Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biochemistry Notes
Biochemistry Notes
Uploaded by
nezuko9780 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views2 pagesThe cytosol is the water-based fluid part of the cytoplasm. Ribosomes are the sites of protein synthesis. Lysosomes contain hydrolytic enzymes for cellular rebuilding, repair, and degradation. Mitochondria generate most of a cell's energy and contain inner and outer membranes. Their interior structure was revealed by electron microscopes in 1962, showing ATP synthase complexes on cristae. Important energy-carrying molecules include ATP, ADP, AMP, NAD+, and FAD, which undergo redox reactions and have oxidized and reduced forms involved in metabolic pathways.
Original Description:
Original Title
Biochemistry-notes
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe cytosol is the water-based fluid part of the cytoplasm. Ribosomes are the sites of protein synthesis. Lysosomes contain hydrolytic enzymes for cellular rebuilding, repair, and degradation. Mitochondria generate most of a cell's energy and contain inner and outer membranes. Their interior structure was revealed by electron microscopes in 1962, showing ATP synthase complexes on cristae. Important energy-carrying molecules include ATP, ADP, AMP, NAD+, and FAD, which undergo redox reactions and have oxidized and reduced forms involved in metabolic pathways.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views2 pagesBiochemistry Notes
Biochemistry Notes
Uploaded by
nezuko978The cytosol is the water-based fluid part of the cytoplasm. Ribosomes are the sites of protein synthesis. Lysosomes contain hydrolytic enzymes for cellular rebuilding, repair, and degradation. Mitochondria generate most of a cell's energy and contain inner and outer membranes. Their interior structure was revealed by electron microscopes in 1962, showing ATP synthase complexes on cristae. Important energy-carrying molecules include ATP, ADP, AMP, NAD+, and FAD, which undergo redox reactions and have oxidized and reduced forms involved in metabolic pathways.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
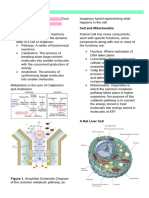
Biochemistry The cytosol is the water-based fluid
part of the cytoplasm of a cell.
Biochemical Energy production
Ribosomes are the sites where protein
Metabolism- is the sum total of all synthesis.
biochemical reactions that take place
in a living organism. A lysosome is an organelle that contains
hydrolytic enzymes needed for
Catabolism- is all metabolic reactions in cellular rebuilding, repair, and
which large biochemical molecules degradation.
are broken down to smaller ones.
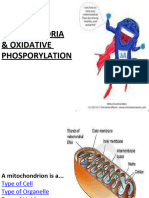
A mitochondrion is an organelle that is
Anabolism- is all metabolic reactions in responsible for the generation of
which small biochemical molecules most of the energy for a cell.
are joined together to form larger
Mitochondria are sausage-shaped
ones.
organelles containing both an outer
Metabolic pathway- is a series of mem brane and a multi folded inner
consecutive biochemical reactions membrane.
used to convert a starting material The invention of high-resolution
into an end product. electron microscopes allowed
There are two types of metabolic researchers to see the interior
structure of the mitochondrion more
pathways:
clearly and led to the discovery, in
- linear 1962, of small spherical knobs
attached to the cristae called ATP
- cyclic
synthase complexes.
o A eukaryotic cell is a cell in Important Nucleotide-containing Compounds in
which the DNA is found in a metabolic pathways
membrane-enclosed nucleus.
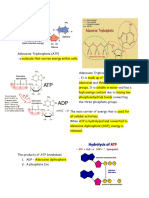
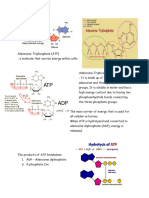
• Adenosine Phosphates (ATP, ADP,
o Prokaryotic cells have no and AMP)
nucleus and are found only • Adenosine Monophosphate (AMP)-
in bacteria. one of the nucleotides
present in RNA molecules
The cytoplasm is the water-based
material of a eukaryotic cell that • Adenosine Diphosphate (ADP)
lies between the nucleus and the • Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP)
outer membrane of the cell. differ structurally from
AMP only in the number
The organelle is a minute structure of phosphate group
within the cytoplasm of a cell that present.
carries out a specific cellular Phosphoester bond - phosphate-ribose
function. bond
Phosphoanhydride bond - phosphate-
phosphate bond
- Chemical bond formed when two atoms than the oxidized form, which is
phosphate groups reacts with each consistent with the process of
other and a water molecule is reduction involving hydrogen atom.
produced. Flavin Subunit - The active portion of
Phosphoryl group (PO32- ) -The functional FAD in redox reaction
group derived from a phosphate ion - The portion that undergoes change
when the latter becomes part of when oxidized form (FAD) is
another molecule. - ATP contains converted to the reduced form (FADH
three phosphoryl groups, ADP 2)
contains 2 phosphoryl groups, and Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD^+,
AMP one phosphoryl groups. NADH)
- Have coenzyme functions in
Other Nitrogen containing basis metabolic redox pathways
associated with nucleotides are also - Have B- Vitamin as a structural
present in triphosphate form: component
• Uridine Triphosphate - involved in - Have an oxidized and reduce form
carbohydrate metabolism.
• Guanosine Triphosphate- Participate in The notation for the oxidized form is the NAD+
protein and carbohydrate metabolism and the reduced form is the NADH
• Cytidine Triphosphate- Involved in lipid - Can be presented structurally by
metabolism using a three sub-unit and six sib-unit
formulation.
Flavin Adenine Dinucleotide (FAD, FADH2)
Flavin Adenine Dinucleotide (FAD) - A Three sub-unit block diagram
coenzyme required in numerous
metabolic reactions. - Can be
visualized as containing either three
subunits or six subunits. Six sub-unit block diagram
FAD from three subunit viewpoint.
FAD from six subunit viewpoint
Coenzyme A (CoA- SH) -Another important
coenzyme in metabolic enzyme. A
derivative of the Vitamin B
pantothenic acid
Ribitol – reduced form of ribose
Two forms of FAD
1. Oxidized form
2. Reduced form
-The notation FAD denotes the
oxidized form
-The notation FADH2 denotes the
reduced form contains two or more H
You might also like
- Strength and Conditioning For Sports PerformanceDocument984 pagesStrength and Conditioning For Sports PerformanceIgorRanisavljev100% (8)
- The 12 Light BodiesDocument24 pagesThe 12 Light Bodieskoochimetal93% (14)
- Hydrogen Peroxide Therapy Drinking Hydrogen Peroxide PDFDocument29 pagesHydrogen Peroxide Therapy Drinking Hydrogen Peroxide PDFBernardo Teixeira100% (1)
- Stuck and Sluggish FermentationsDocument13 pagesStuck and Sluggish Fermentations1ab4cNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Energy Production - BIOCHEMISTRYDocument3 pagesBiochemical Energy Production - BIOCHEMISTRYnezuko978No ratings yet
- MetabolismDocument71 pagesMetabolismBabylyn Austria100% (1)
- Biochem Final ReviewerDocument19 pagesBiochem Final RevieweryjllhallareNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry - Lecture Term01: Introduction To Metabolism Metabolism Metabolism and Cell StructureDocument4 pagesBiochemistry - Lecture Term01: Introduction To Metabolism Metabolism Metabolism and Cell StructureJohn Daniel AriasNo ratings yet
- Biochem ReportDocument65 pagesBiochem ReportBeatrice ChenNo ratings yet
- BioenergeticsDocument14 pagesBioenergeticsmunozayshiaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Mini NotesDocument17 pagesBiochemistry Mini Notesdominguezangela2002No ratings yet
- Biochemical Energy ProductionDocument5 pagesBiochemical Energy ProductionMaria Cyril BaldovinoNo ratings yet
- Cell Chemistry: Sri Wahyuni Biochemistry Department Faculty of Medicine Universitas MalikussalehDocument28 pagesCell Chemistry: Sri Wahyuni Biochemistry Department Faculty of Medicine Universitas Malikussalehviola septinaNo ratings yet
- Chem Finals ReviewerDocument169 pagesChem Finals ReviewerPALATTAO, AUBRIE L. BSMT2-8No ratings yet
- Macromolecules - Are Large Molecules Composed of Thousands of Covalently Connected AtomsDocument6 pagesMacromolecules - Are Large Molecules Composed of Thousands of Covalently Connected AtomsBon Joey BernestoNo ratings yet
- Biology ChecklistDocument29 pagesBiology ChecklistgsapkaiteNo ratings yet
- Traffic Light Topic 1 Biological MoleculesDocument3 pagesTraffic Light Topic 1 Biological MoleculesAlison HillNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 17 The Metabolism An OverviewDocument10 pagesCHAPTER 17 The Metabolism An Overview楊畯凱No ratings yet
- Metabolic PathwaysDocument6 pagesMetabolic Pathwaysgelary sousaNo ratings yet
- BIOL 02 NotesDocument6 pagesBIOL 02 NotesAdam MoncktonNo ratings yet
- Co-Enzymes Role in Metabolic PathwaysDocument23 pagesCo-Enzymes Role in Metabolic PathwaysHarini BalasubramanianNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEMISTRYDocument24 pagesBIOCHEMISTRYXyrielleNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Energy ProductionDocument5 pagesBiochemical Energy ProductionAlexandria StylesNo ratings yet
- Biology GlossaryDocument3 pagesBiology Glossarygapedin173No ratings yet
- CBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) Chapter-09 BiomoleculesDocument5 pagesCBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) Chapter-09 BiomoleculesSIDHARTH SBNo ratings yet
- Energy TransformationDocument5 pagesEnergy TransformationmunozayshiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: The Molecules of LifeDocument8 pagesChapter 3: The Molecules of LifeCourtney FazioNo ratings yet
- ChemistryOfLife NotesDocument9 pagesChemistryOfLife NotesamvooijsNo ratings yet
- Energy and RespirationDocument11 pagesEnergy and Respirationririrachma fitriahNo ratings yet
- He Cell 1Document34 pagesHe Cell 1Le Phuong LyNo ratings yet
- Enzymes and Vitamins NotesDocument14 pagesEnzymes and Vitamins NotesRealyn ZambasNo ratings yet
- Biology NotesDocument5 pagesBiology NotesFaith SNNo ratings yet
- 2238 Unit 4 Microbial Metabolic PathwaysDocument24 pages2238 Unit 4 Microbial Metabolic PathwaystitojhezielanneNo ratings yet
- Essential Elements of Life: TB-BA-2: 18-4-2022Document5 pagesEssential Elements of Life: TB-BA-2: 18-4-2022Khánh NhiNo ratings yet
- Concept of Cell Structures and FunctionsDocument3 pagesConcept of Cell Structures and FunctionsTyron ChuaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Coenzymes and VitaminesDocument6 pagesChapter 7 Coenzymes and VitaminesEhsan HumayunNo ratings yet
- Biochem PDFDocument7 pagesBiochem PDFNhư NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Biology A Level SpecDocument32 pagesBiology A Level SpecszyzypNo ratings yet
- Mid Biochem - Review - TGDocument11 pagesMid Biochem - Review - TGHà Anh Minh LêNo ratings yet
- Mid Biochem Review TG 3Document11 pagesMid Biochem Review TG 3Đặng Thị Kim SangNo ratings yet
- 5 Biochemical PathwaysDocument33 pages5 Biochemical PathwaysYong AlbertoNo ratings yet
- Chem 123 - Lect Finals TransesDocument19 pagesChem 123 - Lect Finals TransesSamantha MendozaNo ratings yet
- Biology Unit 4 TOPIC 5: PhotosynthesisDocument8 pagesBiology Unit 4 TOPIC 5: PhotosynthesisSamara HusainNo ratings yet
- A2 Biology Notes 2016Document252 pagesA2 Biology Notes 2016MohammedKamelNo ratings yet
- General Biology NotesDocument2 pagesGeneral Biology NotesjeayNo ratings yet
- Bio3110 - Biochemistry Ii-Intermediary Metabolism Enzyme and Enzyme KineticsDocument11 pagesBio3110 - Biochemistry Ii-Intermediary Metabolism Enzyme and Enzyme KineticsNaiomiNo ratings yet
- BIOC 315 - Lecture - 6Document46 pagesBIOC 315 - Lecture - 6Kevin KipropNo ratings yet
- 7th Lect. 2017 MetabolismDocument46 pages7th Lect. 2017 MetabolismNedhal Mahmoud KaleefahNo ratings yet
- Selangor AnsDocument4 pagesSelangor AnsChan Yu QianNo ratings yet
- Bioinorganic Chemistry 1Document44 pagesBioinorganic Chemistry 1Abu S. M. GulamaNo ratings yet
- Audio Osmosis - BiologyDocument15 pagesAudio Osmosis - BiologyddNo ratings yet
- Nature of MetabolismDocument12 pagesNature of MetabolismIshanSaneNo ratings yet
- DNA and RNA MetabolismDocument27 pagesDNA and RNA Metabolismazka shahidNo ratings yet
- Biological MoleculesDocument6 pagesBiological MoleculessanaullahNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids are linked by peptide bonds to form formed by linking the α-carboxyl group of one amino acid to the α-amino group of another amino acid with a peptide bond (also called an amide bond)Document2 pagesAmino Acids are linked by peptide bonds to form formed by linking the α-carboxyl group of one amino acid to the α-amino group of another amino acid with a peptide bond (also called an amide bond)Noviemae TuandaNo ratings yet
- Physical Science-Finals ReviewerDocument18 pagesPhysical Science-Finals ReviewerPrecious Miracle Lucas SacataniNo ratings yet
- 8 MitochondriaDocument13 pages8 Mitochondriawhether913No ratings yet
- Enzymes ReglatonDocument11 pagesEnzymes Reglatonhurainsahar21No ratings yet
- General Biology 2Document4 pagesGeneral Biology 2Wee-Weh HamjaNo ratings yet
- Centro, MF. Module - 7Document5 pagesCentro, MF. Module - 7jessa marie marevilesNo ratings yet
- 044BIO11-14 Respiration in Plants (Study Notes)Document13 pages044BIO11-14 Respiration in Plants (Study Notes)Zen FredyNo ratings yet
- MCB201 L-TWO (General Microbiology I)Document16 pagesMCB201 L-TWO (General Microbiology I)omotolaNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Energy ProductionDocument59 pagesBiochemical Energy ProductionShane G.No ratings yet
- A-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Why Strength Training Is So Important For Optimal HealthDocument7 pagesWhy Strength Training Is So Important For Optimal HealthsherryNo ratings yet
- CH 4 Test Bank For Essential Cell Biology 3rd Edition AlbertsDocument29 pagesCH 4 Test Bank For Essential Cell Biology 3rd Edition AlbertsRokia GhariebNo ratings yet
- Biology Rank Edge Series Neet Sample MaterialDocument111 pagesBiology Rank Edge Series Neet Sample MaterialSam MishraNo ratings yet
- MC2 Module 1Document11 pagesMC2 Module 1Valerie Heart GomezNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology Reviewer - Photosynthesis and Cellular RespirationDocument3 pagesBiotechnology Reviewer - Photosynthesis and Cellular RespirationMaribeth VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- NOTES - Bacterial NutritionDocument24 pagesNOTES - Bacterial NutritionDETECTIVE CONANNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Heart DiseaseDocument9 pagesTreatment of Heart DiseaseOriol Borràs Ferré100% (2)
- Atp CycleDocument4 pagesAtp CycleVictoria CoralNo ratings yet
- Cancer Cell Metabolism - Cairns HarrisDocument14 pagesCancer Cell Metabolism - Cairns HarrisGUSTAVO BELLONo ratings yet
- The Science Behind Peak Metabolic Health DR Inigo San Millan The Proof Podcast - YouTubeDocument50 pagesThe Science Behind Peak Metabolic Health DR Inigo San Millan The Proof Podcast - YouTubeDavid RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Cell Injury 2Document23 pagesCell Injury 2Cresha Mae PoloyapoyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14Document12 pagesChapter 14Marie St. LouisNo ratings yet
- Biology Specimen BookletDocument124 pagesBiology Specimen BookletDiana PhiriNo ratings yet
- Ebook Ebook PDF Principles of General Organic Biological Chemistry 2nd Edition PDFDocument42 pagesEbook Ebook PDF Principles of General Organic Biological Chemistry 2nd Edition PDFdonita.nichols650100% (44)
- Biochemistry Module. FinalDocument33 pagesBiochemistry Module. Finalcrystalclairemalinao03No ratings yet
- BG7004 Lecture 2 StudentDocument43 pagesBG7004 Lecture 2 StudentShakya PradeepNo ratings yet
- What Is Flux Balance Analysis? Supplementary Tutorial: Beginner COBRA MethodsDocument28 pagesWhat Is Flux Balance Analysis? Supplementary Tutorial: Beginner COBRA MethodsMridula PrasadNo ratings yet
- Biology Practice EOCDocument76 pagesBiology Practice EOCHeri SetiadiNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Metabolism McKee Chapter8Document44 pagesCarbohydrate Metabolism McKee Chapter8David SeidelNo ratings yet
- WHLP Gen Bio 3 2nd QuarterDocument6 pagesWHLP Gen Bio 3 2nd QuarterSir JoshNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry: Questions & AnswersDocument17 pagesBiochemistry: Questions & AnswersA-Naeem To'mah Al-sawaieNo ratings yet
- Answer Key Si Worksheet 10Document5 pagesAnswer Key Si Worksheet 10Jersey BarquillaNo ratings yet
- CGP Biology NotesDocument1 pageCGP Biology NotesHannah LyNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis QuestionsDocument65 pagesPhotosynthesis QuestionsForm 4B100% (1)
- Calorimetry Lab ReportDocument6 pagesCalorimetry Lab Reportapi-308675225No ratings yet
- Easter Revision Day 3 Workbook New 1712407998Document40 pagesEaster Revision Day 3 Workbook New 1712407998robinsonbryNo ratings yet