Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Macroeconomics - Internal and External Services - Rubillos
Macroeconomics - Internal and External Services - Rubillos
Uploaded by
NATHANIEL VILLAMORCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Investment and Portfolio ManagementDocument46 pagesInvestment and Portfolio Managementaamer shahzad wattu100% (1)
- FinanceDocument9 pagesFinanceTushar KhatriNo ratings yet
- Functions of The Money MarketDocument1 pageFunctions of The Money MarketpremaahokNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Financial InstrumentsDocument4 pagesChapter 3 Financial InstrumentsshaneNo ratings yet
- Common Money Market InstrumentsDocument1 pageCommon Money Market InstrumentspremaahokNo ratings yet
- Bonds and Types of Bonds: Presented by Silpa.P.S MBA110/18 T2 MbaDocument11 pagesBonds and Types of Bonds: Presented by Silpa.P.S MBA110/18 T2 MbaSilpa prasad100% (1)
- Money MarktDocument2 pagesMoney MarktMariyam AbbasiNo ratings yet
- Valuation of SecuritiesDocument12 pagesValuation of Securitiespriyarp5075No ratings yet
- Fixed Income InvestmentsDocument13 pagesFixed Income InvestmentsbubuhomeNo ratings yet
- Financial-Instruments 062927Document4 pagesFinancial-Instruments 062927Antonette GrivialdeNo ratings yet
- Investment AlternativesDocument32 pagesInvestment AlternativesMadihaBhattiNo ratings yet
- Presenters: Ahmad Bilal Qazi (11-005) WAQAR KHALIQ (11-011) SHAKEEL AHMAD (11-026)Document17 pagesPresenters: Ahmad Bilal Qazi (11-005) WAQAR KHALIQ (11-011) SHAKEEL AHMAD (11-026)Faisal khanNo ratings yet
- Ibf SecuritiesDocument9 pagesIbf SecuritiesMuhammad HuzaifaNo ratings yet
- Debentures and BondsDocument14 pagesDebentures and BondsAjilal KadakkalNo ratings yet
- Sources of FinanceDocument17 pagesSources of FinanceChintanNo ratings yet
- Deposit Sources of FundsDocument6 pagesDeposit Sources of FundsSakib Chowdhury0% (1)
- International Financial Market Instruments: Neenu T. Hari Shiji PremDocument20 pagesInternational Financial Market Instruments: Neenu T. Hari Shiji PremNeenu T HariNo ratings yet
- DEFINITION of 'Savings Account': Deposit Interest RateDocument4 pagesDEFINITION of 'Savings Account': Deposit Interest Ratemuyi kunleNo ratings yet
- Treasury 4Document22 pagesTreasury 4MpNo ratings yet
- Money Market Fund Money Market AccountDocument4 pagesMoney Market Fund Money Market AccountMohit TyagiNo ratings yet
- Instruments of Money MarketDocument17 pagesInstruments of Money MarketTanvir Hasan SohanNo ratings yet
- Money Market: TREASURY BILLS. Treasury Bills (T-Bills) Are Short-Term Notes Issued by The U.SDocument9 pagesMoney Market: TREASURY BILLS. Treasury Bills (T-Bills) Are Short-Term Notes Issued by The U.SArslan AkramNo ratings yet
- Capital Markets: Lesson Topics: April 26, 2021 Debt InstrumentsDocument5 pagesCapital Markets: Lesson Topics: April 26, 2021 Debt InstrumentscuteNo ratings yet
- DMMF Cia 3-1 (1720552)Document17 pagesDMMF Cia 3-1 (1720552)Prarthana MNo ratings yet
- Banking Part-VaivaDocument17 pagesBanking Part-VaivaAbrar Alam ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- BONDSDocument15 pagesBONDSN Durga MBANo ratings yet
- Debt MarketDocument11 pagesDebt MarketPsychopheticNo ratings yet
- Debt Market: Presented byDocument8 pagesDebt Market: Presented byPsychopheticNo ratings yet
- Source of Fund (Bank's Liability)Document6 pagesSource of Fund (Bank's Liability)sayed126No ratings yet
- Money MarketsDocument11 pagesMoney MarketsRonah Abigail BejocNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document29 pagesChapter 4Irene Mae BeldaNo ratings yet
- M&B Ch.2 B.2023Document4 pagesM&B Ch.2 B.2023Amgad ElshamyNo ratings yet
- Public Debt TypesDocument11 pagesPublic Debt Typeskaadi4453No ratings yet
- Bonds ch16 by Group 1Document5 pagesBonds ch16 by Group 1EriicpratamaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Fixed Income SecuritiesDocument5 pagesChapter 8 Fixed Income SecuritiesbibekNo ratings yet
- Fixed Incme Sectors and InstrumentsDocument64 pagesFixed Incme Sectors and InstrumentsJIROJBLOGNo ratings yet
- Learning About BondsDocument12 pagesLearning About Bondshammy1480100% (1)
- DocxDocument3 pagesDocxbeyyNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Budgeting For International OperationsDocument4 pagesAssignment 1 Budgeting For International OperationsNiya ThomasNo ratings yet
- IA2Bonds Selfmade ReviewerDocument1 pageIA2Bonds Selfmade ReviewerJyasmine Aura V. AgustinNo ratings yet
- FINMANDocument50 pagesFINMANJanna Hazel Villarino VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- PR1 Financial Instruments MMIDocument18 pagesPR1 Financial Instruments MMIAidə MəmmədzadəNo ratings yet
- Money BankingDocument11 pagesMoney BankingRose DallyNo ratings yet
- FM CH - 2Document19 pagesFM CH - 2Eden BekeleNo ratings yet
- Bonds & DebentureDocument6 pagesBonds & DebentureHemant GaikwadNo ratings yet
- Types of Money Market InstrumentsDocument6 pagesTypes of Money Market Instrumentsrabia liaqatNo ratings yet
- Money Markets and Capital MarketsDocument4 pagesMoney Markets and Capital MarketsEmmanuelle RojasNo ratings yet
- Miralpes Fiona P BSA2BDocument1 pageMiralpes Fiona P BSA2BFiona MiralpesNo ratings yet
- Final Reviewer Mathematics InvestmentDocument2 pagesFinal Reviewer Mathematics InvestmentChello Ann AsuncionNo ratings yet
- 2 TOPIC 2 PartDocument37 pages2 TOPIC 2 PartDomnica TcaciNo ratings yet
- FinancialmarketsDocument9 pagesFinancialmarketssnapyn9No ratings yet
- Notes To Bond ValuationDocument8 pagesNotes To Bond ValuationAngela BonifeNo ratings yet
- FMP TheoryDocument6 pagesFMP TheoryMuhammad Awall RazaNo ratings yet
- Addis Ababa University College of Business and Economics School of Commerce Department of Marketing Management Commodity Derivative MarketingDocument19 pagesAddis Ababa University College of Business and Economics School of Commerce Department of Marketing Management Commodity Derivative Marketingez leNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Valuation of DebtDocument83 pagesAnalysis and Valuation of Debtupvoteintern06No ratings yet
- Instruments of Finance in International Money MarketsDocument32 pagesInstruments of Finance in International Money Marketsapi-372709093% (15)
- Sources of Financing To Non-GovtDocument14 pagesSources of Financing To Non-GovtCorolla SedanNo ratings yet
- Sample No. 2-Kaemag, Wuhg, Pasak - (ER2 - 11-05-2018)Document14 pagesSample No. 2-Kaemag, Wuhg, Pasak - (ER2 - 11-05-2018)NATHANIEL VILLAMORNo ratings yet
- Ebalwasyon Guided Format Pangkat 4Document7 pagesEbalwasyon Guided Format Pangkat 4NATHANIEL VILLAMORNo ratings yet
- Annual Action PlanDocument2 pagesAnnual Action PlanNATHANIEL VILLAMORNo ratings yet
- Asynchronous Activity No. 1Document3 pagesAsynchronous Activity No. 1NATHANIEL VILLAMORNo ratings yet
- PNHS Cmo AdDocument2 pagesPNHS Cmo AdNATHANIEL VILLAMORNo ratings yet
- Researchchap 1Document29 pagesResearchchap 1NATHANIEL VILLAMORNo ratings yet
- Business PlanDocument24 pagesBusiness PlanNATHANIEL VILLAMORNo ratings yet
- My Tasks 6Document4 pagesMy Tasks 6NATHANIEL VILLAMORNo ratings yet
- My Tasks 5Document3 pagesMy Tasks 5NATHANIEL VILLAMORNo ratings yet
Macroeconomics - Internal and External Services - Rubillos
Macroeconomics - Internal and External Services - Rubillos
Uploaded by
NATHANIEL VILLAMOROriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Macroeconomics - Internal and External Services - Rubillos
Macroeconomics - Internal and External Services - Rubillos
Uploaded by
NATHANIEL VILLAMORCopyright:
Available Formats
Name: James Bryan B.
Rubillos Macroeconomics
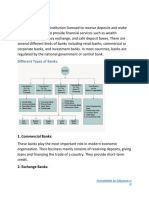
External Sources
Program and Project Loans- Money borrowed from international organizations or
foreign governments to fund specific programs or projects in a country.
Credit Facility Loans- Loans extended by external entities, often banks or financial
institutions, providing a line of credit that a country can draw upon as needed.
Zero Coupon Treasury Bills- Government-issued securities that are sold at a discount
and do not pay interest during their term. The investor receives the face value at
maturity.
Global Bonds- Bonds issued by a country that can be bought and traded
internationally. They allow a nation to raise funds from a global investor base.
Foreign Currencies- Currencies from other countries held by a government or central
bank. They can be used for international trade and as reserves.
Domestic Sources
Treasury Bond- Long-term debt securities issued by the government to raise capital.
Investors receive periodic interest payments and the principal at maturity.
Facility Loan- A loan provided by domestic financial institutions or banks to a
government or organization, often for general funding needs.
Treasury Bill- Short-term debt issued by the government, usually with a maturity of
less than one year. It's a way for the government to raise funds quickly.
Promissory Note- A written promise to repay a specific amount of money by a
certain date. It's a legal commitment to settle a debt.
Term Deposits- Money deposited in a bank for a fixed period (term) with a
predetermined interest rate. It's a type of savings account with a specific maturity
date.
In summary, external sources involve financial instruments and loans obtained from
foreign entities, while domestic sources are related to borrowing and financial
instruments within a country's own borders.
You might also like
- Investment and Portfolio ManagementDocument46 pagesInvestment and Portfolio Managementaamer shahzad wattu100% (1)
- FinanceDocument9 pagesFinanceTushar KhatriNo ratings yet
- Functions of The Money MarketDocument1 pageFunctions of The Money MarketpremaahokNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Financial InstrumentsDocument4 pagesChapter 3 Financial InstrumentsshaneNo ratings yet
- Common Money Market InstrumentsDocument1 pageCommon Money Market InstrumentspremaahokNo ratings yet
- Bonds and Types of Bonds: Presented by Silpa.P.S MBA110/18 T2 MbaDocument11 pagesBonds and Types of Bonds: Presented by Silpa.P.S MBA110/18 T2 MbaSilpa prasad100% (1)
- Money MarktDocument2 pagesMoney MarktMariyam AbbasiNo ratings yet
- Valuation of SecuritiesDocument12 pagesValuation of Securitiespriyarp5075No ratings yet
- Fixed Income InvestmentsDocument13 pagesFixed Income InvestmentsbubuhomeNo ratings yet
- Financial-Instruments 062927Document4 pagesFinancial-Instruments 062927Antonette GrivialdeNo ratings yet
- Investment AlternativesDocument32 pagesInvestment AlternativesMadihaBhattiNo ratings yet
- Presenters: Ahmad Bilal Qazi (11-005) WAQAR KHALIQ (11-011) SHAKEEL AHMAD (11-026)Document17 pagesPresenters: Ahmad Bilal Qazi (11-005) WAQAR KHALIQ (11-011) SHAKEEL AHMAD (11-026)Faisal khanNo ratings yet
- Ibf SecuritiesDocument9 pagesIbf SecuritiesMuhammad HuzaifaNo ratings yet
- Debentures and BondsDocument14 pagesDebentures and BondsAjilal KadakkalNo ratings yet
- Sources of FinanceDocument17 pagesSources of FinanceChintanNo ratings yet
- Deposit Sources of FundsDocument6 pagesDeposit Sources of FundsSakib Chowdhury0% (1)
- International Financial Market Instruments: Neenu T. Hari Shiji PremDocument20 pagesInternational Financial Market Instruments: Neenu T. Hari Shiji PremNeenu T HariNo ratings yet
- DEFINITION of 'Savings Account': Deposit Interest RateDocument4 pagesDEFINITION of 'Savings Account': Deposit Interest Ratemuyi kunleNo ratings yet
- Treasury 4Document22 pagesTreasury 4MpNo ratings yet
- Money Market Fund Money Market AccountDocument4 pagesMoney Market Fund Money Market AccountMohit TyagiNo ratings yet
- Instruments of Money MarketDocument17 pagesInstruments of Money MarketTanvir Hasan SohanNo ratings yet
- Money Market: TREASURY BILLS. Treasury Bills (T-Bills) Are Short-Term Notes Issued by The U.SDocument9 pagesMoney Market: TREASURY BILLS. Treasury Bills (T-Bills) Are Short-Term Notes Issued by The U.SArslan AkramNo ratings yet
- Capital Markets: Lesson Topics: April 26, 2021 Debt InstrumentsDocument5 pagesCapital Markets: Lesson Topics: April 26, 2021 Debt InstrumentscuteNo ratings yet
- DMMF Cia 3-1 (1720552)Document17 pagesDMMF Cia 3-1 (1720552)Prarthana MNo ratings yet
- Banking Part-VaivaDocument17 pagesBanking Part-VaivaAbrar Alam ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- BONDSDocument15 pagesBONDSN Durga MBANo ratings yet
- Debt MarketDocument11 pagesDebt MarketPsychopheticNo ratings yet
- Debt Market: Presented byDocument8 pagesDebt Market: Presented byPsychopheticNo ratings yet
- Source of Fund (Bank's Liability)Document6 pagesSource of Fund (Bank's Liability)sayed126No ratings yet
- Money MarketsDocument11 pagesMoney MarketsRonah Abigail BejocNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document29 pagesChapter 4Irene Mae BeldaNo ratings yet
- M&B Ch.2 B.2023Document4 pagesM&B Ch.2 B.2023Amgad ElshamyNo ratings yet
- Public Debt TypesDocument11 pagesPublic Debt Typeskaadi4453No ratings yet
- Bonds ch16 by Group 1Document5 pagesBonds ch16 by Group 1EriicpratamaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Fixed Income SecuritiesDocument5 pagesChapter 8 Fixed Income SecuritiesbibekNo ratings yet
- Fixed Incme Sectors and InstrumentsDocument64 pagesFixed Incme Sectors and InstrumentsJIROJBLOGNo ratings yet
- Learning About BondsDocument12 pagesLearning About Bondshammy1480100% (1)
- DocxDocument3 pagesDocxbeyyNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Budgeting For International OperationsDocument4 pagesAssignment 1 Budgeting For International OperationsNiya ThomasNo ratings yet
- IA2Bonds Selfmade ReviewerDocument1 pageIA2Bonds Selfmade ReviewerJyasmine Aura V. AgustinNo ratings yet
- FINMANDocument50 pagesFINMANJanna Hazel Villarino VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- PR1 Financial Instruments MMIDocument18 pagesPR1 Financial Instruments MMIAidə MəmmədzadəNo ratings yet
- Money BankingDocument11 pagesMoney BankingRose DallyNo ratings yet
- FM CH - 2Document19 pagesFM CH - 2Eden BekeleNo ratings yet
- Bonds & DebentureDocument6 pagesBonds & DebentureHemant GaikwadNo ratings yet
- Types of Money Market InstrumentsDocument6 pagesTypes of Money Market Instrumentsrabia liaqatNo ratings yet
- Money Markets and Capital MarketsDocument4 pagesMoney Markets and Capital MarketsEmmanuelle RojasNo ratings yet
- Miralpes Fiona P BSA2BDocument1 pageMiralpes Fiona P BSA2BFiona MiralpesNo ratings yet
- Final Reviewer Mathematics InvestmentDocument2 pagesFinal Reviewer Mathematics InvestmentChello Ann AsuncionNo ratings yet
- 2 TOPIC 2 PartDocument37 pages2 TOPIC 2 PartDomnica TcaciNo ratings yet
- FinancialmarketsDocument9 pagesFinancialmarketssnapyn9No ratings yet
- Notes To Bond ValuationDocument8 pagesNotes To Bond ValuationAngela BonifeNo ratings yet
- FMP TheoryDocument6 pagesFMP TheoryMuhammad Awall RazaNo ratings yet
- Addis Ababa University College of Business and Economics School of Commerce Department of Marketing Management Commodity Derivative MarketingDocument19 pagesAddis Ababa University College of Business and Economics School of Commerce Department of Marketing Management Commodity Derivative Marketingez leNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Valuation of DebtDocument83 pagesAnalysis and Valuation of Debtupvoteintern06No ratings yet
- Instruments of Finance in International Money MarketsDocument32 pagesInstruments of Finance in International Money Marketsapi-372709093% (15)
- Sources of Financing To Non-GovtDocument14 pagesSources of Financing To Non-GovtCorolla SedanNo ratings yet
- Sample No. 2-Kaemag, Wuhg, Pasak - (ER2 - 11-05-2018)Document14 pagesSample No. 2-Kaemag, Wuhg, Pasak - (ER2 - 11-05-2018)NATHANIEL VILLAMORNo ratings yet
- Ebalwasyon Guided Format Pangkat 4Document7 pagesEbalwasyon Guided Format Pangkat 4NATHANIEL VILLAMORNo ratings yet
- Annual Action PlanDocument2 pagesAnnual Action PlanNATHANIEL VILLAMORNo ratings yet
- Asynchronous Activity No. 1Document3 pagesAsynchronous Activity No. 1NATHANIEL VILLAMORNo ratings yet
- PNHS Cmo AdDocument2 pagesPNHS Cmo AdNATHANIEL VILLAMORNo ratings yet
- Researchchap 1Document29 pagesResearchchap 1NATHANIEL VILLAMORNo ratings yet
- Business PlanDocument24 pagesBusiness PlanNATHANIEL VILLAMORNo ratings yet
- My Tasks 6Document4 pagesMy Tasks 6NATHANIEL VILLAMORNo ratings yet
- My Tasks 5Document3 pagesMy Tasks 5NATHANIEL VILLAMORNo ratings yet