Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Graphs and Circles Mathematics 10 Q2 Reviewer-1
Graphs and Circles Mathematics 10 Q2 Reviewer-1
Uploaded by
Wendell ParasOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Graphs and Circles Mathematics 10 Q2 Reviewer-1
Graphs and Circles Mathematics 10 Q2 Reviewer-1
Uploaded by
Wendell ParasCopyright:
Available Formats
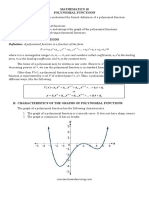
Graphs and Circles: Mathematics 10 Q2
Reviewer
Polynomial Function x- and y-intercepts
A polynomial function wherein n is a non- x-intercepts are the values of the x’s when y = 0, thus the points where
negative integer. The terms of a the graph intersects the x-axis can be determined. The value of the x-
polynomial may be written in any order. intercepts are the roots of the polynomial
The function is commonly written as:
y-intercepts can also be calculated by placing the value of x = 0. The
value of the y-intercept is the same as the constant term.
P (x) = an xn + an−1 xn−1 ...a1 x0
Table of Signs End Behavior of a Graph
The Table of Signs is a table used in helping in locating a The end behavior of a graph is the behavior of the graph
curve in a polynomial function. on the far left and far right. It is determined by its degree
and leading coefficient. It describes the values of the
Create a Table of Signs using the function y = (x +
function as x approaches infinity.
4)(x + 2)(x − 1)(x − 3).
If the leading coefficient…
x<-4 -4<x<-2 -2<x <1 1<x<3 x>3
…is positive, the right side goes up.
T. Val. -5 -3 0 2 4
…is negative, the right side goes down.
x+4 - + + + +
x+2 - - + If the degree…
+ +
x-1 - - - …is even, the+ ends will go on the
+ same direction.
x-3 - - - …is odd, the- ends will go on opposite
+ directions.
P(x) - - + - +
Position above below above below above
Graphs and Circles: Mathematics 10 Q2 Reviewer 1
Multiplicity
Multiplicity tells how many times a given number is a zero or a root of a
polynomial.
When a root is/has a multiplicity of more than one, it becomes a tangent in
relation to its corresponding x-intercepts.
Circles and Parts
A circle is a set of points in which all points are equally distanced from a center point.
1. Radius - the line from the center point to any point 7. Major arc - two endpoints on a circle connected
on a circle. making a measurement of >180°.
2. Chord - any line that connects two edge points in a 8. Minor arc - two endpoints connected making a
circle. measurement of <180°.
3. Diameter - a particular chord in which its line passes 9. Semicircle - two endpoints connected making a
through the center point measurement of 180°.
4. Secant line - a line that passes through two points on 10. Central angle - an angle whose vertex lies on the
a circle. center point.
5. Tangent Line - a line that intersects only at one point 11. Inscribed angle - an angle whose points and vertex
on a circle. lie on the circle’s edge
6. Circumference - the distance around the circle.
Central Angles and Intercepted Arcs
A central angle is an angle whose vertex is in the center
of the circle.
If the endpoints of the angle lie on the side on in the
circumference, the arc it encapsulates can then be called
an intercepted arc.
Graphs and Circles: Mathematics 10 Q2 Reviewer 2
Minor Arc Major Arc Semicircle
The degree of the minor arc is the the degree measurement of the The degree measurement of a
measure of the angle that intercepts major arc is 360° − semicircle is always 180°
the arc. The measurement of the m∠minor arc with the same
minor arc is < 180° endpoints. The major arc must be
> 180°
measure of the arc
Sector Asector = Acircle
360°
A sector of a circle is the region bounded by an arc of the
circle and the two radii to the endpoints of the arc.
The formula for the sector is:
Segment Asegment = Asector − A△
or
A segment of a circle is the region bounded by an arc and 1
the segment joining its endpoints.
Asegment = Asector − ( r 2 sin θ)
2
The formula for the segment is:
Tangents and Secants
Tangent Secant Point of
A line that touches the circle only A line that passes through the Contact/Tangency
once circle twice The point where the tangent line
touches the circle.
Tangent-Radius Theorem Two-Tangent Theorem
1. A circle drawn to the point of tangency with a If two tangent lines are drawn from an external point, then
tangent line is perpendicular to the tangent line. both lines are congruent and so are their tangent
segments.
2. If a line is drawn perpendicular to a radius and its
outer point, then it's tangent to a circle.
Secant and Tangent Segments
Secant Segment Tangent Segment External Tangent
A part of a secant line lying from the Part of a line from the point of Segment
farthest intersection to the outside tangency to an outside point of a Part of a secant line from its outside
point of a secant line. tangent line. point out the nearest intersection
Graphs and Circles: Mathematics 10 Q2 Reviewer 3
point.
Relationships of Circles with Each Other
Internally Tangent Externally Tangent
When two circles touch each other once, and one circle is When two circles that are not inside of each other,
inside the other, it is an internally tangent relationship. intersect only once.
Common Internal Tangent Common External Tangent
The line where two different circles whose center points The line where two different circles whose center points
lie on the same line segment, are tangent to both circles lie on the same line segment, are tangent to both circles
and cross the said line segment. but do not cross the said line segment.
Secant and Tangent Theorems
I-III. For any variants of secants and tangents that intersect at the exterior, the measurement
of the angle formed is half the positive difference of the measures of the intercepted arcs.
IV. If a secant and a tangent intersect at the V. If two secants intersect in the interior of
point of tangency, the measures of each the circle, the measure of an angle formed is
angle formed is half of the measure of its one half the sum of the measures of the arcs
intercepted act. intercepted by the angle and its vertical
angle.
Power Theorems
Graphs and Circles: Mathematics 10 Q2 Reviewer 4
Two-Chord Power Two-Secant Power Theorem Secant-Tangent
Theorem If two secants intersect in the exterior of a Power Theorem
If two chords intersect inside circle, then the product of the lengths of one If a secant and a tangent
the circle, then the products of secant segment and its external segment is intersect at the exterior of a
the lengths of the segments of equal to the product of the lengths of the circle, then the product of the
one chord is equal to the product other secant of the other secant segment secant segment and its external
of the lengths of the segments of segment and its external secant segment. segment is equal to the square of
the other chords. the length of the tangent
segment.
Distance and Midpoint Formula
The distance formula is used to get the length of The midpoint is said the point in the middle of a line segment.
the distance for two points without measuring. The equation is:
The formula is:
x1 + x2 y1 + y2
M(x, y) = ( , )
(x2 − x1 )2 + (y2 − y1 )2 2 2
And the equation to find an endpoint is
(x1 , y1 ) = (2x − x2 , 2y − y2 )
Standard Equation of a Circle
The standard equation of a circle derives from the distance
(x − h)2 + (y − k)2 = r 2
formula, stating that:
Wherein h and k are the x and y coordinates of the center of the
square and r is its radius.
Graphs and Circles: Mathematics 10 Q2 Reviewer 5
You might also like
- Analytic Geometry MATH 004 (TIP Reviewer)Document9 pagesAnalytic Geometry MATH 004 (TIP Reviewer)James Lindo100% (1)
- Plane GeometryDocument7 pagesPlane GeometryKc CheungNo ratings yet
- Slope-Intercept Form: (A and B Cannot Both Be 0)Document3 pagesSlope-Intercept Form: (A and B Cannot Both Be 0)Femie SurNo ratings yet
- Math 1Document3 pagesMath 1Yuki YoshidaNo ratings yet
- Math 3 New Formula Sheet 2Document8 pagesMath 3 New Formula Sheet 2smart.life.studentNo ratings yet
- Math ReviewerDocument10 pagesMath ReviewerRyuji ReyesNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 10Document4 pagesMathematics 10Iya Sicat PatanoNo ratings yet
- IGCSE AMaths 0606 4037 SB Quick Revision GuideDocument7 pagesIGCSE AMaths 0606 4037 SB Quick Revision GuideNITAKSH jain NJNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Pre-CalculusDocument13 pagesChapter 3 Pre-CalculusaiNo ratings yet
- Schoolisfun's Math Level 2 Subject Test Guide and FormulasDocument40 pagesSchoolisfun's Math Level 2 Subject Test Guide and Formulassudhakaralla1100% (2)
- C1 Revision NotesDocument5 pagesC1 Revision Notesxxtrim100% (1)
- Properties of A ParallelogramDocument7 pagesProperties of A ParallelogramKristel Mae CaveroNo ratings yet
- Formulas SheetDocument5 pagesFormulas SheetabdulrehmanNo ratings yet
- Sec 4.3 - Circles & Volume Angles of Circles NameDocument5 pagesSec 4.3 - Circles & Volume Angles of Circles NameJulian PachonNo ratings yet
- ANALYTIC GEOMETRY HandoutsDocument15 pagesANALYTIC GEOMETRY HandoutsReiniel Cirujano AntonioNo ratings yet
- 3 Functions Part 2Document22 pages3 Functions Part 2Rabbin CaracasNo ratings yet
- Important Points and Formulae: e Markedpric Discount Loss ProfitDocument5 pagesImportant Points and Formulae: e Markedpric Discount Loss ProfitNyasha GweruNo ratings yet
- Important Points and Formulae: Mathematics Grade 9 BmiDocument6 pagesImportant Points and Formulae: Mathematics Grade 9 BmiZulfiqar Ali MirNo ratings yet
- Geometry Concept Booklet 025d90b26ada3Document10 pagesGeometry Concept Booklet 025d90b26ada3Khushi AroraNo ratings yet
- Regents Trigonometry: Study GuideDocument12 pagesRegents Trigonometry: Study GuideAdair ContemareroNo ratings yet
- As MathematicsDocument17 pagesAs Mathematicsjupe01No ratings yet
- 2.1 Geometry - Formulas PDFDocument31 pages2.1 Geometry - Formulas PDFManju JNo ratings yet
- Unit 18 - Curved Graphs - DerivativeDocument5 pagesUnit 18 - Curved Graphs - DerivativeRaffaella LaxaldeNo ratings yet
- Mensuration PDFDocument33 pagesMensuration PDFSudhanshu Kumar100% (1)
- Formula Sheet MathDocument5 pagesFormula Sheet MathMata Pronoob100% (1)
- MathsDocument23 pagesMathsabdullahNo ratings yet
- How To FP2 - Revision Notes: Rational FunctionsDocument5 pagesHow To FP2 - Revision Notes: Rational FunctionsTiara TatyanadewiNo ratings yet
- Important Points and Formulae: e Markedpric Discount Loss ProfitDocument4 pagesImportant Points and Formulae: e Markedpric Discount Loss ProfitTaha YousafNo ratings yet
- Coordinate-Geometry-2Document5 pagesCoordinate-Geometry-2JITENDRA KUMAR SONINo ratings yet
- ZTZMGob JDocument7 pagesZTZMGob JObert MupomokiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Arithmetic SequenceDocument12 pagesLesson 1: Arithmetic SequenceLucille PaglingayenNo ratings yet
- Theorems of Central Angles, Arcs and Chords Distance Between Two Points Midpoint FormulaDocument3 pagesTheorems of Central Angles, Arcs and Chords Distance Between Two Points Midpoint FormulaShella VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- STEP Support Programme STEP 2 Curve Sketching Topic NotesDocument3 pagesSTEP Support Programme STEP 2 Curve Sketching Topic NotesHaoyu WangNo ratings yet
- X y X Y: Ratio and Proportion A. Direct ProportionDocument11 pagesX y X Y: Ratio and Proportion A. Direct ProportionJerick Enrique FegaridoNo ratings yet
- Vertical and Horizontal AsymptotesDocument23 pagesVertical and Horizontal AsymptotesAmirul Mohamad KhuldiNo ratings yet
- Common CurvesDocument9 pagesCommon CurvesTagore uNo ratings yet
- Day-4-UPCAMP-2018Document40 pagesDay-4-UPCAMP-2018afunabermudezNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Functions Concept ReviewDocument3 pagesQuadratic Functions Concept ReviewdaanjansenluoNo ratings yet
- A Brief Introduction To Pre-Calculus and Non-Linear EquationsDocument6 pagesA Brief Introduction To Pre-Calculus and Non-Linear EquationsPat ChuNo ratings yet
- Circle: Tycho Crater, One of Many Examples of Circles That Arise in NatureDocument14 pagesCircle: Tycho Crater, One of Many Examples of Circles That Arise in NatureZulaika ZulkifliNo ratings yet
- Circles: Circle Is A Set of Points On A Plane That Are EquidistantDocument34 pagesCircles: Circle Is A Set of Points On A Plane That Are EquidistantJheromeNo ratings yet
- Plane & Solid Geometry 1 - OnlineDocument3 pagesPlane & Solid Geometry 1 - OnlineRasul AmirolNo ratings yet
- 6 Geometry 01apr2009 PDFDocument1 page6 Geometry 01apr2009 PDFNarenNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Easy ModeDocument13 pagesUnit 1 Easy Moderakshapoddar32No ratings yet
- Maths ProjectDocument31 pagesMaths ProjectKushagra VermaNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems: You Can HelpDocument1 pagePractice Problems: You Can HelpL AlcosabaNo ratings yet
- 0-CubicSpline-Bezier - Curve-25oct18Document116 pages0-CubicSpline-Bezier - Curve-25oct18vishwajeet patilNo ratings yet
- Curve Sketching NotesDocument34 pagesCurve Sketching Noteslbwnb.68868No ratings yet
- Try To Graph and Name The Following EquationsDocument46 pagesTry To Graph and Name The Following EquationsStephanie DecidaNo ratings yet
- Maths - Parabola UnacadDocument72 pagesMaths - Parabola UnacadKarthikeyanNo ratings yet
- Mathematics-Form 3-Chapter 3 Circle II by KelvinDocument7 pagesMathematics-Form 3-Chapter 3 Circle II by KelvinKelvinNo ratings yet
- Battery Exam ReviewerDocument11 pagesBattery Exam ReviewerLA WritesNo ratings yet
- 1A CER1 Analytic GeometryDocument2 pages1A CER1 Analytic GeometryJenie EscandorNo ratings yet
- h03 Essential MathDocument13 pagesh03 Essential Mathakyadav123No ratings yet
- Conic Sections: ParabolaDocument92 pagesConic Sections: ParabolaJR DevienteNo ratings yet
- Lec 8- Scan Converting an EllipseDocument18 pagesLec 8- Scan Converting an EllipseShafqat UllahNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Reviewer Version 2 PDFDocument13 pagesMathematics Reviewer Version 2 PDFANA ROSE CIPRIANONo ratings yet
- Pre CalculusDocument1 pagePre Calculuskiellaus6127No ratings yet
- Linear Graphs and Equations: Y1 M (x-x1) When The Gradient and The Co-Ordinates (x1, Y1) of A Single Point That The LineDocument6 pagesLinear Graphs and Equations: Y1 M (x-x1) When The Gradient and The Co-Ordinates (x1, Y1) of A Single Point That The LineSchoolSlackerNo ratings yet
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- 11.1 ParabolasDocument15 pages11.1 ParabolasAnalyn ErederosNo ratings yet
- Multivariable Calculus MCQDocument49 pagesMultivariable Calculus MCQPraneeth AnjanaNo ratings yet
- Unit Circle Elective Math NotesDocument6 pagesUnit Circle Elective Math NotesAgape PonceNo ratings yet
- 1 2 Assignment Points Lines and PlanesDocument3 pages1 2 Assignment Points Lines and PlanesRonald AtibagosNo ratings yet
- WWW PW Live Concepts Kinematics Theory of Physics Class 11Document11 pagesWWW PW Live Concepts Kinematics Theory of Physics Class 11aryan.aru2006No ratings yet
- Junior 05 EngDocument6 pagesJunior 05 EngPei JingNo ratings yet
- 2 Quarter Pre-Calculus Reviewer. AY 2019-2020: Prepared by Leo Matthew SarneDocument6 pages2 Quarter Pre-Calculus Reviewer. AY 2019-2020: Prepared by Leo Matthew SarneAmiel MonsantoNo ratings yet
- CH20Document88 pagesCH20hamidrafique91_83198No ratings yet
- Mathematics: Quarter 2 - Module 3Document14 pagesMathematics: Quarter 2 - Module 3FATIMA ULINo ratings yet
- Motion of A Rigid BodyDocument14 pagesMotion of A Rigid Bodyzoya daccaniNo ratings yet
- DPP - 01 - KinematicsDocument4 pagesDPP - 01 - Kinematicsshivansh mishra roll no. 30No ratings yet
- 3D Geometry Mathematics PDFDocument3 pages3D Geometry Mathematics PDFSuraj YadavNo ratings yet
- Transformations (Matrices) Notes by TrockersDocument52 pagesTransformations (Matrices) Notes by TrockersDakarirayi MutenherwaNo ratings yet
- Netfind The Volume of Each Solid FigureDocument29 pagesNetfind The Volume of Each Solid FigureFynn NiallNo ratings yet
- Euclidean MathsDocument9 pagesEuclidean MathsNaledi xuluNo ratings yet
- Derivation of The Double Angle FormulasDocument14 pagesDerivation of The Double Angle FormulasGelbert SilotNo ratings yet
- 2012 NIMO Problems: Contributors: AIME15, V EnhanceDocument12 pages2012 NIMO Problems: Contributors: AIME15, V EnhanceLulu Arifatun MunasirohNo ratings yet
- Math Category 6 Mock TestDocument6 pagesMath Category 6 Mock TestSamrongNo ratings yet
- 2 Annual Harvard-MIT November Tournament: Team RoundDocument2 pages2 Annual Harvard-MIT November Tournament: Team RoundMaikel AndrilNo ratings yet
- 1-6 Relative VelocityDocument2 pages1-6 Relative VelocityKnowledgeIsTruePowerNo ratings yet
- 27ba821717be68bbcfc7edfd6d62abbfDocument12 pages27ba821717be68bbcfc7edfd6d62abbfaditya devNo ratings yet
- Graphs of Trigonometric Functions PDFDocument2 pagesGraphs of Trigonometric Functions PDFHelbert PaatNo ratings yet
- Lecture 03Document32 pagesLecture 03businessw025No ratings yet
- 11 Angles RevisitDocument8 pages11 Angles Revisitflameplay2234No ratings yet
- Chapter 15Document14 pagesChapter 157217 Mithil PatilNo ratings yet
- 10.2 PerimeterDocument16 pages10.2 Perimeterraja_tanukuNo ratings yet
- Rhombuses, Rectangles and Squares: GPS Geometry Mrs. Cannon Fall 2012Document13 pagesRhombuses, Rectangles and Squares: GPS Geometry Mrs. Cannon Fall 2012Nechie GastardoNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Quarter 3 - Module 4 Illustrating The SAS, ASA and SSS Congruence PostulatesDocument31 pagesMathematics: Quarter 3 - Module 4 Illustrating The SAS, ASA and SSS Congruence PostulatesArnold A. Baladjay67% (3)
- Daily Practice Problems: M-B L-30 (Level-A)Document9 pagesDaily Practice Problems: M-B L-30 (Level-A)Ved NarsekarNo ratings yet