Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NIMP 20303 SmartManufacturing
NIMP 20303 SmartManufacturing
Uploaded by
Ayesha EzaneeCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Industry 4.0 Presentation I Covered Till NowDocument13 pagesIndustry 4.0 Presentation I Covered Till NowDipta Karar100% (1)
- Ch4 - System Security II - Auditing Database SystemsDocument32 pagesCh4 - System Security II - Auditing Database SystemsGonzalo Jr. RualesNo ratings yet
- IoT in Electronics Manufacturing (White Paper)Document17 pagesIoT in Electronics Manufacturing (White Paper)John JalaniNo ratings yet
- Slowly Changing DimensionsDocument26 pagesSlowly Changing DimensionsPavanNo ratings yet
- Dmfa 2Document28 pagesDmfa 2samina.22110159No ratings yet
- AI - 副本Document41 pagesAI - 副本22055419No ratings yet
- 8 - Rise of Digital EconomyDocument19 pages8 - Rise of Digital EconomyAchmad P. RifaiNo ratings yet
- Revolusi Industri 4.0Document7 pagesRevolusi Industri 4.0Jhon WahlaNo ratings yet
- Industry 4.0Document27 pagesIndustry 4.0willy wigia sofyanNo ratings yet
- Unit-3 Industry 4.0Document39 pagesUnit-3 Industry 4.0BALRAM SINGHNo ratings yet
- Relevance of Industry 4.0Document16 pagesRelevance of Industry 4.0Sharon RuthNo ratings yet
- EdgetoCloud IIoT For Condition Monitoring in Manufacturing Systems With Ubiquitous Smart SensorsSensorsDocument15 pagesEdgetoCloud IIoT For Condition Monitoring in Manufacturing Systems With Ubiquitous Smart SensorsSensorsNicolas Anton RamirezNo ratings yet
- Internet of ThingsDocument23 pagesInternet of ThingsVikas VarmaNo ratings yet
- IoT in Manufacturing - GMAP InsiderDocument48 pagesIoT in Manufacturing - GMAP Insidermihirjayaraman100% (2)
- 2015 Advanced Manufacturing Tech ClusterDocument8 pages2015 Advanced Manufacturing Tech ClusterPyae PhyoaungNo ratings yet
- Industria 4.0 National PlanDocument18 pagesIndustria 4.0 National PlaniqpucelaNo ratings yet
- White Paper Edge Data Process 2023 enDocument11 pagesWhite Paper Edge Data Process 2023 ening.serpelNo ratings yet
- Verbrec - Cap Statement - Automation and ControlDocument4 pagesVerbrec - Cap Statement - Automation and Controlarek.kulikowskiNo ratings yet
- Digital Factory: The Information Systems AspectDocument17 pagesDigital Factory: The Information Systems AspectMona IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Industry 4 White PaperDocument24 pagesManufacturing Industry 4 White PaperHoàng Thắng50% (2)
- Zyfra Eng 2020Document31 pagesZyfra Eng 2020Manish ShahNo ratings yet
- Smart Manufacturing With Prescriptive Analytics: A Review of The Current Status and Future WorkDocument5 pagesSmart Manufacturing With Prescriptive Analytics: A Review of The Current Status and Future WorkalejandrozambranoNo ratings yet
- PCA Controlling and Monitoring Semiconductor Manufacturing Process Usingsmart TechnologiesDocument19 pagesPCA Controlling and Monitoring Semiconductor Manufacturing Process Usingsmart TechnologiesPeaceNo ratings yet
- Solution Brief Process 2023 enDocument6 pagesSolution Brief Process 2023 ening.serpelNo ratings yet
- Mastering Digital Transformation Key Strategies For ManufacturingDocument8 pagesMastering Digital Transformation Key Strategies For ManufacturingDhananjaya ReddyNo ratings yet
- Machine Learning in Manufacturing and Industry 4.0 ApplicationsDocument7 pagesMachine Learning in Manufacturing and Industry 4.0 ApplicationsAbhijna AdigaNo ratings yet
- Smart Factory of Industry 4.0: Key Technologies, Application Case, and ChallengesDocument15 pagesSmart Factory of Industry 4.0: Key Technologies, Application Case, and ChallengesMohd Hizami Ab HalimNo ratings yet
- Disruptive Technology Industry 4.0Document8 pagesDisruptive Technology Industry 4.0Abhilash ChessNo ratings yet
- 4th Industrial Revolution in EducationDocument21 pages4th Industrial Revolution in EducationjoewinNo ratings yet
- Nicolas Rafael Palomino W3C ApplicationDocument11 pagesNicolas Rafael Palomino W3C ApplicationLis LisNo ratings yet
- Digital Manufacturing: Industry FocusDocument40 pagesDigital Manufacturing: Industry FocusGeorge ThomasNo ratings yet
- Ajeassp 2024 33 39Document7 pagesAjeassp 2024 33 39Kathirvel AyyaswamyNo ratings yet
- IOT Revisão BibliográficaDocument4 pagesIOT Revisão Bibliográficaaguinaldomendes.jrNo ratings yet
- Industr: Global SummitDocument5 pagesIndustr: Global SummitAarush JainNo ratings yet
- Controlling and Monitoring Semiconductor Manufacturing Process Usingsmart TechnologiesDocument19 pagesControlling and Monitoring Semiconductor Manufacturing Process Usingsmart TechnologiesqxzyNo ratings yet
- AMFG Role Description - QA LeadDocument11 pagesAMFG Role Description - QA LeadОлексій «HELP»No ratings yet
- ME 2021 Digital One Pager PDFDocument4 pagesME 2021 Digital One Pager PDFTuan VuNo ratings yet
- Smart Factory White PaperDocument34 pagesSmart Factory White Paperkevin21790100% (1)
- Que t1 OrangeDocument200 pagesQue t1 OrangeM Sohail IqbalNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument15 pagesPDFNorfazeli JaafarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 01Document24 pagesLecture 01salman haiderNo ratings yet
- Intelligent Engines: Revolutionizing Manufacturing and Supply Chains With AIDocument14 pagesIntelligent Engines: Revolutionizing Manufacturing and Supply Chains With AIInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Impact of Industry 4.0 On Automobile IndustryDocument11 pagesImpact of Industry 4.0 On Automobile IndustryNishita VoraNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence in Electronics Design and ManufacturingDocument9 pagesArtificial Intelligence in Electronics Design and Manufacturingatharvmote521No ratings yet
- Accenture 804893 Smart Production POV FinalDocument20 pagesAccenture 804893 Smart Production POV FinalPraneeth BakkiNo ratings yet
- Advanced Virtual Manufacturing Systems 1Document26 pagesAdvanced Virtual Manufacturing Systems 1Aswin madhuNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Big Data Ecosystem A Systematic Literature ReviewDocument20 pagesManufacturing Big Data Ecosystem A Systematic Literature ReviewLeonardo SanchezNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Log Research BookDocument18 pagesManufacturing Log Research BookAjit Kumar SubramanyamNo ratings yet
- 2024年智能制造行业趋势分析Document5 pages2024年智能制造行业趋势分析xmcloudlessNo ratings yet
- Overcoming Data Silos and Information SaturationDocument7 pagesOvercoming Data Silos and Information SaturationgarmentssNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Part 2 4th UpdatedDocument9 pagesWeek 2 Part 2 4th Updatedmomo AdamNo ratings yet
- Role of It in Industry: 6 Sem ME Industrial EngineeringDocument11 pagesRole of It in Industry: 6 Sem ME Industrial EngineeringShyamNo ratings yet
- Role of It in Industry: 6 Sem ME Industrial EngineeringDocument11 pagesRole of It in Industry: 6 Sem ME Industrial EngineeringShyamNo ratings yet
- Applied Sciences: Smart Manufacturing Real-Time Analysis Based On Blockchain and Machine Learning ApproachesDocument22 pagesApplied Sciences: Smart Manufacturing Real-Time Analysis Based On Blockchain and Machine Learning ApproachesZeinab ShahbaziNo ratings yet
- Iot Project PowerpointDocument17 pagesIot Project Powerpointalissonzkv100% (1)
- 5 Key Digital Technologies That Are Transforming The Manufacturing Industry - Blog - TechigaiDocument15 pages5 Key Digital Technologies That Are Transforming The Manufacturing Industry - Blog - Techigaitechigai 123No ratings yet
- BK-IT26 Sensor Tech (Brochure) 10Document6 pagesBK-IT26 Sensor Tech (Brochure) 10zackyat7976No ratings yet
- SL182 enDocument2 pagesSL182 enMas CarrickNo ratings yet
- Intelligent ManufacturingDocument7 pagesIntelligent ManufacturingAli Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- IoT TillMidsem 1Document270 pagesIoT TillMidsem 1Raja UikeyNo ratings yet
- AI in Manufacturing Driving Innovation and Efficiency: A Comprehensive Toolkit for Startups and Maintenance Ladyluck M: 1, #1From EverandAI in Manufacturing Driving Innovation and Efficiency: A Comprehensive Toolkit for Startups and Maintenance Ladyluck M: 1, #1No ratings yet
- Gym Web ProjectDocument20 pagesGym Web Projectkomal naeemNo ratings yet
- SAP Data Warehouse Cloud Welcome GuideDocument30 pagesSAP Data Warehouse Cloud Welcome GuideSreedhar.DondapatiNo ratings yet
- Decision Support System & Management Information SystemDocument3 pagesDecision Support System & Management Information SystemJacob Snyder100% (1)
- An Introduction To Big DataDocument31 pagesAn Introduction To Big DataDewi ArdianiNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Storage Optical StorageDocument13 pagesMagnetic Storage Optical StorageATS TechnologyNo ratings yet
- DP 2 2 PracticeDocument4 pagesDP 2 2 PracticeNaufal AdliNo ratings yet
- SQL2Document22 pagesSQL2Lakshmi Bhramara Mutte AP21111200002No ratings yet
- Library Management System Adebesin Tobi Tosin-with-cover-page-V2Document71 pagesLibrary Management System Adebesin Tobi Tosin-with-cover-page-V2Khushi SinghNo ratings yet
- Seminar Report AlishaDocument22 pagesSeminar Report AlishaAlisha KhanNo ratings yet
- Activity 1Document4 pagesActivity 1siejuroa23No ratings yet
- DDN Presentation PPTDocument32 pagesDDN Presentation PPTjanmejoy.rayNo ratings yet
- How To Display Information On A Dashboard 1713162874Document15 pagesHow To Display Information On A Dashboard 1713162874imtiazsoftNo ratings yet
- Health Information Technology and Management 1st Edition Gartee Test BankDocument36 pagesHealth Information Technology and Management 1st Edition Gartee Test Bankcourtneyharrisbpfyrkateq100% (36)
- 206-Manasi Bonde-EXPERIMENT NO 1Document10 pages206-Manasi Bonde-EXPERIMENT NO 1Manasi BondeNo ratings yet
- Nhibernate Reference PDFDocument258 pagesNhibernate Reference PDFDaniel Martínez ArceNo ratings yet
- Data Warehouse 14regDocument2 pagesData Warehouse 14regPonni SNo ratings yet
- Data Cleaning Data Transformation Data Reduction Discretization and Generating Concept HierarchiesDocument25 pagesData Cleaning Data Transformation Data Reduction Discretization and Generating Concept HierarchiesMik ClashNo ratings yet
- Suleman Khan: Professional SummaryDocument3 pagesSuleman Khan: Professional SummaryMurtaza AliNo ratings yet
- Looker For Amazon RedshiftDocument9 pagesLooker For Amazon Redshiftsheikh abdullah aleemNo ratings yet
- Intermediate SQLDocument46 pagesIntermediate SQLPaylaşım KanalıNo ratings yet
- 1900 - John Burnet - The Ethics of AristotleDocument593 pages1900 - John Burnet - The Ethics of AristotleRobertoNo ratings yet
- CheatsDocument28 pagesCheatsNeil YoungNo ratings yet
- IT1402 MWT Notes - CSE TUBE PDFDocument112 pagesIT1402 MWT Notes - CSE TUBE PDFsiva sekharNo ratings yet
- Job Finder - Problem DescriptionDocument14 pagesJob Finder - Problem Descriptionsvetoslav k. petkovNo ratings yet
- Course 1 Module 02 Lesson 5Document7 pagesCourse 1 Module 02 Lesson 5Rohit AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Oracle Insert, Delete, Update - DMLDocument4 pagesChapter 3 Oracle Insert, Delete, Update - DMLAli Sheikh AhmedNo ratings yet
- Sample QstnsDocument4 pagesSample QstnsShabeer Ali PCNo ratings yet
- Information Retrieval: DR Sharifullah Khan Nust SeecsDocument32 pagesInformation Retrieval: DR Sharifullah Khan Nust SeecsSaad Bin ShahidNo ratings yet
NIMP 20303 SmartManufacturing
NIMP 20303 SmartManufacturing
Uploaded by
Ayesha EzaneeOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
NIMP 20303 SmartManufacturing
NIMP 20303 SmartManufacturing
Uploaded by
Ayesha EzaneeCopyright:
Available Formats
New Industrial
MISSION 2 : TECH UP FOR A DIGITALLY VIBRANT NATION Master Plan 2030 79
Box Article 5.1:
What is Smart Manufacturing?
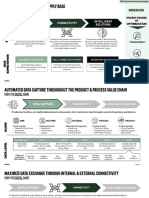
Smart manufacturing40 involves the seamless integration and connectivity of physical and digital
processes across factories and the supply chain to optimise manufacturing operations and processes.
By transforming and improving the ways in which people, processes and technologies operate, smart
manufacturing facilitates the delivery of critical information for quality decision-making, enhanced
efficiency, cost reduction and increased agility.
The element of smart manufacturing includes:
• Internet of Things (IoT) to connect devices, machines and sensors to collect and exchange data
in real time. This creates a networked ecosystem, where machines and systems communicate
seamlessly.
• Data analytics and big data tools to analyse vast amounts of data collected from various
sources within the manufacturing process. This unlocks insights for decision-making, predictive
maintenance and optimisation of production processes.
• Artificial intelligence and machine learning to automate tasks and continuously improve
manufacturing processes. AI-driven systems are capable to identify patterns, adjust to dynamic
conditions and optimise operations in real-time.
• Robotics and automation enable the efficient and precise execution of repetitive and labour-
intensive tasks. These technologies encompass robotic arms, automated guided vehicles (AGVs)
and autonomous systems, which streamline production processes and minimize the need for
human intervention.
• Cloud computing to store, process and analyse manufacturing data. Cloud infrastructure
provides scalable and cost-effective resources for data storage, computing power and
collaborative applications.
• Cybersecurity to protect digital systems, networks and data from cyber threats. Secure networks
and protocols are essential to safeguard sensitive information and maintain the integrity of
manufacturing processes.
Advanced automation Additive
and robotics Artificial intelligence manufacturing
Predictive analytics for:
• Automate tasks such as
• continuous self-
welding, assembling, • Rapid prototyping
optimisation
inspecting defects and of new products
• product design and
packaging
development
Cloud computing
Large data storage and analytics to:
• track production output
• identify improvements
Source: The Global Smart Industry Readiness Index Initiative: Manufacturing Transformation
Insights Report 2022, World Economic Forum
MINISTRY OF INVESTMENT, TRADE AND INDUSTRY
You might also like
- Industry 4.0 Presentation I Covered Till NowDocument13 pagesIndustry 4.0 Presentation I Covered Till NowDipta Karar100% (1)
- Ch4 - System Security II - Auditing Database SystemsDocument32 pagesCh4 - System Security II - Auditing Database SystemsGonzalo Jr. RualesNo ratings yet
- IoT in Electronics Manufacturing (White Paper)Document17 pagesIoT in Electronics Manufacturing (White Paper)John JalaniNo ratings yet
- Slowly Changing DimensionsDocument26 pagesSlowly Changing DimensionsPavanNo ratings yet
- Dmfa 2Document28 pagesDmfa 2samina.22110159No ratings yet
- AI - 副本Document41 pagesAI - 副本22055419No ratings yet
- 8 - Rise of Digital EconomyDocument19 pages8 - Rise of Digital EconomyAchmad P. RifaiNo ratings yet
- Revolusi Industri 4.0Document7 pagesRevolusi Industri 4.0Jhon WahlaNo ratings yet
- Industry 4.0Document27 pagesIndustry 4.0willy wigia sofyanNo ratings yet
- Unit-3 Industry 4.0Document39 pagesUnit-3 Industry 4.0BALRAM SINGHNo ratings yet
- Relevance of Industry 4.0Document16 pagesRelevance of Industry 4.0Sharon RuthNo ratings yet
- EdgetoCloud IIoT For Condition Monitoring in Manufacturing Systems With Ubiquitous Smart SensorsSensorsDocument15 pagesEdgetoCloud IIoT For Condition Monitoring in Manufacturing Systems With Ubiquitous Smart SensorsSensorsNicolas Anton RamirezNo ratings yet
- Internet of ThingsDocument23 pagesInternet of ThingsVikas VarmaNo ratings yet
- IoT in Manufacturing - GMAP InsiderDocument48 pagesIoT in Manufacturing - GMAP Insidermihirjayaraman100% (2)
- 2015 Advanced Manufacturing Tech ClusterDocument8 pages2015 Advanced Manufacturing Tech ClusterPyae PhyoaungNo ratings yet
- Industria 4.0 National PlanDocument18 pagesIndustria 4.0 National PlaniqpucelaNo ratings yet
- White Paper Edge Data Process 2023 enDocument11 pagesWhite Paper Edge Data Process 2023 ening.serpelNo ratings yet
- Verbrec - Cap Statement - Automation and ControlDocument4 pagesVerbrec - Cap Statement - Automation and Controlarek.kulikowskiNo ratings yet
- Digital Factory: The Information Systems AspectDocument17 pagesDigital Factory: The Information Systems AspectMona IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Industry 4 White PaperDocument24 pagesManufacturing Industry 4 White PaperHoàng Thắng50% (2)
- Zyfra Eng 2020Document31 pagesZyfra Eng 2020Manish ShahNo ratings yet
- Smart Manufacturing With Prescriptive Analytics: A Review of The Current Status and Future WorkDocument5 pagesSmart Manufacturing With Prescriptive Analytics: A Review of The Current Status and Future WorkalejandrozambranoNo ratings yet
- PCA Controlling and Monitoring Semiconductor Manufacturing Process Usingsmart TechnologiesDocument19 pagesPCA Controlling and Monitoring Semiconductor Manufacturing Process Usingsmart TechnologiesPeaceNo ratings yet
- Solution Brief Process 2023 enDocument6 pagesSolution Brief Process 2023 ening.serpelNo ratings yet
- Mastering Digital Transformation Key Strategies For ManufacturingDocument8 pagesMastering Digital Transformation Key Strategies For ManufacturingDhananjaya ReddyNo ratings yet
- Machine Learning in Manufacturing and Industry 4.0 ApplicationsDocument7 pagesMachine Learning in Manufacturing and Industry 4.0 ApplicationsAbhijna AdigaNo ratings yet
- Smart Factory of Industry 4.0: Key Technologies, Application Case, and ChallengesDocument15 pagesSmart Factory of Industry 4.0: Key Technologies, Application Case, and ChallengesMohd Hizami Ab HalimNo ratings yet
- Disruptive Technology Industry 4.0Document8 pagesDisruptive Technology Industry 4.0Abhilash ChessNo ratings yet
- 4th Industrial Revolution in EducationDocument21 pages4th Industrial Revolution in EducationjoewinNo ratings yet
- Nicolas Rafael Palomino W3C ApplicationDocument11 pagesNicolas Rafael Palomino W3C ApplicationLis LisNo ratings yet
- Digital Manufacturing: Industry FocusDocument40 pagesDigital Manufacturing: Industry FocusGeorge ThomasNo ratings yet
- Ajeassp 2024 33 39Document7 pagesAjeassp 2024 33 39Kathirvel AyyaswamyNo ratings yet
- IOT Revisão BibliográficaDocument4 pagesIOT Revisão Bibliográficaaguinaldomendes.jrNo ratings yet
- Industr: Global SummitDocument5 pagesIndustr: Global SummitAarush JainNo ratings yet
- Controlling and Monitoring Semiconductor Manufacturing Process Usingsmart TechnologiesDocument19 pagesControlling and Monitoring Semiconductor Manufacturing Process Usingsmart TechnologiesqxzyNo ratings yet
- AMFG Role Description - QA LeadDocument11 pagesAMFG Role Description - QA LeadОлексій «HELP»No ratings yet
- ME 2021 Digital One Pager PDFDocument4 pagesME 2021 Digital One Pager PDFTuan VuNo ratings yet
- Smart Factory White PaperDocument34 pagesSmart Factory White Paperkevin21790100% (1)
- Que t1 OrangeDocument200 pagesQue t1 OrangeM Sohail IqbalNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument15 pagesPDFNorfazeli JaafarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 01Document24 pagesLecture 01salman haiderNo ratings yet
- Intelligent Engines: Revolutionizing Manufacturing and Supply Chains With AIDocument14 pagesIntelligent Engines: Revolutionizing Manufacturing and Supply Chains With AIInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Impact of Industry 4.0 On Automobile IndustryDocument11 pagesImpact of Industry 4.0 On Automobile IndustryNishita VoraNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence in Electronics Design and ManufacturingDocument9 pagesArtificial Intelligence in Electronics Design and Manufacturingatharvmote521No ratings yet
- Accenture 804893 Smart Production POV FinalDocument20 pagesAccenture 804893 Smart Production POV FinalPraneeth BakkiNo ratings yet
- Advanced Virtual Manufacturing Systems 1Document26 pagesAdvanced Virtual Manufacturing Systems 1Aswin madhuNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Big Data Ecosystem A Systematic Literature ReviewDocument20 pagesManufacturing Big Data Ecosystem A Systematic Literature ReviewLeonardo SanchezNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Log Research BookDocument18 pagesManufacturing Log Research BookAjit Kumar SubramanyamNo ratings yet
- 2024年智能制造行业趋势分析Document5 pages2024年智能制造行业趋势分析xmcloudlessNo ratings yet
- Overcoming Data Silos and Information SaturationDocument7 pagesOvercoming Data Silos and Information SaturationgarmentssNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Part 2 4th UpdatedDocument9 pagesWeek 2 Part 2 4th Updatedmomo AdamNo ratings yet
- Role of It in Industry: 6 Sem ME Industrial EngineeringDocument11 pagesRole of It in Industry: 6 Sem ME Industrial EngineeringShyamNo ratings yet
- Role of It in Industry: 6 Sem ME Industrial EngineeringDocument11 pagesRole of It in Industry: 6 Sem ME Industrial EngineeringShyamNo ratings yet
- Applied Sciences: Smart Manufacturing Real-Time Analysis Based On Blockchain and Machine Learning ApproachesDocument22 pagesApplied Sciences: Smart Manufacturing Real-Time Analysis Based On Blockchain and Machine Learning ApproachesZeinab ShahbaziNo ratings yet
- Iot Project PowerpointDocument17 pagesIot Project Powerpointalissonzkv100% (1)
- 5 Key Digital Technologies That Are Transforming The Manufacturing Industry - Blog - TechigaiDocument15 pages5 Key Digital Technologies That Are Transforming The Manufacturing Industry - Blog - Techigaitechigai 123No ratings yet
- BK-IT26 Sensor Tech (Brochure) 10Document6 pagesBK-IT26 Sensor Tech (Brochure) 10zackyat7976No ratings yet
- SL182 enDocument2 pagesSL182 enMas CarrickNo ratings yet
- Intelligent ManufacturingDocument7 pagesIntelligent ManufacturingAli Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- IoT TillMidsem 1Document270 pagesIoT TillMidsem 1Raja UikeyNo ratings yet
- AI in Manufacturing Driving Innovation and Efficiency: A Comprehensive Toolkit for Startups and Maintenance Ladyluck M: 1, #1From EverandAI in Manufacturing Driving Innovation and Efficiency: A Comprehensive Toolkit for Startups and Maintenance Ladyluck M: 1, #1No ratings yet
- Gym Web ProjectDocument20 pagesGym Web Projectkomal naeemNo ratings yet
- SAP Data Warehouse Cloud Welcome GuideDocument30 pagesSAP Data Warehouse Cloud Welcome GuideSreedhar.DondapatiNo ratings yet
- Decision Support System & Management Information SystemDocument3 pagesDecision Support System & Management Information SystemJacob Snyder100% (1)
- An Introduction To Big DataDocument31 pagesAn Introduction To Big DataDewi ArdianiNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Storage Optical StorageDocument13 pagesMagnetic Storage Optical StorageATS TechnologyNo ratings yet
- DP 2 2 PracticeDocument4 pagesDP 2 2 PracticeNaufal AdliNo ratings yet
- SQL2Document22 pagesSQL2Lakshmi Bhramara Mutte AP21111200002No ratings yet
- Library Management System Adebesin Tobi Tosin-with-cover-page-V2Document71 pagesLibrary Management System Adebesin Tobi Tosin-with-cover-page-V2Khushi SinghNo ratings yet
- Seminar Report AlishaDocument22 pagesSeminar Report AlishaAlisha KhanNo ratings yet
- Activity 1Document4 pagesActivity 1siejuroa23No ratings yet
- DDN Presentation PPTDocument32 pagesDDN Presentation PPTjanmejoy.rayNo ratings yet
- How To Display Information On A Dashboard 1713162874Document15 pagesHow To Display Information On A Dashboard 1713162874imtiazsoftNo ratings yet
- Health Information Technology and Management 1st Edition Gartee Test BankDocument36 pagesHealth Information Technology and Management 1st Edition Gartee Test Bankcourtneyharrisbpfyrkateq100% (36)
- 206-Manasi Bonde-EXPERIMENT NO 1Document10 pages206-Manasi Bonde-EXPERIMENT NO 1Manasi BondeNo ratings yet
- Nhibernate Reference PDFDocument258 pagesNhibernate Reference PDFDaniel Martínez ArceNo ratings yet
- Data Warehouse 14regDocument2 pagesData Warehouse 14regPonni SNo ratings yet
- Data Cleaning Data Transformation Data Reduction Discretization and Generating Concept HierarchiesDocument25 pagesData Cleaning Data Transformation Data Reduction Discretization and Generating Concept HierarchiesMik ClashNo ratings yet
- Suleman Khan: Professional SummaryDocument3 pagesSuleman Khan: Professional SummaryMurtaza AliNo ratings yet
- Looker For Amazon RedshiftDocument9 pagesLooker For Amazon Redshiftsheikh abdullah aleemNo ratings yet
- Intermediate SQLDocument46 pagesIntermediate SQLPaylaşım KanalıNo ratings yet
- 1900 - John Burnet - The Ethics of AristotleDocument593 pages1900 - John Burnet - The Ethics of AristotleRobertoNo ratings yet
- CheatsDocument28 pagesCheatsNeil YoungNo ratings yet
- IT1402 MWT Notes - CSE TUBE PDFDocument112 pagesIT1402 MWT Notes - CSE TUBE PDFsiva sekharNo ratings yet
- Job Finder - Problem DescriptionDocument14 pagesJob Finder - Problem Descriptionsvetoslav k. petkovNo ratings yet
- Course 1 Module 02 Lesson 5Document7 pagesCourse 1 Module 02 Lesson 5Rohit AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Oracle Insert, Delete, Update - DMLDocument4 pagesChapter 3 Oracle Insert, Delete, Update - DMLAli Sheikh AhmedNo ratings yet
- Sample QstnsDocument4 pagesSample QstnsShabeer Ali PCNo ratings yet
- Information Retrieval: DR Sharifullah Khan Nust SeecsDocument32 pagesInformation Retrieval: DR Sharifullah Khan Nust SeecsSaad Bin ShahidNo ratings yet