Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CN Ppt1 Intro
CN Ppt1 Intro
Uploaded by
Ajay Sahre0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views10 pagesThis document discusses computer networks and their key components. It begins by listing relevant textbooks and reference books on the topic. It then defines what a computer network is, noting it consists of interconnected autonomous computers that can exchange information. The document outlines several functions and aspects of networks, including transmission utilization, interfacing, routing, and management. It distinguishes between network hardware and software. Finally, it discusses different network types based on transmission technology and scale/size, from personal area networks to wide area networks and the Internet.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses computer networks and their key components. It begins by listing relevant textbooks and reference books on the topic. It then defines what a computer network is, noting it consists of interconnected autonomous computers that can exchange information. The document outlines several functions and aspects of networks, including transmission utilization, interfacing, routing, and management. It distinguishes between network hardware and software. Finally, it discusses different network types based on transmission technology and scale/size, from personal area networks to wide area networks and the Internet.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views10 pagesCN Ppt1 Intro
CN Ppt1 Intro
Uploaded by
Ajay SahreThis document discusses computer networks and their key components. It begins by listing relevant textbooks and reference books on the topic. It then defines what a computer network is, noting it consists of interconnected autonomous computers that can exchange information. The document outlines several functions and aspects of networks, including transmission utilization, interfacing, routing, and management. It distinguishes between network hardware and software. Finally, it discusses different network types based on transmission technology and scale/size, from personal area networks to wide area networks and the Internet.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 10
Text Book :
Computer Networks By Andrew S Tanenbaum (5th Edition)
Reference Books :
1. Computer Networking – Top Down Approach By Ross &
Kurose
2. Data and Communication Networks By Behrouz
Forouzan
3. Data and Communication Networks By William Stallings
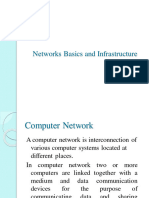
it is a “collection of autonomous computers
interconnected by a single technology”
A computer is said to be autonomous if it is
independent and no other computer can
control it
Two computers are said to be interconnected
if they are able to exchange information
So, ideally we can say that our Computer
Network is a type of Communication System
Transmission System Utilization
Interfacing
Signal Generation
Synchronization
Exchange Management
Error Detection & Correction
Flow Control
Addressing
Routing
Recovery
Message Formatting
Security
Network Management
Design and Organization of these Networks
which are a combination of Hardware and
Software
Network Hardware - The hardware consists of
the physical equipment that carries signals
from one point of the network to another.
Network Software - The software consists of
instruction sets that make possible the
services that we expect from a network.
Various Devices – Hubs, Repeater, Switches,
Router, Gateway etc.
Two technical issues
◦ Transmission technology
Broadcast
Point-to-Point
◦ Scale or size of network
PAN
LAN
MAN
WAN
Internet
Single channel is shared by all devices
At any given time only one device is allowed to
transmit
Access Control mechanism plays an important role
Addressing - all devices need to be uniquely
addressed
Supports transmission to a single machine
(Unicasting)
Supports transmission to a group of machines
(Multicasting)
Supports transmission to all the machines
(Broadcasting)
A device is connected to another device using a
dedicated link (no shared single channel)
Going from one device to another may require
visiting intermediate nodes if no direct link exists
Multiple paths may exist between any source-
destination pair
Routing Algorithms play an important role
Networks differ in terms of the geographical
distance over which they are spread ( ie.
Maximum interprocessor distance permitted)
Networks that are geographically localized
tend to use Broadcasting while networks that
are geographically spread wide apart tend to
use point-to-point transmission technology
Among the networks LAN’s differ in terms of
their size, transmission technology used and
topology
You might also like
- CK13NDocument13 pagesCK13NAngelo Hipten MarcaniNo ratings yet
- Software Engineering 2Document4 pagesSoftware Engineering 2Michalcova Realisan JezzaNo ratings yet
- LR Mobile Diagnostic LogDocument97 pagesLR Mobile Diagnostic LogSalim AlsenaniNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer NetworksDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Computer NetworksMrudul Chaudhari100% (1)
- Unit 1Document67 pagesUnit 1Rohit SharmaNo ratings yet
- CN Notes Unit-1Document66 pagesCN Notes Unit-1SaumyaNo ratings yet
- CSM 478 Lecture1Document35 pagesCSM 478 Lecture1Osei SylvesterNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer Networks: Unit - 1Document39 pagesIntroduction To Computer Networks: Unit - 1Phani VishwaNo ratings yet
- NetworkDocument2 pagesNetworkNabi FaraziNo ratings yet
- Unit - I Introduction To Computer Networks: and HybridDocument15 pagesUnit - I Introduction To Computer Networks: and HybridlakshmitejaNo ratings yet
- Networking Fundamentals: by Praphul KolteDocument31 pagesNetworking Fundamentals: by Praphul KolteayurvedicmNo ratings yet
- Network TLEDocument3 pagesNetwork TLEDian DasmariñasNo ratings yet
- Intro To Netwoks - TCP - IP - OSI - ModelDocument43 pagesIntro To Netwoks - TCP - IP - OSI - ModelSaad AliNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworkingDocument6 pagesComputer NetworkingKhushal BachwaniNo ratings yet
- NetworksDocument5 pagesNetworksErichelle EspineliNo ratings yet
- Ln.5 - Computer NetworkingDocument16 pagesLn.5 - Computer NetworkingKrittika 55No ratings yet
- Network IntroductionDocument22 pagesNetwork IntroductionSyed NaimatullahNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Data Communication: Book: Data Communications and NetworkingDocument51 pagesIntroduction To Data Communication: Book: Data Communications and NetworkingSyed Nabeel AliNo ratings yet
- 5 CS1FC16 Computer NetworksDocument6 pages5 CS1FC16 Computer NetworksAnna AbcxyzNo ratings yet
- VIDEO English SCRIPTDocument4 pagesVIDEO English SCRIPTITworld gyanNo ratings yet
- Basics of NetworkingDocument18 pagesBasics of Networkingdon daliNo ratings yet
- UNIT-4 4.1 Understand The Overview of Networking:: Characteristics of A Computer NetworkDocument14 pagesUNIT-4 4.1 Understand The Overview of Networking:: Characteristics of A Computer NetworkArunNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer NetworksDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Computer Networksjoel lacayNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document5 pagesUnit 1mohammad javedNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks and CommunicationsDocument60 pagesComputer Networks and CommunicationsSamuel GetachewNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Computer NetworkDocument19 pagesUnit 3 Computer NetworkBhavya BhattNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four Computer Networks and Internet: 4.1 Introduction To NetworkingDocument9 pagesChapter Four Computer Networks and Internet: 4.1 Introduction To NetworkingAsaye TesfaNo ratings yet
- PDF FORMAT FOR TUGAS 1 - Inas Rahma Alifia - 11230940000025Document33 pagesPDF FORMAT FOR TUGAS 1 - Inas Rahma Alifia - 11230940000025Inas Rahma AlifiaNo ratings yet
- What Are Computer NetworksDocument5 pagesWhat Are Computer NetworksJASMEET SinghNo ratings yet
- Data Communication, OSI Reference Model: Manojkumar Assistantprofessor Gjus&T, HisarDocument131 pagesData Communication, OSI Reference Model: Manojkumar Assistantprofessor Gjus&T, HisarHardik MarothaNo ratings yet
- Computr NetworkingDocument204 pagesComputr Networkingbiswadeepbasak0212No ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer NetworksDocument101 pagesIntroduction To Computer NetworksFARIHA KARIM INAM UL KARIMNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document131 pagesUnit 126 Rishabh ThakranNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworkDocument20 pagesComputer NetworkyjnNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworkDocument32 pagesComputer NetworkLynnel yapNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks: Presented byDocument34 pagesComputer Networks: Presented byJadedGoth100% (2)
- Networking 1Document7 pagesNetworking 1Rino JaulaNo ratings yet
- Network Architecture ConceptDocument6 pagesNetwork Architecture ConceptScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Netwotking ConceptsDocument20 pagesChapter 1 Netwotking ConceptsPrincess Hann AwitenNo ratings yet
- Report WritingDocument7 pagesReport WritingNeha AsimNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks - Unit IDocument38 pagesComputer Networks - Unit IsreesajeshNo ratings yet
- Unit1IntroductiontoCNpptx - 2021 - 03 - 13 - 15 - 22 - 50 (1) (Autosaved)Document81 pagesUnit1IntroductiontoCNpptx - 2021 - 03 - 13 - 15 - 22 - 50 (1) (Autosaved)komalapcNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks and Types: Submitted By: Submitted ToDocument10 pagesComputer Networks and Types: Submitted By: Submitted ToVinayak “V” KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- Computer Network - Basic ConceptsDocument30 pagesComputer Network - Basic ConceptsAnilNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks (New)Document74 pagesComputer Networks (New)arnold leedoNo ratings yet
- San TiDocument5 pagesSan TiYogesh KadamNo ratings yet
- WT Unit 1 & 2 NotesDocument37 pagesWT Unit 1 & 2 NotesKeshavNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer NetworkingDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Computer NetworkingScribd Dot ComNo ratings yet
- Introduction To LAN ProtocolsDocument20 pagesIntroduction To LAN Protocolsapi-26989621100% (2)
- Introduction to NetworkDocument15 pagesIntroduction to Networkmohsincodes9980No ratings yet
- Computer NetworksDocument17 pagesComputer Networksskartikeyyy222No ratings yet
- It Work Name - VikasDocument8 pagesIt Work Name - VikasVikram PatelNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computing ReviewerDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Computing ReviewerKyle AbiogNo ratings yet
- Networking and Data Communication MBA Sem II FMS MSUDocument91 pagesNetworking and Data Communication MBA Sem II FMS MSUSunit SudarsananNo ratings yet
- CNS Model Answers Unit 1Document29 pagesCNS Model Answers Unit 1asdhdahgadNo ratings yet
- Unit - 3 Data CommunicationDocument54 pagesUnit - 3 Data CommunicationDr. Rupali TaruNo ratings yet
- Review of Network Fundamentals 1Document6 pagesReview of Network Fundamentals 1hilloNo ratings yet
- A Computer NetworkDocument12 pagesA Computer Networkosman100% (1)
- Computer Network NoteDocument81 pagesComputer Network Noteupendrapaudel0No ratings yet
- Computer Network Notes Class 12Document14 pagesComputer Network Notes Class 12Mohit HoodaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Introduction To Computer NetworksDocument9 pagesModule 1 - Introduction To Computer NetworksJohn Paul Alcantara NidoyNo ratings yet
- Csa-Unit1 2Document20 pagesCsa-Unit1 2Chhavi GaggarNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 Number SystemDocument41 pagesUnit-1 Number SystemAjay SahreNo ratings yet
- Unit-2 Binary CodesDocument16 pagesUnit-2 Binary CodesAjay SahreNo ratings yet
- Co 13-10Document14 pagesCo 13-10Ajay SahreNo ratings yet
- Co 20-10Document23 pagesCo 20-10Ajay SahreNo ratings yet
- Prof. ShrinivasDocument48 pagesProf. ShrinivasAjay SahreNo ratings yet
- E Paper Technology Report1Document11 pagesE Paper Technology Report1Ajay SahreNo ratings yet
- Lms DocumentDocument35 pagesLms DocumentAjay SahreNo ratings yet
- Laptop 2023Document1 pageLaptop 2023Ajay SahreNo ratings yet
- MULTAZAM: Jurnal Manajemen Haji Dan UmrahDocument11 pagesMULTAZAM: Jurnal Manajemen Haji Dan Umrahsehu falahNo ratings yet
- Drop BoxDocument5 pagesDrop BoxAndrea ArceNo ratings yet
- MIT6 858F14 q14 2 SolDocument15 pagesMIT6 858F14 q14 2 Soljarod_kyleNo ratings yet
- Stvd-Stm8: ST Visual Develop IDE For Developing STM8 ApplicationsDocument4 pagesStvd-Stm8: ST Visual Develop IDE For Developing STM8 Applicationsdecabg591No ratings yet
- AS400Document9 pagesAS400lakshmiNo ratings yet
- Swing in JavaDocument32 pagesSwing in Javadeborahangel248No ratings yet
- Deep Security Container Protection Customer PresentationDocument42 pagesDeep Security Container Protection Customer PresentationsaurabhbectorNo ratings yet
- Chap 06Document62 pagesChap 06api-26090714No ratings yet
- TryHackMe Investigating Windows - Task 1 Investigating Windows by Haircutfish MediumDocument43 pagesTryHackMe Investigating Windows - Task 1 Investigating Windows by Haircutfish Mediumasma.rezgui.ensi84No ratings yet
- Computer Network NotesDocument4 pagesComputer Network NotesDevika DakhoreNo ratings yet
- To What Extent Can The Random Number Generator Math - Random in Java Be Predicted Before Being Generated?Document22 pagesTo What Extent Can The Random Number Generator Math - Random in Java Be Predicted Before Being Generated?borlandspamNo ratings yet
- Field Installation Guide: EMC Rails and EnclosuresDocument34 pagesField Installation Guide: EMC Rails and EnclosuresMikael IsakssonNo ratings yet
- Department of Information Science and Engineering Technical Seminar (18Css84) Convolutional Neural NetworksDocument15 pagesDepartment of Information Science and Engineering Technical Seminar (18Css84) Convolutional Neural NetworksS VarshithaNo ratings yet
- Computer Science 123789Document15 pagesComputer Science 123789Laxmikant TakNo ratings yet
- Wireless Networks: Jordi SalazarDocument37 pagesWireless Networks: Jordi SalazarMehari TemesgenNo ratings yet
- Esquema Elétrico - ANTONIOSI COLOMBO-GUARANIDocument9 pagesEsquema Elétrico - ANTONIOSI COLOMBO-GUARANIAlan Pessoa PardiniNo ratings yet
- Intertia Testing DocsDocument8 pagesIntertia Testing DocsEsam PcarrascoNo ratings yet
- Qdoc - Tips Informatica Interview Questions Scenario BasedDocument14 pagesQdoc - Tips Informatica Interview Questions Scenario BasedL JanardanaNo ratings yet
- Programming Language Preference Among Undergraduate Students in NigeriaDocument7 pagesProgramming Language Preference Among Undergraduate Students in NigeriaInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Programming InterfacesDocument134 pagesProgramming InterfacesMagdi AbdelhalimNo ratings yet
- Software Defined Radio Implementation of Marine Automatic Identification System (AIS)Document70 pagesSoftware Defined Radio Implementation of Marine Automatic Identification System (AIS)Bhaskar Jyoti LahkarNo ratings yet
- BHack18 - Padding Oracle AttackDocument74 pagesBHack18 - Padding Oracle AttackLuanNo ratings yet
- BER Analysis For Quadrature Amplitude Modulation in MIMO OFDM System Ijariie4460Document12 pagesBER Analysis For Quadrature Amplitude Modulation in MIMO OFDM System Ijariie4460Yimelis EndeshawNo ratings yet
- Catalyst 3850 Switch Hardware Installation Guide: Americas HeadquartersDocument138 pagesCatalyst 3850 Switch Hardware Installation Guide: Americas HeadquartersAnonymous KKSGFIZP7PNo ratings yet
- C For EveryoneDocument5 pagesC For EveryoneVrushabh WarkeNo ratings yet
- QB CP01 EngDocument14 pagesQB CP01 EngPoon Yin KwongNo ratings yet
- Database Programming With PL/SQL 6-2: Practice Activities: Indexing Tables of RecordsDocument2 pagesDatabase Programming With PL/SQL 6-2: Practice Activities: Indexing Tables of RecordsRakha FaturahmanNo ratings yet