrilaterals NotesDocument11 pagesQuadrilaterals NotesJasleen KaurNo ratings yet
- Geometry Reference: Points, Lines and Planes CirclesDocument2 pagesGeometry Reference: Points, Lines and Planes Circlesmarko1234No ratings yet
- Line 3Document12 pagesLine 3msalha2010No ratings yet
- Maths Module 7: GeometryDocument16 pagesMaths Module 7: GeometryRonnie Smith100% (1)
- Math PerewDocument39 pagesMath PerewJo Honey HugoNo ratings yet
- List of Constructions Axioms and CollariesDocument3 pagesList of Constructions Axioms and Collariesapi-242844746No ratings yet
- Quadrilateral 1Document23 pagesQuadrilateral 1Vamsi GuptaNo ratings yet
- High School Math NotesDocument24 pagesHigh School Math NotesaoeusnthidNo ratings yet
- GeometryDocument28 pagesGeometryASHWIN .A.S.No ratings yet
- Geometry:: Map Bearings, Time Difference and Nautical MilesDocument4 pagesGeometry:: Map Bearings, Time Difference and Nautical MilesMae BeginoNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTION GEOMETRY ch4Document24 pagesINTRODUCTION GEOMETRY ch4Jama abdi ibraahim100% (1)
- Geometry and TrigonometryDocument6 pagesGeometry and TrigonometryAbhay SoniNo ratings yet
- Quadrilateral SDocument13 pagesQuadrilateral SBiplabNo ratings yet
- Mathematics (2 Unit) : Based On 1983 Syllabus, Written in 2004Document16 pagesMathematics (2 Unit) : Based On 1983 Syllabus, Written in 2004PaulNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Congruence and Similarity-1Document4 pagesChapter 6 Congruence and Similarity-1ahmed yusufNo ratings yet
- TheoremsDocument8 pagesTheoremsanjustic25No ratings yet
- Chapters 2 and 3 Notes: Parallel Lines and Triangles: ConstructionsDocument3 pagesChapters 2 and 3 Notes: Parallel Lines and Triangles: ConstructionsFiffy Nadiah SyafiahNo ratings yet
- Maths Ch-5 Lines and AnglesDocument3 pagesMaths Ch-5 Lines and Anglespadhnabacha7No ratings yet
- GRE GeometryDocument26 pagesGRE Geometryperwinsharma100% (1)
- Geometry Concept Booklet 025d90b26ada3Document10 pagesGeometry Concept Booklet 025d90b26ada3Khushi AroraNo ratings yet
- Geometry (2D)Document26 pagesGeometry (2D)mnashish619No ratings yet
- Kj's Geometry ProjectDocument7 pagesKj's Geometry ProjectAnonymous lTXTx1fNo ratings yet
- MATH 113 Module Week 9-11Document14 pagesMATH 113 Module Week 9-11Elmar JuegoNo ratings yet
- MATHS Olevels NotesDocument18 pagesMATHS Olevels NotesMahad Imran100% (8)
- Ch1 Geometry 2Document47 pagesCh1 Geometry 2trantuanan123No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Maths NotesDocument11 pagesChapter 3 Maths NotesViral DaftaryNo ratings yet
- Geometry and ConstructionsDocument46 pagesGeometry and ConstructionsAuthachai Gokla Chaysang100% (2)
- Plane and Solid Geometry - 1Document62 pagesPlane and Solid Geometry - 1Regielyn Pagad100% (2)
- CSEC Maths Geometry & TrignometryDocument10 pagesCSEC Maths Geometry & TrignometryDwayne DixonNo ratings yet
- Yr12 Maths in Focus 2U HSCDocument412 pagesYr12 Maths in Focus 2U HSCRichard Yang93% (14)
- Formula Sheet GeometryDocument2 pagesFormula Sheet GeometrysamuthrarajaNo ratings yet
- Geometry Capsule For SSC Railway Exams Watermark - PDF 70Document13 pagesGeometry Capsule For SSC Railway Exams Watermark - PDF 70Tapas SwainNo ratings yet
- Mensuration PDFDocument33 pagesMensuration PDFSudhanshu Kumar100% (1)
- Notes of The Triangles and Its PropertiesDocument3 pagesNotes of The Triangles and Its PropertiesIshanviNo ratings yet
- Japanese Quality Tools and TechniquesDocument36 pagesJapanese Quality Tools and TechniquesNab JiNo ratings yet
- Steffes 5100 Tech Data SheetDocument4 pagesSteffes 5100 Tech Data SheetcringsredNo ratings yet
- Kalsi® Building Board Cladding: Kalsi® Clad Standard DimensionsDocument1 pageKalsi® Building Board Cladding: Kalsi® Clad Standard DimensionsDenis AkingbasoNo ratings yet
- 4final Examination Prof Ed 10Document7 pages4final Examination Prof Ed 10Danelle EsparteroNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheets Signal WordsDocument15 pagesActivity Sheets Signal WordsGrace Ann EscabarteNo ratings yet
- RailTel Annual Report For Web-CompressedDocument228 pagesRailTel Annual Report For Web-CompressedAmit SahooNo ratings yet
- GraphsDocument18 pagesGraphssaloniNo ratings yet
- Conceptual FrameworkDocument4 pagesConceptual FrameworkEustass KiddNo ratings yet
- Lancaster University Dissertation HandbookDocument5 pagesLancaster University Dissertation HandbookPaperWritingServiceCheapAnnArbor100% (1)
- Bcsbi Pictorial BookDocument24 pagesBcsbi Pictorial BookMALAYADRI DUARINo ratings yet
- Effective Phone and Door Scripts 0Document6 pagesEffective Phone and Door Scripts 0Kaso MuseNo ratings yet
- Hot Cool 3 2012Document32 pagesHot Cool 3 2012thermosol5416No ratings yet
- Science TE804Document15 pagesScience TE804carolynhart_415No ratings yet
- CCC-BMG MOON 3-2 - Within Dwarvenholm v2.0Document30 pagesCCC-BMG MOON 3-2 - Within Dwarvenholm v2.0MarianoNo ratings yet
- Indu Lagna - For Waelth and FinanceDocument7 pagesIndu Lagna - For Waelth and Financeybbvvprasada raoNo ratings yet
- 3I Grading Rubric For Output PresentationDocument2 pages3I Grading Rubric For Output PresentationBinibining Michelle CenizaNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Breaks 1840241519 PDFDocument61 pagesThe Little Book of Breaks 1840241519 PDFksrbhaskarNo ratings yet
- City Center Unifier Deployment PDFDocument35 pagesCity Center Unifier Deployment PDFSachin PatilNo ratings yet
- Quick Reference Guide: 65 Degree 1800 MHZ Dual Polarized 90 Degree 1800 MHZ Dual PolarizedDocument20 pagesQuick Reference Guide: 65 Degree 1800 MHZ Dual Polarized 90 Degree 1800 MHZ Dual PolarizedРоманКочневNo ratings yet
- 5054 s16 Ms 41 PDFDocument3 pages5054 s16 Ms 41 PDFKritish RamnauthNo ratings yet
- The Laws On Local Governments SyllabusDocument4 pagesThe Laws On Local Governments SyllabusJohn Kevin ArtuzNo ratings yet
- ANSWERS For ExercisesDocument13 pagesANSWERS For ExercisesAlia HazwaniNo ratings yet
- 01 02 BDocument453 pages01 02 BJose VieraNo ratings yet
- Z19 Tnoo 000517 PDFDocument1 pageZ19 Tnoo 000517 PDFGuna RajNo ratings yet
- 9de13c0f0c009828f703d0103efa820b.xlsDocument70 pages9de13c0f0c009828f703d0103efa820b.xlsPreeti JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Clique Student Sheet (Manteran Lamo)Document4 pagesClique Student Sheet (Manteran Lamo)Dina Rizkia RachmahNo ratings yet
- Explosion Protection - E PDFDocument7 pagesExplosion Protection - E PDFAPCANo ratings yet
- EXOS Quick Guide - Cheat SheetDocument19 pagesEXOS Quick Guide - Cheat Sheetmaverick2689No ratings yet
- Technical Drawings of PlasticwareDocument69 pagesTechnical Drawings of PlasticwareGuldu KhanNo ratings yet
- ANSWERS - PhyLabS6 EX02 Water TowerDocument8 pagesANSWERS - PhyLabS6 EX02 Water TowerGuacNo ratings yet
Bank Job Math Lec 14
Bank Job Math Lec 14
Uploaded by
MusaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bank Job Math Lec 14
Bank Job Math Lec 14
Uploaded by
MusaCopyright:
Available Formats
Excellence in Education; For Admission: 01713289149 Page 0
Important Terms:
Adjacent = msjMœ Adjoining = msjMœ/mwbœwnZ Altitude = D”PZv
Arc = e„ËPvc Base = f~wg Boundary = mxgvbv
Circumference = cwiwa Circumscribed = ewnte¨vmva© Cocentric = mg‡Kw›`ªK
Congruent = me©mg Constructed = wbwg©Z Corresponding = Abyiƒc
Diagonal = KY© Diameter = e¨vm Dimension = gvÎv
Hypotenuse = AwZfzR Incircle = AšÍte„Ë Inradius = AšÍte¨vmva©
Inscribed = AšÍwj©wLZ Perpendicular = j¤^ Rectangle = AvqZ‡ÿÎ
Region = AÂj/GjvKv Rhombus = i¤^m Sector = e„ËKjv
Segment = Ask/‡iLvsk Semi-circle = Aa©e„Ë Semi-perimeter = Aa©-cwimxgv
Symmetrically = cÖwZmgfv‡e Triangular = wÎf~RvK…wZ Vertex = kxl©we›`y
Wheel = PvKv Width = cÖk¯ÍZv/PIov/cÖ¯’ Angle of depression = AebwZ †KvY
Angle of elevation = DbœwZ †KvY Horizontal = Abyf~wgK Ladder = gB
Shadow = Qvqv Vertical = Dj¤^
Excellence in Education; For Admission: 01713289149 Page 1
Introduction:
The word GEOMETRY is derived from two words – GEO meaning earth and METRY meaning
measurement. Hence, it is quite evident that geometry as a mathematical science developed mainly due to
the human need of measuring land masses and distances. The major developments in the fields of
GEOMETRY and MENSURATION are mainly credited to the ancient Egyptian and Greek
civilizations. (In fact, this is one of the reasons why all formulae and theorems primarily carry Greek
names.)
Key Geometrical Concepts
Point: The point should be visualised as a singular dot. In physical terms, a point can be defined
as a single dot that can be created on a plain paper by a very sharp pencil. It could also be
visualised as a singular prick on a piece of paper by a very sharp nail or pin.
Line: Mathematically, lines are defined as a group of points which are straight one after another.
All lines are supposed to extend infinitely in two directions.
Segment of a Line
If a part of a line is cut out, we get a segment of a line.
Physically, the closest representations of a segment of a line would be a tight thread or the straight crease
of a piece of paper.
Plane: The surface of a smooth wall or a table top is the closest representation of a portion of a plane.
Some Geometrical Properties:
Lines Between Points: Let us take two distinct points in a plane. You can easily verify that an
infinite number of lines can be drawn in the plane passing through any one of these two points.
However, if you wanted to draw a line which passes through both the points, you will be able to draw
only one line. This is an important result in Geometry.
Property: Given any two distinct points in a plane, there exists one and only one line containing both the
points. Alternately, we can state that two distinct points in a plane determine a unique line.
Collinearity of Points: Collinear or non-collinear points are only defined in the context of three or
more points.
Consider the situation of three points. There can only be two cases with respect to three points:
1. All the points lie on the same line. (Here, the points are said to be collinear).
2. All the three points do not lie on the same line (In this case the points are said to be non-
collinear).
**Note: It is quite evident that we would discuss collinear or non-collinear points only if the number
or points is more than two. Obviously, if there are only two points they would always be on one line.
Excellence in Education; For Admission: 01713289149 Page 2
Points in Common between Distinct Lines: In the case of distinct lines, there can only be two cases:
(a) There is one point in common in such a case, the common point is called the point of intersection, and
the two lines are called as intersecting lines.
(b) There is no point in common: In such a case, the two lines are non-intersecting and are also called as
parallel lines.
The property can thus be stated as: Property Two distinct lines in a plane cannot have more than one point
in common.
Lines and Points (Property): Given a line and a point in the same plane, such that the point is not on
the line, there is one and only one line which passes through the point and is parallel to the given line.
Lines (Property): Two intersecting lines cannot be parallel to the same line
Multiple Lines: There can be four distinct possibilities in such a case -
1. No two lines intersect each other
2. Some lines intersect
3. Every line intersects all other lines, but their respective points of intersection are different from each
other
4. Every pair of lines is intersecting and all the points of intersection coincide.
Angles: When two straight lines meet at a point, they form an angle. The point is called the vertex of
the angle, and the lines are called the sides of the angle.
The angle to the right can be identified in three ways:
1. ∠x
2. ∠B
A
3. ∠ABC or ∠CBA
x
B
C
Vertically Opposite Angle: When two straight lines meet at a point, they from four angles. The
angles opposite each other are called vertical angles, and they are congruent (equal). In the figure to
the right, a = b, and c = d.
a b
Excellence in Education; For Admission: 01713289149 Page 3
Angles are measured in degrees. By definition, a circle has 360º. So, an angle can be measured by its
fractional part of the circle. For example, an angle that is of the arc of a circle is 1. And an angle that
is of the arc of a circle is × 360 = 90º.
1º 90º 240º
of an arc of a circle
of an arc of a circle of an arc of a circle
Angles formed when two parallel lines, are crossed by a transversal: When two parallel lines are
crossed by a third line. (transversal), 8 angles are formed. Take a look at the following figure:
1 2
5 8
4 3
7 6
Angles 3,4,5,8 are interior angles.
Angles 1,2,6,7 are exterior angles.
Alternate interior angles: Pairs of interior angles on opposite sides of the transversal.
For instance, angle 3 and angle 5 are alternate interior angles. Angle 4 and angle 8 are also alternate
interior angles. Both the angles in a pair of alternate interior angles are equal. Hence, in the figure we
have: Angle 3 = Angle 5: Also Angle 4 = Angle 8.
Alternate exterior angles: Pairs of exterior angles on opposite sides of the transversal.
Excellence in Education; For Admission: 01713289149 Page 4
Angle 2 and angle 7 are alternate exterior angles. Angles 1 and 6 are also alternate exterior angles.
Both the angles in a pair of alternate interior angles are equal. Thus, in figure Angle 2 = Angle 7 and
Angle 1 = Angle 6. Co-interior angles: When two lines are cut by a third line (transversal) co-interior
angles are between the pair of lines on the same side of the transversal. If the lines that are being cut
by the transversal are parallel to each other, the co-interior angles are supplementary add up to 10
degrees). In the given figure angles 3 and 8 are co-interior angles. Also, angles 4 and 5 are co-interior
angles, since the lines being cut are parallel in this case, 23 + 28 180. Also, 24 + 25 = 180.
Co-interior angles: When two lines are cut by third line (transversal) co-interior angles are between
the pair of lines on the same side of the transversal. If the lines that are being cut by the transversal
are parallel to each other, the co-interior angles are supplementary (add up to 180 degrees). In the
given figure angles 3 and 8 are co-interior angles. Also, angles 4 and 5 are co-interior angles, since,
the lines being cut are parallel in this case, ∠3 + ∠8 = 180. Also, ∠4 + ∠5 = 180.
Corresponding angles: Are pairs of angles that are in positions when two parallel lines are interested
similar positions when two parallel lines are intersected by a transversal.
Angle 3 and angle 2 are corresponding angles. Similarly, the pairs of angles, and 4 ; 5 and 7 ; 6 and 8
are corresponding angles. Corresponding angles are equal. Thus, in the figure- ∠1 = ∠4; ∠5 = ∠7; ∠2
= ∠3 and ∠6 = ∠8.
Linear pair: ∠XOY and ∠YOZ are linear pair angles. One side must be common (e.g. OY) and these
two angles must be supplementary.
1 2
X Z
O
Angles on the side of a line: ∠1 + ∠2 + ∠3 = 180º
2
1 3
Excellence in Education; For Admission: 01713289149 Page 5
Angles around the point: ∠1 + ∠2 + ∠3 + ∠4 + ∠5 = 360º
2
1 3
4 5
Angle Bisector: OY is the angle bisector for the ∠XOZ, i.e., ∠XOY = ∠ZOY = ∠XOZ
X
O Z
When a line segment divides an angle equally into two parts, then it is said to be the angle bisector
(OY).
(Angle bisector is equidistant from the two sides of the angle.)
X
Y
O Z
The distance between the lines OX and OY and the lines OY and OZ are equal to each other.
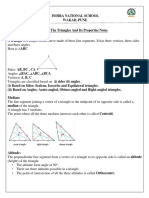
Some properties of Point, Line and Triangle:
1. The sum of all the angles round a point is equal to 360°
2. Two lines parallel to the same line are parallel to each other.
Excellence in Education; For Admission: 01713289149 Page 6
3. The sum of three angles of a triangle is 180°.
4. If a side of a triangle is produced, the exterior angle so formed is equal to the sum of the two interior
opposite angles. (Exterior Angle Theorem)
[
5. If two sides of a triangle are unequal, the longer side has greater angle opposite to it.
6. In a triangle, the greater angle has the longer side opposite to it.
7. The sum of any two sides of a triangle is greater than the third side and the difference of any two sides
is less than the third side. If a, b, c denotes the sides of a triangle then, (a + b) > c > (a - b).
8. If a, b, c denotes the sides of a triangle then,
(ⅰ) If c² < a² + b², triangle is acute angled.
(ⅱ) If c² = a² + b², triangle is right angled.
(ⅲ) If c² > a² + b², triangle is obtuse angled.
9. Two triangles congruent if:
(ⅰ) Any two sides and the included angle of one triangle are equal to any two sides and the included angle
of the other triangle.
(SAS Congruence Theorem)
(ⅱ) Two angles and the included side of one triangle are equal to the corresponding two angles and the
included side of the other triangle.
(ASA Congruence Theorem)
(ⅲ) The three sides of one triangle are equal to the corresponding three sides of the other triangle.
(SSS Congruence Theorem).
Note: Two right triangles are congruent if the hypotenuse and one side of one triangle are equal
respectively equal to the hypotenuse and the corresponding side of the other triangle.
(RHS Congruence Theorem).
10. The line segments joining the mid-points of any two sides of a triangle is parallel to the third side and
equal to half of it.
Excellence in Education; For Admission: 01713289149 Page 7
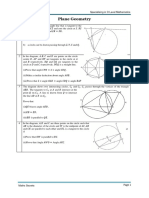
GEOMETRY, MENSURATION AND TRIGONOMETRY
PART- Ⅰ : CONCEPT CLEARING EXERCISE
1. In the figure below, what is the value of b?
2bº 2aº
bº
4aº
a. 9 b.18 c. 27 d. 36 e. 45
2. In the figure below, what is the value of x if y :x = 3:2?
xº yº
a. 18 b. 27 c. 36 d. 35 e. 54
3.In the figure, AD and BC are lines intersecting at O. What is the value of a?
(GNB – 8)
C
A 5x + 5a 2x + 30 D
B
a. 15 b. 30 c. 45 d. 60 e. 135
4. ∠A and ∠B are supplementary to each other. If ∠A = 115º then ∠B is – (BDBL : SO – 2017)
a. 65º b. 110º c. 290º d. 90º e. None of these
Excellence in Education; For Admission: 01713289149 Page 8
5. B and C are points on a straight line AD, where AB = BC = CD. What Percent of AC is AD?
[MBA : Ad Test - (02-03)]
A E
B C D
a. 1.5% b.50% c. 6.67% d. 150% e. None of these
6. Lines L1& L2 are parallel to each other. What is the value of x?
(Eastern Bank – 05)
L1
xº
L2
2yº
yº
a. 120º b. 90º c. 60º d. 30º e. None of these
z C
y
xº
B D E
7. In the figure above, if z = 50, then x + y = ?
a. 230 b. 250 c. 260 d. 270 e. 290
8. The length of two sides of a triangle are 7 and 11. If the length of the third side is an integer, what is
the least possible perimeter of the triangle? (UCBL - PO : 2017)
a. 18 b. 20 c. 23 d. 25 e. 18
Excellence in Education; For Admission: 01713289149 Page 9
9. Which three lines could not construct a triangle?
a. 45 cm, 46 cm, 44 cm b. 24 cm, 27 cm, 23 cm c. 25 cm, 13 cm, 12 cm
d. 15 cm, 16 cm, 17 cm e. 18 cm, 12 cm, 25 cm
10. ABC is a triangle where ∠ABC = 100° and AB = BC, find the measure of ∠BAC. (IBA - BBA : 2005
- 06)
a. 80° b. 60° c. 40° d. 20° e. None of these
11. In the triangle, what is the value of x?
yº+xº
70º-yº 60º+xº
a. 25 b. 55 c. 60 d. 77 e. 85
50º xº
12. What is the value of x in the figure ?
a. 80 b. 100 c.115 d. 120 e. 130
13. In the figure below, triangle ABC is isosceles with base AC. If x = 60º, then AC = ?
(Shahjalal IB Ltd. : Cash – 2013)
B
4
x
A C
a. 2 b. 3 c. 4 d. e. None of these
Excellence in Education; For Admission: 01713289149 Page 10
14. Which of the following is the ratio of the sides of right angled triangle? (IFIC Bank - 2018)
a. 6 : 4 : 3 b. 6 : 5 : 4 c. 11 : 8 : 7 d. 13 : 12 : 5 e. None of these
15. The lengths of two sides of a triangle are 13cm and 5 cm respectively. The length of the third side is -
(BDBL - SO : 2017 ; RupaliBnak - 2018)
a. 13 b. 14 c. 17 d. 11 e. 12
P
20
Q 5 S 11 R
16. What is the value of PS in the triangle above?
a. 5√2 b. 10 c. 11 d. 13 e. 12√2
17. In the figure, ∠BAC = 45°, BD = 4 cm and DC = 2AD. What is the length of the side AC?
B
(IBA – MBA : 2002 – 03)
A D C
a. 24 b. 18 c. 12 d. 8 e. None of these
18. In the following diagram, AB and CD are both perpendicular to BE. If EC = 5 and CD = 4, what is the
ratio of AB to AC?
A
E
B D
a. 1 : 1 b. 4 : 3 c. 5 : 4 d. 5 : 3 e. None of these
Excellence in Education; For Admission: 01713289149 Page 11
19. What is the perimeter of the rectangle with diagonal 10 cm and width 6 cm? (Bangladesh Krishi Bank
: Senior Officer)
10 6
a. 28 b. 24 c. 20 d. 18 e. None of these
20. Given AB = 4, AC = 5, the perimeter of the rectangle is –
B C
A D
a. 18 b. 40 c. 14 d. 22 e. None of these
21. In the figure below ACDH and BCEF are rectangles, AH = 3, GH = 3, and FE = 6, what is the area of
BCDG? (BPC – 2009; Premier Bank – 2009; prime Bank – 2009, Jamuna Oil Company Ltd. -2010)
C D E
6
G
C
B G 3 F
G
C
C
C
A H3
3 G
C
G
C C
a. 72 b. 90 c. 54 C d. 18 e. None of these
22. In rectangle ABCD below, AC = 10, what is the area of rectangle?
B C
10
30°
A D
a. 25√2 b. 25√3 c. 48 d. 50 e. 100
Excellence in Education; For Admission: 01713289149 Page 12
Q R
x°
140° 2y
P S
23. In the figure above, if PQRS is a parallelogram, then y – x = ? (National Bank Ltd.: P. Off – 2013)
a. 30 b. 35 c. 40 d. 70 e. None of these
24. If the figure is a square, what is the perimeter of the figure?
X+4
2x+1
a. 9 b. 12 c. 16 d. 25 e. None of these
25. If a square region has area n, what is the length of the diagonal of the square in terms of n?
(Bank Asia : MTO – 2017)
a. √ b. √n c. 2√n d. 2n e. None of these
26. In this diagram, ABCD is a parallelogram, and BFDE is a square. If AB = 20 and CF = 16, what is the
perimeter of the parallelogram ABCD?
B F 16 C
20
A E D
a. 72 b. 78 c. 86 d. 92 e. 96
27. The diagonals of a rhombus are 32 cm and 24 cm respectively. The perimeter of the rhombus is :
a. 80 cm b. cm c. 68cm d. cm e. None of these
Excellence in Education; For Admission: 01713289149 Page 13
28. In the rhombus beside, side AB = 10 cm and ∠BAE = 30°. What is the area of rhombus in sq.cm?
a. 50
D
b. 50√ C
c. 50√
d. 100√
e. Cannot be determined A B
29. The parallel sides of trapezium are 10 cm and 20 cm respectively. AD = 6 cm and CB = 8 cm. Find
the area of the trapezium.
D C
B
A
a. 120 b. 96 c. 72 d. 48 e. None of these
30. The circumference and the area of a circle are numerically equal, what is the numerical value of a
diameter?
a. b. 4 c. 2 × d. 2 e. 1
31. The radius of a circle is decreased by 10%. By what percent will its area decrease?
(IBA - MBA : 2012)
a. 10% b. 12.5% c. 17.5% d. 19% e. None of these
32. In the figure, O is the center of the circle and ∠OCB = 35°. What is value of ∠BAC?
(IBA – BBA : 1998-98)
B C
a. 65° b. 60° c. 55° d. 50°
Excellence in Education; For Admission: 01713289149 Page 14
33. In the figure, O is the center of the circle. OC is perpendicular to AB and is 2 cm less than AC. If the
diameter of the circle is 20 cm, what is the length of AB in cm? (IBA – BBA : 1998 – 99)
10
(x-2)
A x B
C
a. 8.5 b. 10 c. 15 d. 17 e. None of these
34. In the figure, ABCD and PQRS are two rectangles inscribed in the circle as shown and AB = 4, AD =
3, and QR = 4. What is the value of l?
P Q
A B
4
4
3 l
D C
S R
a. b. c. 3 d. 4 e. 5
35. The length of one side of the square in the picture below is 8. All the four circles are inscribe within
the square and are of equal radii. What is the area of the shaded region?
CC CC
CC CC
a. 16π b. 64 - 16π c. 16 - 4π d. 64 - 32π e. 64 - 26π
Excellence in Education; For Admission: 01713289149 Page 15
36. The side length of a squareinscribed in a circle is 2. What is the area of the circle?
(IBBL – PO : 2017 ; RAKUB – SO : 2015)
a. π b. √ π c. 2π d. 2√ π e. None of these
37. A squaring is inscribed in a circle of diameter 2a and another square is circumscribing circle. The
difference between the areas of outer and inner squares is –
(Combined 8 Bank : SO – 2018 ; Combined 4 Bank – 2018 ; Sonali Bank - 2019)
2 2 2 2
a. a b. 2a c. 3a d. 4a e. None of these
38. What is the area of the equilateral triangle if the base BC = 6?
(Agrani Bank Ltd. : Senior Officer – 2013)
a. √ b. √ c. √ d. √
39. The area of a triangle with sides 3 cm, 5 cm and 6 cm is –
(RupaliBank : Officer Cash – 2018 ; Sonali Bank : SO – 2018)
2 2 2 2
a. √ cm b. √ cm c. √ cm d. √ cm
2
40. What would be the measure of the diagonal of a square whose area is equal to 578cm ?
(JanataBank : AEO – 2019)
a. 34 cm b. 38 cm c. 32 cm d. 42 cm
41. If the diagonal of a square measures √ cm, what is the area of the square in sq.cm?
(Pubali Bank Ltd. : SO – 2013)
a. √ b. √ 0c. 128 d. 256
42. If ∠ADC = 150°, AB = y cm and BC = x cm, find the area of parallelogram ABCD.
D C
A B
√
a. b. c. d. e.
√ √ √
Excellence in Education; For Admission: 01713289149 Page 16
43. In the diagram below, ABCDEF is a regular hexagon. How many degrees are there in ∠ACD?
F B
E C
a. 45° b. 60° c. 75° d. 90° e. None of these
44. If the volume of a cube is 27 cubic meters, find the surface area of the cube –
(Agrani Bank Ltd. : Senior Officer – 2013)
a. 9 sq.m b. 18sq.m c. 54sq.m d. 3sq.m
45. A box is made in the form of a cube. If a second cubical box inside dimensions three times those of
the first box, how many times as much does the second box contain?
(SonaliBank : Officer Cash – 2018 ; Combined 3 Banks : SO – 2018 ; Sonali Bank : Officer FF – 2019)
a. 6 b. 9 c. 12 d. 27
46. The dimensions of a box are 2, 3 and 4 meters. The cost of painting the outer sides of the box, at the
rate of Tk.3 per square meter is - (Agrani Bank - 2017 ; Bangladesh Bank - AD - 2018)
a. Tk. 156 b. Tk. 220 c. Tk. 136 d. Tk.160
47. A rectangular fish tank 25m by 9m has water in it to a level of 2m. This water is carefully poured into
a cylindrical container with a diameter of 10 m. How high will the water reach in the cylindrical
container? (ICB - AE - 2017 ; Sonali Bank - CO - 2018 ; Combined 3 Bank - SO - 2018)
a. b. 18π c. d.
48. If two planes leave the same airport at 1: PM, how many miles apart will they be at 3:00 PM, if one
plane flies north at 150 mph and the other travels directly west at 200 mph? [PKB - (EO Cash) - 2018]
a. 50 miles b. 100 miles c. 500 miles d. 700 miles
Excellence in Education; For Admission: 01713289149 Page 17
49. How much will it cost to fence in a field that is 360 cm long and 160 cm wide with fence that costs
Tk. 100 a meter? (Bangladesh Bank : AD – 2001)
a. 1020 b. 1040 c. 1060 d. None of these
50. A wheel that has 6 cogs is meshed with a wheel of 14 cogs. When the smaller wheel has made 21
revolutions, the number of revolutions made by the larger wheel is- (IBBL : PO – 2017)
a. 4 b. 9 c. 12 d. 49
51. If secθ + tanθ = x, then tanθ is? (RupaliBank : CO – 2018; Sonali Bank : SO – 2018)
a. b. c. d.
2 2 4
52. If sinA + sin A = 1, then the value of the expression cos A + cos A is – (RupaliBank : CO – 2018)
a. 1 b. c. 2 d. 3
53. A pole 6 m high casts a shadow 2√3 m long on the ground, then the Sun’s elevation is -
(Rupali Bank - 2018 ;Sonali Bank - 2018 ; Bangladesh Bank - AD - 2018)
a. 60° b. 45° c. 30° d. 90°
54. The angle of elevation of a ladder leaning against a wall is 60° and the foot of the ladder is 4.6 m
away from the wall. The length of the ladder is-
(Combined 6 Bank – 2019)
a. 2.3 m b. 9.2 m c. 4.6 m d. 7.8 m
55. If C is the midpoint of the points A(- 3, - 4) and B(- 5, 6), then AC = ?
a. 5 b. √26 c. √61 d. 8 e.10
56. Find the slope of the line 5x – 5y = 7 (BKB – 2017)
a. 5 b. c. 1 d.
57. Which of the following equations does not represent a straight line? (BD House Building : SO – 2017)
a. y = 2x + 3 b. y = 2x2 + 3 c. y (2 + x) = 3 d. y + x – 3 = 7
Excellence in Education; For Admission: 01713289149 Page 18
PART- Ⅱ: ADDITIONAL PART FOR SELF PRACTICE
58. Which of the following angle can be constructed with the help of a ruler and a pair of compasses?
(Rupali Bank : Off Cash – 2018)
a. 35º b. 40º c. 37.5º d. 47.5º e. None of these
Ans : (c )
59. What is the perimeter of ∆ABC shown in the figure?
2z°
z° y°
y° C B x°
a. 2 + √ b. 4 + √ c. 8 d. 4 + √ e. 4 + √
Ans : (b)
60. If the hypotenuse of an isosceles right triangle has length of 8, then the are of the triangle is –
(IBBL – 2017)
a. 4 b. 8 c. 16 d. 4√ e. 1
Ans : c
61. If the length of the longest side of the triangles shown below is 36, what is perimeter of the triangle?
9k
6k
12k
a. 51 b. 63 c. 81 d. 81 e. 108
Ans : c
Excellence in Education; For Admission: 01713289149 Page 19
62. In the figure to the right, the area of ∆PQR is 40. What is the area of ∆QRS?
a. 10
b. 15 Q
c. 20
6
d. 25 S
P R
e. 45 5
Ans : d
2
63. ABC is an equilateral triangle, inscribed in a circle. If AB = 6 cm, find the area of the circle in cm .
a. 36π
C
b. 12π
c.
√
A B
d. √
Ans : b
64. A circle is inscribed inside a right angled triangle with equal sides. What is the area of the circle if the
length of one side of the right angled triangle is 4 cm? (Sonali Bank : SO : Written – 2018)
Ans : 8π (3 - √ )
65. What is the area of a regular hexagon with a side measuring 2 inch?
a. 9√ b. 6√ c. 3 d. 9 e. 6√
Ans : b
y-axis
Quadrant Ⅱ 100 Quadrant Ⅰ
A(m, n)
x-axis
- 100 100
Quadrant Ⅳ
Quadrant Ⅲ - 100
Excellence in Education; For Admission: 01713289149 Page 20
66. In the figure, the point A(m, n) lies Quadrant Ⅱ as shown. In which region is the point B(n, m) ?
a. Quadrant Ⅰ
b. Quadrant Ⅱ
c. Quadrant Ⅲ
d. Quadrant Ⅳ
e. On the x-axis
67. In the figure to the right, the radius of the larger circle is twice that of the smaller circle. If the circle
are concentric, what is the ratio of the shaded region’s area to the area of the smaller circle?
a. 10 : 1
b. 9 : 1
c. 3 : 1
d. 2 : 1
O
e. 1 : 1
Ans : c
68. A circular garden with diameter of 20 m is surrounded by a walkway of width 1 m, what is the area of
the walkway? (BD House Building : FC – 2017)
a. 41π b. 41 m2 c. 21πm2 d. 21π
Ans : c
69. The circumference of the circle and the perimeter of the square is equal and the ratio between the
diameter of the circle and the side of the square is 7 : 11. What is the area of the circle? (Combined 4
Bank – 2019)
a. 154 cm2 b. 160 cm2 c. 132 cm2 d. cannot be determined
Ans : d
70. If the radius of cylinder is halved and height is doubled, the what will be the curved surface area?
(Sonali Bank : SO – 2018)
a. Increased by 1 b. The same c. Double d. Triple
Ans : b
Excellence in Education; For Admission: 01713289149 Page 21
71. The triangular base of a prism is a right triangle of sides a and b = 2a. The height of h of the prism
equal to 10 mm and its volume is equal to 40 m. What will be the side a and h of the triangle? (PKB –
2018)
a. 2 mm and 3 mm b. 1 mm and 4 mm c. 2 mm and 2 mm d. 2 mm and 4 mm
Ans : d
72. If 1 + sinθ = xcosθ, then tanθ is- (Bangladesh Bank : AD – 2018)
a. b. c. d.
Ans: d
Excellence in Education; For Admission: 01713289149 Page 22
You might also like
- G8 Term+3 AnglesDocument20 pagesG8 Term+3 AnglesRam AthreyapurapuNo ratings yet
- Plane and Solid Geometry Module Bsed Math1Document50 pagesPlane and Solid Geometry Module Bsed Math1Ces Sy100% (3)
- Geometry EOC Review PacketDocument39 pagesGeometry EOC Review PacketVale Mejia100% (1)
- Group 1 Solid MensurationDocument71 pagesGroup 1 Solid MensurationEjay Abante83% (6)
- MathematicsDocument9 pagesMathematicsRachel AmairaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Key Points: y F (X) + C y F (X) - C y F (X + C) y F (X - C)Document18 pagesChapter 1 Key Points: y F (X) + C y F (X) - C y F (X + C) y F (X - C)Angel Angel100% (1)
- Maths NotesDocument21 pagesMaths NotesSRIKY CHANNELNo ratings yet
- Untitled-document-2024-05-21T120045.065Document9 pagesUntitled-document-2024-05-21T120045.065Jagveer SinghNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry Revision NotesDocument27 pagesCBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry Revision NotesArpita SharmaNo ratings yet
- Class 8 NotesDocument40 pagesClass 8 NotesAvantika SNo ratings yet
- Revcards SSMDocument12 pagesRevcards SSMapi-200177496No ratings yet
- Class IXLines and AnglesDocument40 pagesClass IXLines and AnglesManoj Pandey100% (1)
- Angles: (180°) and Go Full (360°)Document10 pagesAngles: (180°) and Go Full (360°)Fons Roxas-ChuaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Grade 10 Weeks 1-5 - Term 3Document63 pagesMathematics Grade 10 Weeks 1-5 - Term 3Daniel Dowding100% (1)
- Basic TechDocument35 pagesBasic TechOluwagbeminiyi Gabriel OrisunmibareNo ratings yet
- 6th - Maths - Basic Geometrical IdeasDocument20 pages6th - Maths - Basic Geometrical Ideasvaibhav singhNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Geometry - Formulas PDFDocument31 pages2.1 Geometry - Formulas PDFManju JNo ratings yet
- Parallel Lines Cut by A Tranversal 1 AutosavedDocument56 pagesParallel Lines Cut by A Tranversal 1 Autosavedfreid jaredNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Notes PDFDocument24 pagesMathematics Notes PDFIftikhar AhmedNo ratings yet
- GeometryDocument44 pagesGeometryMickey Mouse100% (1)
- Circle GeometryDocument65 pagesCircle GeometrygideonmknNo ratings yet
- DLP g10 Math 2nd QTR Week 7 FinalDocument13 pagesDLP g10 Math 2nd QTR Week 7 FinalCei-Cei100% (1)
- Short Notes For Geometry - PrintDocument8 pagesShort Notes For Geometry - PrintAvinash GudainiyanNo ratings yet
- A Math Plane Geometry PracticesDocument7 pagesA Math Plane Geometry PracticesgraisetaoNo ratings yet
- Geometry Review by Peaceminusone: CHAPTER 1: Points, Lines, Planes, and AnglesDocument15 pagesGeometry Review by Peaceminusone: CHAPTER 1: Points, Lines, Planes, and AnglesHuzaifa MureedNo ratings yet
- Quadrilaterals NotesDocument11 pagesQuadrilaterals NotesJasleen KaurNo ratings yet
- Geometry Reference: Points, Lines and Planes CirclesDocument2 pagesGeometry Reference: Points, Lines and Planes Circlesmarko1234No ratings yet
- Line 3Document12 pagesLine 3msalha2010No ratings yet
- Maths Module 7: GeometryDocument16 pagesMaths Module 7: GeometryRonnie Smith100% (1)
- Math PerewDocument39 pagesMath PerewJo Honey HugoNo ratings yet
- List of Constructions Axioms and CollariesDocument3 pagesList of Constructions Axioms and Collariesapi-242844746No ratings yet
- Quadrilateral 1Document23 pagesQuadrilateral 1Vamsi GuptaNo ratings yet
- High School Math NotesDocument24 pagesHigh School Math NotesaoeusnthidNo ratings yet
- GeometryDocument28 pagesGeometryASHWIN .A.S.No ratings yet
- Geometry:: Map Bearings, Time Difference and Nautical MilesDocument4 pagesGeometry:: Map Bearings, Time Difference and Nautical MilesMae BeginoNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTION GEOMETRY ch4Document24 pagesINTRODUCTION GEOMETRY ch4Jama abdi ibraahim100% (1)
- Geometry and TrigonometryDocument6 pagesGeometry and TrigonometryAbhay SoniNo ratings yet
- Quadrilateral SDocument13 pagesQuadrilateral SBiplabNo ratings yet
- Mathematics (2 Unit) : Based On 1983 Syllabus, Written in 2004Document16 pagesMathematics (2 Unit) : Based On 1983 Syllabus, Written in 2004PaulNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Congruence and Similarity-1Document4 pagesChapter 6 Congruence and Similarity-1ahmed yusufNo ratings yet
- TheoremsDocument8 pagesTheoremsanjustic25No ratings yet
- Chapters 2 and 3 Notes: Parallel Lines and Triangles: ConstructionsDocument3 pagesChapters 2 and 3 Notes: Parallel Lines and Triangles: ConstructionsFiffy Nadiah SyafiahNo ratings yet
- Maths Ch-5 Lines and AnglesDocument3 pagesMaths Ch-5 Lines and Anglespadhnabacha7No ratings yet
- GRE GeometryDocument26 pagesGRE Geometryperwinsharma100% (1)
- Geometry Concept Booklet 025d90b26ada3Document10 pagesGeometry Concept Booklet 025d90b26ada3Khushi AroraNo ratings yet
- Geometry (2D)Document26 pagesGeometry (2D)mnashish619No ratings yet
- Kj's Geometry ProjectDocument7 pagesKj's Geometry ProjectAnonymous lTXTx1fNo ratings yet
- MATH 113 Module Week 9-11Document14 pagesMATH 113 Module Week 9-11Elmar JuegoNo ratings yet
- MATHS Olevels NotesDocument18 pagesMATHS Olevels NotesMahad Imran100% (8)
- Ch1 Geometry 2Document47 pagesCh1 Geometry 2trantuanan123No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Maths NotesDocument11 pagesChapter 3 Maths NotesViral DaftaryNo ratings yet
- Geometry and ConstructionsDocument46 pagesGeometry and ConstructionsAuthachai Gokla Chaysang100% (2)
- Plane and Solid Geometry - 1Document62 pagesPlane and Solid Geometry - 1Regielyn Pagad100% (2)
- CSEC Maths Geometry & TrignometryDocument10 pagesCSEC Maths Geometry & TrignometryDwayne DixonNo ratings yet
- Yr12 Maths in Focus 2U HSCDocument412 pagesYr12 Maths in Focus 2U HSCRichard Yang93% (14)
- Formula Sheet GeometryDocument2 pagesFormula Sheet GeometrysamuthrarajaNo ratings yet
- Geometry Capsule For SSC Railway Exams Watermark - PDF 70Document13 pagesGeometry Capsule For SSC Railway Exams Watermark - PDF 70Tapas SwainNo ratings yet
- Mensuration PDFDocument33 pagesMensuration PDFSudhanshu Kumar100% (1)
- Notes of The Triangles and Its PropertiesDocument3 pagesNotes of The Triangles and Its PropertiesIshanviNo ratings yet
- Japanese Quality Tools and TechniquesDocument36 pagesJapanese Quality Tools and TechniquesNab JiNo ratings yet
- Steffes 5100 Tech Data SheetDocument4 pagesSteffes 5100 Tech Data SheetcringsredNo ratings yet
- Kalsi® Building Board Cladding: Kalsi® Clad Standard DimensionsDocument1 pageKalsi® Building Board Cladding: Kalsi® Clad Standard DimensionsDenis AkingbasoNo ratings yet
- 4final Examination Prof Ed 10Document7 pages4final Examination Prof Ed 10Danelle EsparteroNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheets Signal WordsDocument15 pagesActivity Sheets Signal WordsGrace Ann EscabarteNo ratings yet
- RailTel Annual Report For Web-CompressedDocument228 pagesRailTel Annual Report For Web-CompressedAmit SahooNo ratings yet
- GraphsDocument18 pagesGraphssaloniNo ratings yet
- Conceptual FrameworkDocument4 pagesConceptual FrameworkEustass KiddNo ratings yet
- Lancaster University Dissertation HandbookDocument5 pagesLancaster University Dissertation HandbookPaperWritingServiceCheapAnnArbor100% (1)
- Bcsbi Pictorial BookDocument24 pagesBcsbi Pictorial BookMALAYADRI DUARINo ratings yet
- Effective Phone and Door Scripts 0Document6 pagesEffective Phone and Door Scripts 0Kaso MuseNo ratings yet
- Hot Cool 3 2012Document32 pagesHot Cool 3 2012thermosol5416No ratings yet
- Science TE804Document15 pagesScience TE804carolynhart_415No ratings yet
- CCC-BMG MOON 3-2 - Within Dwarvenholm v2.0Document30 pagesCCC-BMG MOON 3-2 - Within Dwarvenholm v2.0MarianoNo ratings yet
- Indu Lagna - For Waelth and FinanceDocument7 pagesIndu Lagna - For Waelth and Financeybbvvprasada raoNo ratings yet
- 3I Grading Rubric For Output PresentationDocument2 pages3I Grading Rubric For Output PresentationBinibining Michelle CenizaNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Breaks 1840241519 PDFDocument61 pagesThe Little Book of Breaks 1840241519 PDFksrbhaskarNo ratings yet
- City Center Unifier Deployment PDFDocument35 pagesCity Center Unifier Deployment PDFSachin PatilNo ratings yet
- Quick Reference Guide: 65 Degree 1800 MHZ Dual Polarized 90 Degree 1800 MHZ Dual PolarizedDocument20 pagesQuick Reference Guide: 65 Degree 1800 MHZ Dual Polarized 90 Degree 1800 MHZ Dual PolarizedРоманКочневNo ratings yet
- 5054 s16 Ms 41 PDFDocument3 pages5054 s16 Ms 41 PDFKritish RamnauthNo ratings yet
- The Laws On Local Governments SyllabusDocument4 pagesThe Laws On Local Governments SyllabusJohn Kevin ArtuzNo ratings yet
- ANSWERS For ExercisesDocument13 pagesANSWERS For ExercisesAlia HazwaniNo ratings yet
- 01 02 BDocument453 pages01 02 BJose VieraNo ratings yet
- Z19 Tnoo 000517 PDFDocument1 pageZ19 Tnoo 000517 PDFGuna RajNo ratings yet
- 9de13c0f0c009828f703d0103efa820b.xlsDocument70 pages9de13c0f0c009828f703d0103efa820b.xlsPreeti JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Clique Student Sheet (Manteran Lamo)Document4 pagesClique Student Sheet (Manteran Lamo)Dina Rizkia RachmahNo ratings yet
- Explosion Protection - E PDFDocument7 pagesExplosion Protection - E PDFAPCANo ratings yet
- EXOS Quick Guide - Cheat SheetDocument19 pagesEXOS Quick Guide - Cheat Sheetmaverick2689No ratings yet
- Technical Drawings of PlasticwareDocument69 pagesTechnical Drawings of PlasticwareGuldu KhanNo ratings yet
- ANSWERS - PhyLabS6 EX02 Water TowerDocument8 pagesANSWERS - PhyLabS6 EX02 Water TowerGuacNo ratings yet