Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Handouts Hyphotesis
Handouts Hyphotesis
Uploaded by
Buddy OverthinkerCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- CH9 and 10. HYPOTHESIS TESTINGDocument7 pagesCH9 and 10. HYPOTHESIS TESTINGHazell DNo ratings yet
- Statistics & Probability Q4 - Week 1-2Document13 pagesStatistics & Probability Q4 - Week 1-2Rayezeus Jaiden Del Rosario50% (2)
- Chapter 4 Hypothesis TestingDocument13 pagesChapter 4 Hypothesis TestingManchilot TilahunNo ratings yet
- Day 9 - Module Hypothesis TestingDocument14 pagesDay 9 - Module Hypothesis TestingJoven JaravataNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis TestingDocument20 pagesHypothesis TestingHamza KhanNo ratings yet
- Cultural HegemonyDocument6 pagesCultural HegemonyAlbert García100% (1)
- Basic Concepts of Hypothesis Testing: Final Lesson 4Document27 pagesBasic Concepts of Hypothesis Testing: Final Lesson 4Beatriz Helaena RasonableNo ratings yet
- Handout # 1Document6 pagesHandout # 1Perly PeterNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5-BUSINESS STATISTICSDocument15 pagesChapter 5-BUSINESS STATISTICSmeseleNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis TestingDocument60 pagesHypothesis TestingLaiba ZahirNo ratings yet
- Cha 3Document13 pagesCha 3Senay HaftuNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three Hypothesis TestingDocument16 pagesChapter Three Hypothesis Testingtemedebere100% (1)
- One-Tailed Test Two-Tailed TestDocument18 pagesOne-Tailed Test Two-Tailed Testkassandra panganibanNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability: Quarter 2 Week 3 Test of HypothesisDocument6 pagesStatistics and Probability: Quarter 2 Week 3 Test of HypothesisArth LubayNo ratings yet
- MATH 121 Chapter 8 Hypothesis TestingDocument31 pagesMATH 121 Chapter 8 Hypothesis TestingJanine LerumNo ratings yet
- Tests of SignificanceDocument60 pagesTests of SignificancegirmaNo ratings yet
- Statistics & Probability: Tests of HypothesisDocument7 pagesStatistics & Probability: Tests of HypothesisJeffrey R. AbadNo ratings yet
- Testing MeansDocument8 pagesTesting MeansboNo ratings yet
- Lec 7 - Hypothesis TestingDocument29 pagesLec 7 - Hypothesis TestingABDUR -No ratings yet
- Inferential Statistics: Hypothesis Testing: An IntroductionDocument17 pagesInferential Statistics: Hypothesis Testing: An IntroductionMary Roselyn R. EboñaNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Testing For One PopulationDocument57 pagesHypothesis Testing For One PopulationFarah CakeyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document89 pagesChapter 4Afifa SuibNo ratings yet
- CH05 Cheat SheetDocument5 pagesCH05 Cheat SheetISLAM KHALED ZSCNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Tests For One Population Mean: Chapter 9 Part 1Document27 pagesHypothesis Tests For One Population Mean: Chapter 9 Part 1Mohd Nazri OthmanNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Hypothesis Testing: Zoheb Alam KhanDocument82 pagesFundamentals of Hypothesis Testing: Zoheb Alam KhanRetno Ajeng Anissa WidiatriNo ratings yet
- Level of Significance Is Set by The Invigilator and Is Fixed As Possible in Order To Protect The True Null Hypothesis From RejectionDocument9 pagesLevel of Significance Is Set by The Invigilator and Is Fixed As Possible in Order To Protect The True Null Hypothesis From RejectionAisha RanaNo ratings yet
- Testing HypothisisDocument41 pagesTesting HypothisisProtikNo ratings yet
- Chapter ThreeDocument13 pagesChapter ThreeAshu MajaNo ratings yet
- MGMT 222 Ch. V-1Document30 pagesMGMT 222 Ch. V-1Asteway Mesfin100% (1)
- 8 Ypothesis Esting: October 31 - November 7, 2020Document31 pages8 Ypothesis Esting: October 31 - November 7, 2020BENITEZ JOEL R.0% (1)
- Hypothesis TestingDocument45 pagesHypothesis Testingrushilgoelme20a1053No ratings yet
- G11 Hypothesis TestingDocument27 pagesG11 Hypothesis TestingTol AdoNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Testing 08052022 070212pmDocument13 pagesHypothesis Testing 08052022 070212pmAhmed Hassan QureashiNo ratings yet
- Statistical Inference, Decision Theory and Hypothesis TestingDocument4 pagesStatistical Inference, Decision Theory and Hypothesis TestingGold UsenekongNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 HTDocument20 pagesChapter 3 HTmuslim yasinNo ratings yet
- Testing Hypotheses: R. 3. 1. (Introduction)Document16 pagesTesting Hypotheses: R. 3. 1. (Introduction)Moha ShifNo ratings yet
- P&S Unit 5 (1) 111111111111Document16 pagesP&S Unit 5 (1) 111111111111Ganesh DegalaNo ratings yet
- Testing of Hypothesis - SVB NotesDocument20 pagesTesting of Hypothesis - SVB NotesRecoth PaulNo ratings yet
- Signed Off Statistics and Probability11 q2 m5 Test of Hypothesis Lesson 2Document6 pagesSigned Off Statistics and Probability11 q2 m5 Test of Hypothesis Lesson 2jerrymhitorres16No ratings yet
- Colegio de San Gabriel Arcangel of Caloocan, Inc. Escuela San Gabriel de Arcangel FoundationDocument8 pagesColegio de San Gabriel Arcangel of Caloocan, Inc. Escuela San Gabriel de Arcangel FoundationJasmine BalbinNo ratings yet
- Testing HypothesisDocument14 pagesTesting HypothesisAbdul RafayNo ratings yet
- STAL2073 Chapter4 2020 2021 6af2b89854d8f7bccb4ff4 231017 010847Document19 pagesSTAL2073 Chapter4 2020 2021 6af2b89854d8f7bccb4ff4 231017 010847azmina rahamanNo ratings yet
- Statisticsprobability11 q4 Week1 v4Document10 pagesStatisticsprobability11 q4 Week1 v4Sheryn CredoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 105 4Document20 pagesChapter 4 105 4masrawy eduNo ratings yet
- Testing HypothesisDocument11 pagesTesting HypothesisSaif KamalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - Hypothesis TestingDocument100 pagesChapter 9 - Hypothesis TestingLauren MichelleNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Testing Hand NotreDocument6 pagesHypothesis Testing Hand NotreAmzad DPNo ratings yet
- Unlocking The Mysteries of Hypothesis Testing: Brent Griffin Revised Fall 2006Document15 pagesUnlocking The Mysteries of Hypothesis Testing: Brent Griffin Revised Fall 2006nishant1090No ratings yet
- Unlocking The Mysteries of Hypothesis Testing: Brent Griffin Revised Fall 2006Document15 pagesUnlocking The Mysteries of Hypothesis Testing: Brent Griffin Revised Fall 2006ValanArasuNo ratings yet
- Week 1-2 Stats and ProbDocument23 pagesWeek 1-2 Stats and ProbName DeldaNo ratings yet
- 2 Hypothesis Testing (Part 1)Document8 pages2 Hypothesis Testing (Part 1)Von Adrian Inociaan HernandezNo ratings yet
- Rejection RegionDocument21 pagesRejection RegionAlona Nay AgcaoiliNo ratings yet
- Testing of Hypothesis Single Sample Test: Dr. T. T. KachwalaDocument29 pagesTesting of Hypothesis Single Sample Test: Dr. T. T. KachwalaParth Hemant PurandareNo ratings yet
- Rejection RegionDocument22 pagesRejection RegionAlona Nay AgcaoiliNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Testing Is A Procedure of Making DecisionDocument4 pagesHypothesis Testing Is A Procedure of Making DecisionJanah Beado PagayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document18 pagesChapter 6Muhammad Asyraf Bin RusliNo ratings yet
- Quarter4 Statistics Lecture NotesDocument29 pagesQuarter4 Statistics Lecture NotesMalang, Aleah E. NewtonNo ratings yet
- Statistic and Probability - RaymondDocument13 pagesStatistic and Probability - Raymondsalazarraymond098No ratings yet
- Eda Hypothesis Testing For Single SampleDocument6 pagesEda Hypothesis Testing For Single SampleMaryang DescartesNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Testing: SUBJECT: Statistics and Probability Subject Teacher: Marilou A. BasilioDocument29 pagesHypothesis Testing: SUBJECT: Statistics and Probability Subject Teacher: Marilou A. BasilioMalouAndayaBasilioNo ratings yet
- ZtableDocument3 pagesZtableBuddy OverthinkerNo ratings yet
- Quiz #1Document2 pagesQuiz #1Buddy OverthinkerNo ratings yet
- PROBLEM SET 3 Stem LeoDocument1 pagePROBLEM SET 3 Stem LeoBuddy OverthinkerNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 3Document2 pagesProblem Set 3Buddy OverthinkerNo ratings yet
- PROBLEM SET 2 Non AbmDocument2 pagesPROBLEM SET 2 Non AbmBuddy OverthinkerNo ratings yet
- What Is First Philosophy' in Mathematics EducationDocument12 pagesWhat Is First Philosophy' in Mathematics EducationBuddy OverthinkerNo ratings yet
- PROBLEM SET 2.2 MissedDocument1 pagePROBLEM SET 2.2 MissedBuddy OverthinkerNo ratings yet
- Number of Language in NepalDocument25 pagesNumber of Language in NepalBuddy OverthinkerNo ratings yet
- Quiz No 1Document1 pageQuiz No 1Buddy OverthinkerNo ratings yet
- Izmirli - Wittgenstein As A Social ConstructivistDocument11 pagesIzmirli - Wittgenstein As A Social ConstructivistBuddy OverthinkerNo ratings yet
- Trig Identities 2Document8 pagesTrig Identities 2Buddy OverthinkerNo ratings yet
- Atweh - Is The Good A DesireDocument10 pagesAtweh - Is The Good A DesireBuddy OverthinkerNo ratings yet
- Problem Set #3Document2 pagesProblem Set #3Buddy OverthinkerNo ratings yet
- Mesquita and Restivo All Human Beings As Mathematical WorkersDocument14 pagesMesquita and Restivo All Human Beings As Mathematical WorkersBuddy OverthinkerNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1 - Set ADocument1 pageProblem Set 1 - Set ABuddy OverthinkerNo ratings yet
- 3 - Language in NepalDocument10 pages3 - Language in NepalBuddy OverthinkerNo ratings yet
- Secondary Level Mathematics Education in The Present ContextDocument8 pagesSecondary Level Mathematics Education in The Present ContextBuddy OverthinkerNo ratings yet
- Routine Interview Schedule - October 3-7Document2 pagesRoutine Interview Schedule - October 3-7Buddy OverthinkerNo ratings yet
- Language Difficulties in Mathematics Courses For StudentsDocument273 pagesLanguage Difficulties in Mathematics Courses For StudentsBuddy OverthinkerNo ratings yet
- Christian Living & Values EducationDocument11 pagesChristian Living & Values EducationStephen Carl EsguerraNo ratings yet
- Bean Sprout LessonDocument4 pagesBean Sprout Lessonapi-317230123No ratings yet
- Ben Lunn - Article About Radulescu "The Quest", Op. 90Document6 pagesBen Lunn - Article About Radulescu "The Quest", Op. 90Nikolya Ulyanov100% (1)
- Lab Report No-02: Delete and Traverse in ArrayDocument4 pagesLab Report No-02: Delete and Traverse in ArraySyed raghib shahNo ratings yet
- Romeo and Juliet: Question BankDocument8 pagesRomeo and Juliet: Question BankAnjelene TerezNo ratings yet
- Scott Robertson Manifest16.SampleDocument60 pagesScott Robertson Manifest16.Sampleprocrast100% (2)
- Intermediate Grammar - Juni Sari SianturiDocument18 pagesIntermediate Grammar - Juni Sari SianturiNdhshsNo ratings yet
- PH & PH 1 - 4-Pronunciation Teaching Activities and Resources - TareasDocument2 pagesPH & PH 1 - 4-Pronunciation Teaching Activities and Resources - TareasIsabel RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Lab7 State MachineDocument7 pagesLab7 State MachineardserNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 Ethics HandoutDocument5 pagesCHAPTER 1 Ethics HandoutArmy Day DulmanNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Commission On Higher Education Daraga Community College Daraga, AlbayDocument3 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Commission On Higher Education Daraga Community College Daraga, AlbayMaria Angelica Tuella100% (3)
- Gramática I Resumen - Unidades 1, 2, 3Document13 pagesGramática I Resumen - Unidades 1, 2, 3Agos PiñeroNo ratings yet
- Marginalised Groups and Social JusticeDocument10 pagesMarginalised Groups and Social JusticeRiya AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Amazon Alexa Told Child To Put A Penny in A Plug Socket For ChallengeDocument6 pagesAmazon Alexa Told Child To Put A Penny in A Plug Socket For ChallengeMarco le pheonixNo ratings yet
- UNLV/Department of Teaching & Learning Elementary Lesson Plan TemplateDocument3 pagesUNLV/Department of Teaching & Learning Elementary Lesson Plan Templateapi-447880584No ratings yet
- From The Potala: Editions and Translation'. Sanskrit Texts From The Tibetan Autonomous Region 7Document3 pagesFrom The Potala: Editions and Translation'. Sanskrit Texts From The Tibetan Autonomous Region 7Bai HenryNo ratings yet
- 02 Vector GraphicsDocument50 pages02 Vector GraphicsA HegNo ratings yet
- Monika Maron - Animal TristeDocument3 pagesMonika Maron - Animal Triste林苏文No ratings yet
- Program - Inset 2Document5 pagesProgram - Inset 2Rachel ann GolimlimNo ratings yet
- #Include Using Namespace IntDocument7 pages#Include Using Namespace IntDiana Jane Terez LazaroNo ratings yet
- Asymptotic Notations For Time Efficiency AnalysisDocument33 pagesAsymptotic Notations For Time Efficiency AnalysisKancil ShareNo ratings yet
- WILLIAM BLAKE The Chimney Sweeper FINALSDocument6 pagesWILLIAM BLAKE The Chimney Sweeper FINALSZainabNo ratings yet
- CALYPSO Directory Structure enDocument15 pagesCALYPSO Directory Structure enKarl Jennings100% (1)
- Siegfried SassoonDocument13 pagesSiegfried SassoonTaibur RahamanNo ratings yet
- Quiz-Game Written in CDocument12 pagesQuiz-Game Written in CSatwik ShridharNo ratings yet
- PT - English 6 - Q1Document3 pagesPT - English 6 - Q1CARLOS FERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- Xbeacon Instructions V6.0: Xbeacon Configuration Tool App DownloadDocument6 pagesXbeacon Instructions V6.0: Xbeacon Configuration Tool App DownloadachareiNo ratings yet
- Impersonal Passive ExercisesDocument1 pageImpersonal Passive ExerciseslucytenevaNo ratings yet
- Sexing Differances: Anne-Emmanuelle BergerDocument17 pagesSexing Differances: Anne-Emmanuelle BergerM. Pilar Palacios AlamosNo ratings yet
Handouts Hyphotesis
Handouts Hyphotesis
Uploaded by
Buddy OverthinkerOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Handouts Hyphotesis
Handouts Hyphotesis
Uploaded by
Buddy OverthinkerCopyright:
Available Formats
HYPOTHESIS TESTING
HYPOTHESIS
It is an educated guess that can be tested
A statement that describes the population parameter
It is a tentative explanation, a claim, or assertion about people, objects, or events.
Types of Hypothesis
1. Null Hypothesis
Denoted by H 0 is a statement that there is no difference between a parameter and a specific
value, or that there is no difference between the two parameters.
2. Alternative Hypothesis
Denoted by H a ¿ H 1is a statement that there is a difference between a parameter and a specific
value or that there is a difference between tow parameters.
An opposing statement believed to be true whenever the null hypothesis is rejected.
Types Of Error
Type I Error: This type of error rejects the null hypothesis when in fact it is true. Type I error is also
known as alpha α error.
Type II Error: this type of error fails to reject the null hypothesis when in fact it is false. Type II error
is also known as beta β error.
Fact
Decision
H 0 is true H 0 is false
Accept H 0 Correct decision Type II error
Reject H 0 Type I error Correct decision
Level of Significance (α )
The significance level of a hypothesis is defined as the probability of committing a type I error. This is
the probability of rejecting a true null hypothesis.
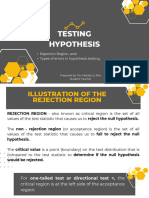
TYPES OF TEST
1. One-Tailed Test
It is a hypothesis test where the rejection region lies at only one tail of the distribution.
It is used when the alternative hypothesis is directional. It means that the value is either greater than
or less than the other measure.
Could be classified as left-tailed or right-tailed.
2. Two-Tailed Test
It is a hypothesis test where the rejection region lies at both end tails of the distribution, one on the
left and one on the right. The alpha level is also divided into two equal parts.
Type of Test
Level of Significance One-Tailed test Two-Tailed test
Both Left- and Right-
Left-Tailed Right-Tailed
Tailed
α = 0.05 Z < - 1.645 Z > 1.645 Z > 1.96 or Z < - 1.96
α = 0.01 Z < - 2.33 Z > 2.33 Z > 2.575 or Z < - 2.575
α = 0.10 Z < - 1.28 Z > 1.28 Z > 1.645 or Z < - 1.645
Key Terms
1. Test Statistic – used as a basis for deciding whether the null hypothesis should be rejected.
2. Rejection Region – this is the set of values of the test statistic that leads to rejection of the null
hypothesis.
3. Non-Rejection Region – this is the set of values of the test statistic that leads to acceptance of the null
hypothesis.
4. Critical Value – this is the set of values of the test statistic that separates the rejection and non-rejection
regions.
You might also like
- CH9 and 10. HYPOTHESIS TESTINGDocument7 pagesCH9 and 10. HYPOTHESIS TESTINGHazell DNo ratings yet
- Statistics & Probability Q4 - Week 1-2Document13 pagesStatistics & Probability Q4 - Week 1-2Rayezeus Jaiden Del Rosario50% (2)
- Chapter 4 Hypothesis TestingDocument13 pagesChapter 4 Hypothesis TestingManchilot TilahunNo ratings yet
- Day 9 - Module Hypothesis TestingDocument14 pagesDay 9 - Module Hypothesis TestingJoven JaravataNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis TestingDocument20 pagesHypothesis TestingHamza KhanNo ratings yet
- Cultural HegemonyDocument6 pagesCultural HegemonyAlbert García100% (1)
- Basic Concepts of Hypothesis Testing: Final Lesson 4Document27 pagesBasic Concepts of Hypothesis Testing: Final Lesson 4Beatriz Helaena RasonableNo ratings yet
- Handout # 1Document6 pagesHandout # 1Perly PeterNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5-BUSINESS STATISTICSDocument15 pagesChapter 5-BUSINESS STATISTICSmeseleNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis TestingDocument60 pagesHypothesis TestingLaiba ZahirNo ratings yet
- Cha 3Document13 pagesCha 3Senay HaftuNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three Hypothesis TestingDocument16 pagesChapter Three Hypothesis Testingtemedebere100% (1)
- One-Tailed Test Two-Tailed TestDocument18 pagesOne-Tailed Test Two-Tailed Testkassandra panganibanNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability: Quarter 2 Week 3 Test of HypothesisDocument6 pagesStatistics and Probability: Quarter 2 Week 3 Test of HypothesisArth LubayNo ratings yet
- MATH 121 Chapter 8 Hypothesis TestingDocument31 pagesMATH 121 Chapter 8 Hypothesis TestingJanine LerumNo ratings yet
- Tests of SignificanceDocument60 pagesTests of SignificancegirmaNo ratings yet
- Statistics & Probability: Tests of HypothesisDocument7 pagesStatistics & Probability: Tests of HypothesisJeffrey R. AbadNo ratings yet
- Testing MeansDocument8 pagesTesting MeansboNo ratings yet
- Lec 7 - Hypothesis TestingDocument29 pagesLec 7 - Hypothesis TestingABDUR -No ratings yet
- Inferential Statistics: Hypothesis Testing: An IntroductionDocument17 pagesInferential Statistics: Hypothesis Testing: An IntroductionMary Roselyn R. EboñaNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Testing For One PopulationDocument57 pagesHypothesis Testing For One PopulationFarah CakeyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document89 pagesChapter 4Afifa SuibNo ratings yet
- CH05 Cheat SheetDocument5 pagesCH05 Cheat SheetISLAM KHALED ZSCNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Tests For One Population Mean: Chapter 9 Part 1Document27 pagesHypothesis Tests For One Population Mean: Chapter 9 Part 1Mohd Nazri OthmanNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Hypothesis Testing: Zoheb Alam KhanDocument82 pagesFundamentals of Hypothesis Testing: Zoheb Alam KhanRetno Ajeng Anissa WidiatriNo ratings yet
- Level of Significance Is Set by The Invigilator and Is Fixed As Possible in Order To Protect The True Null Hypothesis From RejectionDocument9 pagesLevel of Significance Is Set by The Invigilator and Is Fixed As Possible in Order To Protect The True Null Hypothesis From RejectionAisha RanaNo ratings yet
- Testing HypothisisDocument41 pagesTesting HypothisisProtikNo ratings yet
- Chapter ThreeDocument13 pagesChapter ThreeAshu MajaNo ratings yet
- MGMT 222 Ch. V-1Document30 pagesMGMT 222 Ch. V-1Asteway Mesfin100% (1)
- 8 Ypothesis Esting: October 31 - November 7, 2020Document31 pages8 Ypothesis Esting: October 31 - November 7, 2020BENITEZ JOEL R.0% (1)
- Hypothesis TestingDocument45 pagesHypothesis Testingrushilgoelme20a1053No ratings yet
- G11 Hypothesis TestingDocument27 pagesG11 Hypothesis TestingTol AdoNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Testing 08052022 070212pmDocument13 pagesHypothesis Testing 08052022 070212pmAhmed Hassan QureashiNo ratings yet
- Statistical Inference, Decision Theory and Hypothesis TestingDocument4 pagesStatistical Inference, Decision Theory and Hypothesis TestingGold UsenekongNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 HTDocument20 pagesChapter 3 HTmuslim yasinNo ratings yet
- Testing Hypotheses: R. 3. 1. (Introduction)Document16 pagesTesting Hypotheses: R. 3. 1. (Introduction)Moha ShifNo ratings yet
- P&S Unit 5 (1) 111111111111Document16 pagesP&S Unit 5 (1) 111111111111Ganesh DegalaNo ratings yet
- Testing of Hypothesis - SVB NotesDocument20 pagesTesting of Hypothesis - SVB NotesRecoth PaulNo ratings yet
- Signed Off Statistics and Probability11 q2 m5 Test of Hypothesis Lesson 2Document6 pagesSigned Off Statistics and Probability11 q2 m5 Test of Hypothesis Lesson 2jerrymhitorres16No ratings yet
- Colegio de San Gabriel Arcangel of Caloocan, Inc. Escuela San Gabriel de Arcangel FoundationDocument8 pagesColegio de San Gabriel Arcangel of Caloocan, Inc. Escuela San Gabriel de Arcangel FoundationJasmine BalbinNo ratings yet
- Testing HypothesisDocument14 pagesTesting HypothesisAbdul RafayNo ratings yet
- STAL2073 Chapter4 2020 2021 6af2b89854d8f7bccb4ff4 231017 010847Document19 pagesSTAL2073 Chapter4 2020 2021 6af2b89854d8f7bccb4ff4 231017 010847azmina rahamanNo ratings yet
- Statisticsprobability11 q4 Week1 v4Document10 pagesStatisticsprobability11 q4 Week1 v4Sheryn CredoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 105 4Document20 pagesChapter 4 105 4masrawy eduNo ratings yet
- Testing HypothesisDocument11 pagesTesting HypothesisSaif KamalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - Hypothesis TestingDocument100 pagesChapter 9 - Hypothesis TestingLauren MichelleNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Testing Hand NotreDocument6 pagesHypothesis Testing Hand NotreAmzad DPNo ratings yet
- Unlocking The Mysteries of Hypothesis Testing: Brent Griffin Revised Fall 2006Document15 pagesUnlocking The Mysteries of Hypothesis Testing: Brent Griffin Revised Fall 2006nishant1090No ratings yet
- Unlocking The Mysteries of Hypothesis Testing: Brent Griffin Revised Fall 2006Document15 pagesUnlocking The Mysteries of Hypothesis Testing: Brent Griffin Revised Fall 2006ValanArasuNo ratings yet
- Week 1-2 Stats and ProbDocument23 pagesWeek 1-2 Stats and ProbName DeldaNo ratings yet
- 2 Hypothesis Testing (Part 1)Document8 pages2 Hypothesis Testing (Part 1)Von Adrian Inociaan HernandezNo ratings yet
- Rejection RegionDocument21 pagesRejection RegionAlona Nay AgcaoiliNo ratings yet
- Testing of Hypothesis Single Sample Test: Dr. T. T. KachwalaDocument29 pagesTesting of Hypothesis Single Sample Test: Dr. T. T. KachwalaParth Hemant PurandareNo ratings yet
- Rejection RegionDocument22 pagesRejection RegionAlona Nay AgcaoiliNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Testing Is A Procedure of Making DecisionDocument4 pagesHypothesis Testing Is A Procedure of Making DecisionJanah Beado PagayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document18 pagesChapter 6Muhammad Asyraf Bin RusliNo ratings yet
- Quarter4 Statistics Lecture NotesDocument29 pagesQuarter4 Statistics Lecture NotesMalang, Aleah E. NewtonNo ratings yet
- Statistic and Probability - RaymondDocument13 pagesStatistic and Probability - Raymondsalazarraymond098No ratings yet
- Eda Hypothesis Testing For Single SampleDocument6 pagesEda Hypothesis Testing For Single SampleMaryang DescartesNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Testing: SUBJECT: Statistics and Probability Subject Teacher: Marilou A. BasilioDocument29 pagesHypothesis Testing: SUBJECT: Statistics and Probability Subject Teacher: Marilou A. BasilioMalouAndayaBasilioNo ratings yet
- ZtableDocument3 pagesZtableBuddy OverthinkerNo ratings yet
- Quiz #1Document2 pagesQuiz #1Buddy OverthinkerNo ratings yet
- PROBLEM SET 3 Stem LeoDocument1 pagePROBLEM SET 3 Stem LeoBuddy OverthinkerNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 3Document2 pagesProblem Set 3Buddy OverthinkerNo ratings yet
- PROBLEM SET 2 Non AbmDocument2 pagesPROBLEM SET 2 Non AbmBuddy OverthinkerNo ratings yet
- What Is First Philosophy' in Mathematics EducationDocument12 pagesWhat Is First Philosophy' in Mathematics EducationBuddy OverthinkerNo ratings yet
- PROBLEM SET 2.2 MissedDocument1 pagePROBLEM SET 2.2 MissedBuddy OverthinkerNo ratings yet
- Number of Language in NepalDocument25 pagesNumber of Language in NepalBuddy OverthinkerNo ratings yet
- Quiz No 1Document1 pageQuiz No 1Buddy OverthinkerNo ratings yet
- Izmirli - Wittgenstein As A Social ConstructivistDocument11 pagesIzmirli - Wittgenstein As A Social ConstructivistBuddy OverthinkerNo ratings yet
- Trig Identities 2Document8 pagesTrig Identities 2Buddy OverthinkerNo ratings yet
- Atweh - Is The Good A DesireDocument10 pagesAtweh - Is The Good A DesireBuddy OverthinkerNo ratings yet
- Problem Set #3Document2 pagesProblem Set #3Buddy OverthinkerNo ratings yet
- Mesquita and Restivo All Human Beings As Mathematical WorkersDocument14 pagesMesquita and Restivo All Human Beings As Mathematical WorkersBuddy OverthinkerNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1 - Set ADocument1 pageProblem Set 1 - Set ABuddy OverthinkerNo ratings yet
- 3 - Language in NepalDocument10 pages3 - Language in NepalBuddy OverthinkerNo ratings yet
- Secondary Level Mathematics Education in The Present ContextDocument8 pagesSecondary Level Mathematics Education in The Present ContextBuddy OverthinkerNo ratings yet
- Routine Interview Schedule - October 3-7Document2 pagesRoutine Interview Schedule - October 3-7Buddy OverthinkerNo ratings yet
- Language Difficulties in Mathematics Courses For StudentsDocument273 pagesLanguage Difficulties in Mathematics Courses For StudentsBuddy OverthinkerNo ratings yet
- Christian Living & Values EducationDocument11 pagesChristian Living & Values EducationStephen Carl EsguerraNo ratings yet
- Bean Sprout LessonDocument4 pagesBean Sprout Lessonapi-317230123No ratings yet
- Ben Lunn - Article About Radulescu "The Quest", Op. 90Document6 pagesBen Lunn - Article About Radulescu "The Quest", Op. 90Nikolya Ulyanov100% (1)
- Lab Report No-02: Delete and Traverse in ArrayDocument4 pagesLab Report No-02: Delete and Traverse in ArraySyed raghib shahNo ratings yet
- Romeo and Juliet: Question BankDocument8 pagesRomeo and Juliet: Question BankAnjelene TerezNo ratings yet
- Scott Robertson Manifest16.SampleDocument60 pagesScott Robertson Manifest16.Sampleprocrast100% (2)
- Intermediate Grammar - Juni Sari SianturiDocument18 pagesIntermediate Grammar - Juni Sari SianturiNdhshsNo ratings yet
- PH & PH 1 - 4-Pronunciation Teaching Activities and Resources - TareasDocument2 pagesPH & PH 1 - 4-Pronunciation Teaching Activities and Resources - TareasIsabel RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Lab7 State MachineDocument7 pagesLab7 State MachineardserNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 Ethics HandoutDocument5 pagesCHAPTER 1 Ethics HandoutArmy Day DulmanNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Commission On Higher Education Daraga Community College Daraga, AlbayDocument3 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Commission On Higher Education Daraga Community College Daraga, AlbayMaria Angelica Tuella100% (3)
- Gramática I Resumen - Unidades 1, 2, 3Document13 pagesGramática I Resumen - Unidades 1, 2, 3Agos PiñeroNo ratings yet
- Marginalised Groups and Social JusticeDocument10 pagesMarginalised Groups and Social JusticeRiya AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Amazon Alexa Told Child To Put A Penny in A Plug Socket For ChallengeDocument6 pagesAmazon Alexa Told Child To Put A Penny in A Plug Socket For ChallengeMarco le pheonixNo ratings yet
- UNLV/Department of Teaching & Learning Elementary Lesson Plan TemplateDocument3 pagesUNLV/Department of Teaching & Learning Elementary Lesson Plan Templateapi-447880584No ratings yet
- From The Potala: Editions and Translation'. Sanskrit Texts From The Tibetan Autonomous Region 7Document3 pagesFrom The Potala: Editions and Translation'. Sanskrit Texts From The Tibetan Autonomous Region 7Bai HenryNo ratings yet
- 02 Vector GraphicsDocument50 pages02 Vector GraphicsA HegNo ratings yet
- Monika Maron - Animal TristeDocument3 pagesMonika Maron - Animal Triste林苏文No ratings yet
- Program - Inset 2Document5 pagesProgram - Inset 2Rachel ann GolimlimNo ratings yet
- #Include Using Namespace IntDocument7 pages#Include Using Namespace IntDiana Jane Terez LazaroNo ratings yet
- Asymptotic Notations For Time Efficiency AnalysisDocument33 pagesAsymptotic Notations For Time Efficiency AnalysisKancil ShareNo ratings yet
- WILLIAM BLAKE The Chimney Sweeper FINALSDocument6 pagesWILLIAM BLAKE The Chimney Sweeper FINALSZainabNo ratings yet
- CALYPSO Directory Structure enDocument15 pagesCALYPSO Directory Structure enKarl Jennings100% (1)
- Siegfried SassoonDocument13 pagesSiegfried SassoonTaibur RahamanNo ratings yet
- Quiz-Game Written in CDocument12 pagesQuiz-Game Written in CSatwik ShridharNo ratings yet
- PT - English 6 - Q1Document3 pagesPT - English 6 - Q1CARLOS FERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- Xbeacon Instructions V6.0: Xbeacon Configuration Tool App DownloadDocument6 pagesXbeacon Instructions V6.0: Xbeacon Configuration Tool App DownloadachareiNo ratings yet
- Impersonal Passive ExercisesDocument1 pageImpersonal Passive ExerciseslucytenevaNo ratings yet
- Sexing Differances: Anne-Emmanuelle BergerDocument17 pagesSexing Differances: Anne-Emmanuelle BergerM. Pilar Palacios AlamosNo ratings yet