Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PPcytosq
PPcytosq
Uploaded by
Jean-Pierre ZrydOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PPcytosq
PPcytosq
Uploaded by
Jean-Pierre ZrydCopyright:
Available Formats
STUDIES ON PHYSCOMITRELLA PATENS CYTOSKELETON
Jean-Pierre Zrÿd, Pierre-François Perroud, Andrija Finka, Alexander Skripnikov* and Didier G. Schaefer,
Institute of Ecology, Laboratory of Plant Cell Genetics (http://lpc-linux.unil.ch), Biology Building, The University of Lausanne, CH-1015 Lausanne
*Department of Higher Plants, Biological Faculty, Moscow State University, Moscow, Russia
The haplobiontic and monoecious moss We have transformed Physcomitrella patens wild type with a 35S GFP-talin cassette and report here a
(Plantae - Bryophytae) Physcomitrella preliminary description of the moss actin cytoskeleton observed in vivo by confocal microscopy.
patens is known to have a high frequency
(90%) of homologous recombination (
(Schaefer and Zryd, 1997), allowing the use,
for the first time in studies of land plants c
biology, of all reverse genetics approaches
cw n a
that have proved so efficient in yeast a
genetics. cDNA based replacement vectors mfoc a
n cw
with homologous sequences as short as 50 n
to 200 bp can be used for efficient targeted cw
transformation. When the target sequence is cw
known, the use of P. patens, for knockout or
chloronema apical cell chloronema sub apical cell caulonema sub apical cell
gene replacement strategies is faster and
very efficient. Five different actin structures can be recognised in
Mosses have been the object of many studies in the area of cell polarity. protonema cells: a branched network of cortical
bud bud
Different tools, including light of specific wavelength or specific polarization, can cables (a), a diffused fluorescence surrounding the n
be used to alter cell polarity. We are interested in understanding the factors that nucleus (n), a cap-like structure associated with the
chl
control the orientation of cell division and the position of the new cell wall. growing tip of apical cells (c), a strong accumulation chl
of actin near the cell wall separating two cells (cw)
Tubulin-microtubule structure has been studied by immuno-labeling during the and intensively labelled star-like cortical structures
first moss protoplast division induced by linearly polarized light. Microtubule do which may correspond to microfilament organising
not display an oriented pattern before the onset of mitosis, then a polarized center (mfoc). Actin cables are predominantly
arrangement appears which precedes any change in cell shape oriented parallel to the cell axis and seems to
display a polar distribution in chloronema subapical
3-cells stage bud
cells, being more dense at the apical end. With the
exception of mfoc, these structures correspond to
actin structures previously described in plant cells n
(pictures are projections of 1.5 µm slices,
magnification is 200 x). chl n chl
a a
mfoc mfoc a
cw
cw
mfoc
mfoc mfoc
leaf tissue
A weak fluorescence surrounding chloroplasts (chl)
and nucleus (n) can be detected in buds at the 3-cell
stage, but brightly labelled F-actin structures are
not observed. Yet GFP labelling of cortical cables (a),
putative microfilament organising centres cell walls (cw), microfilaments organising centers
Larger magnification of a putative microfilament (mfoc) and nuclei is clearly observed in cells of
organising center observed in a chloronema cell. differentiated leaves of the gametophore. The
These star like structures seems to contain high absence of GFP labelled cortical structures in buds is
not clearly understood and deserves further studies.
concentration of F-actin and are directly connected
The double arrow indicate both the direction of the EV of the polarized light and with the cortical actin cables. We hypothesise that
the scale (10 micrometer. The whole process of division takes approximately 48 they may be centres where actin polymerisation
hours and/or bundle formation occur (projection of 0.3 µm
slices, magnification 500 x)
You might also like
- See The Pages 13 - 20 For The Answer Key To The Exercises!Document20 pagesSee The Pages 13 - 20 For The Answer Key To The Exercises!ana maria reyesNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Function WorksheetDocument3 pagesCell Structure and Function WorksheetKiersten RobertsNo ratings yet
- NISP Safety Course ManualDocument16 pagesNISP Safety Course Manualrichancy100% (4)
- Nuclear Pore ComplexesDocument9 pagesNuclear Pore ComplexesMNo ratings yet
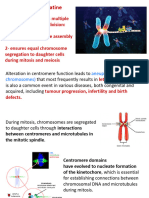
- Kinetochore Assembly and Function Through The Cell Cycle: ReviewDocument15 pagesKinetochore Assembly and Function Through The Cell Cycle: ReviewLê Khánh ToànNo ratings yet
- NucleusDocument9 pagesNucleussoumyadeepsahamondal20No ratings yet
- Nucleus - Structure - FunctionDocument3 pagesNucleus - Structure - Functionbushra sajjadNo ratings yet
- M Phase Macromolecular Crowding: Cell Cycle - Overview G-Phase Electron TomographyDocument244 pagesM Phase Macromolecular Crowding: Cell Cycle - Overview G-Phase Electron Tomographylabm09516No ratings yet
- Micro e Nanoestrutura CelularDocument4 pagesMicro e Nanoestrutura CelularIsis CôrtesNo ratings yet
- E2017001 PDFDocument8 pagesE2017001 PDFComputational and Structural Biotechnology JournalNo ratings yet
- Raymond Lisberger Mauk VOR Science1996Document6 pagesRaymond Lisberger Mauk VOR Science1996IlincaNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0014488617302881 MainDocument7 pages1 s2.0 S0014488617302881 MainsilviaNo ratings yet
- Creuzet 2005Document13 pagesCreuzet 2005asdNo ratings yet
- Why Are Neutrophils PolymorphonuclearDocument9 pagesWhy Are Neutrophils PolymorphonuclearPedro LopesNo ratings yet
- HHS Public Access: Eukaryotic DNA Replication ForkDocument26 pagesHHS Public Access: Eukaryotic DNA Replication ForkGustavo MoraNo ratings yet
- Daissarimilati 4C 4 PDFDocument8 pagesDaissarimilati 4C 4 PDFDais Sari MilatiNo ratings yet
- Biol120 Lecture 7Document55 pagesBiol120 Lecture 7mooosemnNo ratings yet
- Nucleo Kim and Wirtz Biomaterials 2015Document12 pagesNucleo Kim and Wirtz Biomaterials 2015miriamNo ratings yet
- Desvelando El Ciclo Del HCVDocument13 pagesDesvelando El Ciclo Del HCVGuilleBioNo ratings yet
- CellDocument17 pagesCellakg371390No ratings yet
- VbfdbergwDocument38 pagesVbfdbergwSaverioFortunatoNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 0042698995905316 MainDocument1 page1 s2.0 0042698995905316 MainYn Tanzilal ChaniagoNo ratings yet
- Mapping Neuronal DiversityDocument2 pagesMapping Neuronal DiversityJohn MistryNo ratings yet
- Week 3: DNA ReplicationDocument39 pagesWeek 3: DNA ReplicationKEVIN SUNNo ratings yet
- Chromosomes Move Poleward in Anaphase Along Stationary Microtubules That Coordinately Disassemble From Their Kinetochore EndsDocument10 pagesChromosomes Move Poleward in Anaphase Along Stationary Microtubules That Coordinately Disassemble From Their Kinetochore EndsTyu fiorNo ratings yet
- Post Feb Mock Plan: Topics 1-4 PAPER 1 Assessment Focus RPDocument61 pagesPost Feb Mock Plan: Topics 1-4 PAPER 1 Assessment Focus RPEllisNo ratings yet
- Cereb. Cortex-2009-LoTurco-i120-5Document6 pagesCereb. Cortex-2009-LoTurco-i120-5bojun dingNo ratings yet
- The Nuclear Pore ComplexDocument19 pagesThe Nuclear Pore ComplexKunal SethNo ratings yet
- Short-Range Molecular Rearrangements in Ion Channels Detected by Tryptophan Quenching of Bimane FluorescenceDocument10 pagesShort-Range Molecular Rearrangements in Ion Channels Detected by Tryptophan Quenching of Bimane FluorescenceChia-Lin Charles HoNo ratings yet
- L'innervation Parasympathique Dans La Glande SalivaireDocument14 pagesL'innervation Parasympathique Dans La Glande SalivaireMamadou DIENENo ratings yet
- Ynaptic Ransmission: The Human Brain Contains at LeastDocument32 pagesYnaptic Ransmission: The Human Brain Contains at LeastAnonymous Xmb6QQvRNo ratings yet
- CMB CH4Document56 pagesCMB CH4AudreyNo ratings yet
- Cellular BiologyDocument31 pagesCellular BiologyKhang NguyenNo ratings yet
- Kelm306 PDFDocument3 pagesKelm306 PDFbashraaNo ratings yet
- Biology HL - Chapter Summaries - Second Edition - Pearson 2014Document34 pagesBiology HL - Chapter Summaries - Second Edition - Pearson 2014jjkjljNo ratings yet
- Internal Summary Sheet BIOLOLYGYI7729Document14 pagesInternal Summary Sheet BIOLOLYGYI772997hgw484rdNo ratings yet
- Week3 Organel ENGDocument65 pagesWeek3 Organel ENGCem ÖzgenNo ratings yet
- 2 - MITOSIS - PAZ - N2ArDocument13 pages2 - MITOSIS - PAZ - N2ArChristine PazNo ratings yet
- MreB News & Views HPEDocument1 pageMreB News & Views HPEerick barzola galdósNo ratings yet
- Review Epigenetic Control of Nuclear Architecture: Cellular and Molecular Life SciencesDocument9 pagesReview Epigenetic Control of Nuclear Architecture: Cellular and Molecular Life SciencesPaige MunroeNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0092867415001324 Main 2Document15 pages1 s2.0 S0092867415001324 Main 2Daff AlfaNo ratings yet
- Price1991 PDFDocument8 pagesPrice1991 PDFRahmajiMajiNo ratings yet
- BZ Lab 3Document11 pagesBZ Lab 3Alexa Jean D. HonrejasNo ratings yet
- Ert 445Document8 pagesErt 445Mirai AkihitoNo ratings yet
- Bio11 C Chap7Document6 pagesBio11 C Chap7Camille GrefaldiaNo ratings yet
- Mitosis in The Root Meristem of Onion, Allium CepaDocument10 pagesMitosis in The Root Meristem of Onion, Allium CepaJoshuaNo ratings yet
- What's Next For The AI Protein-Folding RevolutionDocument6 pagesWhat's Next For The AI Protein-Folding RevolutionLuis RomeroNo ratings yet
- 2013 Genome Architecture and Global Gene Regulation in Bacteria Making Progress Towards A Unified ModelDocument7 pages2013 Genome Architecture and Global Gene Regulation in Bacteria Making Progress Towards A Unified Models96956No ratings yet
- Summers 2023Document19 pagesSummers 2023Pilar AufrastoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Chapter 8-Cytoskeleton ADocument75 pagesLecture 3 - Chapter 8-Cytoskeleton AKw Chan33% (3)
- A Microfluidic Array For Large-Scale Ordering and Orientation of Embryos-FutureDocument7 pagesA Microfluidic Array For Large-Scale Ordering and Orientation of Embryos-Futurefreesubscriptionpurpose18No ratings yet
- Ephys DeepTissue-AppLetter - ENDocument20 pagesEphys DeepTissue-AppLetter - ENkrishnakumar thondirajNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE WorksheetsDocument53 pagesSCIENCE WorksheetsHsje GhaNo ratings yet
- Bacteria With A Eukaryotic Touch: A Glimpse of Ancient Evolution?Document2 pagesBacteria With A Eukaryotic Touch: A Glimpse of Ancient Evolution?leztlyNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology Knowledge Organiser - Foundation and Higher: e e e e e e e e e e e e eDocument4 pagesCell Biology Knowledge Organiser - Foundation and Higher: e e e e e e e e e e e e eQUAH XIN YUE -No ratings yet
- AQA Cell Biology Knowledge OrganiserDocument2 pagesAQA Cell Biology Knowledge OrganiserDan LiNo ratings yet
- Van Deventer Et Al - 2021Document11 pagesVan Deventer Et Al - 2021SusanaNo ratings yet
- TM-04 Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Chromosome Structure (Genap 2016-2017)Document32 pagesTM-04 Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Chromosome Structure (Genap 2016-2017)Fiy Jannatin AliyahNo ratings yet
- Piezo1 Mechanosensitive ChannelDocument11 pagesPiezo1 Mechanosensitive ChannelPrajna BNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 BioP Notes - 090340Document13 pagesCHAPTER 3 BioP Notes - 090340Kate PedritaNo ratings yet
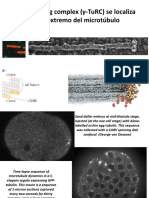
- Γ-Tubulin Ring Complex (Γ-Turc) Se Localiza En Un Extremo Del MicrotúbuloDocument14 pagesΓ-Tubulin Ring Complex (Γ-Turc) Se Localiza En Un Extremo Del MicrotúbuloFELIPE VALBUENANo ratings yet
- THE LOBSTER:: a Model for Teaching Neurophysiological ConceptsFrom EverandTHE LOBSTER:: a Model for Teaching Neurophysiological ConceptsNo ratings yet
- WWW - Drilling.Kr: HYDRAULIC ROCK DRILL HL 710, 710S Drifter PartsDocument5 pagesWWW - Drilling.Kr: HYDRAULIC ROCK DRILL HL 710, 710S Drifter PartsRussell HayesNo ratings yet
- BLDP Fuel Cell TelecomDocument2 pagesBLDP Fuel Cell TelecomWallStreetMannaNo ratings yet
- Contra Max Black: An Examination of Critiques of General SemanticsDocument21 pagesContra Max Black: An Examination of Critiques of General SemanticsBruce I. KodishNo ratings yet
- Arvind Mill Case Analysis: Increasing No of Players Increases Bargaining Power of The SuppliersDocument5 pagesArvind Mill Case Analysis: Increasing No of Players Increases Bargaining Power of The SuppliersPritam D BiswasNo ratings yet
- Process Control System PCS7 Advanced Engineering SystemDocument140 pagesProcess Control System PCS7 Advanced Engineering SystemGrant DouglasNo ratings yet
- 21ST Century - Week 1 4Document39 pages21ST Century - Week 1 4jsudjdbrhdjfNo ratings yet
- These Are Notes For MathsDocument3 pagesThese Are Notes For MathsMuhammad MudassirNo ratings yet
- LV 679 DatasheetDocument2 pagesLV 679 DatasheetWaleed MareeNo ratings yet
- 000 - S4H Certification Courses ListDocument3 pages000 - S4H Certification Courses ListVempati NaveenNo ratings yet
- Adolescent Girls' Nutrition and Prevention of Anaemia: A School Based Multisectoral Collaboration in IndonesiaDocument6 pagesAdolescent Girls' Nutrition and Prevention of Anaemia: A School Based Multisectoral Collaboration in IndonesiamamaazkaNo ratings yet
- Sag-Cookery NC Ii PDFDocument6 pagesSag-Cookery NC Ii PDFArayaskillsdevt InstitutecorpNo ratings yet
- Ba 3094Document29 pagesBa 3094massive85No ratings yet
- Orinoco Training PlanDocument14 pagesOrinoco Training PlanAnand Raj DasNo ratings yet
- LNG. Cargo OperationsDocument13 pagesLNG. Cargo OperationsFernando GrandaNo ratings yet
- Syllabus - PAPER 1 - Application of Computer in MediaDocument39 pagesSyllabus - PAPER 1 - Application of Computer in MediaAbubakar shomarNo ratings yet
- Basic Microeconomics HandoutsDocument12 pagesBasic Microeconomics HandoutsVivien SairaNo ratings yet
- BSH Home Appliances: By: Finn O'Toole Luke Wilson Mohammad Saghir Hannah Morrison Nicole SaundersDocument12 pagesBSH Home Appliances: By: Finn O'Toole Luke Wilson Mohammad Saghir Hannah Morrison Nicole SaundersByan SaghirNo ratings yet
- Hubungan Indeks Massa Tubuh Dengan Siklus Menstruasi Pada Siswi SMP Wahid Hasyim Kota MalangDocument13 pagesHubungan Indeks Massa Tubuh Dengan Siklus Menstruasi Pada Siswi SMP Wahid Hasyim Kota MalangRoslince Umbu patiNo ratings yet
- A Cannibals Sermon - OffprintDocument25 pagesA Cannibals Sermon - OffprintEnéias TavaresNo ratings yet
- World HistoryDocument3 pagesWorld HistoryShahzeb Sha100% (1)
- Circuit Analysis Technique Mesh (Loop) Current Method (Maxwell's Method)Document8 pagesCircuit Analysis Technique Mesh (Loop) Current Method (Maxwell's Method)Rahma HanifaNo ratings yet
- Samsung TV ManualDocument61 pagesSamsung TV ManualAnders MåsanNo ratings yet
- SAP Cloud For Sales Solution Brief - Sap LayoutDocument9 pagesSAP Cloud For Sales Solution Brief - Sap Layoutphogat projectNo ratings yet
- Exam School: GeographyDocument62 pagesExam School: GeographyNathan MwansaNo ratings yet
- Christmas Fruit Cake - Kerala Plum CakeDocument2 pagesChristmas Fruit Cake - Kerala Plum Cakekevinkevz1No ratings yet
- Nfhs-5 India ReportDocument713 pagesNfhs-5 India ReportROHIT DASNo ratings yet
- 3-Phase Distribution Transformers 11 or 33 kV/415-240V (Outdoor Type)Document2 pages3-Phase Distribution Transformers 11 or 33 kV/415-240V (Outdoor Type)Nanban VkyNo ratings yet
- Part 1 Rocks and MineralsDocument9 pagesPart 1 Rocks and MineralsSimon DruryNo ratings yet