Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Code On Wages, 2019
The Code On Wages, 2019
Uploaded by
pratik.shinde170Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- The Need For The Abolition of Secret TrustsDocument11 pagesThe Need For The Abolition of Secret TrustseuodiaNo ratings yet
- Comparative Analysis of The Code On Wages, 2019 With Previous Legislations in ForceDocument14 pagesComparative Analysis of The Code On Wages, 2019 With Previous Legislations in ForcebabuliNo ratings yet
- Contract With ST Vincent de PaulDocument22 pagesContract With ST Vincent de PaulMegan BantaNo ratings yet
- Original Bill of Lading: CarrierDocument12 pagesOriginal Bill of Lading: CarrierLuis Felipe Laurada LiloyNo ratings yet
- Labour Law AssignmentDocument14 pagesLabour Law AssignmentMayank RajpootNo ratings yet
- Decoding The Code On Wages, 2 0 1 9: Four Statutes Amalgamated in Wage CodeDocument4 pagesDecoding The Code On Wages, 2 0 1 9: Four Statutes Amalgamated in Wage CodePramodNo ratings yet
- Betterplace Labour Code 2020Document36 pagesBetterplace Labour Code 2020RAHUL YADAVNo ratings yet
- Code On WagesDocument22 pagesCode On WagesODD 3EANo ratings yet
- Draft Code On Wages (Central) Rules, 2020: Brief HighlightsDocument3 pagesDraft Code On Wages (Central) Rules, 2020: Brief HighlightsPravinkumar VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Principle of Fixation and Revision of Minimum WageDocument3 pagesPrinciple of Fixation and Revision of Minimum WageVishwesh SinghNo ratings yet
- The Code On WagesDocument48 pagesThe Code On WagesHardik ShettyNo ratings yet
- Payment of WagesDocument10 pagesPayment of WagesStuti DoshiNo ratings yet
- Labour Codes and Imapct.1Document28 pagesLabour Codes and Imapct.1Shiva SinghNo ratings yet
- New Labour Code 2024Document24 pagesNew Labour Code 2024nalegel688No ratings yet
- New Labour Codes - Update & Our Value Proposition - GTDocument10 pagesNew Labour Codes - Update & Our Value Proposition - GTvramu_caNo ratings yet
- Code SynopsysDocument19 pagesCode SynopsysAnkitKumarTripathiNo ratings yet
- India: Code On Wages, 2019 - Minimum WagesDocument19 pagesIndia: Code On Wages, 2019 - Minimum WagesTaniya YadavNo ratings yet
- JSA Newsletter Employment Law July 20220620Document6 pagesJSA Newsletter Employment Law July 20220620Vibhu SinghNo ratings yet
- Labour 2Document10 pagesLabour 2Ishika kanyalNo ratings yet
- Four New Labour Codes Which Are To Be ImplementedDocument12 pagesFour New Labour Codes Which Are To Be ImplementedMukta SharmaNo ratings yet
- Code of Wages Act, 2019Document6 pagesCode of Wages Act, 2019Suvendu KarNo ratings yet
- Code On Wages 2020Document8 pagesCode On Wages 2020Vivek MishraNo ratings yet
- The Code On Wages 2019: India's First Step Towards Consolidation of Labour LawsDocument50 pagesThe Code On Wages 2019: India's First Step Towards Consolidation of Labour LawsTanu Priya100% (1)
- Code On Wages 2019Document14 pagesCode On Wages 2019Chaudhary Rajat Dubey100% (1)
- Labour Codes - Legislative ReformsDocument9 pagesLabour Codes - Legislative ReformsSP CONTRACTORNo ratings yet
- The Amendments in Wage Code Act of IndiaDocument16 pagesThe Amendments in Wage Code Act of IndiaADITI SHAHNo ratings yet
- An Analysis of The Labour Code On Wages, 2019: 2018-19 Has Revealed That 1 in 3 Wage Workers Are Not Protected by TheDocument10 pagesAn Analysis of The Labour Code On Wages, 2019: 2018-19 Has Revealed That 1 in 3 Wage Workers Are Not Protected by TheHarsh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Labour Reforms BackgroundDocument8 pagesLabour Reforms Backgroundakky.vns2004No ratings yet
- Payroll Compliance E-bookDocument29 pagesPayroll Compliance E-bookRishabh PandeyNo ratings yet
- Code On Wages, 2019 - Key Features and HighlightsDocument5 pagesCode On Wages, 2019 - Key Features and HighlightsJagmohan SainiNo ratings yet
- Labour Reforms - Labour CodesDocument4 pagesLabour Reforms - Labour CodesAdwitiya MishraNo ratings yet
- Wage Code SummaryDocument7 pagesWage Code Summaryqubrex1100% (1)
- ELP Booklet ELPs New Labour CodesDocument11 pagesELP Booklet ELPs New Labour CodesELP LawNo ratings yet
- New Labour Codes FlyerDocument12 pagesNew Labour Codes Flyerketan goudNo ratings yet
- Wage Code Bill 2019Document52 pagesWage Code Bill 2019Rajeev SaraoNo ratings yet
- New Labor Codes Provident Fund and Other Employment Related Updates On Account of Covid 19Document5 pagesNew Labor Codes Provident Fund and Other Employment Related Updates On Account of Covid 19Chanakya NitiNo ratings yet
- CSB Ias Academy: D E M YDocument3 pagesCSB Ias Academy: D E M Yshinyraj32No ratings yet
- Analysis - Code of Wages, 2019Document8 pagesAnalysis - Code of Wages, 2019Nikhil JainNo ratings yet
- Social Code in IndiaDocument26 pagesSocial Code in Indiaaslam shaNo ratings yet
- Code On WagesDocument24 pagesCode On Wagesjayeetad.m4392No ratings yet
- Code On Wages 2019Document26 pagesCode On Wages 2019SumeetNo ratings yet
- Project Report ON: The Amendments in Wage Code Act of India Industrial Relations Shantanu Sachin Dhavale (HR)Document21 pagesProject Report ON: The Amendments in Wage Code Act of India Industrial Relations Shantanu Sachin Dhavale (HR)SHANTANU DHAVALENo ratings yet
- Code On Wages 2019 (2) 2Document25 pagesCode On Wages 2019 (2) 2devamoyNo ratings yet
- 4 Comparing Previous Act With New Labour Codes (Part - 3)Document13 pages4 Comparing Previous Act With New Labour Codes (Part - 3)abdul gani khanNo ratings yet
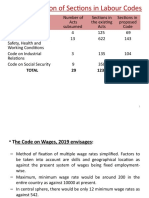
- Rationalization of Sections in Labour Codes: Total 29 1232 480Document49 pagesRationalization of Sections in Labour Codes: Total 29 1232 480AadhityaNo ratings yet
- Code On Wages, 2019Document8 pagesCode On Wages, 2019CHANDA SINGHNo ratings yet
- New Changes in Labour LawDocument14 pagesNew Changes in Labour LawSadhika GuptaNo ratings yet
- The Code of Wages 2019Document14 pagesThe Code of Wages 2019user-468774No ratings yet
- Labour CodeDocument5 pagesLabour Codec2689762No ratings yet
- Labour Policy Lyst6397Document13 pagesLabour Policy Lyst6397UKJ GamingNo ratings yet
- Indias New Employment LawsDocument41 pagesIndias New Employment LawsajayjosephtNo ratings yet
- decoding-the-code-on-social-security-code-2020Document3 pagesdecoding-the-code-on-social-security-code-2020dafbeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10Document11 pagesLecture 10Kertik SinghNo ratings yet
- Aditya Labour 2Document16 pagesAditya Labour 2aditya.dwivediNo ratings yet
- Code On Wages ActDocument19 pagesCode On Wages ActRafunsel PresentationNo ratings yet
- Min Wages ActDocument17 pagesMin Wages ActHarman GillNo ratings yet
- FICCI Note On Labour Policy ReformsDocument19 pagesFICCI Note On Labour Policy ReformsVishwanath ReddyNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument20 pagesAssignmentaryanNo ratings yet
- Recap of Key Labour Law Developments of 2019 & Looking Forward To 2020 - Employment and HR - IndiaDocument3 pagesRecap of Key Labour Law Developments of 2019 & Looking Forward To 2020 - Employment and HR - Indiakamath.t.manjulaNo ratings yet
- D-Minimum Wages ActDocument9 pagesD-Minimum Wages ActÑàdààñ ShubhàmNo ratings yet
- Minimum Wages Act, 1948Document19 pagesMinimum Wages Act, 1948Shantanu Srivastava74% (19)
- THE LABOUR LAW IN UGANDA: [A TeeParkots Inc Publishers Product]From EverandTHE LABOUR LAW IN UGANDA: [A TeeParkots Inc Publishers Product]No ratings yet
- CMC Cy 2016 Reg Prom Program PDFDocument44 pagesCMC Cy 2016 Reg Prom Program PDFEla MaeNo ratings yet
- AideD&D n4 Le Rachat (Suite L'Auberge Du Sanglier Gris)Document7 pagesAideD&D n4 Le Rachat (Suite L'Auberge Du Sanglier Gris)Etan KrelNo ratings yet
- Standard Oil Vs Codina ArenasDocument1 pageStandard Oil Vs Codina ArenasCathy BelgiraNo ratings yet
- The Caesar of DeceitDocument5 pagesThe Caesar of Deceitapi-319241369No ratings yet
- 53 Iowa LRev 810Document23 pages53 Iowa LRev 810DEEPANJALI K SNo ratings yet
- Graphics Properties Holdings v. DellDocument5 pagesGraphics Properties Holdings v. DellPriorSmartNo ratings yet
- Final Labor Case Digest-04.25Document70 pagesFinal Labor Case Digest-04.25Sometimes goodNo ratings yet
- Filters Filtros FiltresDocument154 pagesFilters Filtros FiltresPacoNo ratings yet
- 6 PFC Secretary's Certificate FormatDocument1 page6 PFC Secretary's Certificate Formatjasmosende25No ratings yet
- TweeeshaDocument7 pagesTweeeshaInsolent PotatoNo ratings yet
- MR V P Mittal Vs Punjab National Bank On 13 December 2011Document3 pagesMR V P Mittal Vs Punjab National Bank On 13 December 2011Sukhbir Singh SandhuNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Province of Sorsogon Municipality of Sta. Magdalena Barangay 2 PoblacionDocument9 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Province of Sorsogon Municipality of Sta. Magdalena Barangay 2 PoblacionRemar Garalde GamitNo ratings yet
- Affidavit of Denial: Republic of The Philippines) Municipality of Legazpi) S.S Province of Albay)Document2 pagesAffidavit of Denial: Republic of The Philippines) Municipality of Legazpi) S.S Province of Albay)Sherjohn tombocNo ratings yet
- 1 Lopez vs. Atty RamosDocument3 pages1 Lopez vs. Atty RamosPIKACHUCHIENo ratings yet
- Minutes of MeetingDocument3 pagesMinutes of MeetingJanine PigaoNo ratings yet
- Sas 4Document2 pagesSas 4chantoy bersalesNo ratings yet
- Deed of Absolute SaleDocument2 pagesDeed of Absolute SaleLDNo ratings yet
- Contract 14040631Document6 pagesContract 14040631معيضNo ratings yet
- CandlesDocument6 pagesCandlesJAY PATELNo ratings yet
- Admin. Law C.K Takwani 1st Chap.Document18 pagesAdmin. Law C.K Takwani 1st Chap.Rohan BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Cse Review Day 1Document7 pagesCse Review Day 1Rj Parayno ArenasNo ratings yet
- Odoo INV - 2022 - 6596Document2 pagesOdoo INV - 2022 - 6596Khurram ShahzadNo ratings yet
- A.L. ANG NETWORK, INC. v. MONDEJAR (G.R. No. 200804, January 22, 2014)Document2 pagesA.L. ANG NETWORK, INC. v. MONDEJAR (G.R. No. 200804, January 22, 2014)Rochelle Joy SolisNo ratings yet
- Title Xvii Miscellaneous ProvisionsDocument3 pagesTitle Xvii Miscellaneous ProvisionsLGNo ratings yet
- Has Racism Changed Over TimeDocument8 pagesHas Racism Changed Over Timeapi-548668159No ratings yet
- Rule 47 Docs 2Document4 pagesRule 47 Docs 2mbendijo15No ratings yet
- DTC Doa 76Q - Surber 1 NewDocument20 pagesDTC Doa 76Q - Surber 1 NewTaeseok YangNo ratings yet
The Code On Wages, 2019
The Code On Wages, 2019
Uploaded by
pratik.shinde170Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Code On Wages, 2019
The Code On Wages, 2019
Uploaded by
pratik.shinde170Copyright:
Available Formats
THE CODE OF WAGES, 2019
July 23, 2019 July 30, 2019 July 30, 2019
Introduced in Lok Sabha Passed in Lok Sabha Passed in Rajya Sabha
Whats’ the need of Wage Code?
62% 1,709 33%
Of the workforce is made of up of scheduled employments rates fixed Of wage workers were paid less
casual workers who need a right to by states, 45 by centre; making it a than the indicative minimum wages
the minimum wages complex wage system in 2009-10
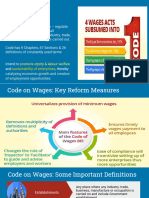
INTRODUCTION KEY HIGHLIGHTS
The Code on Wages, 2019 intends to increase the • Seeks to regulate wages and bonus payments
legislative protection of minimum wages and to in all areas of employment where any trade,
transform the old and obsolete labour laws into business, or manufacturing is carried out
more accountable and transparent ones. It is the including organized and unorganized sectors
first bill to become an Act out of the four Codes, • Wages include salary, allowance, or any other
namely: component expressed in monetary terms. This
(i) The Code on Wages 2019 does not include bonus payable to employees
(ii) The Occupational Safety, Health and Working or any travelling allowance, among others
Conditions Code 2019
• It aims to ensure process of registration and
(iii) The Code on Social Security 2019 filing of returns is standardised and streamlined.
(iv) The Industrial Relations Code 2019
With various labour-related definitions getting
standardised, it is expected that there shall be
The Code on Wages Act 2019 amalgamates,
less dispute
simplifies and rationalizes the relevant provisions of
four central labour enactments relating to wages, • Covers definition of wages, reducing categories
namely: for minimum wages, web-based randomized
computerized inspection scheme, statutory
(i) The Payment of Wages Act 1936
protection for minimum wage and timely
(ii) The Minimum Wages Act 1948
payment of wages
(iii) The Payment of Bonus Act 1965
(iv) The Equal Remuneration Act 1976 • Currently, many states have multiple minimum
wages but by enactment of this Code, the
SCOPE methodology to fix the minimum wages has
• The Code will apply to all employees; aims to been simplified and rationalized by eradicating
universalise the provision of minimum wages type of employment is one of the criteria for
and timely payment of wages to all employees fixation of minimum wage
irrespective of sector and wage ceiling • The minimum wage fixation would now primarily
• The central government will make wage-related be based on geography and skills
decisions for employments such as railways, • It will substantially reduce the number of
mines, and oil fields, among others minimum wages in the country from existing
• State governments will make decisions for all more than 2000 rates of minimum wages
other employments • Enactment of this new code will facilitate easier
compliance by businesses
Data Source: Labour Ministry & leading publications
• Definition of Wages to bear, hazardous occupations, processes or
It will have a wide impact on costs of employers as underground work are to be considered while
well as in hand salary for employees as this would determining and/or revising the wages by the
also ensure that every worker gets a minimum Government.
wage, which will also be accompanied by an • Duty of Inspectors & Penalties
increase in the purchasing power of the worker The code provides the appropriate government to
thereby formalizing the economy and provide appoint Inspectors-cum-Facilitators (in the place of
more monetary funds to the employees to live their Inspectors), to carry out inspections. Such
livelihood thus, promoting productivity as well as Inspectors-cum-Facilitators may advise employers
reduction in inequalities and business revenue. and employees for better compliance. This has
The government is also proposing to replace been done with the objective of removing the
existing definition of “basic wages” in Employees’ arbitrariness and malpractices in inspection.
Provident Funds and Miscellaneous Provisions The maximum penalty for any offence is limited to
Act, 1952 (the EPF Act) with that of “wages” as imprisonment for three months and/ or with a fine
provided in the code. of up to INR 100,000.
• Payment of Wages
Settlement period for monthly wages has been Points to watch out
specified as on 7th against 10th of succeeding • Section 9 of the Code introduces the concept of
month. In case employee is removed, dismissed, ‘floor wage’ which is to be fixed by the Central
retrenched, resigns or becomes unemployed due Government for different geographical areas
to closure of an establishment, the wages are taking into account the minimum living standards
required to be paid within two working days. and Section 9(2) of the Code prohibits the State
Government from lowering their minimum wages
The earlier Act had different provisions for below such floor wage as may be fixed by the
termination cases in different states and did not Central Government.
provide any specific timelines for resignation
cases. • This will increase the business labour cost and
therefore the industries will hire less workers to
• Equal Remuneration keep the total labour costs same which will result
Section 3 has included the word ‘gender’ so as to in increase of unemployment rate.
widen the duty of an employer to pay equal wages • The code shall bring social disparity as minimum
to its employees, thereby promoting gender
wages are to be fixed at varying rate from states to
equality. states or zones to zones depending upon the
The amendment will ensure no discrimination in geographical conditions as; North zone, South
payment of wages amongst males, females and zone, East Zone, West zone and North East zone.
individuals falling within the definition of This may lead to job outsourcing as industries/
‘transgender’. establishments can move their facilities to
• Limitation period for claims countries where labour costs are lower.
The period of limitation for filing of claims for • The new Code can also raise the cost of living as
minimum wages, bonus, equal remuneration etc., higher wages will allow the employees to pay more
by workers has been enhanced to 3 years as for housing and living.
against existing time period varying from 6 months
to 2 years, to provide more time to file their claims. Conclusion
• Other provisions With Wage Code intending to cover 50 crore+
employees and ensure “Right to Sustenance” for
- Pursuant to enactment of the Code, Section 8(2)
will stipulates a procedure to fix minimum wages every worker by increasing the legislative protection of
and it will become a right of every worker thereby minimum wage; its a welcome move making India a
more formal economy and fulfilling India's aim to
providing legislative protection to workers in the
unorganized sector as well. become a $5 Trillion economy.
The HR, Legal, Finance and business users must
- Inclusion of workers in the committee will ensure
appropriate representation of the workers in familiarise themselves with the code and evaluate
procedure for determination of wages and while potential impact on their operations and make use of
time in hand before states start rolling out their rules.
considerations for fixing & revising minimum
wages.
- This Code seeks to provide a methodology to be
followed by the Appropriate Government which is ANJALI SINGH
primarily based on the skills of the workers. She is a lawyer by profession and is Senior
- Arduousness of working conditions of workers Associate - Regulatory Compliance, Lawrbit
such as temperature or humidity normally difficult
ABOUT US
Lawrbit offers RegTech & Lextech solutions for Enterprises, Audit, Compliance & Legal
Professionals globally.
• Our decade of experience in creating Global Regulatory Intelligence and understanding real-
life challenges of managing them have helped us create innovative, best in class solutions
that are scalable & easy to implement.
• Our solutions integrate Regulatory Intelligence across laws for 70+ countries with technology,
making it easy for users to understand compliance obligations and be informed of the
Regulatory changes.
• Our Legal Network comprises 1000’s of legal experts from 100’s of Legal, CPA & Consulting
Firms across 70+ countries having domain and territory expertise across areas of law.
• Our Reverse Outsourcing model of engaging legal experts for multi-country roll-outs helps
reducing time, cost and efforts for such implementations.
OUR SOLUTION PORTFOLIO
Enterprise Solutions Professional Solutions
• Global Compliance Management • Compliance Audit Management
• Legal Matter Management • Compliance Service Management
• Risk & Controls Management • Litigation Service Management
OUR LOCATIONS
DELHI / NCR JAIPUR
CORPORATE OFFICE: 865-A, Tower - B1, Spaze I- KNOWLEDGE CENTRE: 32, Gopal Tower, Dadu
Tech Park | Sector 49, Gurgaon - 122002 Marg, GopalBari, Jaipur - 302001
MUMBAI AHMEDABAD
WeWork Chromium, JVLR, Opp. L&T Business Park, A2/512, Palladium Complex, Corporate Road,
Andheri, Mumbai - 400076 Prahladnagar, Ahmedabad, Gujarat - 380015
GET IN TOUCH WITH US
+91-9560-83-4141 | info@lawrbit.com | www.lawrbit.com
Copyright © 2020 Lawrbit Lextech India Private Limited, all rights reserved. Lawrbit makes every effort to use reliable and
comprehensive information, but Lawrbit does not represent that the contents of the report are accurate or complete. This document
has been prepared without regard to the objectives or opinions of those who may receive it. Opinions expressed herein are entirely
those of author(s) & the document is being furnished to you for your information only.
Lawrbit is registered in India having Corporate Identity Number or CIN : U74995RJ2018PTC062060.
FOLLOW US AT:
You might also like
- The Need For The Abolition of Secret TrustsDocument11 pagesThe Need For The Abolition of Secret TrustseuodiaNo ratings yet
- Comparative Analysis of The Code On Wages, 2019 With Previous Legislations in ForceDocument14 pagesComparative Analysis of The Code On Wages, 2019 With Previous Legislations in ForcebabuliNo ratings yet
- Contract With ST Vincent de PaulDocument22 pagesContract With ST Vincent de PaulMegan BantaNo ratings yet
- Original Bill of Lading: CarrierDocument12 pagesOriginal Bill of Lading: CarrierLuis Felipe Laurada LiloyNo ratings yet
- Labour Law AssignmentDocument14 pagesLabour Law AssignmentMayank RajpootNo ratings yet
- Decoding The Code On Wages, 2 0 1 9: Four Statutes Amalgamated in Wage CodeDocument4 pagesDecoding The Code On Wages, 2 0 1 9: Four Statutes Amalgamated in Wage CodePramodNo ratings yet
- Betterplace Labour Code 2020Document36 pagesBetterplace Labour Code 2020RAHUL YADAVNo ratings yet
- Code On WagesDocument22 pagesCode On WagesODD 3EANo ratings yet
- Draft Code On Wages (Central) Rules, 2020: Brief HighlightsDocument3 pagesDraft Code On Wages (Central) Rules, 2020: Brief HighlightsPravinkumar VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Principle of Fixation and Revision of Minimum WageDocument3 pagesPrinciple of Fixation and Revision of Minimum WageVishwesh SinghNo ratings yet
- The Code On WagesDocument48 pagesThe Code On WagesHardik ShettyNo ratings yet
- Payment of WagesDocument10 pagesPayment of WagesStuti DoshiNo ratings yet
- Labour Codes and Imapct.1Document28 pagesLabour Codes and Imapct.1Shiva SinghNo ratings yet
- New Labour Code 2024Document24 pagesNew Labour Code 2024nalegel688No ratings yet
- New Labour Codes - Update & Our Value Proposition - GTDocument10 pagesNew Labour Codes - Update & Our Value Proposition - GTvramu_caNo ratings yet
- Code SynopsysDocument19 pagesCode SynopsysAnkitKumarTripathiNo ratings yet
- India: Code On Wages, 2019 - Minimum WagesDocument19 pagesIndia: Code On Wages, 2019 - Minimum WagesTaniya YadavNo ratings yet
- JSA Newsletter Employment Law July 20220620Document6 pagesJSA Newsletter Employment Law July 20220620Vibhu SinghNo ratings yet
- Labour 2Document10 pagesLabour 2Ishika kanyalNo ratings yet
- Four New Labour Codes Which Are To Be ImplementedDocument12 pagesFour New Labour Codes Which Are To Be ImplementedMukta SharmaNo ratings yet
- Code of Wages Act, 2019Document6 pagesCode of Wages Act, 2019Suvendu KarNo ratings yet
- Code On Wages 2020Document8 pagesCode On Wages 2020Vivek MishraNo ratings yet
- The Code On Wages 2019: India's First Step Towards Consolidation of Labour LawsDocument50 pagesThe Code On Wages 2019: India's First Step Towards Consolidation of Labour LawsTanu Priya100% (1)
- Code On Wages 2019Document14 pagesCode On Wages 2019Chaudhary Rajat Dubey100% (1)
- Labour Codes - Legislative ReformsDocument9 pagesLabour Codes - Legislative ReformsSP CONTRACTORNo ratings yet
- The Amendments in Wage Code Act of IndiaDocument16 pagesThe Amendments in Wage Code Act of IndiaADITI SHAHNo ratings yet
- An Analysis of The Labour Code On Wages, 2019: 2018-19 Has Revealed That 1 in 3 Wage Workers Are Not Protected by TheDocument10 pagesAn Analysis of The Labour Code On Wages, 2019: 2018-19 Has Revealed That 1 in 3 Wage Workers Are Not Protected by TheHarsh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Labour Reforms BackgroundDocument8 pagesLabour Reforms Backgroundakky.vns2004No ratings yet
- Payroll Compliance E-bookDocument29 pagesPayroll Compliance E-bookRishabh PandeyNo ratings yet
- Code On Wages, 2019 - Key Features and HighlightsDocument5 pagesCode On Wages, 2019 - Key Features and HighlightsJagmohan SainiNo ratings yet
- Labour Reforms - Labour CodesDocument4 pagesLabour Reforms - Labour CodesAdwitiya MishraNo ratings yet
- Wage Code SummaryDocument7 pagesWage Code Summaryqubrex1100% (1)
- ELP Booklet ELPs New Labour CodesDocument11 pagesELP Booklet ELPs New Labour CodesELP LawNo ratings yet
- New Labour Codes FlyerDocument12 pagesNew Labour Codes Flyerketan goudNo ratings yet
- Wage Code Bill 2019Document52 pagesWage Code Bill 2019Rajeev SaraoNo ratings yet
- New Labor Codes Provident Fund and Other Employment Related Updates On Account of Covid 19Document5 pagesNew Labor Codes Provident Fund and Other Employment Related Updates On Account of Covid 19Chanakya NitiNo ratings yet
- CSB Ias Academy: D E M YDocument3 pagesCSB Ias Academy: D E M Yshinyraj32No ratings yet
- Analysis - Code of Wages, 2019Document8 pagesAnalysis - Code of Wages, 2019Nikhil JainNo ratings yet
- Social Code in IndiaDocument26 pagesSocial Code in Indiaaslam shaNo ratings yet
- Code On WagesDocument24 pagesCode On Wagesjayeetad.m4392No ratings yet
- Code On Wages 2019Document26 pagesCode On Wages 2019SumeetNo ratings yet
- Project Report ON: The Amendments in Wage Code Act of India Industrial Relations Shantanu Sachin Dhavale (HR)Document21 pagesProject Report ON: The Amendments in Wage Code Act of India Industrial Relations Shantanu Sachin Dhavale (HR)SHANTANU DHAVALENo ratings yet
- Code On Wages 2019 (2) 2Document25 pagesCode On Wages 2019 (2) 2devamoyNo ratings yet
- 4 Comparing Previous Act With New Labour Codes (Part - 3)Document13 pages4 Comparing Previous Act With New Labour Codes (Part - 3)abdul gani khanNo ratings yet
- Rationalization of Sections in Labour Codes: Total 29 1232 480Document49 pagesRationalization of Sections in Labour Codes: Total 29 1232 480AadhityaNo ratings yet
- Code On Wages, 2019Document8 pagesCode On Wages, 2019CHANDA SINGHNo ratings yet
- New Changes in Labour LawDocument14 pagesNew Changes in Labour LawSadhika GuptaNo ratings yet
- The Code of Wages 2019Document14 pagesThe Code of Wages 2019user-468774No ratings yet
- Labour CodeDocument5 pagesLabour Codec2689762No ratings yet
- Labour Policy Lyst6397Document13 pagesLabour Policy Lyst6397UKJ GamingNo ratings yet
- Indias New Employment LawsDocument41 pagesIndias New Employment LawsajayjosephtNo ratings yet
- decoding-the-code-on-social-security-code-2020Document3 pagesdecoding-the-code-on-social-security-code-2020dafbeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10Document11 pagesLecture 10Kertik SinghNo ratings yet
- Aditya Labour 2Document16 pagesAditya Labour 2aditya.dwivediNo ratings yet
- Code On Wages ActDocument19 pagesCode On Wages ActRafunsel PresentationNo ratings yet
- Min Wages ActDocument17 pagesMin Wages ActHarman GillNo ratings yet
- FICCI Note On Labour Policy ReformsDocument19 pagesFICCI Note On Labour Policy ReformsVishwanath ReddyNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument20 pagesAssignmentaryanNo ratings yet
- Recap of Key Labour Law Developments of 2019 & Looking Forward To 2020 - Employment and HR - IndiaDocument3 pagesRecap of Key Labour Law Developments of 2019 & Looking Forward To 2020 - Employment and HR - Indiakamath.t.manjulaNo ratings yet
- D-Minimum Wages ActDocument9 pagesD-Minimum Wages ActÑàdààñ ShubhàmNo ratings yet
- Minimum Wages Act, 1948Document19 pagesMinimum Wages Act, 1948Shantanu Srivastava74% (19)
- THE LABOUR LAW IN UGANDA: [A TeeParkots Inc Publishers Product]From EverandTHE LABOUR LAW IN UGANDA: [A TeeParkots Inc Publishers Product]No ratings yet
- CMC Cy 2016 Reg Prom Program PDFDocument44 pagesCMC Cy 2016 Reg Prom Program PDFEla MaeNo ratings yet
- AideD&D n4 Le Rachat (Suite L'Auberge Du Sanglier Gris)Document7 pagesAideD&D n4 Le Rachat (Suite L'Auberge Du Sanglier Gris)Etan KrelNo ratings yet
- Standard Oil Vs Codina ArenasDocument1 pageStandard Oil Vs Codina ArenasCathy BelgiraNo ratings yet
- The Caesar of DeceitDocument5 pagesThe Caesar of Deceitapi-319241369No ratings yet
- 53 Iowa LRev 810Document23 pages53 Iowa LRev 810DEEPANJALI K SNo ratings yet
- Graphics Properties Holdings v. DellDocument5 pagesGraphics Properties Holdings v. DellPriorSmartNo ratings yet
- Final Labor Case Digest-04.25Document70 pagesFinal Labor Case Digest-04.25Sometimes goodNo ratings yet
- Filters Filtros FiltresDocument154 pagesFilters Filtros FiltresPacoNo ratings yet
- 6 PFC Secretary's Certificate FormatDocument1 page6 PFC Secretary's Certificate Formatjasmosende25No ratings yet
- TweeeshaDocument7 pagesTweeeshaInsolent PotatoNo ratings yet
- MR V P Mittal Vs Punjab National Bank On 13 December 2011Document3 pagesMR V P Mittal Vs Punjab National Bank On 13 December 2011Sukhbir Singh SandhuNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Province of Sorsogon Municipality of Sta. Magdalena Barangay 2 PoblacionDocument9 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Province of Sorsogon Municipality of Sta. Magdalena Barangay 2 PoblacionRemar Garalde GamitNo ratings yet
- Affidavit of Denial: Republic of The Philippines) Municipality of Legazpi) S.S Province of Albay)Document2 pagesAffidavit of Denial: Republic of The Philippines) Municipality of Legazpi) S.S Province of Albay)Sherjohn tombocNo ratings yet
- 1 Lopez vs. Atty RamosDocument3 pages1 Lopez vs. Atty RamosPIKACHUCHIENo ratings yet
- Minutes of MeetingDocument3 pagesMinutes of MeetingJanine PigaoNo ratings yet
- Sas 4Document2 pagesSas 4chantoy bersalesNo ratings yet
- Deed of Absolute SaleDocument2 pagesDeed of Absolute SaleLDNo ratings yet
- Contract 14040631Document6 pagesContract 14040631معيضNo ratings yet
- CandlesDocument6 pagesCandlesJAY PATELNo ratings yet
- Admin. Law C.K Takwani 1st Chap.Document18 pagesAdmin. Law C.K Takwani 1st Chap.Rohan BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Cse Review Day 1Document7 pagesCse Review Day 1Rj Parayno ArenasNo ratings yet
- Odoo INV - 2022 - 6596Document2 pagesOdoo INV - 2022 - 6596Khurram ShahzadNo ratings yet
- A.L. ANG NETWORK, INC. v. MONDEJAR (G.R. No. 200804, January 22, 2014)Document2 pagesA.L. ANG NETWORK, INC. v. MONDEJAR (G.R. No. 200804, January 22, 2014)Rochelle Joy SolisNo ratings yet
- Title Xvii Miscellaneous ProvisionsDocument3 pagesTitle Xvii Miscellaneous ProvisionsLGNo ratings yet
- Has Racism Changed Over TimeDocument8 pagesHas Racism Changed Over Timeapi-548668159No ratings yet
- Rule 47 Docs 2Document4 pagesRule 47 Docs 2mbendijo15No ratings yet
- DTC Doa 76Q - Surber 1 NewDocument20 pagesDTC Doa 76Q - Surber 1 NewTaeseok YangNo ratings yet



























































![THE LABOUR LAW IN UGANDA: [A TeeParkots Inc Publishers Product]](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/702714789/149x198/ac277f344e/1706724197?v=1)



























