Professional Documents
Culture Documents
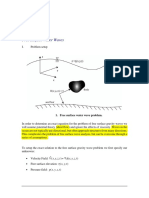
2.2 Lubrication Approximation For Flow in A Thin Layer
2.2 Lubrication Approximation For Flow in A Thin Layer
Uploaded by
Fahad Al-MutairiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2.2 Lubrication Approximation For Flow in A Thin Layer
2.2 Lubrication Approximation For Flow in A Thin Layer
Uploaded by
Fahad Al-MutairiCopyright:
Available Formats
1
Lecture Notes on Fluid Dynamics
(1.63J/2.21J)
by Chiang C. Mei, MIT
2007 Spring
2-2lubri.tex
2.2 Lubrication approximation for ow in a thin layer
An essential rst step of any analytical approximtation is the art of scaling, which we shall
emphasize repeatedly throughout this course.
Let H be the characteristic depth and L the characteristic length in the direction of the
ow, and assume a shallow layer, i.e.,
H/L 1 (2.2.1)
Let U be the scale of u, then by continuity, the scale of v must be U
H
L
in order not to violate
mass conservation. Leaving the velocity and pressure scales U, P undermined for the time
being, we introduce the following scales and normalized variables, denoted by primes,
t = Tt
, x = Lx
, y = Hy
, u = Uu
, v = U
H
L
v
, p = Pp
, (2.2.2)
The normalized continuity equation is
u
+
v
= 0 (2.2.3)
Both terms are equally important, reecting the holyness of the law of mass concentration.
The longitudinal momentum equation is normalized to
U
T
u
+
U
2
L
_
u
+ v
_
= g sin
P
L
p
+
U
H
2
_
H
2
L
2
2
u
x
2
+
2
v
y
2
_
(2.2.4)
Dividing by
U
H
2
, we get
H
2
T
u
t
+
UH
H
L
_
u
+ v
_
=
g sin H
2
U
PH
2
LU
p
+
_
H
2
L
2
2
u
x
2
+
2
u
y
2
_
(2.2.5)
For a shallow layer (H/L 1) we assume in addition,
UH
= O(1) (2.2.6)
2
and
H
2
T
1 (2.2.7)
Omitting terms of the order H/L and smaller, the above equation can be approximated to
the leading order by
0 =
g sin H
2
U
PH
2
LU
p
+
2
u
y
2
(2.2.8)
or in dimensional form,
0 = g sin
1
p
x
+
2
u
y
2
(2.2.9)
All inertia terms are inconsequential; the most important balance is among gravity, the
pressure gredient and the dominant viscous stress. This balance also implies a pressure
scale,
P =
LU
H
2
(2.2.10)
From the transverse momentum equation,
H
L
_
U
T
v
+
U
2
L
_
u
+ v
__
= g cos
P
H
p
+
H
L
U
H
2
_
2
v
x
2
+
2
v
y
2
_
(2.2.11)
or
H
2
L
2
_
H
2
T
v
+
UH
H
L
_
u
+ v
__
=
g sin H
2
U
H
Ltan
PH
2
LU
p
+
H
2
L
2
_
H
2
L
2
2
v
x
2
+
2
v
y
2
_
(2.2.12)
Either for nite bed slope or for small slope but
O
_
H
L
_
= tan 1 (2.2.13)
the left hand side above is negligible with an error of O(H/L)
3
. In physical variables the
approximate result is
0 = g cos
1
p
y
(2.2.14)
Not only the inertia terms are insignicant, the pressure is hydrostatic. This balance also
implies the pressure scale
P = gH cos (2.2.15)
Note that (2.2.10) and (2.2.15) together implies the velocity scale
U =
H
L
gH cos
(2.2.16)
3
The distinguishing feature of negligible inertia is shared by the slow ow through thin
gaps of bearings in the theory of lubrication. Hence (2.2.9) and (2.2.14) can be called the
lubrication approximation.
We leave it as an exercise to show by similar normalization, that the dynamic boundary
conditions on y = h can be approximated to the leading order by
u
y
= 0 (2.2.17)
for the tangential stress, and
p = 0 (2.2.18)
for the normal stress. It follows by integrating (2.2.14)) that
p(x, y, t) = g cos [h(x, t) y] (2.2.19)
The longitudinal momentum equation can also be readily integrated,
u =
g
_
sin cos
h
x
__
y
2
2
hy
_
(2.2.20)
The total discharge is
Q = uh =
_
h
0
udy =
gh
3
3
_
sin cos
h
x
_
(2.2.21)
which can be inserted in the integrated mass conservation equation (2.1.12) to give
h
t
+
Q
x
=
h
t
+
g
3
x
_
h
3
_
sin cos
h
x
__
= 0 (2.2.22)
This is a nonlinear diusion equation governing the evolution of the uid depth.
In the special limit of a uniform ow, /x 0. The velocity prole is then
u =
gh
2
sin
_
y
h
y
2
2h
2
_
(2.2.23)
with h being a pure constant. The coresponding discharge is
Q =
gh
3
3
sin (2.2.24)
You might also like
- Printetti Drifry Healthy Fryer ManualDocument13 pagesPrintetti Drifry Healthy Fryer Manualganguly147147100% (4)
- CAIE A Level Physics 3E SAMPLE PDFDocument16 pagesCAIE A Level Physics 3E SAMPLE PDFJimmy Teh0% (1)
- Lab 4 Determination of An Equilibrium Constant 1Document7 pagesLab 4 Determination of An Equilibrium Constant 1Mohammad IzadiNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Lubrication Approximation For Flow in A Thin LayerDocument3 pages2.2 Lubrication Approximation For Flow in A Thin LayerFiaz Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Lubrication Approximation For Flow in A Thin LayerDocument3 pages2.2 Lubrication Approximation For Flow in A Thin LayerHarshil TejaniNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Lubrication Approximation For Flow in A Thin LayerDocument3 pages2.2 Lubrication Approximation For Flow in A Thin LayerHarshil TejaniNo ratings yet
- Mass Conservation of Finite Element Methods For Coupled Flow-Transport ProblemsDocument8 pagesMass Conservation of Finite Element Methods For Coupled Flow-Transport ProblemsmohxaviNo ratings yet
- 'Airy' (Linear) Wave TheoryDocument18 pages'Airy' (Linear) Wave TheorysandysrNo ratings yet
- (1957) Water Waves of Finite Amplitude On Sloping BeachDocument13 pages(1957) Water Waves of Finite Amplitude On Sloping BeachWangJuliusNo ratings yet
- Darcy's Law: Week 2 Physical EquationsDocument4 pagesDarcy's Law: Week 2 Physical Equationsdownloader1983No ratings yet
- Ns EquationsDocument9 pagesNs EquationsTahok24No ratings yet
- An Adaptive Finite Element Discretisation For A Simplified Signorini ProblemDocument13 pagesAn Adaptive Finite Element Discretisation For A Simplified Signorini ProblemFelipe IgnazioNo ratings yet
- Fluid Dynamics: Formulae SheetDocument3 pagesFluid Dynamics: Formulae SheetRyan PittsNo ratings yet
- Keywords: Dimension Reduction, Nonlinear Elasticity, Thin Beams, Equilibrium Configura-Tions 2000 Mathematics Subject Classification: 74K10Document19 pagesKeywords: Dimension Reduction, Nonlinear Elasticity, Thin Beams, Equilibrium Configura-Tions 2000 Mathematics Subject Classification: 74K10dfgsrthey53tgsgrvsgwNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2. Thermodynamics: 2.11.5 Joule Effect: Free Expansion of A GasDocument10 pagesChapter 2. Thermodynamics: 2.11.5 Joule Effect: Free Expansion of A GasVictor EnemNo ratings yet
- 1 Governing Equations For Waves On The Sea Surface: 1.138J/2.062J/18.376J, WAVE PROPAGATIONDocument39 pages1 Governing Equations For Waves On The Sea Surface: 1.138J/2.062J/18.376J, WAVE PROPAGATIONwenceslaoflorezNo ratings yet
- Analytic Solution of Stokes Second Problem For Second-Grade FluidDocument9 pagesAnalytic Solution of Stokes Second Problem For Second-Grade FluidricljrNo ratings yet
- Deriving The Path Integral: 2.1 Recall of Quantum MechanicsDocument10 pagesDeriving The Path Integral: 2.1 Recall of Quantum Mechanicsnom nomNo ratings yet
- Inequalities EstiDocument18 pagesInequalities EstidibekayaNo ratings yet
- The Vertical Píate in Laminar Free Convection: Effects of Leading and Trailing Edges and Discontinuous TemperatureDocument19 pagesThe Vertical Píate in Laminar Free Convection: Effects of Leading and Trailing Edges and Discontinuous TemperatureMarko's Brazon'No ratings yet
- Analitik Pengeringan TankDocument4 pagesAnalitik Pengeringan TankReliusman DachiNo ratings yet
- CFD NotesDocument44 pagesCFD Notessubha_aeroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document18 pagesChapter 2Lucy BrownNo ratings yet
- Ambrosio e Gangbo Hamilton Ian ODEDocument35 pagesAmbrosio e Gangbo Hamilton Ian ODEelismar01No ratings yet
- Epitaxial Growth Without Slope Selection: Energetics, Coarsening, and Dynamic ScalingDocument23 pagesEpitaxial Growth Without Slope Selection: Energetics, Coarsening, and Dynamic ScalingNikos PapanikolaouNo ratings yet
- 10 1 1 23 3515Document22 pages10 1 1 23 3515R PasNo ratings yet
- Regularity Criterion For The 3D Fluid Passing Through Porous Medium in Terms of The Gradient of One Velocity ComponentDocument17 pagesRegularity Criterion For The 3D Fluid Passing Through Porous Medium in Terms of The Gradient of One Velocity ComponentBrandie ButlerNo ratings yet
- Necessary Conditions For Minimax Control Problems of Second Order Elliptic Partial Dierential EquationsDocument22 pagesNecessary Conditions For Minimax Control Problems of Second Order Elliptic Partial Dierential EquationsLuca BallestraNo ratings yet
- Flow in An Inclined Plane PDFDocument6 pagesFlow in An Inclined Plane PDFAbimbolaNo ratings yet
- International Journal of C 2009 Institute For Scientific Numerical Analysis and Modeling Computing and InformationDocument15 pagesInternational Journal of C 2009 Institute For Scientific Numerical Analysis and Modeling Computing and InformationUrmi AkterNo ratings yet
- Set8 PDFDocument16 pagesSet8 PDFcemnuy100% (1)
- Advanced Fluid Mechanics - Chapter 05 - Boundary Layer TheoryDocument33 pagesAdvanced Fluid Mechanics - Chapter 05 - Boundary Layer Theorysunil481No ratings yet
- Solutions 1Document6 pagesSolutions 1Christopher GalasNo ratings yet
- Helge Holden and Xavier Raynaud - Periodic Conservative Solutions of The Camassa-Holm EquationDocument31 pagesHelge Holden and Xavier Raynaud - Periodic Conservative Solutions of The Camassa-Holm EquationQMDhidnwNo ratings yet
- 02 - Physical Interpretation of Fractional Diffusion-Wave EquationDocument6 pages02 - Physical Interpretation of Fractional Diffusion-Wave EquationNilson EvilásioNo ratings yet
- Unsteady Bernoulli Equation: Advanced Fluid M Ech AnicsDocument13 pagesUnsteady Bernoulli Equation: Advanced Fluid M Ech AnicsThomas SantosaNo ratings yet
- The Shallow Water Equations Model Tsunamis and Waves in BathtubsDocument4 pagesThe Shallow Water Equations Model Tsunamis and Waves in BathtubsLuigi1721No ratings yet
- Lý thuyết sóngDocument11 pagesLý thuyết sóngtiktiktakNo ratings yet
- Jung 2019 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1365 012005 PDFDocument9 pagesJung 2019 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1365 012005 PDFSungki JungNo ratings yet
- Report 1Document5 pagesReport 1khalinminNo ratings yet
- Higher-Order Stokes Theory: T KX KH KH KH L H T KX HDocument8 pagesHigher-Order Stokes Theory: T KX KH KH KH L H T KX HharrifsNo ratings yet
- Integral Methods For The Wave Operator On Lipschitz CylindersDocument12 pagesIntegral Methods For The Wave Operator On Lipschitz CylindersLuis FuentesNo ratings yet
- CWI, Centre For Mathematics and Computer Science P.O.Box 4079, 1009 AB Amsterdam, The NetherlandsDocument16 pagesCWI, Centre For Mathematics and Computer Science P.O.Box 4079, 1009 AB Amsterdam, The NetherlandsGönenç Can AltunNo ratings yet
- Topic 4: Computational Fluid Dynamics: Lecture 4-1: Burgers EquationDocument10 pagesTopic 4: Computational Fluid Dynamics: Lecture 4-1: Burgers Equationrdeepak01No ratings yet
- Wiener SpaceDocument22 pagesWiener SpaceforwardhoNo ratings yet
- FEM3Document22 pagesFEM3Paul RebourNo ratings yet
- Chap 4 PDFDocument40 pagesChap 4 PDFxongassilvaNo ratings yet
- ATAUKSSDocument10 pagesATAUKSSbullo hindebuNo ratings yet
- 4.2 The Falkner-Skan EquationDocument4 pages4.2 The Falkner-Skan EquationmecharashNo ratings yet
- Cap 2Document22 pagesCap 2MaggyBalcazarNo ratings yet
- Generalized Solutions To Parabolic-Hyperbolic EquationsDocument6 pagesGeneralized Solutions To Parabolic-Hyperbolic EquationsLuis FuentesNo ratings yet
- On The Compactenss of The Support of Solutions of Dispersive Equations - Int Math Res Notices-1997-Bourgain-437-47Document11 pagesOn The Compactenss of The Support of Solutions of Dispersive Equations - Int Math Res Notices-1997-Bourgain-437-47raphaelsantos08No ratings yet
- Start Up Couette Flow Second Order Fluid Analytical Solution Viscoelastic FlowsDocument23 pagesStart Up Couette Flow Second Order Fluid Analytical Solution Viscoelastic Flowsswapnil_dalalNo ratings yet
- Fractional Camassa Holm DeterministicDocument28 pagesFractional Camassa Holm DeterministicdiegoaloranNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Water Waves: 6.1 Exact (Nonlinear) Governing Equations For Surface Gravity Waves, Assuming Potential FlowDocument14 pagesChapter 6 - Water Waves: 6.1 Exact (Nonlinear) Governing Equations For Surface Gravity Waves, Assuming Potential Flowamit_bs2002No ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document11 pagesChapter 2muhammad qasimNo ratings yet
- Free Surface Water Waves Part 1Document13 pagesFree Surface Water Waves Part 1Ahmad Zuhairi AbdollahNo ratings yet
- A Relaxation Method For Two-Phase Flow Models With Hydrodynamic Closure LawDocument33 pagesA Relaxation Method For Two-Phase Flow Models With Hydrodynamic Closure LawdidNo ratings yet
- Linear Stability of Double-Diffusive Two-Fluid Channel Flow: J. Fluid Mech. (2011), Vol. 687, Pp. 529-539Document11 pagesLinear Stability of Double-Diffusive Two-Fluid Channel Flow: J. Fluid Mech. (2011), Vol. 687, Pp. 529-539Deepak Kumar Singh Res. Scholar., Dept. of Mechanical Engg., IIT (BHU)No ratings yet
- Dynamic OceanographyDocument107 pagesDynamic Oceanographyayanbanerjee1No ratings yet
- Euler KortewegDocument10 pagesEuler KortewegGianfranco GambiniNo ratings yet
- Symmetry Analysis, Explicit Power Series Solutions and Conservation Laws of The Space-Time Fractional Variant Boussinesq SystemDocument19 pagesSymmetry Analysis, Explicit Power Series Solutions and Conservation Laws of The Space-Time Fractional Variant Boussinesq SystemBaljinderNo ratings yet
- 9601ph PKDocument15 pages9601ph PKRana HazemNo ratings yet
- Butterowrth LamboDocument13 pagesButterowrth LamboAdhip kurianNo ratings yet
- Linear MomentumDocument30 pagesLinear Momentumyuxing lieNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure - IiDocument9 pagesAtomic Structure - IiSUMITH K SNo ratings yet
- CH 1.9e (CH 1.10) Vector IntegrationDocument14 pagesCH 1.9e (CH 1.10) Vector IntegrationAaron MangampoNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics Advance Level ProblemsDocument69 pagesElectrostatics Advance Level Problemsraj kumar singhNo ratings yet
- Nucl - Phys.B v.603Document578 pagesNucl - Phys.B v.603buddy72No ratings yet
- Shimadzu RF-5301 Fluorimeter Operation Guide For Students: General DirectionsDocument5 pagesShimadzu RF-5301 Fluorimeter Operation Guide For Students: General DirectionsalinessanNo ratings yet
- c14 Trans LineDocument11 pagesc14 Trans LineKevin VerulaNo ratings yet
- JEE Main 2021 - Aug 27th - Morning SessionDocument20 pagesJEE Main 2021 - Aug 27th - Morning SessionJaynandan KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Short-Term Oxidation Resistance and Degradation of CR AlC Coating On M38G Superalloy at 900-1100 C 2Document8 pagesShort-Term Oxidation Resistance and Degradation of CR AlC Coating On M38G Superalloy at 900-1100 C 2Miruna PetriaNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Cheat SheetDocument1 pageFinal Exam Cheat SheetDanielle GuindonNo ratings yet
- Basic Technical Mathematics 10th Edition Washington Solutions Manual 1Document63 pagesBasic Technical Mathematics 10th Edition Washington Solutions Manual 1thomas100% (44)
- UEB-Troy GEO 1050, Spring 2024 Nguyen Quoc Hung Homework 6: ChemistryDocument4 pagesUEB-Troy GEO 1050, Spring 2024 Nguyen Quoc Hung Homework 6: ChemistryDang Linh NhiNo ratings yet
- Pow Sat-3 WepDocument10 pagesPow Sat-3 WepMarcus PoonNo ratings yet
- ElectroquimicaDocument8 pagesElectroquimicaPaula Andrea Martínez ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding Advance (Micro)Document28 pagesChemical Bonding Advance (Micro)Anant JainNo ratings yet
- Physics Complete NotesDocument111 pagesPhysics Complete Notesmd ibraheem altafNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument17 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular StructureRIHAN ABDULKADERNo ratings yet
- Miscellaneous Problems2Document3 pagesMiscellaneous Problems2Jesus Ray M. MansayonNo ratings yet
- M Nov 2003Document2 pagesM Nov 2003Leonardo TiabaNo ratings yet
- Jms-2 Paper - 1 - SolutionsDocument12 pagesJms-2 Paper - 1 - SolutionsjanmanchiNo ratings yet
- Aknu SyllabusDocument55 pagesAknu SyllabussanjeevchsNo ratings yet
- Fiitjee Xi Practice PaperDocument19 pagesFiitjee Xi Practice Paperrupal_jain108100% (2)
- G O T F: Graph of The Tangent FunctionDocument11 pagesG O T F: Graph of The Tangent FunctionVenesia WirandaNo ratings yet
- Hyper ConjugationDocument3 pagesHyper ConjugationKeval MaldeNo ratings yet
- Points of Special Interest On The Unit Circle:: Cosine Functions Repeat Is 2Document17 pagesPoints of Special Interest On The Unit Circle:: Cosine Functions Repeat Is 2SnubOfficial GamerNo ratings yet