Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Carboxylic Acids Worksheet1 Key 2
Carboxylic Acids Worksheet1 Key 2
Uploaded by
Ana Pamela MejiaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Carboxylic Acids Worksheet1 Key 2
Carboxylic Acids Worksheet1 Key 2
Uploaded by
Ana Pamela MejiaCopyright:
Available Formats
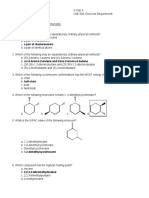
CARBOXYLIC ACIDS WORKSHEET KEY
1. Name the following:
a. methanoic acid b. ethanoic acid
c. propanoic acid d. butanoic acid
e. 3-bromobutanoic acid f. 2-methylbutanoic acid
g. 2-isopropylpentanoic acid h. 2,2,5-trimethylhexanoic acid
i. 2-phenylpropanoic acid j. 2,5-dimethylbenzoic acid
k. 3-chlorobenzoic acid l. 4-isoproplybenzoic acid
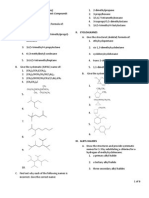
2. Draw condensed structural formulas for the following:
2-methylpropanoic acid 2,2,5-trimethylhexanoic acid
4,5-dimethyl-3-nitrooctanoic acid para-bromobenzoic acid
2,4,6-trinitrobenzoic acid 2-ethylpentanoic acid
3. Arrange the following compounds in order of increasing boiling point. (All of the
compounds have about the same molar mass.)
–1-pentanol
– hexane
– butanoic acid
– pentanal
The correct order is: hexane, pentanal, 1-pentanol, butanoic acid
4. Which member of each of the following pairs of compounds would you expect to
have a higher solubility in water?
a. 2-butanone OR propanoic acid
propanoic acid because it can form hydrogen bonds with water (between the hydrogens of
water and the oxygen in the hydroxyl group) . In addition the carboxylic group is the most polar
of the functional groups making carboxylic acids soluble in polar water (recall the thumb rule of
solubility- polar dissolves polar, non-polar dissolves non-polar). In 2-butanone the carbonyl
group though polar it is not as accessible to water as it is in the carboxylic group causing
ketones to be less soluble in water relative to carboxylic acids
b. hexanoic acid OR ethanoic acid
ethanoic acid. Because C-H bonds are nonpolar then the shorter chain carboxylic acids are
more soluble in a polar solvent
You might also like
- Organic Chemistry Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument4 pagesOrganic Chemistry Multiple Choice QuestionsRonald Angelo LopezNo ratings yet
- Naming Alkanes Ws 1 and Ws 2Document4 pagesNaming Alkanes Ws 1 and Ws 2usmanzubair50% (4)
- Naming Alkanes Ws 1 and Ws 2gdgDocument4 pagesNaming Alkanes Ws 1 and Ws 2gdgusmanzubair100% (1)
- Organic WorksheetsDocument16 pagesOrganic WorksheetsjcdanezNo ratings yet
- He Following Are The List of Aliphatic Compounds, According To The Number of Carbon Atoms They Contain. Complete The Table BelowDocument17 pagesHe Following Are The List of Aliphatic Compounds, According To The Number of Carbon Atoms They Contain. Complete The Table BelowJohn Rafael DiazNo ratings yet
- Ola ChemDocument10 pagesOla ChemChan ChanNo ratings yet
- Work Sheet Alkanes Sbi 09Document6 pagesWork Sheet Alkanes Sbi 09neneng rohayatiNo ratings yet
- Work Sheet Alkanes Sbi 09Document5 pagesWork Sheet Alkanes Sbi 09Elfi Susanti VHNo ratings yet
- Module 5 OrgchemDocument9 pagesModule 5 OrgchemJHUNNTY LOZANONo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Ortho & ParanitrophenolDocument1 pageChemistry: Ortho & ParanitrophenolOzaswi EnterprisesNo ratings yet
- Q2 GC Summative W 5-6Document2 pagesQ2 GC Summative W 5-6Shane RickzelleNo ratings yet
- Nomenclature - Prob SetDocument7 pagesNomenclature - Prob SetGenny MarantanNo ratings yet
- Important Questions For PracticeDocument1 pageImportant Questions For Practicethirumalaivasan GNo ratings yet
- Kish Salas Bschem 2H2 Activity No. 1 Nomenclature of Saturated HydrocarbonsDocument2 pagesKish Salas Bschem 2H2 Activity No. 1 Nomenclature of Saturated HydrocarbonsKish Floran SalasNo ratings yet
- Organic and Biochemistry For Today 8Th Edition Seager Solutions Manual PDFDocument22 pagesOrganic and Biochemistry For Today 8Th Edition Seager Solutions Manual PDFruth.cave622100% (14)
- CHEMDocument8 pagesCHEMRyle AquinoNo ratings yet
- Lec m4 Check-In Activity 2Document5 pagesLec m4 Check-In Activity 2leoleoleoNo ratings yet
- Mod 5 Alcohol, Phenol and EtherDocument50 pagesMod 5 Alcohol, Phenol and EtherLeigh Ann PortacionNo ratings yet
- HYDROCARBONSDocument15 pagesHYDROCARBONSJaxene Breanna AbuanNo ratings yet
- GENCHEMMID1Document10 pagesGENCHEMMID1Metran Arvic Earl JustinNo ratings yet
- Oxygen-Containing Hydrocarbon DerivativesDocument53 pagesOxygen-Containing Hydrocarbon DerivativesOmaiwa Mo ShinderuNo ratings yet
- Practice - Organic Nomenclature: Directions: Write Your Answers To The Following Questions in The Space Provided. UseDocument8 pagesPractice - Organic Nomenclature: Directions: Write Your Answers To The Following Questions in The Space Provided. UseKeshav GuptaNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 4 PDFDocument2 pagesProblem Set 4 PDFLouisNo ratings yet
- Tugas Buat SoalDocument3 pagesTugas Buat Soalaliefyan4769No ratings yet
- Organic and Biochemistry For Today 8Th Edition Seager Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesOrganic and Biochemistry For Today 8Th Edition Seager Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFpaula.caldeira652100% (11)
- Key Quiz Organic CompoundsDocument3 pagesKey Quiz Organic CompoundsMA. ESTHER FAUSTA TIAMZONNo ratings yet
- 6 and 7Document20 pages6 and 7Abhi RamNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry: Tutor: Abhiram Date: 29/11/2016 Cambridge IGCSEDocument20 pagesOrganic Chemistry: Tutor: Abhiram Date: 29/11/2016 Cambridge IGCSEAbhi RamNo ratings yet
- Weekly Assignment-6Document3 pagesWeekly Assignment-6anish.chandrasekar.bloreNo ratings yet
- Determination of Proteins and Amino AcidsDocument12 pagesDetermination of Proteins and Amino AcidsKrithika Bhaskar RathishNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument94 pagesOrganic Chemistrybj primeNo ratings yet
- Question Bank On Aldehydes Ketiones Carboxylic AcidsDocument3 pagesQuestion Bank On Aldehydes Ketiones Carboxylic Acidseeshwar saagarNo ratings yet
- CONS Orgchem WorksheetsDocument18 pagesCONS Orgchem Worksheetssan_cdkeyNo ratings yet
- Aldehyde Ketone and CarboxylicDocument2 pagesAldehyde Ketone and CarboxylicSaransh KumarNo ratings yet
- ARRANGE THE FOLLOWING ORGANIC FinalDocument2 pagesARRANGE THE FOLLOWING ORGANIC Finalmunsifmohammed501No ratings yet
- Chemistry NOtesDocument5 pagesChemistry NOtesSe HunNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 12 - Unit 1 ORGANIC UNIT QuizDocument5 pagesChemistry 12 - Unit 1 ORGANIC UNIT QuizKelvin WNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam BiochemDocument4 pagesMidterm Exam BiochemMargie Fe AntiquinaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 8. Aromatic HCDocument2 pagesWorksheet 8. Aromatic HCHafza MacabatoNo ratings yet
- Amino AcidsDocument7 pagesAmino Acidsimsinyee23No ratings yet
- Grade Xii (Chemistry) : Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids (Term - 2) : Most Expecting QuestionsDocument5 pagesGrade Xii (Chemistry) : Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids (Term - 2) : Most Expecting QuestionsSupreeta KhatiwadaNo ratings yet
- Cetona SDocument6 pagesCetona SLuna SuárezNo ratings yet
- Review NotesDocument7 pagesReview NotesKatie MoreeNo ratings yet
- WS SL NamingPracticeDocument1 pageWS SL NamingPracticeGüşta İrem SakızNo ratings yet
- Organic MenuDocument18 pagesOrganic MenuelishamahubiNo ratings yet
- Naming Organic Compounds 2023Document9 pagesNaming Organic Compounds 2023Joecel May Gabino HalipanNo ratings yet
- Carbon & Its Compounds L-3Document12 pagesCarbon & Its Compounds L-3dakshdav.mehraNo ratings yet
- Table of Content: Organic Synthesis: Formation of An Ester Lab ReportDocument11 pagesTable of Content: Organic Synthesis: Formation of An Ester Lab ReportMuhammad Irfan Malik100% (1)
- Alcohol and EtherDocument30 pagesAlcohol and EtherSamratNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1.4 Nomenclature of Some Hydrocarbon DerivativesDocument18 pagesChapter 1.4 Nomenclature of Some Hydrocarbon DerivativesTrishaNo ratings yet
- 5 - AlkenesDocument12 pages5 - AlkenesSean Gabriel LacambraNo ratings yet
- Workbook - Course 1 Final 2021 2022Document51 pagesWorkbook - Course 1 Final 2021 2022Ali AbuchillehNo ratings yet
- 2016 Worksheet For Medicine StudentsDocument2 pages2016 Worksheet For Medicine StudentsbedadadenbalprosperityNo ratings yet
- Proteins Work BookletDocument17 pagesProteins Work BookletTheZiggyNo ratings yet
- Advances in The Krapcho DecarboxylationDocument8 pagesAdvances in The Krapcho DecarboxylationchidambaramrNo ratings yet
- Aaravee Ketheeswaran - SCH4U Full Naming Practice PDFDocument8 pagesAaravee Ketheeswaran - SCH4U Full Naming Practice PDFAaravee KNo ratings yet
- Student Worksheet 1Document26 pagesStudent Worksheet 1sanihgholiyahNo ratings yet
- AldehydesDocument28 pagesAldehydesElsaeed TalhaNo ratings yet
- The Total Synthesis of Natural ProductsFrom EverandThe Total Synthesis of Natural ProductsJohn ApSimonNo ratings yet