Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Science 6 Worksheet
Science 6 Worksheet
Uploaded by
maribel magnayeOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Science 6 Worksheet
Science 6 Worksheet
Uploaded by
maribel magnayeCopyright:
Available Formats
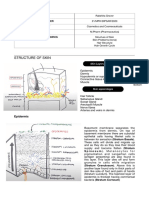
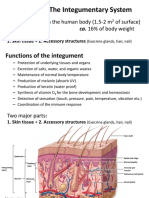
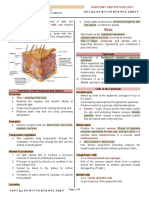
Epidermis
SKIN Protection
Cushions and insulates and is waterproof
Protects from chemicals, heat, cold,
bacteria
Screens UV
Synthesizes vitamin D with UV
Regulates body heat
Prevents unnecessary water loss
Sensory reception (nerve endings)
Hypodermis
“Hypodermis” (Gk) = below the skin
“Subcutaneous” (Latin) = below the skin
Also called “superficial fascia”
“fascia” (Latin) =band; in anatomy: sheet of
connective tissue
Fatty tissue which stores fat and anchors
skin (areolar tissue and adipose cells)
Different patterns of accumulation
of hard keratin (male/female)
Nail corresponds to hooves and claws
grows from nail matrix
Dermis
Strong, flexible
connective tissue: your
“hide”
Cells: fibroblasts,
macrophages, mast cells,
WBCs
Fiber types: collagen,
elastic, reticular
Rich supply of nerves
and vessels
Critical role in
temperature regulation
Parts and Functions of Digestive System (the vessels)
Two layers (see next
slides)
Papillary – areolar
connective tissue;
includes dermal papillae
Reticular – “reticulum”
(network) of collagen
and reticular fibers
You might also like
- Anatomy & Physiology With Pathophysiology Lecture (Midterms)Document4 pagesAnatomy & Physiology With Pathophysiology Lecture (Midterms)Millen ArenasNo ratings yet
- E1.4 Integumentary SystemDocument6 pagesE1.4 Integumentary SystemhzntrpNo ratings yet
- 7 Integumentary System PDFDocument38 pages7 Integumentary System PDFdaisysintszwaiNo ratings yet
- Structure of Skin, Skin Problems, Hair Structure and Hair Growth CycleDocument8 pagesStructure of Skin, Skin Problems, Hair Structure and Hair Growth CycleRakshita GroverNo ratings yet
- Histology Module 1 Review PT 2Document13 pagesHistology Module 1 Review PT 2Neera SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System 2Document7 pagesIntegumentary System 220237445No ratings yet
- Burns SemDocument29 pagesBurns SemEsther Marie SazonNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument6 pagesIntegumentary SystemDelosreyes Joy Ann ANo ratings yet
- Skin, Hair, and NailsDocument9 pagesSkin, Hair, and NailsJustine JimenezNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - The Integumentary SystemDocument6 pagesLesson 3 - The Integumentary SystemJoseayn EspenidoNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Integumentary System 1Document5 pagesAnaphy Integumentary System 1xz598vbhjnNo ratings yet
- Safari - Feb 21, 2024 at 11:49 AM 2Document1 pageSafari - Feb 21, 2024 at 11:49 AM 2syansyncNo ratings yet
- CH - 04 - SKIN AND BODY MEMBRANESDocument76 pagesCH - 04 - SKIN AND BODY MEMBRANESCheska DillupacNo ratings yet
- C5-Integumentary SystemDocument7 pagesC5-Integumentary SystemLorrine MagramoNo ratings yet
- Integ NotesDocument10 pagesInteg Notesannj.ras.swuNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology-NotesDocument6 pagesAnatomy and Physiology-NotesAkirah Jewelle JaenNo ratings yet
- SkinDocument7 pagesSkincycyycNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9: Skin and ITS APPENDAGES: (Vital Organs)Document4 pagesChapter 9: Skin and ITS APPENDAGES: (Vital Organs)Hannah Beatrice Adame TamayoNo ratings yet
- The Integumentary SystemDocument2 pagesThe Integumentary SystemKARYLLE JUNE PONTERASNo ratings yet
- III. Integumentary SystemDocument10 pagesIII. Integumentary SystemNhell HoyohoyNo ratings yet
- WEEK 5 TRANS AnaphyDocument2 pagesWEEK 5 TRANS AnaphygazzyngsalvadorNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument6 pagesIntegumentary SystemHannah SchwartzNo ratings yet
- BIOL 2210 Chapter 6, Integument System-1Document15 pagesBIOL 2210 Chapter 6, Integument System-1KellyPatrick SpencerNo ratings yet
- PowerPoint - Presentation - About - Integumentary - SystemDocument27 pagesPowerPoint - Presentation - About - Integumentary - SystemPrayl Hope NapanoNo ratings yet
- Integumentary and Nervous System: 5141 CN 111 - Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument8 pagesIntegumentary and Nervous System: 5141 CN 111 - Anatomy and PhysiologyAlthea Joyce OngNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument3 pagesIntegumentary SystemRav Evan VigillaNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Integumentary System LectureDocument10 pagesAnaphy Integumentary System LectureAira PayadNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Rev Chapt 3Document8 pagesAnaphy Rev Chapt 3crptzxraffNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System HistologyDocument10 pagesIntegumentary System HistologyDonto KonoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument27 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyFaithNo ratings yet
- NeoNotes Derma HighlightedDocument32 pagesNeoNotes Derma Highlightedyomna.saaNo ratings yet
- Workbook Activity #13: Integumentary System (Skin) General ObjectiveDocument5 pagesWorkbook Activity #13: Integumentary System (Skin) General ObjectiveAmbaw PutiiNo ratings yet
- Skin and Body MembranesDocument8 pagesSkin and Body MembranesVincent AlgarmeNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Mia Rev4Document4 pagesAnaphy Mia Rev4antonettevegamia3No ratings yet
- Integ PPT BasedDocument12 pagesInteg PPT BasedKathleen BalauagNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument8 pagesIntegumentary SystemDOROLA CRIS JANELICA R.No ratings yet
- Physiology: Afta. A.Fteeh - EomDocument8 pagesPhysiology: Afta. A.Fteeh - Eomانس ابوهيبةNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument5 pagesIntegumentary SystemChan TalNo ratings yet
- MT1 HSCI LEC L3 Integumentary SystemDocument9 pagesMT1 HSCI LEC L3 Integumentary SystemSEBASTIEN ANDREI BUENAFENo ratings yet
- Lab 5 Tissues - Lab ReportDocument5 pagesLab 5 Tissues - Lab ReportbrittNo ratings yet
- Tissues, SkinDocument11 pagesTissues, SkinkimcheeseNo ratings yet
- Integumentary - EmbryoDocument6 pagesIntegumentary - EmbryoMeow CattoNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Lab IntegDocument5 pagesAnaphy Lab IntegPhoemela Reign GregorioNo ratings yet
- Chap3 Integ Anaphy NotesDocument11 pagesChap3 Integ Anaphy NotesAxel Neil VidalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 IntegumentaryDocument2 pagesChapter 5 IntegumentaryElle UgaddanNo ratings yet
- Connective TissueDocument15 pagesConnective TissueFer LópezNo ratings yet
- 1.03 - Evidence of Science and Technology During The Ancient TimesDocument13 pages1.03 - Evidence of Science and Technology During The Ancient Timeselio pascualNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument4 pagesIntegumentary SystemOddysa EstorqueNo ratings yet
- Skin and Appendages (PFOS-1 2014-15 Students Version)Document24 pagesSkin and Appendages (PFOS-1 2014-15 Students Version)Chris Jardine LiNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument3 pagesIntegumentary SystemCarmela Cordon FelixNo ratings yet
- The Integumentary System: Prepared byDocument12 pagesThe Integumentary System: Prepared byErick Torres Gozum100% (1)
- Lab Act 3 - Integumentary SystemdocxDocument8 pagesLab Act 3 - Integumentary SystemdocxmendozakaceeyNo ratings yet
- Quick Study Guide To The Integumentary SystemDocument3 pagesQuick Study Guide To The Integumentary SystemMc Luis Glen AserdanoNo ratings yet
- Connective TissueDocument24 pagesConnective TissueIssa AvenaNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument4 pagesIntegumentary SystemCarylle Era DensingNo ratings yet
- DawitDocument14 pagesDawitSaid AbdelaNo ratings yet
- 5 - IntegDocument8 pages5 - IntegGel Austin PascuaNo ratings yet
- Skin Physiology: Lecturer:Dr Herman Mulijadi MS, SPKPDocument59 pagesSkin Physiology: Lecturer:Dr Herman Mulijadi MS, SPKPJosephine SNo ratings yet
- Skin and Its AppendagesDocument3 pagesSkin and Its AppendagesMarchylle Faye JimenezNo ratings yet
- Neonatal HematologyDocument83 pagesNeonatal HematologyJay-Anne RapanoNo ratings yet
- 4D OvaryDocument108 pages4D OvaryrubenNo ratings yet
- Principais Sistemas Do OrganismoDocument5 pagesPrincipais Sistemas Do OrganismoDiana VieiraNo ratings yet
- Histology: Lecture NotesDocument232 pagesHistology: Lecture NotesAdrian PuscasNo ratings yet
- Notes On Anatomy and Physiology For Yoga PDFDocument195 pagesNotes On Anatomy and Physiology For Yoga PDFPetar MogilskiNo ratings yet
- DLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W2Document5 pagesDLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W2Geoffrey Tolentino-Unida100% (1)
- Atlas of StainsDocument120 pagesAtlas of StainsMarko ZavbiNo ratings yet
- Tas Kantung Darah BPS-Terumo-CatalogDocument4 pagesTas Kantung Darah BPS-Terumo-CatalogDoni VingkyNo ratings yet
- Ms SEEMABALAYAN 9 24 2022 7 04 10 PMDocument9 pagesMs SEEMABALAYAN 9 24 2022 7 04 10 PMMohammad Ali NPNo ratings yet
- Final Draft of Sample Autopsy From Lawson CaseDocument8 pagesFinal Draft of Sample Autopsy From Lawson CaseMyra Beatriz de LeonNo ratings yet
- For 350 MbbsDocument48 pagesFor 350 MbbsNAYAB HASSANo ratings yet
- Epithelium SummaryDocument7 pagesEpithelium SummaryElena ArvanitiNo ratings yet
- Immune Response To Infectious DiseaseDocument2 pagesImmune Response To Infectious Diseasekiedd_04100% (1)
- Jurnal 1 PapilitisDocument10 pagesJurnal 1 PapilitisCut Keumala PutriNo ratings yet
- Paget Disease (Osteitis Deformans)Document14 pagesPaget Disease (Osteitis Deformans)Orson SimonNo ratings yet
- 06 Ra Abdominal TuberculosisDocument10 pages06 Ra Abdominal TuberculosisMade Oka HeryanaNo ratings yet
- Biology - Google Drive 123456Document168 pagesBiology - Google Drive 123456Nirmal ChakravarthyNo ratings yet
- Colour Atlas of The Anatomy and Pathology of The EpitympanumDocument110 pagesColour Atlas of The Anatomy and Pathology of The Epitympanumapi-26081450No ratings yet
- Muscular System: The Medica ZoneDocument12 pagesMuscular System: The Medica ZoneJury AlghannamNo ratings yet
- 6 Amelogenesis, Dentinogenesis and Root FormationDocument4 pages6 Amelogenesis, Dentinogenesis and Root FormationAsma AnjumNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life 2Q ExamDocument5 pagesEarth and Life 2Q ExamImmanuel GranadaNo ratings yet
- Muscle BiomechanicsDocument4 pagesMuscle BiomechanicsPratyaksha TiwariNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument46 pagesAnimal TissuesTrisha ZamboangaNo ratings yet
- Myelo Blog PDFDocument158 pagesMyelo Blog PDFNino GumbanNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument9 pagesBiologyvibesatevenNo ratings yet
- A Newly Married Couple Does Not Want Have Children For Few YearsDocument6 pagesA Newly Married Couple Does Not Want Have Children For Few YearsSHILPA AGARWALNo ratings yet
- When The Tummy Gets BusyDocument59 pagesWhen The Tummy Gets BusyChris Reubal BuscayNo ratings yet
- Pathophysio DengueDocument1 pagePathophysio DengueDANICA BONBONNo ratings yet
- CSF Shift Edema PublishedDocument15 pagesCSF Shift Edema PublishedIype CherianNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Anatomy and Physiology and HomeostasisDocument33 pagesIntroduction of Anatomy and Physiology and HomeostasisJean Rose SalahayNo ratings yet