Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 viewsThe Spirit School 10th Unit 9,10 MCQ
The Spirit School 10th Unit 9,10 MCQ
Uploaded by
Rida ShahThe document contains a quiz on concepts related to chemical equilibrium and acid-base chemistry. It includes 20 multiple choice questions testing understanding of key terms like reactants, equilibrium constants, Le Chatelier's principle, and properties of acids, bases, and salts. The questions cover topics such as writing equilibrium expressions, factors that affect equilibrium, acid-base definitions and nomenclature, and examples of common acids and bases.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- 10.1 Science Notebook (Answer Key)Document5 pages10.1 Science Notebook (Answer Key)Black arab GaladimaNo ratings yet
- 1st Year Chemistry All MCQS/Short Questions For Federal Board, Punjab Board.Document10 pages1st Year Chemistry All MCQS/Short Questions For Federal Board, Punjab Board.Mahnain Khattak74% (34)
- Preparation of K (Cu (C O) ) .2H ODocument3 pagesPreparation of K (Cu (C O) ) .2H Omick100% (1)
- Encyclopedia of Controlled Drug Delivery (2 Vols) - E. Mathiowitz (Wiley, 1999) WWDocument903 pagesEncyclopedia of Controlled Drug Delivery (2 Vols) - E. Mathiowitz (Wiley, 1999) WWCiontu Valentin100% (4)
- Problems and Solutions On Electricity and MagnetismDocument15 pagesProblems and Solutions On Electricity and MagnetismMuhammad Ashfaq Ahmed33% (3)
- Lab 12 SolutionDocument3 pagesLab 12 SolutionsharvabhasinNo ratings yet
- Full Book Mcqs Chemistry 10thDocument12 pagesFull Book Mcqs Chemistry 10thasghar198523No ratings yet
- Year 11 Exam 24Document4 pagesYear 11 Exam 24Michael oniNo ratings yet
- Chem-Xii-2 QPDocument8 pagesChem-Xii-2 QPSourav BhowalNo ratings yet
- Chemistry-FUNGAT/ECAT: (Chapter 10+11+12 B-II)Document2 pagesChemistry-FUNGAT/ECAT: (Chapter 10+11+12 B-II)XXXNo ratings yet
- DPP 8Document5 pagesDPP 8reva.maakadeNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: (Mock Test-1) 41Document5 pagesChemistry: (Mock Test-1) 41hazeNo ratings yet
- CH-8 O.KDocument26 pagesCH-8 O.KRana Hassan TariqNo ratings yet
- AP1984MCDocument19 pagesAP1984MCdenisNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsDocument7 pagesAldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acidskavitha2511977No ratings yet
- 1523959102MU OET Chemistry Section PaperDocument4 pages1523959102MU OET Chemistry Section PaperNishant KumarNo ratings yet
- Nsec 1999Document12 pagesNsec 1999CorneliaNo ratings yet
- Learning Progress Test - Readiness For Grade 11 - ChemistryDocument17 pagesLearning Progress Test - Readiness For Grade 11 - ChemistryKIngNo ratings yet
- CH# 10 XII (Chem 12 Exam Task)Document3 pagesCH# 10 XII (Chem 12 Exam Task)daniyal.king55No ratings yet
- Chemical Equations and Reactions Ws SolvedDocument2 pagesChemical Equations and Reactions Ws SolvedimbhoomiguptaNo ratings yet
- June 24 25 McqsDocument4 pagesJune 24 25 Mcqswww.sanjaykeerthuNo ratings yet
- Term-1 Practice Test (Complete Syllabus) : Sample PaperDocument6 pagesTerm-1 Practice Test (Complete Syllabus) : Sample PaperDarshan NayakNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument5 pagesHaloalkanes and Haloareneskavitha2511977No ratings yet
- Du Entrance Chemistry 2017Document15 pagesDu Entrance Chemistry 2017Arnav ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules and Polymers-03 - Assignments (New)Document11 pagesBiomolecules and Polymers-03 - Assignments (New)Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper: Time: 90 Minutes Max. Marks: 35Document9 pagesSample Paper: Time: 90 Minutes Max. Marks: 35Harsh PatelNo ratings yet
- CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM MCQsDocument6 pagesCHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM MCQsNaveedNo ratings yet
- NSEJS Camp Equilibrium AssignmentDocument5 pagesNSEJS Camp Equilibrium Assignmentaryan aggarwalNo ratings yet
- Assignment Acid BasesDocument10 pagesAssignment Acid Basesaryan aggarwalNo ratings yet
- Chemistry-FUNGAT/ECAT: (Chapter 8+9 B-I)Document2 pagesChemistry-FUNGAT/ECAT: (Chapter 8+9 B-I)XXXNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Q.p.set-1Document6 pages12 Chemistry Q.p.set-1HpNo ratings yet
- Chemistry (Inter) Set 1 10Document186 pagesChemistry (Inter) Set 1 10Valerie LaneNo ratings yet
- Term 2 Online Class Xi Chemistry 043Document4 pagesTerm 2 Online Class Xi Chemistry 043kumaryashxd07No ratings yet
- Sample Paper: General InstructionsDocument7 pagesSample Paper: General InstructionsTuRbO gAmErNo ratings yet
- HydrocarbonsDocument116 pagesHydrocarbonsabhisheksingh27zxNo ratings yet
- AP Chemistry 1984 With AnswersDocument22 pagesAP Chemistry 1984 With AnswersjhbmleeNo ratings yet
- Entry Test Master Book: ChemistryDocument8 pagesEntry Test Master Book: ChemistryShakeel AhmedNo ratings yet
- Marking Scheme: Single Correct (+3,-1) M M: 138 Time: 1 HR 30 MinDocument7 pagesMarking Scheme: Single Correct (+3,-1) M M: 138 Time: 1 HR 30 MinPRITHVIRAJ GHOSHNo ratings yet
- Chemistry NTSE Stage 2 PDFDocument66 pagesChemistry NTSE Stage 2 PDFJatin SinglaNo ratings yet
- Kcet - Chemistry - 2019: Version Code: D-5Document7 pagesKcet - Chemistry - 2019: Version Code: D-5Manoj CNo ratings yet
- Chemistry-FUNGAT/ECAT: (Chapter 6+7 B-I)Document2 pagesChemistry-FUNGAT/ECAT: (Chapter 6+7 B-I)XXXNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Chemistry Chemical Reactions MCQsDocument3 pagesCBSE Class 10 Chemistry Chemical Reactions MCQsMifrah KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document57 pagesChapter 2ayush.rai1068No ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions Practice Test 75/75Document4 pagesChemical Reactions Practice Test 75/75Irina StefaniaNo ratings yet
- Marking Scheme: Single Correct (+3,-1) M M: 138 Time: 1 HR 30 MinDocument7 pagesMarking Scheme: Single Correct (+3,-1) M M: 138 Time: 1 HR 30 Minnobita nobiNo ratings yet
- Chem Equation WWW MCQDocument17 pagesChem Equation WWW MCQrp2683387No ratings yet
- Alcohol & EtherDocument217 pagesAlcohol & EtherAmitNo ratings yet
- Science - Doc (1) 10 TH AnswerDocument30 pagesScience - Doc (1) 10 TH Answerparmila raniNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper 3: ChemistryDocument13 pagesSample Paper 3: ChemistryPr SathishNo ratings yet
- Ample Aper: Section - ADocument13 pagesAmple Aper: Section - AShriyaa BhatnagarNo ratings yet
- Class XII NEET Chemistry Paper (05.08.2018) - MVADocument9 pagesClass XII NEET Chemistry Paper (05.08.2018) - MVAParas ThakurNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon and Isomerism TestDocument6 pagesHydrocarbon and Isomerism TestveerlocusNo ratings yet
- Hydrocar SHEET3Document4 pagesHydrocar SHEET3Aayush SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Mega Test (06-05-2024) - 240606 - 153839Document23 pagesMega Test (06-05-2024) - 240606 - 153839Regidrago 2No ratings yet
- Unit - 9 Ionic Equilbrium: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument25 pagesUnit - 9 Ionic Equilbrium: Multiple Choice QuestionsSAMBASIVA RAO YEMINENINo ratings yet
- Chemistry-Chapter 1 PyqDocument9 pagesChemistry-Chapter 1 PyqDhilfa Eleyedath International Indian School - Abu DhabiNo ratings yet
- Set-B: Section ADocument6 pagesSet-B: Section ADrk ZeusNo ratings yet
- 12TH CBSE DPP 37. Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids MCQ ASSERTION REASON CS QDocument20 pages12TH CBSE DPP 37. Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids MCQ ASSERTION REASON CS Q123No ratings yet
- Practice Test Chemistry CL 12Document10 pagesPractice Test Chemistry CL 12Coopin loopNo ratings yet
- CS - Ap ReviewDocument16 pagesCS - Ap ReviewGernanNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRYDocument100 pagesCHEMISTRYmadhumathiNo ratings yet
- Poooooowaoebc@Aogoaa: Chemical Reactions & EquationsDocument7 pagesPoooooowaoebc@Aogoaa: Chemical Reactions & Equationssaurabh shaurya guptaNo ratings yet
- Alkyl and Aryl Halides SheetDocument11 pagesAlkyl and Aryl Halides SheetRajeev GangwarNo ratings yet
- PRE BOARD Class XII 21-22Document6 pagesPRE BOARD Class XII 21-22Kavin SatyaNo ratings yet
- 1.1 English and Communication Skills - I L T P 3 - 2 RationaleDocument20 pages1.1 English and Communication Skills - I L T P 3 - 2 RationaleSehna SerajNo ratings yet
- 0620 s13 Ms 32 PDFDocument6 pages0620 s13 Ms 32 PDFShad muhammad KhanNo ratings yet
- The Solution Is Dilution! Lab InvestigationDocument1 pageThe Solution Is Dilution! Lab InvestigationyeehawmanNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Chem CH 1 WorksheetDocument3 pagesClass 11 Chem CH 1 WorksheetRupanshi GuptaNo ratings yet
- 13.kinetic Theory PDFDocument30 pages13.kinetic Theory PDFNaliniNo ratings yet
- Writing and Naming Chemical FormulasDocument3 pagesWriting and Naming Chemical FormulasCarlo Joseph Moskito100% (1)
- Experiment 1 - Basic Chem FARISHDocument8 pagesExperiment 1 - Basic Chem FARISHMUHAMMAD FAIDZ DARWISH BIN FAIDZAL MoeNo ratings yet
- Scholastic Aptitude Test (Sat) - Paper & Hints & Solution: National Talent Search Examination-2019-20Document18 pagesScholastic Aptitude Test (Sat) - Paper & Hints & Solution: National Talent Search Examination-2019-20Technical AyushNo ratings yet
- 3 Chemical Thermodynamics and Energetics PDFDocument12 pages3 Chemical Thermodynamics and Energetics PDFKD TechnicalNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution Experiment PDFDocument5 pagesChemistry Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution Experiment PDFMaii MendiiölaNo ratings yet
- 1 Measurements Olfu Canvas PDFDocument35 pages1 Measurements Olfu Canvas PDFJames PalmonesNo ratings yet
- Konsep Dasar Kimia 1Document40 pagesKonsep Dasar Kimia 1RianAwanggaNo ratings yet
- Qdoc - Tips Chemical Engg ReviewerDocument53 pagesQdoc - Tips Chemical Engg ReviewerMa Theresa CabiazaNo ratings yet
- Practice estimating to find the best answer.: Δt 5 x rate = -Δ (B) 5 x 0.0243 M/s = - Δ (B) -0.12125~ - 0.122 M/sDocument10 pagesPractice estimating to find the best answer.: Δt 5 x rate = -Δ (B) 5 x 0.0243 M/s = - Δ (B) -0.12125~ - 0.122 M/sjeffrey XiaoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Winter 2a Exam KeyDocument10 pagesChemistry Winter 2a Exam KeyKaren ZhaoNo ratings yet
- Gas Stoichiometry: Worksheet 17.3: SolutionsDocument2 pagesGas Stoichiometry: Worksheet 17.3: SolutionsHaris MughalNo ratings yet
- Science 10 NotesDocument17 pagesScience 10 NotesDerik Resultay100% (1)
- 1001-Class XI - C-232.Mole Concept Assignment - 1Document5 pages1001-Class XI - C-232.Mole Concept Assignment - 1The GentlemanNo ratings yet
- Stoichiometry 2Document5 pagesStoichiometry 2hey mama don’t stress your mindNo ratings yet
- WKSHT 23 Molar Mass WorksheetDocument3 pagesWKSHT 23 Molar Mass WorksheetCarlo RobloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document7 pagesChapter 2Hina RabbaniNo ratings yet
- MCQ in General Chemistry Part 13 - ECE Board ExamDocument10 pagesMCQ in General Chemistry Part 13 - ECE Board ExamDominic Nicole ManuelNo ratings yet
- Nano PhysicsDocument32 pagesNano PhysicsApuNo ratings yet
- 11th STD Chemistry em 2023 24 KalviexpressDocument55 pages11th STD Chemistry em 2023 24 KalviexpressMani KandanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry The Molecular Nature of Matter and Change Silberberg 5th Edition Test BankDocument20 pagesChemistry The Molecular Nature of Matter and Change Silberberg 5th Edition Test Bankanthonyramosscdkyoagqn100% (43)
The Spirit School 10th Unit 9,10 MCQ
The Spirit School 10th Unit 9,10 MCQ
Uploaded by
Rida Shah0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views5 pagesThe document contains a quiz on concepts related to chemical equilibrium and acid-base chemistry. It includes 20 multiple choice questions testing understanding of key terms like reactants, equilibrium constants, Le Chatelier's principle, and properties of acids, bases, and salts. The questions cover topics such as writing equilibrium expressions, factors that affect equilibrium, acid-base definitions and nomenclature, and examples of common acids and bases.
Original Description:
Original Title
the spirit school 10th Unit 9,10 MCQ_
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document contains a quiz on concepts related to chemical equilibrium and acid-base chemistry. It includes 20 multiple choice questions testing understanding of key terms like reactants, equilibrium constants, Le Chatelier's principle, and properties of acids, bases, and salts. The questions cover topics such as writing equilibrium expressions, factors that affect equilibrium, acid-base definitions and nomenclature, and examples of common acids and bases.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views5 pagesThe Spirit School 10th Unit 9,10 MCQ
The Spirit School 10th Unit 9,10 MCQ
Uploaded by
Rida ShahThe document contains a quiz on concepts related to chemical equilibrium and acid-base chemistry. It includes 20 multiple choice questions testing understanding of key terms like reactants, equilibrium constants, Le Chatelier's principle, and properties of acids, bases, and salts. The questions cover topics such as writing equilibrium expressions, factors that affect equilibrium, acid-base definitions and nomenclature, and examples of common acids and bases.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 5
The Spirit School Scholastic Campus
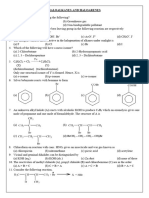
1. In a chemical reaction, the substances that combine are called:
(a) reactants (b) products (c) masses (d) materials
2. ‘Kc’ represents:
(a) ionic product of water (b) equilibrium constant
(c) reaction quotient (d) proportionality constant
3. Dynamic means, reaction is:
(a) in forward direction (b) stopped (c) in reverse direction (d) still continuing
4. The forward reaction takes place from:
(a) right to left (b) left to right (c) Both a & b (d) None of the above
5. The units of molar concentration:
(a) mol. dm2 (b) mol. dm1 (c) mol. dm (d) mol. dm3
6. “Kc” is always equal to:
(a) Rf/Rr (b) kr/kf (c) kf/kr (d) Rr/Rf
7. Which chemical is called king of chemicals?
(a) KNO3 (b) H2SO4 (c) HCl (d) HNO3
8. If Qc < Kc, the reaction goes in:
(a) forward (b) reverse (c) at equilibrium state (d) none of the above
9. Who proposed the Law of Mass Action?
(a) Newton (b) Boyles (c) Guldberg and Waage (d) Lavoisier
10. The unit of equilibrium constant for the following reaction is: N2 + 3H2 ⇋ 2NH3
(a) moldm-3 (b) mol-2dm6 (c) moldm-6 (d) mol-1dm3
11. The value of Kc depends on:
(a) Initial concentration of the reactants (b) Initial concentration of the products
(c) Temperature of the system (d) Initial concentration of both reactants and products.
12. For the following reaction : aA + bB ⇋ cC + dD
According to Law of Mass Action the rate of forward reaction is directly proportional to:
(a) [A]a [B]b (b) kf [A]a [B]b (c) [C]c [D]d (d) kr [C]c [d]d
13. Law of Mass Action describes the relationship between active masses of the reactants and:
(a) Concentration of products (b) Rate of the reaction
(c) Conditions of the reaction (d) All of the above
14. Molar concentration of a substance having units of mol dm-3 and expressed in square brackets
is termed as:
(a) Molarity (b) Molar concentration (c) Active mass (d) None of these
15. While writing the Kc expression of the reaction, products and reactants are written
respectively as:
(a) Numerator and denominator (b) Denominator and numerator (c) Numerator (d) None of these
16. Oxidation of carbon monoxide goes to completion at:
(a) 500 K (b) 700 K (c) 1000 K (d) 1200 K
17. Formation of water by the combination of H2 and O2 is catalyzed by:
(a) Ni (b) Pt (c) Cd (d) Pd
18. CaCO3 decomposes to produce:
(a) CaO (b) CaO + CO2 (c) CaO + CO (d) CO2 + CO
19. The colour of iodine is:
(a) purple (b) black (c) red (d) pink
20. The colour of hydrogen iodide is:
(a) colourless (b) black (c) red (d) pink
21. Equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction is represented as:
H2(g) + I2(g) ⇋ 2HI(g
)
2 2
H I 2HI H I
2 2
HI 2
(a) (b) (d)
2HI H 2 I 2 (c)
2HI H2 I2
22. When we put concentrations of substances into the equilibrium constant expression, we obtain
a value called:
(a) Equilibrium constant (b) Equilibrium quotient (c) Reaction quotient (d) Stability quotient
23. Which of the following reactions can be represented with the Kc expression:
PC 5
PCl 3 Cl2
Kc =
(a) PC (b) PC
(c) 3PC (g) 2C ( g) 5PC (g) (d) None of these
24. Equilibrium state is achievable in:
(a) Closed system (b) Open system (c) Both (a) & (b) (d) None of these
25. In the beginning the rate of reverse reaction is:
(a) Moderate (b) Negligible (c) Slow (d) Very fast
26. The unit of molar concentration is:
(a) mol dm-1 (b) mol dm-2 (c) mol dm3 (d) mol dm-3
27. Which gas is used to manufacture king of chemicals (sulphuric acid)?
(a) N2 (b) O2 (c) Cl2 (d) CO2
28. Equilibrium constant has no unit when number of moles of reactants and products are:
(a) same (b) different (c) both (a) & (b) (d) none of these
29. For reaction having large Kc value, the reaction proceeds to:
(a) completion (b) equilibrium state (c) backward (d) none of the above
30. The two major components of Atmosphere are:
(a)carbon and nitrogen (b) nitrogen and oxygen (c)oxygen and chlorine (d) none of the above
31. Such reactions which continue in both directions are called:
(a) Irreversible (b) Reversible (c) Non-reactive (d) Dynamic
32. When the rate of the forward reaction takes place at the rate of reverse reaction the composition
of the reaction mixture remains constant, it is called:
(a) chemical equilibrium (b) static equilibrium (c) both (a) & (b) (d) none of the above
33. Guldberg and Waage put forward law of mass action in:
(a) 1860 (b) 1869 (c) 1870 (d) 1879
34. The % age of nitrogen and oxygen in our atmosphere is:
(a) 80% (b) 90% (c) 95% (d) 99%
35. Which gas is used to prepare ammonia?
(a) N2 (b) O2 (c) Cl2 (d) S
36. If Qc ˃ Kc, the reaction goes in:
(a) forward (b) reverse (c) at equilibrium state (d) none of the above
37. If Qc = Kc, the reaction goes in:
(a) forward (b) reverse (c) at equilibrium state (d) none of the above
38. When a reaction ceases to proceed, it is called:
(a)chemical equilibrium state (b) static equilibrium state
(c) dynamic equilibrium state (d) all of these
39. Which type of reactions speed up gradually?
(a) irreversible reactions (b) reversible reactions
(c) addition reactions (d) decomposition reactions
40. Which type of reactions do not go to completion?
(a) irreversible reactions (b) reversible reactions
(c) addition reactions (d) decomposition reactions
The Spirit School Scholastic Campus
1. Lactic acid is found in:
(a) citrus fruit (b) sour milk (c) rancid butter d) apple
2. Which of the following does not have pH value greater than 7:
(a) shampoo (b) detergents (c) butter (d) soap
3. Which acid is used to manufacture fertilizers like calciumsuperphosphate:
(a) hydrochloric acid (b) benzoic acid (c) acetic acid (d) Sulphuric acid
4. Acid used in printing industries is:
(a) HCl (b) HNO3 (c) H2SO4 (d) CH3COOH
5. Conjugate base of HCN is:
(a) H3O+ (b) H2CN (c) CN– (d) HCN–
6. The time required to remain in an upright position, after taking a meal, to avoid
hyperacidity is:
(a) 20 min (b) 35 min (c) 45 min (d) 50 min
7. What is the colour of methyl orange in strongly acidic solution?
(a) red (b) blue (c) yellow (d) pink
8. Alkalis on reaction with the salts of heavy metals produce which of the following:
(a) hydroxides (b) peroxides (c) oxides (d) all of these
9. Sodium bisulphite (NaHSO3), on reaction with HCl produces:
(a) salt (b) water (c) sulphur dioxide gas (d) all of these
10. Brown ppt of Fe(OH)3 are produced when FeCl3 reacts with a/an:
(a) base (b) acid (c) salt (d) none of these
11. Cu(OH)2 is precipitated out when CuSO4 reacts with NaOH as:
CuSO4 (aq) + 2NaOH(aq)2(s) CuOH + Na2SO4(aq)
What is the colour of the precipitate:
(a) white (b) blue (c) brown (d) dirty green
12. Which of the following is a much more reliable and accurate method of
measuring pH of a solution:
(a) litmus paper (b) universal indicator (c) pH meter (d) none of these
13. pH of 0.01M H2SO4 solution is:
(a) 10 (b) 2 (c) 1.7 (d) 0.3
14. NH4NO3 is an example of a:
(a) normal salt (b) acidic salt (c) basic salt (d) mixed salt
15. Which of the following is not a basic salt:
(a) Al(OH)2Cl (b) NaH2PO4 (c) Pb(OH)CH3COO (d) Zn(OH)NO3
16. Chemical formula of potash alum is:
(a) K2SO4Al2(SO4)324H2O (b) FeSO4(NH4)2SO46H2O
(c) K2SO4Fe2(SO4)324H2O (d) FeSO4Al2(SO4)324H2O
17. Bleaching powder Ca(OCl)Cl is an example of:
(a) acidic salt (b) basic salt (c) double salt (d) mixed salt
18. FeSO4(NH4)2SO46H2O is the chemical formula of:
(a) Mohr’s salt (b) potash alum (c) ferric alum (d) caustic potash
19. A conjugate acid is a specie formed by accepting a by a base:
(a) proton (b) electron pair (c) neutron (d) electron
20. According to Bronsted and Lowry concept a base is a substance that can accept:
(a) proton (b) electron pair (c) neutron (d) electron
21. A conjugate base is a specie formed by donating a by an acid:
(a) proton (b) electron pair (c) neutron (d) electron
22. A substance which can behave as an acid as well as a base is called:
(a) acid (b) base (c) amphoteric specie (d) neutral specie
23. According to Lewis concept a base is a substance which can donate:
(a) proton (b) electron pair (c) neutron (d) electron
24. The product of any Lewis acid base reaction is a single specie called:
(a) salt (b) water (c) adduct (d) none of these
25. Carbonate and bicarbonates, which gas is evolved?
(a) H2 (b) CO2 (c) Cl2 (d) N2
26. When acid reacts with sulphites and bisulphites, which gas is evolved?
(a) H2 (b) CO2 (c) SO2 (d) NH3
27. Which one is a mineral acid?
(a) HCl (b) H2SO4 (c) HNO3 (d) All of these
28. Which acid is used as an electrolyte in lead storage battery?
(a) H2SO4 (b) HNO3 (c) HCl (d) CH3COOH
29. Which acid is used for etching designs on copper plates?
(a) H2SO4 (b) HNO3 (c) HCl (d) CH3COOH
30. Which acid is used for food preservation?
(a) H2SO4 (b) HNO3 (c) HCl (d) CH3COOH
31. Citric acid is present in:
(a) citrus fruits (b) sour milk (c) rancid butter (d) apple
32. Butyric acid is present in:
(a) citrus fruits (b) sour milk (c) rancid butter (d) apple
33. Malic acid is present in:
(a) apples (b) fats (c) rancid butter (d) grapes
34. Uric acid is present in:
(a) apples (b) fats (c) rancid butter (d) grapes
35. Alkalies react with ammonium salts to liberate:
(a) SO2 (b) CO2 (c) NH3 (d) H2
36. Which is used to manufacture soap?
(a) NaOH (b) Ca(OH)2 (c) NH4OH (d) Mg(OH)2
37. Which one is a Lewis acid?
(a) BF3 (b) AlCl3 (c) FeCl3 (d) All of these
38. When acids react with metals, which gas is evolved?
(a) H2 (b) O2 (c) Cl2 (d) N2
39. Jabir Bin Hayan prepared:
(a) nitric acid (b) hydrochloric acid (c) sulphuric acid (d) all of the above
40. Who proved the presence of hydrogen as the main constituent of all acids?
(a) Lavoisier (b) Humphrey Davy (c) Dalton (d) Arrhenius
41. The word acid is derived from the
(a) Greek word (b) Latin word (c) English word (d) Arabic word
42. Acidus means:
(a) sour (b) bitter (c) sweet (d) salty
43. Which acid is present in our stomach?
(a) nitric acid (b) hydrochloric acid (c) sulphuric acid (d) all of the above
44. All acids turn blue litmus:
(a) red (b) colourless (c) pink (d) white
45. All bases turn red litmus:
(a) colourless (b) blue (c) pink (d) white
46. According to Arrhenius concept acid is a substance which dissociates in aqueous
solution to give:
(a) hydrogen ions (b) hydroxide ions (c) protons (d) pair of electrons
47. According to Arrhenius concept base is a substance which dissociates in aqueous
solution to give:
(a) hydrogen ions (b) hydroxide ions (c) protons (d) pair of electrons
48. Which one is not an Arrhenius acid?
(a) HCl (b) H2SO4 (c) CO2 (d) HNO3
49. Which one is not an Arrhenius base?
(a) NaOH (b) KOH (c) Ca(OH)2 (d) NH3
50. which gas is evolved?
(a) H2 (b) CO2 (c) Cl2 (d) N2
51. Which of the following is not a use of calcium chloride?
(a) de-icing of roads in winter (b) use as a drying agent
(c) manufacture of flint glass (d) use as a freezing agent
52. Potassium nitrate is used to:
(a) prepare plaster of paris (b) prepare slaked lime
(c) manufacture glazes and enamels (d) manufacture flint glass
53. Formula of sodium tetraborate is:
(a) NaBO4.5H2O (b) Na2B4O7.10H2O (c) Na4B2O7.5H2O (d) Na4B2O7.10H2O
54. Which of the following salts is used to manufacture explosives and plastics:
(a) NaClO3 (b) Na2SiO3 (c) Na2SO4 (d) Na2CO3
55. Which one of the following is acidic salt?
(a) KHSO4 (b) A (c) NaC (d) Ca OC C
56. Which one is used in alkaline batteries?
(a) NaOH (b) Ca(OH)2 (c) KOH (d) Mg(OH)2
57. Which is used as foaming agent in fire extinguishers?
(a) NaOH (b) KOH (c) Al(OH)3 (d) NH4OH
58. Which is used to remove the grease stains from clothes?
(a) NaOH (b) KOH (c) Al(OH)3 (d) NH4OH
o
59. The value of constant of ionic product of water Kw at 25 Cis:
(a) 1.010-4 (b) 1.010-14 (c) 1.0 107 (d) 1.010-7
60. pH value normally varies from:
(a) 0 – 14 (b) 1-14 (c) 7 – 14 (d) 10 - 14
61. pH of neutral solution is always:
(a) 6 (b) 5 (c) 7 (d) 10
62. Acidic solutions have pH value:
(a) less than 7 (b) greater than 7 (c) equal to 7 (d) none of these
63. Basic solutions have pH value:
(a) less than 7 (b) greater than 7 (c) equal to 7 (d) none of these
64. Indicators are the:
(a) inorganic compounds (b) organic compounds
(c) ionic compounds (d) covalent compounds
65. Phenolphthalein produces red colour in:
(a) acid (b) base (c) both (a) & (b) (d) none of these
66. Methyl orange produces which colour in basic solution:
(a) red (b) yellow (c) pink (d) white
67. Which salt is used as a table salt?
(a) NaCl (b) Na2CO3 (c) Na2SiO3 (d) NaHCO3
You might also like
- 10.1 Science Notebook (Answer Key)Document5 pages10.1 Science Notebook (Answer Key)Black arab GaladimaNo ratings yet
- 1st Year Chemistry All MCQS/Short Questions For Federal Board, Punjab Board.Document10 pages1st Year Chemistry All MCQS/Short Questions For Federal Board, Punjab Board.Mahnain Khattak74% (34)
- Preparation of K (Cu (C O) ) .2H ODocument3 pagesPreparation of K (Cu (C O) ) .2H Omick100% (1)
- Encyclopedia of Controlled Drug Delivery (2 Vols) - E. Mathiowitz (Wiley, 1999) WWDocument903 pagesEncyclopedia of Controlled Drug Delivery (2 Vols) - E. Mathiowitz (Wiley, 1999) WWCiontu Valentin100% (4)
- Problems and Solutions On Electricity and MagnetismDocument15 pagesProblems and Solutions On Electricity and MagnetismMuhammad Ashfaq Ahmed33% (3)
- Lab 12 SolutionDocument3 pagesLab 12 SolutionsharvabhasinNo ratings yet
- Full Book Mcqs Chemistry 10thDocument12 pagesFull Book Mcqs Chemistry 10thasghar198523No ratings yet
- Year 11 Exam 24Document4 pagesYear 11 Exam 24Michael oniNo ratings yet
- Chem-Xii-2 QPDocument8 pagesChem-Xii-2 QPSourav BhowalNo ratings yet
- Chemistry-FUNGAT/ECAT: (Chapter 10+11+12 B-II)Document2 pagesChemistry-FUNGAT/ECAT: (Chapter 10+11+12 B-II)XXXNo ratings yet
- DPP 8Document5 pagesDPP 8reva.maakadeNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: (Mock Test-1) 41Document5 pagesChemistry: (Mock Test-1) 41hazeNo ratings yet
- CH-8 O.KDocument26 pagesCH-8 O.KRana Hassan TariqNo ratings yet
- AP1984MCDocument19 pagesAP1984MCdenisNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsDocument7 pagesAldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acidskavitha2511977No ratings yet
- 1523959102MU OET Chemistry Section PaperDocument4 pages1523959102MU OET Chemistry Section PaperNishant KumarNo ratings yet
- Nsec 1999Document12 pagesNsec 1999CorneliaNo ratings yet
- Learning Progress Test - Readiness For Grade 11 - ChemistryDocument17 pagesLearning Progress Test - Readiness For Grade 11 - ChemistryKIngNo ratings yet
- CH# 10 XII (Chem 12 Exam Task)Document3 pagesCH# 10 XII (Chem 12 Exam Task)daniyal.king55No ratings yet
- Chemical Equations and Reactions Ws SolvedDocument2 pagesChemical Equations and Reactions Ws SolvedimbhoomiguptaNo ratings yet
- June 24 25 McqsDocument4 pagesJune 24 25 Mcqswww.sanjaykeerthuNo ratings yet
- Term-1 Practice Test (Complete Syllabus) : Sample PaperDocument6 pagesTerm-1 Practice Test (Complete Syllabus) : Sample PaperDarshan NayakNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument5 pagesHaloalkanes and Haloareneskavitha2511977No ratings yet
- Du Entrance Chemistry 2017Document15 pagesDu Entrance Chemistry 2017Arnav ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules and Polymers-03 - Assignments (New)Document11 pagesBiomolecules and Polymers-03 - Assignments (New)Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper: Time: 90 Minutes Max. Marks: 35Document9 pagesSample Paper: Time: 90 Minutes Max. Marks: 35Harsh PatelNo ratings yet
- CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM MCQsDocument6 pagesCHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM MCQsNaveedNo ratings yet
- NSEJS Camp Equilibrium AssignmentDocument5 pagesNSEJS Camp Equilibrium Assignmentaryan aggarwalNo ratings yet
- Assignment Acid BasesDocument10 pagesAssignment Acid Basesaryan aggarwalNo ratings yet
- Chemistry-FUNGAT/ECAT: (Chapter 8+9 B-I)Document2 pagesChemistry-FUNGAT/ECAT: (Chapter 8+9 B-I)XXXNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Q.p.set-1Document6 pages12 Chemistry Q.p.set-1HpNo ratings yet
- Chemistry (Inter) Set 1 10Document186 pagesChemistry (Inter) Set 1 10Valerie LaneNo ratings yet
- Term 2 Online Class Xi Chemistry 043Document4 pagesTerm 2 Online Class Xi Chemistry 043kumaryashxd07No ratings yet
- Sample Paper: General InstructionsDocument7 pagesSample Paper: General InstructionsTuRbO gAmErNo ratings yet
- HydrocarbonsDocument116 pagesHydrocarbonsabhisheksingh27zxNo ratings yet
- AP Chemistry 1984 With AnswersDocument22 pagesAP Chemistry 1984 With AnswersjhbmleeNo ratings yet
- Entry Test Master Book: ChemistryDocument8 pagesEntry Test Master Book: ChemistryShakeel AhmedNo ratings yet
- Marking Scheme: Single Correct (+3,-1) M M: 138 Time: 1 HR 30 MinDocument7 pagesMarking Scheme: Single Correct (+3,-1) M M: 138 Time: 1 HR 30 MinPRITHVIRAJ GHOSHNo ratings yet
- Chemistry NTSE Stage 2 PDFDocument66 pagesChemistry NTSE Stage 2 PDFJatin SinglaNo ratings yet
- Kcet - Chemistry - 2019: Version Code: D-5Document7 pagesKcet - Chemistry - 2019: Version Code: D-5Manoj CNo ratings yet
- Chemistry-FUNGAT/ECAT: (Chapter 6+7 B-I)Document2 pagesChemistry-FUNGAT/ECAT: (Chapter 6+7 B-I)XXXNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Chemistry Chemical Reactions MCQsDocument3 pagesCBSE Class 10 Chemistry Chemical Reactions MCQsMifrah KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document57 pagesChapter 2ayush.rai1068No ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions Practice Test 75/75Document4 pagesChemical Reactions Practice Test 75/75Irina StefaniaNo ratings yet
- Marking Scheme: Single Correct (+3,-1) M M: 138 Time: 1 HR 30 MinDocument7 pagesMarking Scheme: Single Correct (+3,-1) M M: 138 Time: 1 HR 30 Minnobita nobiNo ratings yet
- Chem Equation WWW MCQDocument17 pagesChem Equation WWW MCQrp2683387No ratings yet
- Alcohol & EtherDocument217 pagesAlcohol & EtherAmitNo ratings yet
- Science - Doc (1) 10 TH AnswerDocument30 pagesScience - Doc (1) 10 TH Answerparmila raniNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper 3: ChemistryDocument13 pagesSample Paper 3: ChemistryPr SathishNo ratings yet
- Ample Aper: Section - ADocument13 pagesAmple Aper: Section - AShriyaa BhatnagarNo ratings yet
- Class XII NEET Chemistry Paper (05.08.2018) - MVADocument9 pagesClass XII NEET Chemistry Paper (05.08.2018) - MVAParas ThakurNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon and Isomerism TestDocument6 pagesHydrocarbon and Isomerism TestveerlocusNo ratings yet
- Hydrocar SHEET3Document4 pagesHydrocar SHEET3Aayush SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Mega Test (06-05-2024) - 240606 - 153839Document23 pagesMega Test (06-05-2024) - 240606 - 153839Regidrago 2No ratings yet
- Unit - 9 Ionic Equilbrium: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument25 pagesUnit - 9 Ionic Equilbrium: Multiple Choice QuestionsSAMBASIVA RAO YEMINENINo ratings yet
- Chemistry-Chapter 1 PyqDocument9 pagesChemistry-Chapter 1 PyqDhilfa Eleyedath International Indian School - Abu DhabiNo ratings yet
- Set-B: Section ADocument6 pagesSet-B: Section ADrk ZeusNo ratings yet
- 12TH CBSE DPP 37. Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids MCQ ASSERTION REASON CS QDocument20 pages12TH CBSE DPP 37. Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids MCQ ASSERTION REASON CS Q123No ratings yet
- Practice Test Chemistry CL 12Document10 pagesPractice Test Chemistry CL 12Coopin loopNo ratings yet
- CS - Ap ReviewDocument16 pagesCS - Ap ReviewGernanNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRYDocument100 pagesCHEMISTRYmadhumathiNo ratings yet
- Poooooowaoebc@Aogoaa: Chemical Reactions & EquationsDocument7 pagesPoooooowaoebc@Aogoaa: Chemical Reactions & Equationssaurabh shaurya guptaNo ratings yet
- Alkyl and Aryl Halides SheetDocument11 pagesAlkyl and Aryl Halides SheetRajeev GangwarNo ratings yet
- PRE BOARD Class XII 21-22Document6 pagesPRE BOARD Class XII 21-22Kavin SatyaNo ratings yet
- 1.1 English and Communication Skills - I L T P 3 - 2 RationaleDocument20 pages1.1 English and Communication Skills - I L T P 3 - 2 RationaleSehna SerajNo ratings yet
- 0620 s13 Ms 32 PDFDocument6 pages0620 s13 Ms 32 PDFShad muhammad KhanNo ratings yet
- The Solution Is Dilution! Lab InvestigationDocument1 pageThe Solution Is Dilution! Lab InvestigationyeehawmanNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Chem CH 1 WorksheetDocument3 pagesClass 11 Chem CH 1 WorksheetRupanshi GuptaNo ratings yet
- 13.kinetic Theory PDFDocument30 pages13.kinetic Theory PDFNaliniNo ratings yet
- Writing and Naming Chemical FormulasDocument3 pagesWriting and Naming Chemical FormulasCarlo Joseph Moskito100% (1)
- Experiment 1 - Basic Chem FARISHDocument8 pagesExperiment 1 - Basic Chem FARISHMUHAMMAD FAIDZ DARWISH BIN FAIDZAL MoeNo ratings yet
- Scholastic Aptitude Test (Sat) - Paper & Hints & Solution: National Talent Search Examination-2019-20Document18 pagesScholastic Aptitude Test (Sat) - Paper & Hints & Solution: National Talent Search Examination-2019-20Technical AyushNo ratings yet
- 3 Chemical Thermodynamics and Energetics PDFDocument12 pages3 Chemical Thermodynamics and Energetics PDFKD TechnicalNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution Experiment PDFDocument5 pagesChemistry Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution Experiment PDFMaii MendiiölaNo ratings yet
- 1 Measurements Olfu Canvas PDFDocument35 pages1 Measurements Olfu Canvas PDFJames PalmonesNo ratings yet
- Konsep Dasar Kimia 1Document40 pagesKonsep Dasar Kimia 1RianAwanggaNo ratings yet
- Qdoc - Tips Chemical Engg ReviewerDocument53 pagesQdoc - Tips Chemical Engg ReviewerMa Theresa CabiazaNo ratings yet
- Practice estimating to find the best answer.: Δt 5 x rate = -Δ (B) 5 x 0.0243 M/s = - Δ (B) -0.12125~ - 0.122 M/sDocument10 pagesPractice estimating to find the best answer.: Δt 5 x rate = -Δ (B) 5 x 0.0243 M/s = - Δ (B) -0.12125~ - 0.122 M/sjeffrey XiaoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Winter 2a Exam KeyDocument10 pagesChemistry Winter 2a Exam KeyKaren ZhaoNo ratings yet
- Gas Stoichiometry: Worksheet 17.3: SolutionsDocument2 pagesGas Stoichiometry: Worksheet 17.3: SolutionsHaris MughalNo ratings yet
- Science 10 NotesDocument17 pagesScience 10 NotesDerik Resultay100% (1)
- 1001-Class XI - C-232.Mole Concept Assignment - 1Document5 pages1001-Class XI - C-232.Mole Concept Assignment - 1The GentlemanNo ratings yet
- Stoichiometry 2Document5 pagesStoichiometry 2hey mama don’t stress your mindNo ratings yet
- WKSHT 23 Molar Mass WorksheetDocument3 pagesWKSHT 23 Molar Mass WorksheetCarlo RobloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document7 pagesChapter 2Hina RabbaniNo ratings yet
- MCQ in General Chemistry Part 13 - ECE Board ExamDocument10 pagesMCQ in General Chemistry Part 13 - ECE Board ExamDominic Nicole ManuelNo ratings yet
- Nano PhysicsDocument32 pagesNano PhysicsApuNo ratings yet
- 11th STD Chemistry em 2023 24 KalviexpressDocument55 pages11th STD Chemistry em 2023 24 KalviexpressMani KandanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry The Molecular Nature of Matter and Change Silberberg 5th Edition Test BankDocument20 pagesChemistry The Molecular Nature of Matter and Change Silberberg 5th Edition Test Bankanthonyramosscdkyoagqn100% (43)