Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 viewsAQA GCSE Chem C2 Summary Question Answers
AQA GCSE Chem C2 Summary Question Answers
Uploaded by
anusha.barira1. The document contains answers to summary questions about chemistry concepts including groups in the periodic table, properties of halogens, reactions of alkali metals like rubidium, and the development of the periodic table.
2. It provides explanations for trends in properties like ion formation and reactivity down groups and across periods, and how the periodic table organizes elements based on atomic structure and properties.
3. Mendeleev predicted properties of undiscovered elements and his periodic table was supported when new elements matched the predictions, showing its validity in organizing known and yet to be discovered elements.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- MCE Cambridge IGCSE Chemistry SB SampleDocument26 pagesMCE Cambridge IGCSE Chemistry SB SampleDvmmy40% (5)
- Topic 9 QDocument19 pagesTopic 9 QIndraneel BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- C6 Book AnswersDocument4 pagesC6 Book AnswersvijahatNo ratings yet
- AQA GCSE Chem End of Topic C5Document9 pagesAQA GCSE Chem End of Topic C5joeNo ratings yet
- GCSE Trilogy Chemistry 1H MSDocument6 pagesGCSE Trilogy Chemistry 1H MSshehryar iftikharNo ratings yet
- AQA Chem GCSE Combined C6 Practice AnswersDocument2 pagesAQA Chem GCSE Combined C6 Practice AnswersLeslie MasiyandimaNo ratings yet
- Johor Jaya Answer 2020Document7 pagesJohor Jaya Answer 2020Muhd FaiZNo ratings yet
- Form Four Mid Term Paper 1Document16 pagesForm Four Mid Term Paper 1Marylyn Ace TeeNo ratings yet
- AQA Chem GCSE Combined C2 Practice AnswersDocument2 pagesAQA Chem GCSE Combined C2 Practice AnswersLeslie MasiyandimaNo ratings yet
- AQA GCSE Chem Combined End of Topic C1Document9 pagesAQA GCSE Chem Combined End of Topic C1joeNo ratings yet
- 9 and 19 MCQDocument18 pages9 and 19 MCQrania samirNo ratings yet
- IBDP Chemistry Bonding Questions MSDocument10 pagesIBDP Chemistry Bonding Questions MSsquailgeNo ratings yet
- Study of The First Element - HydrogenDocument5 pagesStudy of The First Element - HydrogenKOVLEEN SAHNINo ratings yet
- C2 The Periodic Table Student Book AnswersDocument7 pagesC2 The Periodic Table Student Book AnswersjoeNo ratings yet
- Edgcse TTPP cc13 15 SB AnswersDocument6 pagesEdgcse TTPP cc13 15 SB Answersegcarty1009No ratings yet
- 4TH QUARTER EXAM ADVANCE CHEM - EditedDocument2 pages4TH QUARTER EXAM ADVANCE CHEM - EditedWilsonNo ratings yet
- Group 1 ElementsDocument5 pagesGroup 1 ElementsLeong Kit WaiNo ratings yet
- Alkali MetalsDocument7 pagesAlkali Metalsokguserfucker idontgiveashitNo ratings yet
- Chemistry U3&4 TEST 2 Suggested Solutions - 2017Document4 pagesChemistry U3&4 TEST 2 Suggested Solutions - 2017Neyaz RazaviNo ratings yet
- Quiz Period3 G2Document2 pagesQuiz Period3 G2Simmon SasmitaNo ratings yet
- First Term Exam Chemistry Answer KeyDocument9 pagesFirst Term Exam Chemistry Answer KeyRutujaNo ratings yet
- AQA Chem Combined C6 GCSE Summary AnswersDocument2 pagesAQA Chem Combined C6 GCSE Summary AnswersMohamed AbdiNo ratings yet
- 2122 CHEM UT2-F4-P1B-M - 已檢查Document4 pages2122 CHEM UT2-F4-P1B-M - 已檢查s202001001No ratings yet
- Ionic, Covalent - Metallic Bonds 2 MSDocument9 pagesIonic, Covalent - Metallic Bonds 2 MSlaronaselebogo04No ratings yet
- S Block PDFDocument22 pagesS Block PDFRoshita G PillaiNo ratings yet
- Ib Chemistry Answers S3Document14 pagesIb Chemistry Answers S3Carlos JesúsNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry (Paper-01) WYDocument12 pagesElectrochemistry (Paper-01) WYgreedy AsunaNo ratings yet
- Bks IGCC2 Ccuu An06 XxaannDocument9 pagesBks IGCC2 Ccuu An06 XxaannHakan OlgunNo ratings yet
- Ess Chem Unit 12 AnswersDocument2 pagesEss Chem Unit 12 AnswersSumathi GanasenNo ratings yet
- Uppp2 Sem 2 2017Document5 pagesUppp2 Sem 2 2017Loh Wai YeeNo ratings yet
- Groupings of Elements in The Periodic Table Group I A - The Alkali Metals NaDocument6 pagesGroupings of Elements in The Periodic Table Group I A - The Alkali Metals NaGlad YsNo ratings yet
- p2 Task 3 AnsDocument4 pagesp2 Task 3 AnsSabeen Ahmed/TCHR/EKNNCNo ratings yet
- Practicetopic 9 Papers 1&2Document6 pagesPracticetopic 9 Papers 1&2mccano99No ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Rate of ReactionDocument3 pagesChapter 10 Rate of ReactionLei YinNo ratings yet
- REDOX - Review Questions Standard Level Chemistry DP 1Document12 pagesREDOX - Review Questions Standard Level Chemistry DP 1Jessie CASNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 EM Theory Book 1 (Group 1-15) v23.0Document20 pagesUnit 6 EM Theory Book 1 (Group 1-15) v23.0Thilanka LiyanageNo ratings yet
- Skema - Bab 1 Ting. 5Document4 pagesSkema - Bab 1 Ting. 5SMK MERSING (SEK-JEA4035)No ratings yet
- Polarizing Power of Common CationsDocument1 pagePolarizing Power of Common CationsiPad YoutubeNo ratings yet
- Group 1-2Document22 pagesGroup 1-2Gudia kumariNo ratings yet
- Exam Chew 1Document7 pagesExam Chew 1ThilagaNo ratings yet
- Answred Chem Mid TermDocument12 pagesAnswred Chem Mid Termlife of yomnaNo ratings yet
- 3.1.2 Group 2 MCQDocument4 pages3.1.2 Group 2 MCQanwins46No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument9 pagesUntitledemanNo ratings yet
- Redox SL StudentsDocument18 pagesRedox SL StudentsMiaNo ratings yet
- Answer Scheme PPT Paper 2 Form 5Document7 pagesAnswer Scheme PPT Paper 2 Form 5sahira othmanNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Cells MSDocument14 pagesElectrochemical Cells MSJesulayomi BolajiNo ratings yet
- Oxford Resources For IB: Structure 3.1 - The Periodic Table: Classification of ElementsDocument19 pagesOxford Resources For IB: Structure 3.1 - The Periodic Table: Classification of ElementsGian Paolo GerzonNo ratings yet
- Electricity & Chemistry 1 MSDocument7 pagesElectricity & Chemistry 1 MSTanakaNo ratings yet
- AQA GCSE Chem C5 Practice Question AnswersDocument2 pagesAQA GCSE Chem C5 Practice Question AnswersJawaria MazharNo ratings yet
- Paper 2 November 2001Document4 pagesPaper 2 November 2001MSH50% (4)
- Set 1-Paper 2 (Skema)Document13 pagesSet 1-Paper 2 (Skema)NajwaAbdullahNo ratings yet
- AQA Chem 1 Answers ch03Document6 pagesAQA Chem 1 Answers ch03Ellie AndersonNo ratings yet
- The S-Block Elements: Dr. Vatsala Soni PGGC Sector - 11 ChandigarhDocument55 pagesThe S-Block Elements: Dr. Vatsala Soni PGGC Sector - 11 ChandigarhNagendra MadineniNo ratings yet
- The S-Block Elements: Dr. Vatsala Soni PGGC Sector - 11 ChandigarhDocument55 pagesThe S-Block Elements: Dr. Vatsala Soni PGGC Sector - 11 ChandigarhAVR BroZNo ratings yet
- The S-Block Elements: Dr. Vatsala Soni PGGC Sector - 11 ChandigarhDocument55 pagesThe S-Block Elements: Dr. Vatsala Soni PGGC Sector - 11 ChandigarhAVR BroZNo ratings yet
- AQA - A Level - Chem - 1 - Answers Ch09.inddDocument5 pagesAQA - A Level - Chem - 1 - Answers Ch09.inddMahebul MazidNo ratings yet
- The S-Block ElementsDocument51 pagesThe S-Block ElementsDiksha TNo ratings yet
- 6.5 Electricity and Chemistry Ms - Igcse Cie Chemistry - Extended Theory PaperDocument6 pages6.5 Electricity and Chemistry Ms - Igcse Cie Chemistry - Extended Theory PaperBerryNo ratings yet
- Modul A Paper2answerDocument13 pagesModul A Paper2answerNur SyakirahNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Resistance of Aluminum and Magnesium Alloys: Understanding, Performance, and TestingFrom EverandCorrosion Resistance of Aluminum and Magnesium Alloys: Understanding, Performance, and TestingNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Item Kbat Chemistry Form Four Structure of The AtomDocument35 pagesItem Kbat Chemistry Form Four Structure of The AtomSiva GuruNo ratings yet
- SC 2024 SP-3Document15 pagesSC 2024 SP-3Swostik RoutNo ratings yet
- Science9 Q2 Weeks1to4 Binded Ver.1.0Document41 pagesScience9 Q2 Weeks1to4 Binded Ver.1.0alonzomonitaroseNo ratings yet
- Learning The Periodic Table of ElementsDocument31 pagesLearning The Periodic Table of ElementshypezakramNo ratings yet
- Science Bowl Practice Questions Biology - 1Document111 pagesScience Bowl Practice Questions Biology - 1Kavita KrishnamorthiNo ratings yet
- Tabla PeriodicaDocument1 pageTabla PeriodicaOmar BenítezNo ratings yet
- Aviation PhysiologyDocument47 pagesAviation PhysiologyMoses RajasekaranNo ratings yet
- Know The Name of The Elements and Compounds KimiaDocument73 pagesKnow The Name of The Elements and Compounds KimiaNova SinagaNo ratings yet
- Ionic BondingDocument7 pagesIonic BondingDrcreeperPhdNo ratings yet
- Electrons Activity SheetDocument8 pagesElectrons Activity SheetTonette ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces and Periodicity Worksheet PDFDocument5 pagesIntermolecular Forces and Periodicity Worksheet PDFAlejandra Barrera MNo ratings yet
- Eva Chamorro-Perez Et Al - Low Argon Solubility in Silicate Melts at High PressureDocument4 pagesEva Chamorro-Perez Et Al - Low Argon Solubility in Silicate Melts at High PressureDrebuioNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table WorksheetDocument3 pagesPeriodic Table WorksheetAri A Siddiqui100% (2)
- IGCSE Chemistry NotesDocument46 pagesIGCSE Chemistry NotesRenée ReimiNo ratings yet
- 4.1 - 4.2 & 4.3 The Ionic Bond-1Document24 pages4.1 - 4.2 & 4.3 The Ionic Bond-1서태현No ratings yet
- Class 10 Chemistry Part 2 of 2 - RedactedDocument62 pagesClass 10 Chemistry Part 2 of 2 - Redactedraza anandNo ratings yet
- Classification of Elements & Periodic Table Part-A (Periodic Table)Document51 pagesClassification of Elements & Periodic Table Part-A (Periodic Table)Abhishek NNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Chemistry - Chapter 1Document51 pagesTest Bank For Chemistry - Chapter 1Giovanni Almeyda Lonergan100% (2)
- The Periodic Table, Electron Shells, and OrbitalsDocument13 pagesThe Periodic Table, Electron Shells, and OrbitalsCandyAnonymousNo ratings yet
- Gce Chemistry ReviewDocument41 pagesGce Chemistry Review7a4374 hisNo ratings yet
- Chapter-7: P-Block Element: Nitrogen Family (Group 15Document28 pagesChapter-7: P-Block Element: Nitrogen Family (Group 15Aditya VijayvargiyaNo ratings yet
- Hkdse Chemistry - A Modern View (Chemistry and Combined Science)Document104 pagesHkdse Chemistry - A Modern View (Chemistry and Combined Science)梁儀50% (2)
- List of 20 Elements and UsesDocument3 pagesList of 20 Elements and Usestanhuikuan100% (1)
- Chemical Engineering MCQsDocument4 pagesChemical Engineering MCQsRexel ReedusNo ratings yet
- CHEM Grade 10 WK 6Document14 pagesCHEM Grade 10 WK 6Anasatcia Mcpherson 9c FNo ratings yet
- 4 Periodic Table of ElementsDocument17 pages4 Periodic Table of ElementsWong Wai LunNo ratings yet
- 01 CHEM X ICSE SUMMARY Periodic Properties& VariationsDocument9 pages01 CHEM X ICSE SUMMARY Periodic Properties& VariationsNatasha DalalNo ratings yet
- Wave Assisted Propulsion by Lieutenant General SPC Cory A. HofstadDocument6 pagesWave Assisted Propulsion by Lieutenant General SPC Cory A. HofstadCory Andrew HofstadNo ratings yet
- Modern Periodic TableDocument8 pagesModern Periodic TableSabbir HossainNo ratings yet
AQA GCSE Chem C2 Summary Question Answers
AQA GCSE Chem C2 Summary Question Answers
Uploaded by
anusha.barira0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views4 pages1. The document contains answers to summary questions about chemistry concepts including groups in the periodic table, properties of halogens, reactions of alkali metals like rubidium, and the development of the periodic table.
2. It provides explanations for trends in properties like ion formation and reactivity down groups and across periods, and how the periodic table organizes elements based on atomic structure and properties.
3. Mendeleev predicted properties of undiscovered elements and his periodic table was supported when new elements matched the predictions, showing its validity in organizing known and yet to be discovered elements.
Original Description:
Chem C2 Summary Question answer
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. The document contains answers to summary questions about chemistry concepts including groups in the periodic table, properties of halogens, reactions of alkali metals like rubidium, and the development of the periodic table.
2. It provides explanations for trends in properties like ion formation and reactivity down groups and across periods, and how the periodic table organizes elements based on atomic structure and properties.
3. Mendeleev predicted properties of undiscovered elements and his periodic table was supported when new elements matched the predictions, showing its validity in organizing known and yet to be discovered elements.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views4 pagesAQA GCSE Chem C2 Summary Question Answers
AQA GCSE Chem C2 Summary Question Answers
Uploaded by
anusha.barira1. The document contains answers to summary questions about chemistry concepts including groups in the periodic table, properties of halogens, reactions of alkali metals like rubidium, and the development of the periodic table.
2. It provides explanations for trends in properties like ion formation and reactivity down groups and across periods, and how the periodic table organizes elements based on atomic structure and properties.
3. Mendeleev predicted properties of undiscovered elements and his periodic table was supported when new elements matched the predictions, showing its validity in organizing known and yet to be discovered elements.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 4
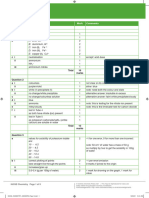
Student Book answers C2 Summary questions
Question Answer Marks Guidance
number
1ai Group 7 1
1 a ii Group 0 1
1 a iii Group 1 1
GCSE Chemistry only
1 a iv between Groups 2 and 3 1
1bi transition elements 1
1 b ii Group 1 / alkali metals 1
1 b iii Group 0 / noble gases 1
1 b iv Group 7 / halogens 1
2a 7 electrons as Group 7 1
2b solid 1
2ci ionic 1
2 c ii white 1
2 c iii NaAt 1
2 c iv sodium + astatine sodium astatide 1
2Na + At2 → 2NaAt 1
2cv yes, chlorine more reactive than astatine 1
so At displaced 1
© Oxford University Press 2016 www.oxfordsecondary.co.uk/acknowledgements
This resource sheet may have been changed from the original. 1
Student Book answers C2 Summary questions
Question Answer Marks Guidance
number
2d F, Cl, Br, I, At 1
The smaller the halogen atom, the more readily it 1
accepts/ gains extra electron into its outermost shell,
becomes halide ion with single negative charge, 1
the stronger the electrostatic force of attraction between 1
nucleus and extra electron entering smaller atom’s
outermost shell as electron closer to nuclear charge,
and it becomes less shielded from nuclear charge than 1
larger atoms with more inner shells of electrons.
These two factors outweigh fact that nuclear charge is 1
more positive going down Group 7.
3a soft good 1
electrical conductivity 1
low melting point 1
3bi 1+ 1
3 b ii Rubidium compound Chemical formula 3
rubidium iodide RbI
rubidium fluoride RbF
rubidium hydroxide RbOH
3ci 2Rb(s) + 2H2O(l) → 2RbOH(aq) + H2(g) 3
3 c ii 2Rb(s) + Cl2(g) → 2RbCl(s) 2
© Oxford University Press 2016 www.oxfordsecondary.co.uk/acknowledgements
This resource sheet may have been changed from the original. 2
Student Book answers C2 Summary questions
Question Answer Marks Guidance
number
3d more vigorous, 1
because loses its outer electron more easily 1
further from nucleus than in potassium, 1
shielded from nuclear charge by extra inner shell of 1
electrons,
these two factors overcome larger nuclear charge of 1
rubidium atom compared with potassium atom
GCSE Chemistry only
4ai copper(II) sulfate blue, sodium sulfate white 1
4 a ii Copper forms two types of ion whereas sodium only 1
forms a 1+ ion.
4b Copper has a much higher melting point, 1
is harder, 1
and denser than sodium. 1
4c sodium is much more reactive than copper, 1
reacts vigorously with water, 1
giving off hydrogen gas and forming sodium hydroxide, 1
copper does not react with water 1
5a arranged elements in order of atomic weight, 1
started new rows to allow elements with similar properties 1
to align
© Oxford University Press 2016 www.oxfordsecondary.co.uk/acknowledgements
This resource sheet may have been changed from the original. 3
Student Book answers C2 Summary questions
Question Answer Marks Guidance
number
5b Mendeleev predicted properties of ‘as yet undiscovered’ 1
elements
in gaps left in his table 1
so that similar elements would line up. 1
When new elements discovered, 1
they closely matched properties predicted, 1
→ powerful evidence Mendeleev’s table was valid 1
5c They did not know about atomic structure 1
or existence of isotopes 1
so did not know elements are ordered by atomic number. 1
6a Metal atoms lose electrons to form positive ions 1
with the stable electronic structure of a noble gas. 1
Magnesium atom (2, 8, 2) loses its two outermost 1
electrons to attain electronic structure of neon (2, 8) in
Mg2+ ion.
Non-metal atoms gain electrons to form negatively 1
charged ions
with the stable electronic structure of a noble gas. 1
Oxygen atom (2, 6) gains two electrons to form oxide ion 1
(2, 8), also with stable electronic configuration of neon.
6b radius of ion smaller 1
because no electrons in outermost shell 1
© Oxford University Press 2016 www.oxfordsecondary.co.uk/acknowledgements
This resource sheet may have been changed from the original. 4
You might also like
- MCE Cambridge IGCSE Chemistry SB SampleDocument26 pagesMCE Cambridge IGCSE Chemistry SB SampleDvmmy40% (5)
- Topic 9 QDocument19 pagesTopic 9 QIndraneel BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- C6 Book AnswersDocument4 pagesC6 Book AnswersvijahatNo ratings yet
- AQA GCSE Chem End of Topic C5Document9 pagesAQA GCSE Chem End of Topic C5joeNo ratings yet
- GCSE Trilogy Chemistry 1H MSDocument6 pagesGCSE Trilogy Chemistry 1H MSshehryar iftikharNo ratings yet
- AQA Chem GCSE Combined C6 Practice AnswersDocument2 pagesAQA Chem GCSE Combined C6 Practice AnswersLeslie MasiyandimaNo ratings yet
- Johor Jaya Answer 2020Document7 pagesJohor Jaya Answer 2020Muhd FaiZNo ratings yet
- Form Four Mid Term Paper 1Document16 pagesForm Four Mid Term Paper 1Marylyn Ace TeeNo ratings yet
- AQA Chem GCSE Combined C2 Practice AnswersDocument2 pagesAQA Chem GCSE Combined C2 Practice AnswersLeslie MasiyandimaNo ratings yet
- AQA GCSE Chem Combined End of Topic C1Document9 pagesAQA GCSE Chem Combined End of Topic C1joeNo ratings yet
- 9 and 19 MCQDocument18 pages9 and 19 MCQrania samirNo ratings yet
- IBDP Chemistry Bonding Questions MSDocument10 pagesIBDP Chemistry Bonding Questions MSsquailgeNo ratings yet
- Study of The First Element - HydrogenDocument5 pagesStudy of The First Element - HydrogenKOVLEEN SAHNINo ratings yet
- C2 The Periodic Table Student Book AnswersDocument7 pagesC2 The Periodic Table Student Book AnswersjoeNo ratings yet
- Edgcse TTPP cc13 15 SB AnswersDocument6 pagesEdgcse TTPP cc13 15 SB Answersegcarty1009No ratings yet
- 4TH QUARTER EXAM ADVANCE CHEM - EditedDocument2 pages4TH QUARTER EXAM ADVANCE CHEM - EditedWilsonNo ratings yet
- Group 1 ElementsDocument5 pagesGroup 1 ElementsLeong Kit WaiNo ratings yet
- Alkali MetalsDocument7 pagesAlkali Metalsokguserfucker idontgiveashitNo ratings yet
- Chemistry U3&4 TEST 2 Suggested Solutions - 2017Document4 pagesChemistry U3&4 TEST 2 Suggested Solutions - 2017Neyaz RazaviNo ratings yet
- Quiz Period3 G2Document2 pagesQuiz Period3 G2Simmon SasmitaNo ratings yet
- First Term Exam Chemistry Answer KeyDocument9 pagesFirst Term Exam Chemistry Answer KeyRutujaNo ratings yet
- AQA Chem Combined C6 GCSE Summary AnswersDocument2 pagesAQA Chem Combined C6 GCSE Summary AnswersMohamed AbdiNo ratings yet
- 2122 CHEM UT2-F4-P1B-M - 已檢查Document4 pages2122 CHEM UT2-F4-P1B-M - 已檢查s202001001No ratings yet
- Ionic, Covalent - Metallic Bonds 2 MSDocument9 pagesIonic, Covalent - Metallic Bonds 2 MSlaronaselebogo04No ratings yet
- S Block PDFDocument22 pagesS Block PDFRoshita G PillaiNo ratings yet
- Ib Chemistry Answers S3Document14 pagesIb Chemistry Answers S3Carlos JesúsNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry (Paper-01) WYDocument12 pagesElectrochemistry (Paper-01) WYgreedy AsunaNo ratings yet
- Bks IGCC2 Ccuu An06 XxaannDocument9 pagesBks IGCC2 Ccuu An06 XxaannHakan OlgunNo ratings yet
- Ess Chem Unit 12 AnswersDocument2 pagesEss Chem Unit 12 AnswersSumathi GanasenNo ratings yet
- Uppp2 Sem 2 2017Document5 pagesUppp2 Sem 2 2017Loh Wai YeeNo ratings yet
- Groupings of Elements in The Periodic Table Group I A - The Alkali Metals NaDocument6 pagesGroupings of Elements in The Periodic Table Group I A - The Alkali Metals NaGlad YsNo ratings yet
- p2 Task 3 AnsDocument4 pagesp2 Task 3 AnsSabeen Ahmed/TCHR/EKNNCNo ratings yet
- Practicetopic 9 Papers 1&2Document6 pagesPracticetopic 9 Papers 1&2mccano99No ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Rate of ReactionDocument3 pagesChapter 10 Rate of ReactionLei YinNo ratings yet
- REDOX - Review Questions Standard Level Chemistry DP 1Document12 pagesREDOX - Review Questions Standard Level Chemistry DP 1Jessie CASNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 EM Theory Book 1 (Group 1-15) v23.0Document20 pagesUnit 6 EM Theory Book 1 (Group 1-15) v23.0Thilanka LiyanageNo ratings yet
- Skema - Bab 1 Ting. 5Document4 pagesSkema - Bab 1 Ting. 5SMK MERSING (SEK-JEA4035)No ratings yet
- Polarizing Power of Common CationsDocument1 pagePolarizing Power of Common CationsiPad YoutubeNo ratings yet
- Group 1-2Document22 pagesGroup 1-2Gudia kumariNo ratings yet
- Exam Chew 1Document7 pagesExam Chew 1ThilagaNo ratings yet
- Answred Chem Mid TermDocument12 pagesAnswred Chem Mid Termlife of yomnaNo ratings yet
- 3.1.2 Group 2 MCQDocument4 pages3.1.2 Group 2 MCQanwins46No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument9 pagesUntitledemanNo ratings yet
- Redox SL StudentsDocument18 pagesRedox SL StudentsMiaNo ratings yet
- Answer Scheme PPT Paper 2 Form 5Document7 pagesAnswer Scheme PPT Paper 2 Form 5sahira othmanNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Cells MSDocument14 pagesElectrochemical Cells MSJesulayomi BolajiNo ratings yet
- Oxford Resources For IB: Structure 3.1 - The Periodic Table: Classification of ElementsDocument19 pagesOxford Resources For IB: Structure 3.1 - The Periodic Table: Classification of ElementsGian Paolo GerzonNo ratings yet
- Electricity & Chemistry 1 MSDocument7 pagesElectricity & Chemistry 1 MSTanakaNo ratings yet
- AQA GCSE Chem C5 Practice Question AnswersDocument2 pagesAQA GCSE Chem C5 Practice Question AnswersJawaria MazharNo ratings yet
- Paper 2 November 2001Document4 pagesPaper 2 November 2001MSH50% (4)
- Set 1-Paper 2 (Skema)Document13 pagesSet 1-Paper 2 (Skema)NajwaAbdullahNo ratings yet
- AQA Chem 1 Answers ch03Document6 pagesAQA Chem 1 Answers ch03Ellie AndersonNo ratings yet
- The S-Block Elements: Dr. Vatsala Soni PGGC Sector - 11 ChandigarhDocument55 pagesThe S-Block Elements: Dr. Vatsala Soni PGGC Sector - 11 ChandigarhNagendra MadineniNo ratings yet
- The S-Block Elements: Dr. Vatsala Soni PGGC Sector - 11 ChandigarhDocument55 pagesThe S-Block Elements: Dr. Vatsala Soni PGGC Sector - 11 ChandigarhAVR BroZNo ratings yet
- The S-Block Elements: Dr. Vatsala Soni PGGC Sector - 11 ChandigarhDocument55 pagesThe S-Block Elements: Dr. Vatsala Soni PGGC Sector - 11 ChandigarhAVR BroZNo ratings yet
- AQA - A Level - Chem - 1 - Answers Ch09.inddDocument5 pagesAQA - A Level - Chem - 1 - Answers Ch09.inddMahebul MazidNo ratings yet
- The S-Block ElementsDocument51 pagesThe S-Block ElementsDiksha TNo ratings yet
- 6.5 Electricity and Chemistry Ms - Igcse Cie Chemistry - Extended Theory PaperDocument6 pages6.5 Electricity and Chemistry Ms - Igcse Cie Chemistry - Extended Theory PaperBerryNo ratings yet
- Modul A Paper2answerDocument13 pagesModul A Paper2answerNur SyakirahNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Resistance of Aluminum and Magnesium Alloys: Understanding, Performance, and TestingFrom EverandCorrosion Resistance of Aluminum and Magnesium Alloys: Understanding, Performance, and TestingNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Item Kbat Chemistry Form Four Structure of The AtomDocument35 pagesItem Kbat Chemistry Form Four Structure of The AtomSiva GuruNo ratings yet
- SC 2024 SP-3Document15 pagesSC 2024 SP-3Swostik RoutNo ratings yet
- Science9 Q2 Weeks1to4 Binded Ver.1.0Document41 pagesScience9 Q2 Weeks1to4 Binded Ver.1.0alonzomonitaroseNo ratings yet
- Learning The Periodic Table of ElementsDocument31 pagesLearning The Periodic Table of ElementshypezakramNo ratings yet
- Science Bowl Practice Questions Biology - 1Document111 pagesScience Bowl Practice Questions Biology - 1Kavita KrishnamorthiNo ratings yet
- Tabla PeriodicaDocument1 pageTabla PeriodicaOmar BenítezNo ratings yet
- Aviation PhysiologyDocument47 pagesAviation PhysiologyMoses RajasekaranNo ratings yet
- Know The Name of The Elements and Compounds KimiaDocument73 pagesKnow The Name of The Elements and Compounds KimiaNova SinagaNo ratings yet
- Ionic BondingDocument7 pagesIonic BondingDrcreeperPhdNo ratings yet
- Electrons Activity SheetDocument8 pagesElectrons Activity SheetTonette ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces and Periodicity Worksheet PDFDocument5 pagesIntermolecular Forces and Periodicity Worksheet PDFAlejandra Barrera MNo ratings yet
- Eva Chamorro-Perez Et Al - Low Argon Solubility in Silicate Melts at High PressureDocument4 pagesEva Chamorro-Perez Et Al - Low Argon Solubility in Silicate Melts at High PressureDrebuioNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table WorksheetDocument3 pagesPeriodic Table WorksheetAri A Siddiqui100% (2)
- IGCSE Chemistry NotesDocument46 pagesIGCSE Chemistry NotesRenée ReimiNo ratings yet
- 4.1 - 4.2 & 4.3 The Ionic Bond-1Document24 pages4.1 - 4.2 & 4.3 The Ionic Bond-1서태현No ratings yet
- Class 10 Chemistry Part 2 of 2 - RedactedDocument62 pagesClass 10 Chemistry Part 2 of 2 - Redactedraza anandNo ratings yet
- Classification of Elements & Periodic Table Part-A (Periodic Table)Document51 pagesClassification of Elements & Periodic Table Part-A (Periodic Table)Abhishek NNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Chemistry - Chapter 1Document51 pagesTest Bank For Chemistry - Chapter 1Giovanni Almeyda Lonergan100% (2)
- The Periodic Table, Electron Shells, and OrbitalsDocument13 pagesThe Periodic Table, Electron Shells, and OrbitalsCandyAnonymousNo ratings yet
- Gce Chemistry ReviewDocument41 pagesGce Chemistry Review7a4374 hisNo ratings yet
- Chapter-7: P-Block Element: Nitrogen Family (Group 15Document28 pagesChapter-7: P-Block Element: Nitrogen Family (Group 15Aditya VijayvargiyaNo ratings yet
- Hkdse Chemistry - A Modern View (Chemistry and Combined Science)Document104 pagesHkdse Chemistry - A Modern View (Chemistry and Combined Science)梁儀50% (2)
- List of 20 Elements and UsesDocument3 pagesList of 20 Elements and Usestanhuikuan100% (1)
- Chemical Engineering MCQsDocument4 pagesChemical Engineering MCQsRexel ReedusNo ratings yet
- CHEM Grade 10 WK 6Document14 pagesCHEM Grade 10 WK 6Anasatcia Mcpherson 9c FNo ratings yet
- 4 Periodic Table of ElementsDocument17 pages4 Periodic Table of ElementsWong Wai LunNo ratings yet
- 01 CHEM X ICSE SUMMARY Periodic Properties& VariationsDocument9 pages01 CHEM X ICSE SUMMARY Periodic Properties& VariationsNatasha DalalNo ratings yet
- Wave Assisted Propulsion by Lieutenant General SPC Cory A. HofstadDocument6 pagesWave Assisted Propulsion by Lieutenant General SPC Cory A. HofstadCory Andrew HofstadNo ratings yet
- Modern Periodic TableDocument8 pagesModern Periodic TableSabbir HossainNo ratings yet