Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Physics - Audiofrequencies
Physics - Audiofrequencies
Uploaded by
johnreyutadOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Physics - Audiofrequencies
Physics - Audiofrequencies
Uploaded by
johnreyutadCopyright:
Available Formats
PHYSICS
AUDIOFREQUENCIES
FORM 5
The human ear can detect sound with the following frequencies: 20Hz – 20000Hz (20Hz –
20kHz). Frequencies below or above this range are not detected. All waves undergo reflection,
refraction, diffraction and interference.
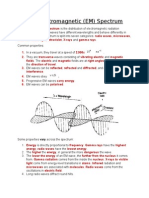
Electromagnetic Waves
These are waves with the following properties:
1. Identical speed in a vacuum 3.0 × 108 𝑚/𝑠
2. They are transverse waves.
3. They can travel in a vacuum.
4. They transmit energy from a source.
5. They obey the laws of reflection and refraction.
6. Can undergo diffraction.
7. Can undergo interference.
8. Can be emitted and absorbed by matter.
9. Carries no charge.
The Electromagnet Spectrum
Name Wavelength Source Special Properties
Cosmic rays, radioactive Very dangerous. Used to kill
Gamma Rays 10−12m
nuclei cells,, eg. Sterilisation
Used to detect bone fractures,
used to treat skin disorders and
X-Rays 10−10m X-Ray tube
the study of the structure of
crystals
Is absorbed by glass, causes
Very hot objects, sparks, chemical reactions, treatment
UV Light 10−8m
mercury vapour, lamps of skin diseases, skin cancer
and damage to the retina
Detected by the retina to allow
Visible Light 0.6 × 10−6 m Sun lasers
vision. Used for photosynthesis
Infrared Rays 10−4m Any hot object, sun or fire Causes heating when absorbed.
TV and Radio Communication, radar
Radiowaves 3m transmitters/microwave detection, microwaves for
ovens cooking.
PHYSICS
AUDIOFREQUENCIES
FORM 5
Light Waves
Visible light forms part of the electromagnetic spectrum and therefore has all the properties of
the electromagnetic spectrum.
Nature of Light
There are two proposed theories as to the nature of light, combined they are called the Dual
Nature of Light.
Two Theories are as follows:
1. Corpuscular Theory – This was proposed by Newton which suggested that light travels as
small particles called corpuscles.
Evidence for this theory was based on the fact that these tiny particles would obey Newton’s
Laws of motion, hence the reason light waves reflect and refract. This theory cannot explain
how light waves diffract or undergo interference.
2. Wave Theory – Evidence of wave theory was demonstrated by Thomas Young. In this
theory, light is considered to be an electromagnetic wave. Being a wave it explains how
light can undergo reflection, refraction, diffraction and interference.
Albert Einstein proposed that both theories had merit. He suggested that the particles were tiny
packets of energy and were called photons. The photons contained a certain quantum of energy.
The photons were so tiny that they possess wave properties. This has led to a branch of Physics
called Quantum Physics.
PHYSICS
AUDIOFREQUENCIES
FORM 5
The alternating dark and light lines indicate that light waves undergo diffraction and interference
and therefore light must exist as a wave form.
You might also like
- Therapeutic Modalities in Rehabilitation 3rd Edition Therapeutic Modalities For Physical Therapists PDFDocument921 pagesTherapeutic Modalities in Rehabilitation 3rd Edition Therapeutic Modalities For Physical Therapists PDFSherief Mansour100% (2)
- Electromagnetic Waves ProjectDocument13 pagesElectromagnetic Waves ProjectDiya Kumar82% (61)
- Grade 10 Science ReviewerDocument4 pagesGrade 10 Science ReviewerMarian Evangelio100% (10)
- Huawei AMB4519R0v06Document2 pagesHuawei AMB4519R0v06NOKIAXL CJ100% (1)
- Ophthalmic Dispensing Revision Guide: First Year Part OneFrom EverandOphthalmic Dispensing Revision Guide: First Year Part OneRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Physics - AudiofrequenciesDocument3 pagesPhysics - Audiofrequenciesrenatogalvez332No ratings yet
- Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument10 pagesElectromagnetic SpectrumMaria ArshadNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic WavesDocument12 pagesElectromagnetic WavesINSIDIOUSNo ratings yet
- G10 Science Q2-W5 - Electromagnetic Effects To LivingDocument37 pagesG10 Science Q2-W5 - Electromagnetic Effects To LivingKarina GentonNo ratings yet
- Properties of LightDocument25 pagesProperties of LightAhmad Dhiyaul WahidNo ratings yet
- Spectrum) of Electromagnetic Radiation and Their RespectiveDocument10 pagesSpectrum) of Electromagnetic Radiation and Their RespectiveJabez Edwin SivaNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Spectrum HWDocument11 pagesElectromagnetic Spectrum HWmahmoodkhan3818No ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Spectrum FormsDocument32 pagesElectromagnetic Spectrum FormsRuih PadillaNo ratings yet
- Integrantes:: Laura María Baquero Cuéllar Joan Camilo Caicedo Daniela Delmar Vásquez Ingrid Jhoana Sánchez CharrupiDocument49 pagesIntegrantes:: Laura María Baquero Cuéllar Joan Camilo Caicedo Daniela Delmar Vásquez Ingrid Jhoana Sánchez CharrupiFabricio Echeverri LondoñoNo ratings yet
- 8.2. EMW-source, Frequency Range, UsesDocument3 pages8.2. EMW-source, Frequency Range, UsesRamananNo ratings yet
- Quarter2 Electromagnetic WavesDocument25 pagesQuarter2 Electromagnetic WavesTrendi Printing ServicesNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Waves (Review)Document3 pagesElectromagnetic Waves (Review)kiaty kiatNo ratings yet
- SpectroDocument11 pagesSpectrochkamran32bNo ratings yet
- EM WavesDocument3 pagesEM WavesVansh SinghaiNo ratings yet
- EM WavesDocument11 pagesEM WavesHomok Noki100% (1)
- Electro Magnetic Waves M@trix FoundationDocument7 pagesElectro Magnetic Waves M@trix FoundationdjbabuNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Spectrum: Learning OutcomesDocument7 pagesElectromagnetic Spectrum: Learning OutcomesAbhishek KunalNo ratings yet
- Physics1101 - Course MaterialDocument332 pagesPhysics1101 - Course MaterialAhmad RazaNo ratings yet
- SM Sains Muzaffar SyahDocument5 pagesSM Sains Muzaffar SyahLyana MalekNo ratings yet
- By Ojal Grover, Adorcille Abat, Patrick Trollope & Vijay MahatmaDocument62 pagesBy Ojal Grover, Adorcille Abat, Patrick Trollope & Vijay MahatmaDuy NguyenNo ratings yet
- X-Ray Radiation and Gamma RadiationDocument13 pagesX-Ray Radiation and Gamma RadiationVence MeraNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Science Unit 2: Optics: Chapter 4: Many PropertiesDocument45 pagesGrade 8 Science Unit 2: Optics: Chapter 4: Many PropertiesMary-Rose CasuyonNo ratings yet
- Team Leader - Ibasan, Michael Ellise: I. Cover Page II. Members and Assigned TasksDocument12 pagesTeam Leader - Ibasan, Michael Ellise: I. Cover Page II. Members and Assigned TasksJOHN ASHLEY RANIN CARIAGANo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument28 pagesElectromagnetic SpectrumAbhishek N Rokhade50% (2)
- Radiation - AstroPhysics - WowDocument22 pagesRadiation - AstroPhysics - WowGuidor ProNo ratings yet
- Elecromagnetic SpectrumDocument11 pagesElecromagnetic SpectrumTIJIN ABE THOMASNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument23 pagesElectromagnetic SpectrumGrantt ChristianNo ratings yet
- EM SpectrumDocument10 pagesEM Spectrumabhinavsingh22012006No ratings yet
- Notes: Science & Computer - Term 1, Cycle 2Document23 pagesNotes: Science & Computer - Term 1, Cycle 2chy marizNo ratings yet
- Electrotherapy 2Document138 pagesElectrotherapy 2nagyrashad123No ratings yet
- What Is Electromagnetc Spectrum?Document11 pagesWhat Is Electromagnetc Spectrum?Rodrigo SeriozaNo ratings yet
- ScieneDocument6 pagesScieneOkay JoshNo ratings yet
- Final OneDocument63 pagesFinal OneAmanda TeacaNo ratings yet
- Science-Reviewer 2Document4 pagesScience-Reviewer 2abygaelreyesNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Spectrum GCLDocument64 pagesElectromagnetic Spectrum GCLsucculentcactirootsNo ratings yet
- Engineering Physics Unit-1Document51 pagesEngineering Physics Unit-1FatherNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic WavesDocument12 pagesElectromagnetic WaveskdNo ratings yet
- Em SpectrumDocument13 pagesEm SpectrumKaran YadavNo ratings yet
- Module 8 PhysicsDocument7 pagesModule 8 PhysicsLopez AeraNo ratings yet
- Class 12 PhysicsDocument37 pagesClass 12 PhysicsKartik SharmaNo ratings yet
- SpectrumDocument22 pagesSpectrumG̷U̷N̷M̷A̷N̷ ꓕIHNo ratings yet
- SS3 Ist Term PhysicsDocument52 pagesSS3 Ist Term Physicsojo ayodeji johnsonNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Spectrum:: Common Properties of em WavesDocument3 pagesElectromagnetic Spectrum:: Common Properties of em Wavesgwen_frenz2500No ratings yet
- EM SpectrumDocument6 pagesEM SpectrumKaren100% (1)
- Atomic & Nuclear PhysicsDocument9 pagesAtomic & Nuclear PhysicsPyay Lin ThantNo ratings yet
- Science 10 SECOND QuarterDocument152 pagesScience 10 SECOND QuarterAPPLE GRACE MARIE SEBASTIAN100% (1)
- Electromagnetic WavesDocument10 pagesElectromagnetic WavesJahleel TroupeNo ratings yet
- Radiant Energy & Nuclear EnergyDocument42 pagesRadiant Energy & Nuclear EnergyChristine Marielle Claroniño ApoNo ratings yet
- 8 Unit 2 CH 4 Slideshow 09Document45 pages8 Unit 2 CH 4 Slideshow 09api-238589602No ratings yet
- Grade 10 Reviewer ScienceDocument7 pagesGrade 10 Reviewer ScienceAntonette TabilNo ratings yet
- Insmeth Lecture 2.1Document39 pagesInsmeth Lecture 2.1nofacejackNo ratings yet
- Xray FundamentalsDocument27 pagesXray FundamentalsABISHKAR SARKARNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Spectrum Formative Task - 10a - TrishaDocument25 pagesElectromagnetic Spectrum Formative Task - 10a - TrishaMadhavi KapadiaNo ratings yet
- Victoreen Radiation & You Handbook 1999Document33 pagesVictoreen Radiation & You Handbook 1999Jake PetersNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjektDocument12 pagesPhysics Projektrupendrajain20No ratings yet
- ScienceDocument3 pagesScienceJames Darren TadeoNo ratings yet
- Practical Introduction to Laser DermatologyFrom EverandPractical Introduction to Laser DermatologyVishal MadanNo ratings yet
- Calculo Luminico, Canchas de FutbolDocument15 pagesCalculo Luminico, Canchas de FutbolRodrigo AriasNo ratings yet
- Praxis GuideDocument43 pagesPraxis GuideRyan NegadNo ratings yet
- Test Question 4rth Quarter Phycical ScienceDocument3 pagesTest Question 4rth Quarter Phycical ScienceEden Garin AmadorNo ratings yet
- Dialux BRP391 40W DM CT Cabinet SystemDocument20 pagesDialux BRP391 40W DM CT Cabinet SystemRahmat mulyanaNo ratings yet
- Master PL-C 18W/865/2P 1CTDocument3 pagesMaster PL-C 18W/865/2P 1CTgegerkalongciwaruaNo ratings yet
- Design of Compact Millimeter Wave Massive Mimo Dual-Band (28/38 GHZ) Antenna Array For Future 5G Communication SystemsDocument2 pagesDesign of Compact Millimeter Wave Massive Mimo Dual-Band (28/38 GHZ) Antenna Array For Future 5G Communication SystemsSofia Kara MostefaNo ratings yet
- Fisika 11. Ifrared LightDocument14 pagesFisika 11. Ifrared LightnadhiraseptiaskNo ratings yet
- 3 19三维建模Document8 pages3 19三维建模Nostalgia BlueNo ratings yet
- PPFD To Watts ConversionDocument1 pagePPFD To Watts ConversiontoygurNo ratings yet
- Dual-Band Dual-Polarized Microstrip Antenna Array Using Double-Layer Gridded Patches For 5G Millimeter-Wave ApplicationsDocument10 pagesDual-Band Dual-Polarized Microstrip Antenna Array Using Double-Layer Gridded Patches For 5G Millimeter-Wave Applicationsvikas chawlaNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Waves 1 QPDocument18 pagesElectromagnetic Waves 1 QPNaeemNo ratings yet
- Chapt2 PDFDocument4 pagesChapt2 PDFDrjasmeet KaurNo ratings yet
- Unguided MediaDocument16 pagesUnguided MediaAnirban Guha100% (1)
- Wide-Lite Supra-Lyte Brochure 1996Document24 pagesWide-Lite Supra-Lyte Brochure 1996Alan MastersNo ratings yet
- Comment On Photo StabDocument4 pagesComment On Photo StabMarkus JeremiaNo ratings yet
- UNIT 5 Electromagnetic WavesDocument8 pagesUNIT 5 Electromagnetic WavesRobin BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Visual TestingDocument48 pagesVisual Testingoulfa2013No ratings yet
- Lab Manual Microbiology For Allied Health Students 1.3Document115 pagesLab Manual Microbiology For Allied Health Students 1.3IconMaicoNo ratings yet
- Odi-065r15mjjjj02-Q-Ru V1 DS 1-Ru-0Document4 pagesOdi-065r15mjjjj02-Q-Ru V1 DS 1-Ru-0Иван КадигробNo ratings yet
- f2 Paper 2 Physics Term 3 PractiseDocument35 pagesf2 Paper 2 Physics Term 3 PractiseShepherd W NgwenyaNo ratings yet
- Hunterlab ColorDocument47 pagesHunterlab ColorMd. Sazzadul IslamNo ratings yet
- The Transition To Led Illumination: A Case Study On Energy ConservationDocument5 pagesThe Transition To Led Illumination: A Case Study On Energy ConservationTarun ImandiNo ratings yet
- ERBA XL-200 With ISE v2011.00.03Document389 pagesERBA XL-200 With ISE v2011.00.03JohnkevinGarcia C. JohnkevinGarcia67% (3)
- Grade 10 Term 1 Learner Guide SSIP 2024Document42 pagesGrade 10 Term 1 Learner Guide SSIP 2024duduzilemsimango682No ratings yet
- Atomic Structure FULLDocument127 pagesAtomic Structure FULLAsimNo ratings yet
- Properties of LightDocument27 pagesProperties of Lightgeopaok165No ratings yet
- 3rd Periodic Test in Sci 5 With TosDocument5 pages3rd Periodic Test in Sci 5 With TosEricson M Macapuno100% (2)
- RGB StampingUpDocument12 pagesRGB StampingUpConnie PierceNo ratings yet