Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views@acelleisboring - NCP Risk For Aspiration
@acelleisboring - NCP Risk For Aspiration
Uploaded by
Angela NeriThe nursing care plan addresses the risks of aspiration in a patient receiving bottled formula feeding. Short term goals within 4 hours include performing proper bottled feeding positioning at least 3 times after demonstration. Long term goals within 8 hours include demonstrating effective feeding with bottled formula through absence of coughing, choking or other signs of trouble. Interventions include instructing on proper positioning, monitoring feeding cues, and evaluating respiratory signs. The plan aims to prevent aspiration and respiratory complications through safe feeding practices.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Standards of Care in Diabetes - 2024Document9 pagesStandards of Care in Diabetes - 2024josueraulbalandran100% (1)
- The Longevity Diet: Discover The New Science Behind Stem Cell Activation and Regeneration To Slow Aging, Fight Disease, and Optimize Weight - Valter LongoDocument5 pagesThe Longevity Diet: Discover The New Science Behind Stem Cell Activation and Regeneration To Slow Aging, Fight Disease, and Optimize Weight - Valter Longozyrybosi14% (7)
- BionoteDocument4 pagesBionoteAngela Neri100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Short Term: Difficulty in Swallowing Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan: Short Term: Difficulty in Swallowing Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationNico Angelo Hibaya TugononNo ratings yet
- 7 Household Items For Faster Fat LossDocument30 pages7 Household Items For Faster Fat LossLinda PrideNo ratings yet
- NCM 105 Lesson 1Document35 pagesNCM 105 Lesson 1Roshin TejeroNo ratings yet
- Michael R., M.D. Eades, Mary Da M.D. Eades - The 30-Day Low-Carb Diet Solution (2003) PDFDocument194 pagesMichael R., M.D. Eades, Mary Da M.D. Eades - The 30-Day Low-Carb Diet Solution (2003) PDFAmelia Thalib100% (1)
- Teach Proper Breastfeeding Techniques To MotherDocument3 pagesTeach Proper Breastfeeding Techniques To MotherSaimon ReighNo ratings yet
- Breast Feeding Tec.Document9 pagesBreast Feeding Tec.Chairali DodiyaNo ratings yet
- NIH Public Access: Lack of Feeding Progression in A Preterm Infant: A Case StudyDocument16 pagesNIH Public Access: Lack of Feeding Progression in A Preterm Infant: A Case StudyFarah PramestyNo ratings yet
- Steps To Successfully Breastfeed The Premature InfantDocument10 pagesSteps To Successfully Breastfeed The Premature InfantKholis FaisolNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Goal of Care Outcome Criteria Interventions and Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Goal of Care Outcome Criteria Interventions and Rationale EvaluationMariah Angela PonceNo ratings yet
- Achalasia NCPDocument6 pagesAchalasia NCPkarl davidNo ratings yet
- Cleft Lip and PalateDocument8 pagesCleft Lip and PalateSHEILA MAE SACLOTNo ratings yet
- Feeding in The Preterm Infant: ObjectivesDocument9 pagesFeeding in The Preterm Infant: ObjectivesFonoaudiólogaRancaguaNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals and Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals and Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationCarmina DinerosNo ratings yet
- Viernes, Jemalyn BSN 2-3 Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument8 pagesViernes, Jemalyn BSN 2-3 Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationJeMalyn VieRnesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of A Child With Physical AND Developmental ChallengesDocument9 pagesNursing Care of A Child With Physical AND Developmental ChallengesAngelo ArabejoNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument7 pagesNCPJulianne Jeamer FabroaNo ratings yet
- Fesalbon AsthmaDocument6 pagesFesalbon AsthmaogiskuadzNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan (During Labor) : Subjective CuesDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan (During Labor) : Subjective CuesNatalie Antipolo100% (1)
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goals and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale Evaluation Subjective: NOC: Swallowing Status Goal: NIC: SwallowingDocument10 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goals and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale Evaluation Subjective: NOC: Swallowing Status Goal: NIC: SwallowingSkyla FiestaNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPJohn RyNo ratings yet
- Lippincott's PEDIATRIC4 ANSWERSDocument13 pagesLippincott's PEDIATRIC4 ANSWERSNursyNurseNo ratings yet
- NCP 101Document2 pagesNCP 101Mary Joy FrancoNo ratings yet
- Impaired SwallowingDocument2 pagesImpaired SwallowingfaizaNo ratings yet
- Disfagia Na Crianca (11998)Document4 pagesDisfagia Na Crianca (11998)martaNo ratings yet
- NCP GcsDocument15 pagesNCP GcsMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Teaching Plan For Proper Breast Feeding Begh ErDocument7 pagesTeaching Plan For Proper Breast Feeding Begh ErAmira Fatmah QuilapioNo ratings yet
- Swallowing Difficulties Can Have A Detrimental Effect On Dietary Intake And, Hence, Growth and DevelopmentDocument9 pagesSwallowing Difficulties Can Have A Detrimental Effect On Dietary Intake And, Hence, Growth and DevelopmentYenny FramelaNo ratings yet
- Nursing History: Patient Is in Active Phase in Stage of Cervical DilationDocument8 pagesNursing History: Patient Is in Active Phase in Stage of Cervical DilationVince BalisiNo ratings yet
- Health Talk On BFDocument28 pagesHealth Talk On BFpriyanka75% (8)
- Safe and Competent Oral Feeding Requires The Proper Integration of Physical and Neurophysiologic Functions That May Not Necessarily Be Mature at The Time Oral Feeding Is IntroducedDocument9 pagesSafe and Competent Oral Feeding Requires The Proper Integration of Physical and Neurophysiologic Functions That May Not Necessarily Be Mature at The Time Oral Feeding Is IntroducedVishnu Priya KarthikNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Nursing CareDocument5 pagesPediatric Nursing CareValerie BeteNo ratings yet
- 2 NCP Impaired Swallowing EditedDocument4 pages2 NCP Impaired Swallowing EditedZharm MayNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Ineffective Infant Feeding PatternDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Ineffective Infant Feeding PatternBasema HashhashNo ratings yet
- Risk For AspirationDocument2 pagesRisk For AspirationErica FabrigasNo ratings yet
- BSN2 C Ihps NCP FinalDocument7 pagesBSN2 C Ihps NCP FinalAdrian DecolongonNo ratings yet
- Kaitlin NCPDocument6 pagesKaitlin NCPJovel CortezNo ratings yet
- University of The East Ramon Magsaysay Memorial Medical Center, Inc. College of NursingDocument23 pagesUniversity of The East Ramon Magsaysay Memorial Medical Center, Inc. College of NursingReina RamonesNo ratings yet
- NCP - Pott's DiseaseDocument23 pagesNCP - Pott's Diseasemhean azneitaNo ratings yet
- 2 NCP Impaired Swallowing EditedDocument4 pages2 NCP Impaired Swallowing EditedLeonardo Montemayor100% (3)
- DiarrheaDocument3 pagesDiarrheaBert GasalNo ratings yet
- BrestfeedingDocument2 pagesBrestfeedingBuhkz Hermoso100% (1)
- David Achalasia NCPDocument4 pagesDavid Achalasia NCPkarl davidNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: STG: STGDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: STG: STGLiana Louisse JoseNo ratings yet
- IMCI StrategyDocument7 pagesIMCI StrategyAngelica Charisse BuliganNo ratings yet
- Dr. Nellie D. Gundao: Feeding Healthy Infants, Children and AdolescentsDocument5 pagesDr. Nellie D. Gundao: Feeding Healthy Infants, Children and AdolescentsGian Carla SoNo ratings yet
- Breastfeeding Techniques-Lesson PlanDocument12 pagesBreastfeeding Techniques-Lesson Planmonika makwanaNo ratings yet
- Aireen S. Papa Diana Rose PetilonaDocument3 pagesAireen S. Papa Diana Rose PetilonaMichael AmandyNo ratings yet
- Dysphagia: Ethan A. Mezoff, MDDocument5 pagesDysphagia: Ethan A. Mezoff, MDYenny FramelaNo ratings yet
- Amat Ncma 219 Pedia Week 5 CTDocument3 pagesAmat Ncma 219 Pedia Week 5 CTRaf AmatNo ratings yet
- Impaired Swallowing: Esophageal Phase ImpairmentDocument9 pagesImpaired Swallowing: Esophageal Phase ImpairmentK Jayakumar KandasamyNo ratings yet
- Quiaoit G3 BSN 2B NCPDocument3 pagesQuiaoit G3 BSN 2B NCPQuiaoit, Jackqueline T.No ratings yet
- Review Questionnaire MTRNALDocument13 pagesReview Questionnaire MTRNALKevin Vincent AquinoNo ratings yet
- Cough or Difficult Breathing: Distance Learning CourseDocument39 pagesCough or Difficult Breathing: Distance Learning Courseinno so qtNo ratings yet
- Assesment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssesment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationTrisha Suazo100% (1)
- Ob Nursing Care Plan For Maternal Database Maternal and NewbornDocument2 pagesOb Nursing Care Plan For Maternal Database Maternal and Newbornapi-403051801No ratings yet
- Altered Nutrition NCPDocument2 pagesAltered Nutrition NCPLeiAnnManaleseNo ratings yet
- Health Teaching PlanDocument4 pagesHealth Teaching PlannicanicsraakinNo ratings yet
- Acute Pain - Ineffective Breathing Pattern NCPDocument12 pagesAcute Pain - Ineffective Breathing Pattern NCPAngela NeriNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan ANPDocument24 pagesLesson Plan ANPKaruna NidhiNo ratings yet
- NCP For Hyperemesis GravidarumDocument5 pagesNCP For Hyperemesis Gravidarumclaire parkNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Food Allergy and Intolerance In.13Document4 pagesGastrointestinal Food Allergy and Intolerance In.13akbar alituNo ratings yet
- Case Study (DS)Document3 pagesCase Study (DS)Erica DumriqueNo ratings yet
- Level 4 Modules For Nursing Skills AuditDocument95 pagesLevel 4 Modules For Nursing Skills AuditAngela NeriNo ratings yet
- Colonic Mass PathophysioDocument1 pageColonic Mass PathophysioAngela NeriNo ratings yet
- Training Design Iec Material BSN 409 Grp2b SNDocument17 pagesTraining Design Iec Material BSN 409 Grp2b SNAngela NeriNo ratings yet
- Ramirez - Research Scientific PosterDocument1 pageRamirez - Research Scientific PosterAngela NeriNo ratings yet
- OR CommsDocument4 pagesOR CommsAngela NeriNo ratings yet
- Nle FC Manila 2023 May - EDITEDDocument12 pagesNle FC Manila 2023 May - EDITEDAngela NeriNo ratings yet
- @lfnursingcomms - DRUG STUDY FAJARDO ANDREA LAUREN A.Document6 pages@lfnursingcomms - DRUG STUDY FAJARDO ANDREA LAUREN A.Angela NeriNo ratings yet
- Renal Fabs Post Test Answer KeyDocument4 pagesRenal Fabs Post Test Answer KeyAngela NeriNo ratings yet
- Medication Administration Group 2Document32 pagesMedication Administration Group 2Angela NeriNo ratings yet
- Education, by Ellen G. White. Chapter 14 - Science and The BibleDocument4 pagesEducation, by Ellen G. White. Chapter 14 - Science and The BibleAngela NeriNo ratings yet
- Impact of A Modified Nursing Handover ModelDocument9 pagesImpact of A Modified Nursing Handover ModelAngela NeriNo ratings yet
- Sacraments 2Document68 pagesSacraments 2Angela NeriNo ratings yet
- @aryanehct.11 - Infographic 3 Computerized Order EntryDocument1 page@aryanehct.11 - Infographic 3 Computerized Order EntryAngela NeriNo ratings yet
- Typhoon Yunya (1991) - WikipediaDocument6 pagesTyphoon Yunya (1991) - WikipediaAngela NeriNo ratings yet
- Chan ReferencesDocument93 pagesChan ReferencesAngela NeriNo ratings yet
- AristotleDocument7 pagesAristotleAngela NeriNo ratings yet
- What Is Lacking in Us?: What Do You Think We, Human Beings, When We Lack The Sanctifying Grace of ?Document20 pagesWhat Is Lacking in Us?: What Do You Think We, Human Beings, When We Lack The Sanctifying Grace of ?Angela NeriNo ratings yet
- Crash Cart Check ListDocument2 pagesCrash Cart Check ListAngela NeriNo ratings yet
- Training DesignDocument1 pageTraining DesignAngela NeriNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Physical Fitness: Prepared by Professor Elenita LeabresDocument11 pagesIntroduction To Physical Fitness: Prepared by Professor Elenita LeabresAngela NeriNo ratings yet
- Program Flow DraftDocument1 pageProgram Flow DraftAngela NeriNo ratings yet
- Angela P. Neri March 4, 2021 BSN 309 Mad Rle Act # 2Document3 pagesAngela P. Neri March 4, 2021 BSN 309 Mad Rle Act # 2Angela NeriNo ratings yet
- Sample Problem Solving ProcessDocument5 pagesSample Problem Solving ProcessAngela NeriNo ratings yet
- A Social Life in Reality: Facebook From The Funny Memes To Videos That Simply Make Me Laugh. in Observation As Well ToDocument2 pagesA Social Life in Reality: Facebook From The Funny Memes To Videos That Simply Make Me Laugh. in Observation As Well ToAngela NeriNo ratings yet
- ReflectivePaper DAY1 NERIDocument2 pagesReflectivePaper DAY1 NERIAngela NeriNo ratings yet
- Movie Review: "What A Beautiful Mind"Document4 pagesMovie Review: "What A Beautiful Mind"Angela NeriNo ratings yet
- FA#2 Essay - NERI (Elderly Health)Document2 pagesFA#2 Essay - NERI (Elderly Health)Angela NeriNo ratings yet
- Group 2B: A Pulmonary Histoplasmosis CaseDocument58 pagesGroup 2B: A Pulmonary Histoplasmosis CaseAngela NeriNo ratings yet
- (Last) (Given) (Unit/Lot No.) (Bldg. No.) (Street) (Barangay) (Municipality)Document78 pages(Last) (Given) (Unit/Lot No.) (Bldg. No.) (Street) (Barangay) (Municipality)Angela NeriNo ratings yet
- How To Lose Weight Without Dieting PDFDocument2 pagesHow To Lose Weight Without Dieting PDFBetter WeighNo ratings yet
- Eat Healthy, Stay HealthyDocument3 pagesEat Healthy, Stay Healthyrampoudel649No ratings yet
- 1 PBDocument10 pages1 PBA'Lin Valerine FerreNo ratings yet
- Vitamin D DeficinyDocument11 pagesVitamin D DeficinyسالمNo ratings yet
- Medical Nutrition Therapy in Obesity Management - Canadian Adult Obesity Clinical Practice GuidelinesDocument28 pagesMedical Nutrition Therapy in Obesity Management - Canadian Adult Obesity Clinical Practice GuidelinesNitanluisNo ratings yet
- Nutrients 12 03660 v3Document17 pagesNutrients 12 03660 v3Mark OmbaoNo ratings yet
- The Culture of CrossFit. A Lifestyle Prescription For Optimal Health and Fitness (Inglés) Autor Steven KuhnDocument15 pagesThe Culture of CrossFit. A Lifestyle Prescription For Optimal Health and Fitness (Inglés) Autor Steven KuhnRosa Martin HuelvesNo ratings yet
- Pitta Final BookDocument42 pagesPitta Final Bookkabirtrivedi7No ratings yet
- Kamalnayan Bajaj Nursingcollege, Aurangabad .: Visit Report On Anganwadi at Turkabad TQ Gangapur, Aurangabad DistrictDocument14 pagesKamalnayan Bajaj Nursingcollege, Aurangabad .: Visit Report On Anganwadi at Turkabad TQ Gangapur, Aurangabad DistrictAkshata Bansode78% (9)
- (STAMP) :: Screening Tool For The Assessment of Malnutrition PediatricsDocument10 pages(STAMP) :: Screening Tool For The Assessment of Malnutrition PediatricsHabib RehmanNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 1Document6 pagesLesson Plan 1Antonio Jeremiah TurzarNo ratings yet
- Persuasive Writing 2Document30 pagesPersuasive Writing 2ALBA JANET GRANDA GARCIANo ratings yet
- PT G7 MapehDocument5 pagesPT G7 MapehWendilyne TababaNo ratings yet
- Best Practices: For Feeding Your Child From 0 To 5 Years of AgeDocument17 pagesBest Practices: For Feeding Your Child From 0 To 5 Years of AgeEd SeraficaNo ratings yet
- Lab No. 2 - ANS141Document7 pagesLab No. 2 - ANS141Janah Mariz LoquillanoNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Fitness Challenge 2023-2024Document6 pagesSyllabus Fitness Challenge 2023-2024api-224225781No ratings yet
- Nutrition Factor in Women in Backward AreasDocument7 pagesNutrition Factor in Women in Backward AreaspranjalNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Diet TherapyDocument70 pagesNutrition Diet TherapyMay Rodeo100% (1)
- Broiler Feeding Guide: Population: 100 HeadsDocument1 pageBroiler Feeding Guide: Population: 100 HeadsMA DapNo ratings yet
- Wardlaws Contemporary Nutrition A Functional Approach 5th Edition Wardlaw Test BankDocument38 pagesWardlaws Contemporary Nutrition A Functional Approach 5th Edition Wardlaw Test BankChristinaMcmahondbkfa100% (10)
- Answer Key To P24Document10 pagesAnswer Key To P24tmNo ratings yet
- Nutrition ArticleDocument5 pagesNutrition ArticleAafiah IfadaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Exam Quantatative AblityDocument6 pagesNursing Exam Quantatative AblitysamloviniNo ratings yet
- Good Topics For Nutrition Research PaperDocument6 pagesGood Topics For Nutrition Research Paperqhujvirhf100% (1)
- Practical Research Ii CH.1 3Document16 pagesPractical Research Ii CH.1 3Louie Jay JadraqueNo ratings yet
@acelleisboring - NCP Risk For Aspiration
@acelleisboring - NCP Risk For Aspiration
Uploaded by
Angela Neri0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views6 pagesThe nursing care plan addresses the risks of aspiration in a patient receiving bottled formula feeding. Short term goals within 4 hours include performing proper bottled feeding positioning at least 3 times after demonstration. Long term goals within 8 hours include demonstrating effective feeding with bottled formula through absence of coughing, choking or other signs of trouble. Interventions include instructing on proper positioning, monitoring feeding cues, and evaluating respiratory signs. The plan aims to prevent aspiration and respiratory complications through safe feeding practices.
Original Description:
Original Title
@acelleisboring_NCP Risk for Aspiration
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe nursing care plan addresses the risks of aspiration in a patient receiving bottled formula feeding. Short term goals within 4 hours include performing proper bottled feeding positioning at least 3 times after demonstration. Long term goals within 8 hours include demonstrating effective feeding with bottled formula through absence of coughing, choking or other signs of trouble. Interventions include instructing on proper positioning, monitoring feeding cues, and evaluating respiratory signs. The plan aims to prevent aspiration and respiratory complications through safe feeding practices.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views6 pages@acelleisboring - NCP Risk For Aspiration
@acelleisboring - NCP Risk For Aspiration
Uploaded by
Angela NeriThe nursing care plan addresses the risks of aspiration in a patient receiving bottled formula feeding. Short term goals within 4 hours include performing proper bottled feeding positioning at least 3 times after demonstration. Long term goals within 8 hours include demonstrating effective feeding with bottled formula through absence of coughing, choking or other signs of trouble. Interventions include instructing on proper positioning, monitoring feeding cues, and evaluating respiratory signs. The plan aims to prevent aspiration and respiratory complications through safe feeding practices.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 6
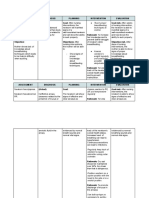
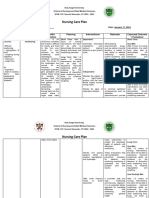
NURSING CARE PLAN
Nursing Analysis Goals and Nursing Rationale Evaluation
Cues Diagnosis Objectives Interventions
Subjective: Risk for Scientific LONG TERM: INDEPENDENT INDEPENDENT OUTCOME:
● The aspiration Analysis: Within 8 hours, a) Assess the a) To immediately Within 8 hours,
patient related to Risk for the patient and causative signs of resolve the the patient was
verbalized feeding aspiration is patient’s mother aspiration to symptoms that can able to have
that she is alteration with generally shall be able to prevent worsening lead to swallowing
willngly bottled- regarded to of feeding trouble problems and Demonstrate
ready to formula include factors 1. Demonstrate such as: aspiration which effective feeding
temporaril such as effective feeding - Mild fever may compromise with bottled-
y feed her intermittent with bottled- after eating respiratory function formula through
baby with feeding of formula through - Choking or in breathing. absence of
a bottled- delivery absence of coughing cough, choking
formula methods, cough, choking - Wheezing or other signs of
intubation and/or or other signs of or voice trouble in
Further cues are feeding tubes, trouble in that sounds feeding.
not applicable for and disorder feeding. dry __ Goal Met
a risk problem regarding - Faster or __ Goal
since it is only respiratory 2. Maintain slower Partially Met
potential. functions or patent airway breathing __ Goal Unmet
deficient upon sucking during Why?
nutrients for from the feeding
regulatory blottled-formula - Sucking Maintain patent
mechanisms of during meals weakly airway upon
the body. For the b.) Proper sucking from the
relative factors in 3. Observe and b) Instruct the positioning of blottled-formula
feeding, usage of demonstrate the patient’s mother bottle feeding is the during meals
bottled formula safety about the proper vital key in __ Goal Met
for infants are in precautions of bottled-formula by preventing __ Goal
great risk of bottled-formula tilting the patient’s aspiration since it Partially Met
aspiration due to upon sterile head with the neck, focuses on having a __ Goal Unmet
the conditions of making and and supporting it patent entry of the Why?
the possibility of consumption. over the shoulder. formula milk in the
the milk as a mouth that Observe and
foreign material decreases the demonstrate the
to enter in the likelihood of safety
lungs, since directing into lungs precautions of
gastric contents instead of in the bottled-formula
disrupts stomach. upon sterile
structural lung c) Encourage the making and
abnormalities. patient’s mother to consumption.
have resting c) Monitoring the __ Goal Met
Situational periods with the baby’s __ Goal
Analysis: patients during manifestation Partially Met
Feeding an infant meals and observe whether in body __ Goal Unmet
with a bottled feeding cues that movement and/or Why?
formula is manifest as facial expression
presumed to be fullness, allows immediate
easier than specifically prevention of the
breastfeeding burping. symptoms of
since it does not aspiration.
require such d) Assess rate and
establishing good depth of d) Tachypnea,
attachment, and respirations and shallow
generally known chest movement. respirations, and
to be easier in Monitor for signs asymmetric chest
consumption for of respiratory movement are
feeding. failure such severe frequently present
However, bottled tachypnea. because of
feeding also compromised
causes aspiration airway in the lungs.
when the milk When aspiration
directly goes into occurs,
the lungs instead the patient may
in the stomach require
which may endotracheal
compromise intubation and
chest infections. mechanical
Through clinical e) Evaluate cough, ventilation to keep
symptoms of swallow, and gag airways clear.
feeding trouble, reflexes movement
primarily frequently. Notify e) Frequent
choking and health care evaluation of
coughing, which providers if absent. reflexes is needed
can be to prevent
accompanied by aspiration
watery eyes, red associated with
face complexion DEPENDENT respiratory
due to lack of a) Evaluate the problems.
airway need for enteral
obstruction,weak feeding, if needed
sucking, and as doctor’s order,
other signs once impaired DEPENDENT
indicating swallowing a) Further actions
difficulty in function or no for pharmacologic
feeding. movement of air therapy be SHORT
SHORT has occurred. considered as an TERM:
The patient’s TERM: invasive procedure Within 4 hours
condition Within 4 hours for a baby should the patient was
indicates the patient shall be significantly able to
temporary be able to evaluated and
bottled feeding consider its
that also suffers traumatic risk Perform proper
from nutrient 1. Perform b) Administer factors into the positioning of
deficiency. This proper medications, as mouth and bottled-feeding
shows relative positioning of indicated, for pharynx. at least 3 times
demand for bottled-feeding example, after
effective feeding at least 3 times mucolytics, demonstration
towards the after expectorants, b) Aids in __ Goal Met
patient to meet demonstration bronchodilators, reduction of __ Goal
the metabolic and analgesics, as bronchospasm and Partially Met
needs concerning 2. Display good ordered by the mobilization of __ Goal Unmet
poor nutritional “latch”without physician. slung expansion. Why?
status and immediate Analgesics are
potential withdrawal given to improve Display good
inflammation. cough effort by “latch”without
3. Verbalize reducing immediate
REFERENCE: understanding discomfort but withdrawal
Doenges, M.E., about the should be used __ Goal Met
Moorhouse, causative effects cautiously because __ Goal
M.F., Murr, A.C. of being at risk they can decrease Partially Met
(2014). Nursing of aspiration. COLLABORATIV cough effort and __ Goal Unmet
Care Plans: E depress respirations Why?
guidelines for a) Perform
individualizing assistive treatments Verbalize
client care across such as feeding COLLABORATIV understanding
the life span 9th tubes if prescribed E about the
edition. Davis by the doctor. a) Coordination of causative effects
Company: treatments, of being at risk
Philadelphia, PA. schedules, and oral of aspiration.
ISBN 978-0- intake reduces __ Goal Met
8036-3041-3 likelihood of __ Goal
compromising the Partially Met
Udan-Quiambao, b) Follow up nutrition status of __ Goal Unmet
J. (2007). monitoring of serial the client and its Why?
Medical-Surgical chest x-rays, effect on organ
Nursing: ABGs, and pulse metabolism.
Concepts and oximetry readings,
Clinical as well as b) Follows
Application 2nd laboratory results. progress and
edition. effects of
Educational respiratory
publishing functions and
house: Manila, therapeutic
Ph. ISBN 978- c) Provide teaching regimen and
971-513-268-8 based on the needs facilitates
of the patient and necessary
the relatives alterations in
regarding the: therapy
• Illness and its
possible
complication c) Reduces anxiety
• Procedures and for a stressful
related nursing care situation that the
client’s relative is
facing by starting
appropriate
planning.
assists the family in
dealing with the
health-care system
on the client’s
critical condition.
References:
Doenges, M., Moorhouse, M. F., & Murr, A. (2019).Nurse’s Pocket Guide.(15th ed.). F.A. Davis.
Cox, H. C., & Newfield, S. A. M. (2007). Cox's clinical applications of nursing diagnosis: Adult, child, women's, mental health,
gerontic, and home health considerations (5th ed.). Philadelphia: F.A. Davis Company.
Udan, J.Q. (2009). Medical Surgical Nursing: Concepts and Application 2nd ed. Ermita, Manila: Giuani Prints Houes, Educational
Publishing House.
You might also like
- Standards of Care in Diabetes - 2024Document9 pagesStandards of Care in Diabetes - 2024josueraulbalandran100% (1)
- The Longevity Diet: Discover The New Science Behind Stem Cell Activation and Regeneration To Slow Aging, Fight Disease, and Optimize Weight - Valter LongoDocument5 pagesThe Longevity Diet: Discover The New Science Behind Stem Cell Activation and Regeneration To Slow Aging, Fight Disease, and Optimize Weight - Valter Longozyrybosi14% (7)
- BionoteDocument4 pagesBionoteAngela Neri100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Short Term: Difficulty in Swallowing Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan: Short Term: Difficulty in Swallowing Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationNico Angelo Hibaya TugononNo ratings yet
- 7 Household Items For Faster Fat LossDocument30 pages7 Household Items For Faster Fat LossLinda PrideNo ratings yet
- NCM 105 Lesson 1Document35 pagesNCM 105 Lesson 1Roshin TejeroNo ratings yet
- Michael R., M.D. Eades, Mary Da M.D. Eades - The 30-Day Low-Carb Diet Solution (2003) PDFDocument194 pagesMichael R., M.D. Eades, Mary Da M.D. Eades - The 30-Day Low-Carb Diet Solution (2003) PDFAmelia Thalib100% (1)
- Teach Proper Breastfeeding Techniques To MotherDocument3 pagesTeach Proper Breastfeeding Techniques To MotherSaimon ReighNo ratings yet
- Breast Feeding Tec.Document9 pagesBreast Feeding Tec.Chairali DodiyaNo ratings yet
- NIH Public Access: Lack of Feeding Progression in A Preterm Infant: A Case StudyDocument16 pagesNIH Public Access: Lack of Feeding Progression in A Preterm Infant: A Case StudyFarah PramestyNo ratings yet
- Steps To Successfully Breastfeed The Premature InfantDocument10 pagesSteps To Successfully Breastfeed The Premature InfantKholis FaisolNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Goal of Care Outcome Criteria Interventions and Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Goal of Care Outcome Criteria Interventions and Rationale EvaluationMariah Angela PonceNo ratings yet
- Achalasia NCPDocument6 pagesAchalasia NCPkarl davidNo ratings yet
- Cleft Lip and PalateDocument8 pagesCleft Lip and PalateSHEILA MAE SACLOTNo ratings yet
- Feeding in The Preterm Infant: ObjectivesDocument9 pagesFeeding in The Preterm Infant: ObjectivesFonoaudiólogaRancaguaNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals and Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals and Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationCarmina DinerosNo ratings yet
- Viernes, Jemalyn BSN 2-3 Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument8 pagesViernes, Jemalyn BSN 2-3 Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationJeMalyn VieRnesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of A Child With Physical AND Developmental ChallengesDocument9 pagesNursing Care of A Child With Physical AND Developmental ChallengesAngelo ArabejoNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument7 pagesNCPJulianne Jeamer FabroaNo ratings yet
- Fesalbon AsthmaDocument6 pagesFesalbon AsthmaogiskuadzNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan (During Labor) : Subjective CuesDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan (During Labor) : Subjective CuesNatalie Antipolo100% (1)
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goals and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale Evaluation Subjective: NOC: Swallowing Status Goal: NIC: SwallowingDocument10 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goals and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale Evaluation Subjective: NOC: Swallowing Status Goal: NIC: SwallowingSkyla FiestaNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPJohn RyNo ratings yet
- Lippincott's PEDIATRIC4 ANSWERSDocument13 pagesLippincott's PEDIATRIC4 ANSWERSNursyNurseNo ratings yet
- NCP 101Document2 pagesNCP 101Mary Joy FrancoNo ratings yet
- Impaired SwallowingDocument2 pagesImpaired SwallowingfaizaNo ratings yet
- Disfagia Na Crianca (11998)Document4 pagesDisfagia Na Crianca (11998)martaNo ratings yet
- NCP GcsDocument15 pagesNCP GcsMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Teaching Plan For Proper Breast Feeding Begh ErDocument7 pagesTeaching Plan For Proper Breast Feeding Begh ErAmira Fatmah QuilapioNo ratings yet
- Swallowing Difficulties Can Have A Detrimental Effect On Dietary Intake And, Hence, Growth and DevelopmentDocument9 pagesSwallowing Difficulties Can Have A Detrimental Effect On Dietary Intake And, Hence, Growth and DevelopmentYenny FramelaNo ratings yet
- Nursing History: Patient Is in Active Phase in Stage of Cervical DilationDocument8 pagesNursing History: Patient Is in Active Phase in Stage of Cervical DilationVince BalisiNo ratings yet
- Health Talk On BFDocument28 pagesHealth Talk On BFpriyanka75% (8)
- Safe and Competent Oral Feeding Requires The Proper Integration of Physical and Neurophysiologic Functions That May Not Necessarily Be Mature at The Time Oral Feeding Is IntroducedDocument9 pagesSafe and Competent Oral Feeding Requires The Proper Integration of Physical and Neurophysiologic Functions That May Not Necessarily Be Mature at The Time Oral Feeding Is IntroducedVishnu Priya KarthikNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Nursing CareDocument5 pagesPediatric Nursing CareValerie BeteNo ratings yet
- 2 NCP Impaired Swallowing EditedDocument4 pages2 NCP Impaired Swallowing EditedZharm MayNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Ineffective Infant Feeding PatternDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Ineffective Infant Feeding PatternBasema HashhashNo ratings yet
- Risk For AspirationDocument2 pagesRisk For AspirationErica FabrigasNo ratings yet
- BSN2 C Ihps NCP FinalDocument7 pagesBSN2 C Ihps NCP FinalAdrian DecolongonNo ratings yet
- Kaitlin NCPDocument6 pagesKaitlin NCPJovel CortezNo ratings yet
- University of The East Ramon Magsaysay Memorial Medical Center, Inc. College of NursingDocument23 pagesUniversity of The East Ramon Magsaysay Memorial Medical Center, Inc. College of NursingReina RamonesNo ratings yet
- NCP - Pott's DiseaseDocument23 pagesNCP - Pott's Diseasemhean azneitaNo ratings yet
- 2 NCP Impaired Swallowing EditedDocument4 pages2 NCP Impaired Swallowing EditedLeonardo Montemayor100% (3)
- DiarrheaDocument3 pagesDiarrheaBert GasalNo ratings yet
- BrestfeedingDocument2 pagesBrestfeedingBuhkz Hermoso100% (1)
- David Achalasia NCPDocument4 pagesDavid Achalasia NCPkarl davidNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: STG: STGDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: STG: STGLiana Louisse JoseNo ratings yet
- IMCI StrategyDocument7 pagesIMCI StrategyAngelica Charisse BuliganNo ratings yet
- Dr. Nellie D. Gundao: Feeding Healthy Infants, Children and AdolescentsDocument5 pagesDr. Nellie D. Gundao: Feeding Healthy Infants, Children and AdolescentsGian Carla SoNo ratings yet
- Breastfeeding Techniques-Lesson PlanDocument12 pagesBreastfeeding Techniques-Lesson Planmonika makwanaNo ratings yet
- Aireen S. Papa Diana Rose PetilonaDocument3 pagesAireen S. Papa Diana Rose PetilonaMichael AmandyNo ratings yet
- Dysphagia: Ethan A. Mezoff, MDDocument5 pagesDysphagia: Ethan A. Mezoff, MDYenny FramelaNo ratings yet
- Amat Ncma 219 Pedia Week 5 CTDocument3 pagesAmat Ncma 219 Pedia Week 5 CTRaf AmatNo ratings yet
- Impaired Swallowing: Esophageal Phase ImpairmentDocument9 pagesImpaired Swallowing: Esophageal Phase ImpairmentK Jayakumar KandasamyNo ratings yet
- Quiaoit G3 BSN 2B NCPDocument3 pagesQuiaoit G3 BSN 2B NCPQuiaoit, Jackqueline T.No ratings yet
- Review Questionnaire MTRNALDocument13 pagesReview Questionnaire MTRNALKevin Vincent AquinoNo ratings yet
- Cough or Difficult Breathing: Distance Learning CourseDocument39 pagesCough or Difficult Breathing: Distance Learning Courseinno so qtNo ratings yet
- Assesment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssesment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationTrisha Suazo100% (1)
- Ob Nursing Care Plan For Maternal Database Maternal and NewbornDocument2 pagesOb Nursing Care Plan For Maternal Database Maternal and Newbornapi-403051801No ratings yet
- Altered Nutrition NCPDocument2 pagesAltered Nutrition NCPLeiAnnManaleseNo ratings yet
- Health Teaching PlanDocument4 pagesHealth Teaching PlannicanicsraakinNo ratings yet
- Acute Pain - Ineffective Breathing Pattern NCPDocument12 pagesAcute Pain - Ineffective Breathing Pattern NCPAngela NeriNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan ANPDocument24 pagesLesson Plan ANPKaruna NidhiNo ratings yet
- NCP For Hyperemesis GravidarumDocument5 pagesNCP For Hyperemesis Gravidarumclaire parkNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Food Allergy and Intolerance In.13Document4 pagesGastrointestinal Food Allergy and Intolerance In.13akbar alituNo ratings yet
- Case Study (DS)Document3 pagesCase Study (DS)Erica DumriqueNo ratings yet
- Level 4 Modules For Nursing Skills AuditDocument95 pagesLevel 4 Modules For Nursing Skills AuditAngela NeriNo ratings yet
- Colonic Mass PathophysioDocument1 pageColonic Mass PathophysioAngela NeriNo ratings yet
- Training Design Iec Material BSN 409 Grp2b SNDocument17 pagesTraining Design Iec Material BSN 409 Grp2b SNAngela NeriNo ratings yet
- Ramirez - Research Scientific PosterDocument1 pageRamirez - Research Scientific PosterAngela NeriNo ratings yet
- OR CommsDocument4 pagesOR CommsAngela NeriNo ratings yet
- Nle FC Manila 2023 May - EDITEDDocument12 pagesNle FC Manila 2023 May - EDITEDAngela NeriNo ratings yet
- @lfnursingcomms - DRUG STUDY FAJARDO ANDREA LAUREN A.Document6 pages@lfnursingcomms - DRUG STUDY FAJARDO ANDREA LAUREN A.Angela NeriNo ratings yet
- Renal Fabs Post Test Answer KeyDocument4 pagesRenal Fabs Post Test Answer KeyAngela NeriNo ratings yet
- Medication Administration Group 2Document32 pagesMedication Administration Group 2Angela NeriNo ratings yet
- Education, by Ellen G. White. Chapter 14 - Science and The BibleDocument4 pagesEducation, by Ellen G. White. Chapter 14 - Science and The BibleAngela NeriNo ratings yet
- Impact of A Modified Nursing Handover ModelDocument9 pagesImpact of A Modified Nursing Handover ModelAngela NeriNo ratings yet
- Sacraments 2Document68 pagesSacraments 2Angela NeriNo ratings yet
- @aryanehct.11 - Infographic 3 Computerized Order EntryDocument1 page@aryanehct.11 - Infographic 3 Computerized Order EntryAngela NeriNo ratings yet
- Typhoon Yunya (1991) - WikipediaDocument6 pagesTyphoon Yunya (1991) - WikipediaAngela NeriNo ratings yet
- Chan ReferencesDocument93 pagesChan ReferencesAngela NeriNo ratings yet
- AristotleDocument7 pagesAristotleAngela NeriNo ratings yet
- What Is Lacking in Us?: What Do You Think We, Human Beings, When We Lack The Sanctifying Grace of ?Document20 pagesWhat Is Lacking in Us?: What Do You Think We, Human Beings, When We Lack The Sanctifying Grace of ?Angela NeriNo ratings yet
- Crash Cart Check ListDocument2 pagesCrash Cart Check ListAngela NeriNo ratings yet
- Training DesignDocument1 pageTraining DesignAngela NeriNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Physical Fitness: Prepared by Professor Elenita LeabresDocument11 pagesIntroduction To Physical Fitness: Prepared by Professor Elenita LeabresAngela NeriNo ratings yet
- Program Flow DraftDocument1 pageProgram Flow DraftAngela NeriNo ratings yet
- Angela P. Neri March 4, 2021 BSN 309 Mad Rle Act # 2Document3 pagesAngela P. Neri March 4, 2021 BSN 309 Mad Rle Act # 2Angela NeriNo ratings yet
- Sample Problem Solving ProcessDocument5 pagesSample Problem Solving ProcessAngela NeriNo ratings yet
- A Social Life in Reality: Facebook From The Funny Memes To Videos That Simply Make Me Laugh. in Observation As Well ToDocument2 pagesA Social Life in Reality: Facebook From The Funny Memes To Videos That Simply Make Me Laugh. in Observation As Well ToAngela NeriNo ratings yet
- ReflectivePaper DAY1 NERIDocument2 pagesReflectivePaper DAY1 NERIAngela NeriNo ratings yet
- Movie Review: "What A Beautiful Mind"Document4 pagesMovie Review: "What A Beautiful Mind"Angela NeriNo ratings yet
- FA#2 Essay - NERI (Elderly Health)Document2 pagesFA#2 Essay - NERI (Elderly Health)Angela NeriNo ratings yet
- Group 2B: A Pulmonary Histoplasmosis CaseDocument58 pagesGroup 2B: A Pulmonary Histoplasmosis CaseAngela NeriNo ratings yet
- (Last) (Given) (Unit/Lot No.) (Bldg. No.) (Street) (Barangay) (Municipality)Document78 pages(Last) (Given) (Unit/Lot No.) (Bldg. No.) (Street) (Barangay) (Municipality)Angela NeriNo ratings yet
- How To Lose Weight Without Dieting PDFDocument2 pagesHow To Lose Weight Without Dieting PDFBetter WeighNo ratings yet
- Eat Healthy, Stay HealthyDocument3 pagesEat Healthy, Stay Healthyrampoudel649No ratings yet
- 1 PBDocument10 pages1 PBA'Lin Valerine FerreNo ratings yet
- Vitamin D DeficinyDocument11 pagesVitamin D DeficinyسالمNo ratings yet
- Medical Nutrition Therapy in Obesity Management - Canadian Adult Obesity Clinical Practice GuidelinesDocument28 pagesMedical Nutrition Therapy in Obesity Management - Canadian Adult Obesity Clinical Practice GuidelinesNitanluisNo ratings yet
- Nutrients 12 03660 v3Document17 pagesNutrients 12 03660 v3Mark OmbaoNo ratings yet
- The Culture of CrossFit. A Lifestyle Prescription For Optimal Health and Fitness (Inglés) Autor Steven KuhnDocument15 pagesThe Culture of CrossFit. A Lifestyle Prescription For Optimal Health and Fitness (Inglés) Autor Steven KuhnRosa Martin HuelvesNo ratings yet
- Pitta Final BookDocument42 pagesPitta Final Bookkabirtrivedi7No ratings yet
- Kamalnayan Bajaj Nursingcollege, Aurangabad .: Visit Report On Anganwadi at Turkabad TQ Gangapur, Aurangabad DistrictDocument14 pagesKamalnayan Bajaj Nursingcollege, Aurangabad .: Visit Report On Anganwadi at Turkabad TQ Gangapur, Aurangabad DistrictAkshata Bansode78% (9)
- (STAMP) :: Screening Tool For The Assessment of Malnutrition PediatricsDocument10 pages(STAMP) :: Screening Tool For The Assessment of Malnutrition PediatricsHabib RehmanNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 1Document6 pagesLesson Plan 1Antonio Jeremiah TurzarNo ratings yet
- Persuasive Writing 2Document30 pagesPersuasive Writing 2ALBA JANET GRANDA GARCIANo ratings yet
- PT G7 MapehDocument5 pagesPT G7 MapehWendilyne TababaNo ratings yet
- Best Practices: For Feeding Your Child From 0 To 5 Years of AgeDocument17 pagesBest Practices: For Feeding Your Child From 0 To 5 Years of AgeEd SeraficaNo ratings yet
- Lab No. 2 - ANS141Document7 pagesLab No. 2 - ANS141Janah Mariz LoquillanoNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Fitness Challenge 2023-2024Document6 pagesSyllabus Fitness Challenge 2023-2024api-224225781No ratings yet
- Nutrition Factor in Women in Backward AreasDocument7 pagesNutrition Factor in Women in Backward AreaspranjalNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Diet TherapyDocument70 pagesNutrition Diet TherapyMay Rodeo100% (1)
- Broiler Feeding Guide: Population: 100 HeadsDocument1 pageBroiler Feeding Guide: Population: 100 HeadsMA DapNo ratings yet
- Wardlaws Contemporary Nutrition A Functional Approach 5th Edition Wardlaw Test BankDocument38 pagesWardlaws Contemporary Nutrition A Functional Approach 5th Edition Wardlaw Test BankChristinaMcmahondbkfa100% (10)
- Answer Key To P24Document10 pagesAnswer Key To P24tmNo ratings yet
- Nutrition ArticleDocument5 pagesNutrition ArticleAafiah IfadaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Exam Quantatative AblityDocument6 pagesNursing Exam Quantatative AblitysamloviniNo ratings yet
- Good Topics For Nutrition Research PaperDocument6 pagesGood Topics For Nutrition Research Paperqhujvirhf100% (1)
- Practical Research Ii CH.1 3Document16 pagesPractical Research Ii CH.1 3Louie Jay JadraqueNo ratings yet