Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2nd Quarter Exam
2nd Quarter Exam
Uploaded by
Jewel June Estacion0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views4 pagesThis document appears to be a science examination for 7th grade students covering topics related to microscopes, cells, and organ systems. It consists of 45 multiple choice questions testing students' knowledge of the parts and proper use of microscopes, the structures and functions of plant and animal cells, photosynthesis, and the main organ systems of the human body. The exam was given to students at Medellin National High School in the Philippines as part of their 2nd quarter grading period.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document appears to be a science examination for 7th grade students covering topics related to microscopes, cells, and organ systems. It consists of 45 multiple choice questions testing students' knowledge of the parts and proper use of microscopes, the structures and functions of plant and animal cells, photosynthesis, and the main organ systems of the human body. The exam was given to students at Medellin National High School in the Philippines as part of their 2nd quarter grading period.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views4 pages2nd Quarter Exam
2nd Quarter Exam
Uploaded by
Jewel June EstacionThis document appears to be a science examination for 7th grade students covering topics related to microscopes, cells, and organ systems. It consists of 45 multiple choice questions testing students' knowledge of the parts and proper use of microscopes, the structures and functions of plant and animal cells, photosynthesis, and the main organ systems of the human body. The exam was given to students at Medellin National High School in the Philippines as part of their 2nd quarter grading period.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
MEDELLIN NATIONAL HIGH SCHOOL
Poblacion Medellin, Cebu
2nd Quarter Examination
Grade 7 SCIENCE
Name:_________________________________ Date:_____________Grade & Section: ____________Score:
___________
Directions: Read each item carefully. Encircle the letter of the correct answer for each question.
1. In what year did the father-and-son duo spectacles- makers create the first microscope?
A. 1565 B. 1590 C. 1675 D. 1830
2. Who uses the microscope with only one lens to observe insects and other specimens?
A. Robert Hooke
B. Richard Zsigmondy
C. Hans & Zacharias Janssen
D. Anton van Leeuwenhoek
3. Who invented the ultra- microscope which allows the observation of specimens beyond the wavelength of light?
A. Robert Hooke
B. Richard Zsigmondy
C. Anton van Leeuwenhoek
D. Hans & Zacharias Janssen
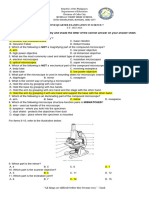
For items 4 to 6, use the letters in the figure to answer the questions.
4. Which part supports the entire weight of the microscope?
A. Part B B. Part C C. Part D D. Part E
5. Edgar needs to raise the stage to focus the specimen he is studying
using the low power objective. Which part should he manipulate?
A. Part A B. Part B C. Part C D. Part E
6. You are to transfer the microscope to the next room. What parts
should you hold to carry the microscope properly?
A. Part C & E
B. Part B & C
C. Part A & F
D. Part E & J
7. Which part will you adjust if the object you are observing under the
HPO is NOT clear?
A. Coarse adjustment
B. Inclination joint
C. fine adjustment
D. Diaphragm
8. Which of the following describes the function of the mirror?
A. It facilitates the changing of the objectives.
B. It reflects light up to the diaphragm and to the specimen to be observed.
C. It allows one to tilt the microscope, so viewing is possible while seated.
D. Regulates the amount of light reflected to the object to be viewed.
9. Which of the following describes the function of diaphragm?
A. It facilitates the changing of the objectives.
B. It reflects light up to the diaphragm and the specimen to be observed.
C. Regulates the amount of light reflected to the object to be viewed.
D. It allows one to tilt the microscope, so viewing is possible while seated.
10. What is the correct way of carrying a microscope?
A. Hold the arm by grasping with one hand.
B. Hold the base by grasping with two hands.
C. Hold the arm by grasping with one hand and the stage with the other hand.
D. Hold the arm by grasping with one hand and the base with the other hand
11. To obtain total magnification, you should ______ the magnification of the eyepiece to the objective lens power.
A. add B. divide C. multiply D. subtract
12. What two parts do you place your hands while carrying a microscope?
A. Arm and Base
B. Arm and Ocular
C. Base and Nosepiece
D. Base and High-Power Objective
13. What do you use to clean the microscope lenses?
A. Cotton B. Wet Wipes C. Lens Paper D. Tissue Paper
14. If the eyepiece magnification on light microscope is 10x and the objective is 40x, what is the overall
magnification?
A. 4x B. 10x C. 40x D. 400x
15. The magnification of a microscope with a 10x eyepiece and a 10x objective will be 1000x.
A. True B. False C. Maybe D. Unnecessary
16. Find the magnification: Eyepiece= 10x Objective lens= 55x
A. 10x B. 55x C. 65x D. 550x
17. Find the magnification: Eyepiece= 20x Objective lens= 20x
A. 20x B. 40x C. 200x D. 400x
18. The higher the magnification, the ________ you see of specimen.
A. less B. moreC. lower D. higher
19. An increase in magnification causes _____________.
A. a decrease in the field of view
B. an increase in the working time
C. a decrease in the working distance
D. an increase in the working distance
20.Which of the following should you NOT do while using the microscope?
A. Use low power objectives lens first.
B. Use stage clips to hold the slide in place.
C. Use direct sunlight when mirror is the light source.
D. Use fine adjustment only under the high-power objective
21. Which of the following organs does NOT belong to the digestive system?
A. Ears B. Esophagus C. Mouth D. Nose
22. Which of the following organs does NOT belong to the Circulatory system?
A. Artery B. Heart C. NoseD. Vein
23. Which of the following is NOT an organ system?
A. Digestive B. Population C. Excretory D. Respiratory
24. What do you call a group of individuals belonging to the same species and living in a particular area?
A. organism B. community C. Population D. Ecosystem
25. Which of the following is NOT a plant part for reproduction?
A. Petals B. PistilC. Stamen D. Stem
26. Which of the following organs are used for pumping of blood and nutrients throughout the body?
A. Artery B. Heart C. StemD. Vein
27. Which organ is responsible for eliminating metabolic waste?
A. Digestive System
B. Excretory System
C. Circulatory System
D. Respiratory System
28. Which organ system responsible in processing oxygen into our body?
A. Nervous System
B. Circulatory System
C. Respiratory System
D. Integumentary System
29. Which is the correct sequence of the level of biological organization in an organism?
A. cell- tissue –organ- organ system- organism
B. cell- organ system–organ- tissue - organism
C. cell- organ –- tissue organ system- organism
D. cell- organ- organ system- organism-tissue
30. Which of the following is NOT correctly matched?
A. Roots-Excretion
B. Stem-Circulation
C. Leaves-Respiration
D. Flower- Reproduction
31. Which of the following are present in plant cell and are absent in animal cell?
A. Cell Wall and Chloroplast
B. Lysosomes and Ribosomes
C. Golgi Bodies and Mitochondria
D. Cell Membrane and Cytoplasm
32. How do the major parts or layers of the plant cell and animal cell differ?
A. Plant cells and animal cell have both four major parts.
B. Plant cells have six major parts while animal cells have four.
C. Plants cell have three major parts while animal cells have five.
D. Plants cells have five major parts while animal cells have three.
33. What is photosynthesis?
A. It is the ability of plant cells to reproduce.
B. It is the capability of plant cells to undergo cell division.
C. It is the process of the plants cells to make their own food.
D. It is the capacity of plant cells to have additional support and protection.
34. What are the end products of photosynthesis?
A. Starch, water and fats
B. Fats, water and nitrogen
C. Sugar, water and oxygen
D. Water, energy and carbon dioxide
35. Which of the following is the external stiff and rigid additional support for plant cell that cannot be found in
animal cell?
A. Cell Wall B. Chromoplast C. Plastid D. Vacuole
36. What fluid is located inside the central vacuoles?
A. Water B. Cell sap C. Protoplasm D. Nucleoplasm
37. Papayas, tangerines, sunflower and yellow bells are yellow and orange. What kind of plastid is causing their fruits
and flowers with these colors?
A. Amyloplast B. Chloroplast C. Chromoplast D. Leucoplast
38. What kind of plastid is located in the roots and other non-pigmented parts of plants that stores starch,
carbohydrates, proteins and fats?
A. Amyloplast B. Chloroplast C. Chromoplast D. Leucoplast
39. Which of the following in general is true for plants in terms of the number of mitochondria present in its cells?
A. Plant cells have less mitochondria than animal cell.
B. Plant cell have more mitochondria than animal cell.
C. Plant cells and animal cells have the same number of mitochondria.
D. Plant cells and animals cells number of mitochondria depends on the cell’s size.
40. What do you think is most likely to happen if plants do not have cell wall and chloroplast?
A. Plant cells will undergo cell division and reproduce.
B. Plant cells will shrink in size and will be non-pigmented.
C. Plant cells will be more protected and can do photosynthesis.
D. Plant cells will be easily damaged and cannot do photosynthesis.
41. What is known as the building blocks of life?
A. Cell B. Organ C. Organ systems D. Tissue
42. How do you call an organism with only one cell?
A. Cellula B. Dominant C. Multicellular D. Unicellular
43. How are organisms with many cells termed?
A. cellular B. multicellular C. organizational D. unicellular
44. In what particular year were cells first discovered?
A. 1655B. 1665 C. 1675 D. 1685
45. Who theorized that “All cells come from pre-existing cells.”?
A. Matthias Schleiden
B. Theodor Schwann
C. Rudolf Virchow
D. Robert Hooke
46. Who among the scientists below did NOT study cells?
A. Dmitri Mendeleev
B. Rudolph Virchow
C. Matthias Schleiden
D. Theodore Schwann
47. Who concluded that all animals are composed of cells?
A. Robert Hooke
B. Rudolph Virchow
C. Theodore Schwann
D. Matthias Schleiden
48. Which of the following is the contribution of Anton Van Leeuwenhoek in the study of cell?
A. He studied single-celled organisms.
B. He observed red blood cells.
C. Neither A nor B
D. Both A and B
49. Which of the following substances is NOT a component of cells?
A. DNA B. Mineral C. RNA D. Water
50. What is a cell?
A. A number B. An animal C. An imagination D. A microscopic structure
Prepared by:
JEWEL JUNE ESTACION BOJOS
Grade 7 Science Teacher
You might also like
- 92103565-Rev3 - ECO-08079 - 600-DV-Maint-Manual Feb 11 16Document533 pages92103565-Rev3 - ECO-08079 - 600-DV-Maint-Manual Feb 11 16Stoyan Georgiev100% (11)
- S7Q2 ExamDocument2 pagesS7Q2 ExamCatleah ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Second PT7 For PrintDocument3 pagesSecond PT7 For PrintMarlene Tubieros - InducilNo ratings yet
- Sci 7 - Q2 Long Quiz M1-3Document2 pagesSci 7 - Q2 Long Quiz M1-3aiza arcilloNo ratings yet
- Second Periodical Examination in Grade 7 Science NAME: - SCORE: - YEAR & SECTION: - Parents' SignatureDocument6 pagesSecond Periodical Examination in Grade 7 Science NAME: - SCORE: - YEAR & SECTION: - Parents' SignatureelynNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter Summative Test#1Document3 pages2nd Quarter Summative Test#1Erwin MagsisiNo ratings yet
- Sci 2Document3 pagesSci 2RonalynAlonsabeBernadasNo ratings yet
- 2nd-Quarter-Exam-in-Science-7 FINALDocument4 pages2nd-Quarter-Exam-in-Science-7 FINALMyth LiliNo ratings yet
- Second Quarter Summative Test in Science 7Document3 pagesSecond Quarter Summative Test in Science 7Robert L. Comedero100% (1)
- 2ND QuarterDocument5 pages2ND QuarterTEACHER MILLAN TVNo ratings yet
- Pre Test - Q2Document9 pagesPre Test - Q2Jon-Jon ManlapasNo ratings yet
- KEY - Q2 - Science - 7 - Michelle Joan Balicao - ASTERIO MADALLADocument5 pagesKEY - Q2 - Science - 7 - Michelle Joan Balicao - ASTERIO MADALLAPrincess AnnNo ratings yet
- Long TestDocument5 pagesLong TestEmmanuel LouiseNo ratings yet
- First Exam in AolDocument6 pagesFirst Exam in AolUnknown FbNo ratings yet
- Direction: Read The Statement Carefully and Select The Letter of The BEST Answer. Write Your Answer On A Separate Sheet of PaperDocument2 pagesDirection: Read The Statement Carefully and Select The Letter of The BEST Answer. Write Your Answer On A Separate Sheet of PaperJosh AndradeNo ratings yet
- q2 Scince 7 Parallel TestDocument2 pagesq2 Scince 7 Parallel Testmalifi ciadoNo ratings yet
- Biology Worksht Grade 9 1Document5 pagesBiology Worksht Grade 9 1Qne DanielNo ratings yet
- MULTIPLE CHOICE: Encircle The Letter of The Correct AnswerDocument2 pagesMULTIPLE CHOICE: Encircle The Letter of The Correct AnswerAllan RolomaNo ratings yet
- Summat IveDocument2 pagesSummat IveRonalynAlonsabeBernadasNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Science Second Quarterly Exam 2019 2020Document5 pagesGrade 7 Science Second Quarterly Exam 2019 2020Sir LexNo ratings yet
- Science 7 2nd Summative TestDocument3 pagesScience 7 2nd Summative TestEmerlyn JosephNo ratings yet
- Inbound 3235111451063110529Document7 pagesInbound 3235111451063110529Monica P. RamosNo ratings yet
- A Group of The Same Species Living Together Is A/an Population B. Ecosystem C. Biome D. CommunityDocument5 pagesA Group of The Same Species Living Together Is A/an Population B. Ecosystem C. Biome D. CommunityKeneth PalaumaNo ratings yet
- LCC Biology (Model Exam)Document6 pagesLCC Biology (Model Exam)Emma Mohamed KhalidNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter Grade 7Document2 pages2nd Quarter Grade 7Genalyn Cirpo TayoneNo ratings yet
- 2nd Periodical ExamDocument4 pages2nd Periodical ExamLourie Jean Tupaz TelinNo ratings yet
- Pretest-Science 7Document2 pagesPretest-Science 7Henry CastilloNo ratings yet
- Science 7 Diagnostic TestDocument5 pagesScience 7 Diagnostic TestRealm MaghirangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 ExamDocument12 pagesChapter 4 Examm_frajmanNo ratings yet
- 2ND Summative in Science 7Document5 pages2ND Summative in Science 7Christine RamosNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Final Exam Quarter 2Document4 pagesGrade 7 Final Exam Quarter 2Rizalyn DiazNo ratings yet
- Second Periodical Test - For ReDocument4 pagesSecond Periodical Test - For ReJessica Manawes Navor100% (1)
- Science 7 Q2 ExamDocument4 pagesScience 7 Q2 Examkenneth loNo ratings yet
- Biology Model Exam For G-12 2016 Addis KetemaDocument12 pagesBiology Model Exam For G-12 2016 Addis Ketemamuller.eshetu12No ratings yet
- RAT Science 7Document8 pagesRAT Science 7Ann Geddies Lotino100% (1)
- G7 ExamfDocument6 pagesG7 ExamfMichelle Jean BaligodNo ratings yet
- PT g7 ScienceDocument5 pagesPT g7 ScienceHAROLD MORALESNo ratings yet
- Second Qaurter Exam in Science 7Document5 pagesSecond Qaurter Exam in Science 7sheila mae tadoNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE-7-SUMMATIVE - 2nd-Q Week 1-4Document2 pagesSCIENCE-7-SUMMATIVE - 2nd-Q Week 1-4EDWIN DUMOPOYNo ratings yet
- Second Periodic Test in Science G7 17-18Document6 pagesSecond Periodic Test in Science G7 17-18Julius Ryan HipolitoNo ratings yet
- Directions: Read and Analyze The Questions Carefully. Write Your Answer On The Test Paper. 1Document3 pagesDirections: Read and Analyze The Questions Carefully. Write Your Answer On The Test Paper. 1Eirojram Carreon CastilNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE-7-SUMMATIVE - 2nd-Q Week 1-4Document3 pagesSCIENCE-7-SUMMATIVE - 2nd-Q Week 1-4EDWIN DUMOPOYNo ratings yet
- Science 9 PeriodicalDocument5 pagesScience 9 PeriodicalJester M. SorianoNo ratings yet
- Science 7 - Summative Test - Q2 - Week 1-Week 4 - SY 2021-2022Document2 pagesScience 7 - Summative Test - Q2 - Week 1-Week 4 - SY 2021-2022Lenette AlagonNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Science 7Document22 pagesReviewer Science 7Arlynda LampaNo ratings yet
- Science 7 - Summative Test - Q2 - PrintDocument2 pagesScience 7 - Summative Test - Q2 - PrintLenette AlagonNo ratings yet
- Class Number: B - G - : Midterm Examination-Life Science 11Document6 pagesClass Number: B - G - : Midterm Examination-Life Science 11Rodge AniceteNo ratings yet
- G72 ND PTScienceDocument6 pagesG72 ND PTScienceRachell PobleteNo ratings yet
- Pre-Test Science 7 - BiologyDocument5 pagesPre-Test Science 7 - BiologyMark Wendel Murillo0% (1)
- Ste ReviewerDocument14 pagesSte ReviewerPaul Vincent FortonNo ratings yet
- Kirkos Biology Model Exame Grade 8 PDFDocument8 pagesKirkos Biology Model Exame Grade 8 PDFEmma Mohamed KhalidNo ratings yet
- Q2 Science Answer KeyDocument2 pagesQ2 Science Answer KeysunnyamarNo ratings yet
- 2nd Qe Sci 7Document5 pages2nd Qe Sci 7Elsa Geagoni AbrasaldoNo ratings yet
- S7Q2, LC-1Document2 pagesS7Q2, LC-1kismetlaoshiNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument3 pagesUntitledEDWIN DUMOPOYNo ratings yet
- Second Quarter Test Science 7Document5 pagesSecond Quarter Test Science 7QUEENIE BUTALIDNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument9 pagesBiologyMatthi ADNo ratings yet
- Long Test Earth and LifeDocument3 pagesLong Test Earth and LifeAnalynAsuncionAtaydeNo ratings yet
- Second Quarter Exam in Science 7Document4 pagesSecond Quarter Exam in Science 7Jonah JabulinNo ratings yet
- Second Periodical Test in Science 7Document3 pagesSecond Periodical Test in Science 7tolisNo ratings yet
- Assessment 5Document2 pagesAssessment 5Jewel June EstacionNo ratings yet
- Lac Session RepotDocument5 pagesLac Session RepotJewel June EstacionNo ratings yet
- Minutes Meeting PtaDocument5 pagesMinutes Meeting PtaJewel June EstacionNo ratings yet
- My ApplicationDocument2 pagesMy ApplicationJewel June EstacionNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Unity ScienceDocument21 pagesGrade 8 Unity ScienceJewel June EstacionNo ratings yet
- Ippd Form 1 - Teacher'S Individual Plan For Professional Development (Ippd)Document2 pagesIppd Form 1 - Teacher'S Individual Plan For Professional Development (Ippd)Jewel June EstacionNo ratings yet
- Song LyricsDocument5 pagesSong LyricsJewel June EstacionNo ratings yet
- Letter For SwappingDocument2 pagesLetter For SwappingJewel June EstacionNo ratings yet
- 3rd Quarter CertificteDocument68 pages3rd Quarter CertificteJewel June EstacionNo ratings yet
- Table of Specification: Medellin National High School Poblacion, Medellin, CebuDocument1 pageTable of Specification: Medellin National High School Poblacion, Medellin, CebuJewel June EstacionNo ratings yet
- Medellin National High School Poblacion, Medellin, Cebu: S8Es-Iia-14Document1 pageMedellin National High School Poblacion, Medellin, Cebu: S8Es-Iia-14Jewel June Estacion100% (2)
- DLPDocument6 pagesDLPJewel June EstacionNo ratings yet
- Artikel Dalam Bahasa InggrisDocument9 pagesArtikel Dalam Bahasa InggrisEfrinaldiNo ratings yet
- Independent Speed Test Analysis of 4G Mobile Networks Performed by DIKW ConsultingDocument50 pagesIndependent Speed Test Analysis of 4G Mobile Networks Performed by DIKW ConsultingAditya ChandavaleNo ratings yet
- Bhel Training ReportDocument32 pagesBhel Training ReportVivek PrasadNo ratings yet
- Sentiment Analysis With NLP Deep LearningDocument8 pagesSentiment Analysis With NLP Deep LearningAnkush ChajgotraNo ratings yet
- IWE - 1.7 - Handout - TIG Only - 2015Document28 pagesIWE - 1.7 - Handout - TIG Only - 2015Adil MalkicNo ratings yet
- The MIT Press: The MIT Press Is Collaborating With JSTOR To Digitize, Preserve and Extend Access To TDR (1988-)Document16 pagesThe MIT Press: The MIT Press Is Collaborating With JSTOR To Digitize, Preserve and Extend Access To TDR (1988-)LazarovoNo ratings yet
- ASTM E1269 - 0specific Heat by DSCDocument6 pagesASTM E1269 - 0specific Heat by DSCnolanjcNo ratings yet
- Quick Test 2 - LEVEL 7Document3 pagesQuick Test 2 - LEVEL 7Matías MocilnikarNo ratings yet
- NBRK0200 Installation Configuration ManualDocument32 pagesNBRK0200 Installation Configuration ManualGoran JovanovicNo ratings yet
- The Great El Ni o of 1789-93 and Its Global Consequences: Reconstructing An Extreme Climate Event in World Environmental HistoryDocument25 pagesThe Great El Ni o of 1789-93 and Its Global Consequences: Reconstructing An Extreme Climate Event in World Environmental HistoryVictoria PadillaNo ratings yet
- NT115UsersMan EngDocument48 pagesNT115UsersMan EngThai Binh MinhNo ratings yet
- Taboo Game 02Document6 pagesTaboo Game 02Sorin FluturNo ratings yet
- 1/4" X 1-1/4" Fuses: MDA Series, Time Delay, Ceramic TubeDocument2 pages1/4" X 1-1/4" Fuses: MDA Series, Time Delay, Ceramic TubeStuxnetNo ratings yet
- Reclaim Feeders BrochureDocument8 pagesReclaim Feeders Brochureelsieazcuna024No ratings yet
- AR8035 Integrated 10/100/1000 Mbps Ethernet Transceiver: Data SheetDocument66 pagesAR8035 Integrated 10/100/1000 Mbps Ethernet Transceiver: Data SheetIon PetruscaNo ratings yet
- Price - The Fun Palace Cedric PriceDocument20 pagesPrice - The Fun Palace Cedric PricewhatsinausernameNo ratings yet
- Zerner ClassicismPower 1988Document3 pagesZerner ClassicismPower 1988MatejaNo ratings yet
- CKD NCPDocument4 pagesCKD NCPArlene Macatangay100% (1)
- Hanwha Qcell Data SheetDocument2 pagesHanwha Qcell Data Sheetachmad zulfikar f100% (1)
- Theory and Applications of Monte Carlo SimulationsDocument284 pagesTheory and Applications of Monte Carlo SimulationsDouglas Figueiredo100% (3)
- FSSC Iac PTM-02Document1 pageFSSC Iac PTM-02Faisal RehmanNo ratings yet
- RCA SystemLink3Document9 pagesRCA SystemLink3JerônimoNo ratings yet
- KSR Institute For Engineering and Technology TIRUCHENGODE - 637 215Document5 pagesKSR Institute For Engineering and Technology TIRUCHENGODE - 637 215Karthikeyan SelvaNo ratings yet
- Orthopaedics and Traumatology MCQDocument3 pagesOrthopaedics and Traumatology MCQSeh Seh E HNo ratings yet
- G7 1Q SETS Activity-WorksheetDocument2 pagesG7 1Q SETS Activity-WorksheetluiNo ratings yet
- Glossary CambridgeDocument14 pagesGlossary CambridgeAlexey PetrovNo ratings yet
- Big Bang Edge TestDocument11 pagesBig Bang Edge TestAman VimayuNo ratings yet
- Eros and Psyche Print 2 PDFDocument8 pagesEros and Psyche Print 2 PDFNizzy Hope Nulada CartagoNo ratings yet
- Asuhan Pasien Dengan Terminall IllnessDocument50 pagesAsuhan Pasien Dengan Terminall IllnessCieciel Silviaa FebrianiiNo ratings yet