Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biology - All About Transportation of Cells, Cellular Respiration + Photosynthesis
Biology - All About Transportation of Cells, Cellular Respiration + Photosynthesis
Uploaded by
Adelaide Fleona Marie TrinidadOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Biology - All About Transportation of Cells, Cellular Respiration + Photosynthesis
Biology - All About Transportation of Cells, Cellular Respiration + Photosynthesis
Uploaded by
Adelaide Fleona Marie TrinidadCopyright:
Available Formats
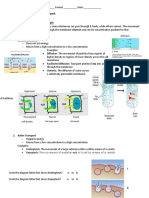
INTEGRATED SCIENCE 2 - BIOLOGY Diffusion - movement of molecules from an area of Active transport
higher concentration to an area of lower
SLG 15.1 - TRANSPORT ACROSS MEMBRANE energy is needed to transport materials, across the
concentration.
membrane.
(ex: Applying cologne)
energy is needed because the movement is against
Cell Membrane
Osmosis - special type of diffusion which focuses on the concentration gradient.
It serves as a gatekeeper of the cell-also called as the movement of water molecules across the
moves from an area of low concentration to an area of
fluid mosaic. It has 3 primary components: membrane.
high concentration.
phospholipid bilayer, proteins, and carbohydrates.The
a. isotonic
fluidity of the cell membrane is essential to its ability
- when a cell is in its natural
to control the movement of substances into and out of
environment
the cell.
- normal and functioning
Phospholipid bilayer b. Hypotonic
- solution outside the cell has lower
Primary structure responsible for the semi-permeable concentration water will move into
of the cell membrane. the cell & the cell will swell and
burst. Endocytosis
2 parts: Hydrophilic head (always face the watery
surroundings), hydrophobic tails (“water-heating”, c. Hypertonic
encloses material within a vesicle inside the cell.
avoids water). - solution outside the cell has higher
solute concentration and water will “cellular eating” -> solid molecules -> phagocytosis
Proteins - also help in cellular communication move out of the cell to dissolve the
extra solute. “cellular drinking” -> liquid molecules -> pinocytosis
Carbohydrates - help in cell recognition, the ability to
- cell loses water, shrinks, and dies. Exocytosis
distinguish one cell from another.
dumps its contents outside the cell
TRANSPORT ACROSS THE MEMBRANE cell transports molecules out of the cell
Passive transport vesice fuses its membrane
does not require of energy or ATP (Adenosine (pagawason ang proteins/waste products for or
Triphosphate) - the energy currency of life. anything na gi carry)
happens when substances move from an area of
higher concentration to an area of lower Facilitated diffusion - Diffusion of solutes through
concentration. transport of proteins ins plasma membrane.Molecules
(The three types of passive transport are diffusion, pass through special gates called transport proteins.
osmosis, and facilitated diffusion.)
___________________________________________
SLG 15.2 - CELLULAR RESPIRATION
Consumers get their energy from the food they eat,
such as plants, and other organisms, in a process
known as cellular respiration.
Internal and External respiration
Respiration has two major parts: the external
(physiological) respiration and the internal (cellular) Aerobic and Anaerobic respiration
respiration.
These types differ on whether oxygen is present or
absent. cellular respiration allows our cells to get energy from
External respiration, commonly known as breathing, Anaerobic respiration is a cellular respiration that the food we eat. Food need to be digested and
refers to the (inhalation) and releases air from the occurs without oxygen. broken down into smaller sugar, glucose. The energy
body that brings air into the lungs (exhalation). It also stored in glucose is transferred to ATP, which is the
Aerobic respiration occurs in the presence of energy-carrier molecule that provides the energy for
refers to the gas exchange of oxygen and carbon
oxygen. cellular (biological) processes.
dioxide into the bloodstream through diffusion.
(food - glucose - ATP)
Internal respiration: gas exchange (carbon dioxide
and oxygen between the blood vessel and
tissue/cells. Aerobic respiration
Glucose & oxygen undergo synthesis reaction,
producing ATP. CO2 and H2O are formed and
released as by products.
Aerobic respiration occurs in the cytoplasm and
Internal respiration occurs at the cellular and tissue mitochondria of the cells of eukaryotes.
level when oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged In prokaryotes, it occurs in the cytoplasm and the
between the cells and the bloodstream in the blood special structure of their cell membrane.
vessels. Internal respiration has two types: aerobic
and anaerobic respiration.
Anaerobic respiration In photosynthesis, plants use the light energy from layer carries out photosynthesis and it s where gas is
the sun to build simple molecules of carbon dioxide stored.
Does not require the presence of oxygen to occur.
(CO2) and water (H2O) to move complex organic
Glucose undergoes decomposition, turning ATP
molecule sugar (C6H1206). Aside from sugar, water
which is caused by the cell and lactic acid in animals
(H2O) is also released during evapotranspiration and
or ethanol in plants, and yeast.
oxygen (O2) as the byproduct.
(New word - Evapotranspiration: Evaporation +
Transpiration-release of water vapor from plant
leaves)
CAM Photosynthesis
open stomata at night PHOTOSYNTHESIS AND CHLORPLAST
avoid opening stomata at the heat of the day In all photosynthetic eukaryotes, photosynthesis
occurs in the organelle called chloroplast.
SLG 15.3.1 - PHOTOSYNTHESIS
SLG 15.3.2 - PHOTOSYNTHESIS A double membrane organelle consisting of inner and
Humans - secondary consumers outer membranes.
Photosynthesis and Plant leaves
Primary consumers rely on the producers as their Organelles:
food, while producers get their energy from the sun as Photosynthesis occurs in leaves of plants, which are
the primary source. basically composed of layers of cells: upper Thylakoid (captures/traps the light) - a disc-shaped
epidermis, mesophyll, and lower epidermis. structure where chlorophyll is embedded in its
Producers, like plants, make use of the sun’s energy membrane.
to manufacture their own food in a process known as
photosynthesis. Each thylakoid has luman, which is an internal space
The Lower epidermis typically contains small between the thylakoid and membrane.
openings called stomata, which regulate the release
of water and exchange of 6CO2 and O2. An Granum (pl: grana) - a stack of thylakoids, which
Photosynthesis. is a multi-step process by which accessory cell called guard cell regulates the opening aims to form the third membrane later of the
plants use sunlight, water and carbon dioxide to and closing of each stomata. chloroplast.
produce oxygen (as a waste product) and energy in
the form of sugar. Stroma - a liquid-filled space that surrounds the
granum.
Mesophyll, is composed of palisade (this is where
the chloroplast is stored) & spongy layers. The
palisade layer is where most of the chloroplasts are
found that efficiently captures sun’s energy and where
photosynthesis is mostly carried out. The spongy
called photolysis into its constituent molecules
Hydrogen (H + ) and Oxygen (O2 ) through the
process called photolysis. Oxygen will then be
released in the atmosphere as a by-product.
An electron from water is removed and transferred to
NADP+ to form NADPH. In the process, a
phosphorus (Pi) is added to ADP to produce ATP.
ATP and NADPH are energy-carrier molecules, which
will be soon used in the light-independent reaction.
STAGES OF PHOTOSYNTHESIS In the light-independent reactions, the energy from
Photosynthesis involves two stages that occur the products of light-dependent reactions, ATP and
sequentially: light-dependent reactions and NADP, are used to drive the production of glucose.
light-independent reactions (Calvin cycle). As the After the energy from ATP and NADPH is used up,
name implies, light-dependent reactions occur with they revert to ADP and NADP + , return to the
the aid of sunlight while light-independent reactions light-dependent reactions, and the process goes on
occur even without sunlight. These two stages are and on.
compared in the table below.
Additional notes:
Chlorophyll
- absorbs the light
- pigment can be found in chloroplasts
Pi - Inorganic Phosphorus
ADP - Adenosine Diphosphate
ATP - Adenosine Triphosphate
Convert first to Acetyl CoA para ma transport to the
citric acid cycle.
In the light dependent reactions, the different
processes occur simultaneously. The green pigments
chlorophyll in the chloroplast captures light energy
and becomes highly energized, this is called
photoactivation. Water absorbed by the plants
through its roots will be broken through the process
You might also like
- Chapter 15-Basics of Electrical Systems: True/FalseDocument190 pagesChapter 15-Basics of Electrical Systems: True/FalsewesamNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument6 pagesUntitled49 - Kaycee JoaquinNo ratings yet
- Botany Midterms Reviewer - Millen O. Arenas Transport MechanismDocument11 pagesBotany Midterms Reviewer - Millen O. Arenas Transport MechanismAleczandra QuesadaNo ratings yet
- General Biology (Grade 11 STEM - 1st Semester)Document4 pagesGeneral Biology (Grade 11 STEM - 1st Semester)alfonsogwenmnqNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Chapter 3 Cell Structures and Their FunctionsDocument27 pagesAnaphy Chapter 3 Cell Structures and Their FunctionsVince Martin ManaigNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For Genbio 3RD QTRDocument6 pagesReviewer For Genbio 3RD QTRvmargajavierNo ratings yet
- Cell StructureDocument8 pagesCell StructureCRYSTAL A. ARIETANo ratings yet
- Part I: Cells: Overview of The Cellular Basis of LifeDocument5 pagesPart I: Cells: Overview of The Cellular Basis of LifeAldrin OjalesNo ratings yet
- Cell 1Document48 pagesCell 1Mihai ChirniciniiNo ratings yet
- GenBio9 051716Document35 pagesGenBio9 051716salihuddinalkaizarNo ratings yet
- Movement of Substances Across Cell MembraneDocument4 pagesMovement of Substances Across Cell MembraneNNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 ReveiwerDocument8 pagesChapter 3 ReveiwerrizzamaegomezoctavianoNo ratings yet
- Biology Short NoteDocument10 pagesBiology Short NotePatrix ParkerNo ratings yet
- PRINTED Cell HandoutsDocument8 pagesPRINTED Cell HandoutsKate GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Three Types of Osmotic Solutions A. IsotonicDocument5 pagesThree Types of Osmotic Solutions A. IsotonicRuby Jane LaquihonNo ratings yet
- Transport MechanismDocument31 pagesTransport MechanismCecillia Evan100% (1)
- GenBio - 1st QuarterDocument13 pagesGenBio - 1st QuarterCc TvNo ratings yet
- Biology NotesDocument14 pagesBiology NotesZuZZi PlayNo ratings yet
- Animal CellDocument4 pagesAnimal CellCristel WeeNo ratings yet
- Rev Notes ch03 eDocument7 pagesRev Notes ch03 ekathk2016No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Cell Structures & Their Functions: Certain Molecules To Enter/exit The Cell)Document5 pagesChapter 3 Cell Structures & Their Functions: Certain Molecules To Enter/exit The Cell)Gellyace A.No ratings yet
- Reviewer (Cells)Document6 pagesReviewer (Cells)Sophia Mae ClavecillaNo ratings yet
- Biology - Module 4Document6 pagesBiology - Module 4ASHLEY MONICA PLATANo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3: Cell Structures and Their Functions CellDocument2 pagesCHAPTER 3: Cell Structures and Their Functions CellCELLINA CLARISSE DE LEONNo ratings yet
- Week 3Document3 pagesWeek 3naomimarielleNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane Membrane: How Substances Get Across The MembraneDocument15 pagesCell Membrane Membrane: How Substances Get Across The MembraneMariane CarandangNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument8 pagesBiologyClare Anne Therese EsbietoNo ratings yet
- Anph Cells and TissuesDocument6 pagesAnph Cells and Tissues屋鈴No ratings yet
- Cell Membrane & HomeostasisDocument50 pagesCell Membrane & Homeostasisapi-233187566No ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology Reviewer: CHAPTER 3: Cell Structure and Their Functions 3.1 Cell StructureDocument4 pagesAnatomy & Physiology Reviewer: CHAPTER 3: Cell Structure and Their Functions 3.1 Cell StructureChris Deinielle Marcoleta SumaoangNo ratings yet
- Transport MembraneDocument2 pagesTransport Membranesna240839No ratings yet
- The Cellular Level of Organization PDFDocument7 pagesThe Cellular Level of Organization PDFGol D. AceNo ratings yet
- Hydrophobic or Water Fearing Hydrophilic or Water-Loving: Non Polar Tails Polar HeadsDocument2 pagesHydrophobic or Water Fearing Hydrophilic or Water-Loving: Non Polar Tails Polar Headsjust jungkookedNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane ReviewerDocument3 pagesCell Membrane ReviewerJohn Rey Magno SabalNo ratings yet
- Cells The Generalized Animal CellDocument5 pagesCells The Generalized Animal Cell'Ani RahcNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane Structure and FunctionDocument16 pagesCell Membrane Structure and FunctionKimberly SalarzaNo ratings yet
- ANAPHY - Cellular and Tissue Level of OrganizationDocument14 pagesANAPHY - Cellular and Tissue Level of OrganizationReed YangNo ratings yet
- Reviewer AnaphysDocument42 pagesReviewer AnaphysReed YangNo ratings yet
- Transport MechanismsDocument1 pageTransport MechanismsJayrelle D. SafranNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 - Cell Exchange of Materials Tissues Tonicity 2021Document72 pagesTopic 2 - Cell Exchange of Materials Tissues Tonicity 2021Ralph Rezin MooreNo ratings yet
- The Cell Theory States ThatDocument2 pagesThe Cell Theory States ThatMike MesaNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 Reviewer 1Document5 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Reviewer 1Shane Patricia CalmaNo ratings yet
- Act2 Bio SciDocument4 pagesAct2 Bio SciPamaran, Kristel DenishNo ratings yet
- Cell Boundaries Module 2Document17 pagesCell Boundaries Module 2Vedha SinghNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 Cell MembraneDocument3 pagesLesson 7 Cell MembraneThea MillanesNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1Document15 pagesGeneral Biology 1Beejae ApalisNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 (Reviewer)Document4 pagesLesson 1 (Reviewer)Faith Angela VillasfirNo ratings yet
- Edexcel IGCSE Human Biology Answers 2015Document32 pagesEdexcel IGCSE Human Biology Answers 2015George ApidiNo ratings yet
- GENERAL BIOLOGY 1 NotesDocument4 pagesGENERAL BIOLOGY 1 NotesAlfie Lyn PedregosaNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Processes Practice Worksheet: Name: Pidlaoan, Coleen LDocument5 pagesCell Structure and Processes Practice Worksheet: Name: Pidlaoan, Coleen LColeenNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Homeostasis and Transport Review PacketDocument9 pagesUnit 4 Homeostasis and Transport Review PacketShannon ErdmanNo ratings yet
- Prelecture Questions 2Document7 pagesPrelecture Questions 2kaslana kianaNo ratings yet
- Cell MembraneDocument3 pagesCell MembraneQaran PrintingNo ratings yet
- Is Reviewer 2B Cell PhysiologyDocument5 pagesIs Reviewer 2B Cell Physiologyajuj jerNo ratings yet
- Mahan 2Document7 pagesMahan 2KANT JAMES D. MAHANNo ratings yet
- Bio Exchange of MaterialsDocument12 pagesBio Exchange of Materials3.4 (2022) LAU JING XUAN DESTINEENo ratings yet
- Hap Chapter 3Document17 pagesHap Chapter 3jenf7481No ratings yet
- The Plasma Membrane and HomeostasisDocument13 pagesThe Plasma Membrane and HomeostasisMaxellLanceClementNo ratings yet
- Transport MechanismDocument6 pagesTransport MechanismJessie Katrisha Tayag100% (2)
- Cell Physiology by WRCDocument4 pagesCell Physiology by WRCWenzy Razzie cruzNo ratings yet
- Comparacion Entre G.usbamp y Open BciDocument10 pagesComparacion Entre G.usbamp y Open BciFISORGNo ratings yet
- Mpreg Birth HomeDocument3 pagesMpreg Birth HomeSatya Nur AzizahNo ratings yet
- N45-N67 Opm PDFDocument45 pagesN45-N67 Opm PDFAndres Sorin100% (4)
- Product Manual 3055Document5 pagesProduct Manual 3055North EastNo ratings yet
- Rice Pests (Sucking Group)Document10 pagesRice Pests (Sucking Group)Biresh KoleyNo ratings yet
- (MRCP Study Guides) S. Hughes - Complete Data Interpretation For The MRCP-Churchill Livingstone (2001)Document2 pages(MRCP Study Guides) S. Hughes - Complete Data Interpretation For The MRCP-Churchill Livingstone (2001)basocdovnch0% (1)
- Pyara Paneer: IngredientsDocument54 pagesPyara Paneer: IngredientsRashmi PrakashNo ratings yet
- The Agriculture Sector: Crop ProductionDocument5 pagesThe Agriculture Sector: Crop ProductionMark Lorenz DiolataNo ratings yet
- Terapi Keluarga StrategikDocument18 pagesTerapi Keluarga StrategikNurulArifahNo ratings yet
- Food Technology Question PaperDocument4 pagesFood Technology Question PaperKaunteya PatilNo ratings yet
- Mounted On Rails or Rubber Tyres and Is Able To Straddle Several Rows of ContainersDocument2 pagesMounted On Rails or Rubber Tyres and Is Able To Straddle Several Rows of ContainersIcha AfNo ratings yet
- McElroy PP CatalogDocument52 pagesMcElroy PP Catalogsealion72No ratings yet
- 2 Definition and Applications: Estimation of Physiological RequirementsDocument7 pages2 Definition and Applications: Estimation of Physiological RequirementsRj SantiagoNo ratings yet
- REVMAX Hotel Case Study Exercises - Student VersionDocument28 pagesREVMAX Hotel Case Study Exercises - Student VersionlydiaNo ratings yet
- Agri Network of Interventions Card (ANI-Kard)Document14 pagesAgri Network of Interventions Card (ANI-Kard)Joyap MogsNo ratings yet
- Manure Fiber Separation Drying - Rickland Dairy - Case Study - Prf3Document4 pagesManure Fiber Separation Drying - Rickland Dairy - Case Study - Prf3Héctor Magaña SuelvesNo ratings yet
- Work at Heights Risk Assessment and PermitDocument4 pagesWork at Heights Risk Assessment and PermitNikola StojanovNo ratings yet
- Insurance Bar Questions and Suggested Answers 1. Question A. 6 (2019 Bar)Document7 pagesInsurance Bar Questions and Suggested Answers 1. Question A. 6 (2019 Bar)Brandon CrisostomoNo ratings yet
- Phy Investigatory Project Tangent GalvanDocument11 pagesPhy Investigatory Project Tangent Galvankomal mahelaNo ratings yet
- John The Baptists DietDocument2 pagesJohn The Baptists DietAnida Maria Moraes GomesNo ratings yet
- Technical Data Demag Hoist Units Volume 2: Double-Rail Crab EZDH 600 - EZDH 1000 Double-Rail Crab EZLDH 600 - EZLDH 2000Document88 pagesTechnical Data Demag Hoist Units Volume 2: Double-Rail Crab EZDH 600 - EZDH 1000 Double-Rail Crab EZLDH 600 - EZLDH 2000mohammad khoraminiaNo ratings yet
- Moving To A World Beyond P 0 05Document20 pagesMoving To A World Beyond P 0 05Frank LopezNo ratings yet
- RPZ Testing Form 215bDocument2 pagesRPZ Testing Form 215bSam ChoiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document52 pagesChapter 7Shir Ahmad LaiwalNo ratings yet
- 44.1.16 AOAC of Fi Cial Method 906.03 in Vert Sugar in Sugars and SyrupsDocument1 page44.1.16 AOAC of Fi Cial Method 906.03 in Vert Sugar in Sugars and Syrupsc2haNo ratings yet
- File 274804260391Document22 pagesFile 274804260391Nemanja NikolicNo ratings yet
- Climate Action Incentive Payment Notice 2022 06 25 09 46 45 07823 PDFDocument3 pagesClimate Action Incentive Payment Notice 2022 06 25 09 46 45 07823 PDFalex mac dougallNo ratings yet
- Skripsi Alvi AkmaliaDocument94 pagesSkripsi Alvi Akmaliakhoiriah nasutionNo ratings yet
- Garments Workers in BangladeshDocument4 pagesGarments Workers in BangladeshtasnianasirNo ratings yet