Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Organic Chemistry Reviewer
Organic Chemistry Reviewer
Uploaded by
enriquezchloe1670 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views3 pagesThis document provides an overview of organic chemistry concepts including alkanes, alkenes, and cycloalkanes. It discusses their structures, naming conventions, and physical properties such as boiling points, solubility, density. Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons that have higher boiling points with increasing molecular weight. Alkenes contain carbon-carbon double bonds and are unsaturated. Their naming involves indicating the location of double bonds. Cycloalkanes have ring structures.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides an overview of organic chemistry concepts including alkanes, alkenes, and cycloalkanes. It discusses their structures, naming conventions, and physical properties such as boiling points, solubility, density. Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons that have higher boiling points with increasing molecular weight. Alkenes contain carbon-carbon double bonds and are unsaturated. Their naming involves indicating the location of double bonds. Cycloalkanes have ring structures.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views3 pagesOrganic Chemistry Reviewer
Organic Chemistry Reviewer
Uploaded by
enriquezchloe167This document provides an overview of organic chemistry concepts including alkanes, alkenes, and cycloalkanes. It discusses their structures, naming conventions, and physical properties such as boiling points, solubility, density. Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons that have higher boiling points with increasing molecular weight. Alkenes contain carbon-carbon double bonds and are unsaturated. Their naming involves indicating the location of double bonds. Cycloalkanes have ring structures.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
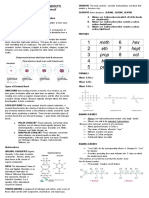
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY REVIEWER High molecular weight alkanes (those
containing 18 or more carbons) are white
waxy solids.
4 Halogens
F- Fluoro
B- Bromo - Boiling Points
Cl- Chloro Increase with increasing # of carbons
I- Iodo More atoms, more electrons, more opportunities for
induced dipole included dipole forces.
Decrease with chain branching
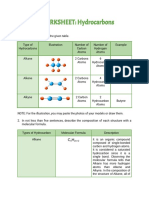
Cycloalkanes Branched molecules are more compact with smaller
CnH2n surface area-fewer points of contact with other
Cyclopropane- shortest/smallest cycloalkanes molecules.
A class of hydrocarbon that have a ring like structure
- Solubility: A case of Like Dissolve Like
Physical Properties of Alkanes Because alkanes are non-polar, they are not soluble in
water, which dissolves only ionic and polar
compounds.
- Melting and Boiling Points Alkanes do not dissolve in water because they cannot
The boiling points of alkanes are lower than those of form hydrogen bonds with water.
almost any type of compound of the same molecular Alkanes are soluble in each other, is an example of
weight. like dissolve like.
Both boiling and melting points of alkanes increase
with increasing molecular weight. – Directly
proportional. - Density
Alkanes containing 1 to 4 carbons are gases at All liquid and solid alkanes are less dense than water
room temperature. and because they are insoluble in water, they float in
Alkanes containing 5 to 17 carbons are water.
colorless liquids.
Alkenes
Contain at least one C=C double bond
- Dienes
Gen. formula: CnH2n
o Have two or more carbon=carbon double bonds which
Each member contains one double covalent bond
may be either isolated, cumulated or conjugated.
between two C atoms.
Unsaturated Isolated or Non-Conjugated
Only 3 atoms joined to each C, not 4 Double bonds are separated by more than one
single bond.
Cumulated
-Saturation vs. Unsaturation Double bonds are adjacent to each other.
Simply put, a saturated hydrocarbon has no double Conjugated
bonds between Carbon atoms (ex. Alkanes) double bonds are separated by one single
Unsaturated has one or more double or triple bonds bond.
between carbons (alkenes, alkynes)
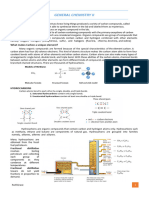
Alkene Nomenclature (Naming) Naming Dienes
1. The first C atom in the C=C bond indicates the double o Name the longest chain that contains both double bonds.
bond’s location (or number in naming) End it with diene.
2. The double bonds have priority and must have the lowest o When necessary, use the lowest numbers to give the
number(s) possible. locations of both double bonds.
3. Name, number, & alphabetize substituents as usual.
4. Parent chain- longest chain that includes the double Naming Trienes
bond(s) o Name the longest chain that contains both double bonds.
5. Replace -ane ending with -ene ending. End it with triene.
o Two double bonds: - diene o When necessary, use the lowest numbers to give the
Three double bonds: -triene locations of both double bonds.
6. Put double bond number in front of entire root name (i.e.
2-pentene indicates the double bond starts on carbon 2)
Naming Cycloalkenes
o Cycloalkenes are named in a similar way. Number the
Cyclic alkenes: number the atoms in the ring starting with double cycloalkene so the double bond carbons get number 1 and
bond. 2, and the first substituent is the lowest possible number.
o If there is a substituent on one of the double bond carbons,
it gets number 1.
You might also like
- Human Reproduction Unit Review Worksheet KEY 2015-2016Document4 pagesHuman Reproduction Unit Review Worksheet KEY 2015-2016Lalaine Angela Denuna86% (7)
- PEM4 Fuel Configuration and SelectionDocument3 pagesPEM4 Fuel Configuration and SelectionSergei GovorkoNo ratings yet
- CACIBAJAGA - Cave of The AncestorsDocument14 pagesCACIBAJAGA - Cave of The AncestorsAlex Moore-Minott100% (1)
- Chem Lec Week 5Document4 pagesChem Lec Week 5Alexandra Nicole EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Lecture On Organic Chemistry Part 2Document6 pagesLecture On Organic Chemistry Part 2ARRIANE CYREL CAMACHONo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 HydrocarbonsDocument16 pagesChapter 15 HydrocarbonsVjayan DharmaNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its CompoundsDocument1 pageCarbon and Its CompoundsSK CreationsNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons and Benzene: MVPS (2020)Document4 pagesHydrocarbons and Benzene: MVPS (2020)Paul Alfred SoNo ratings yet
- Coek - Info AlkynesDocument12 pagesCoek - Info AlkynesDũng NgôNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry: Alkenes, Alkynes, and Aromatic CompoundsDocument43 pagesOrganic Chemistry: Alkenes, Alkynes, and Aromatic CompoundsDarius Gan100% (1)
- Exp.5-Reaction of Alkanes, Alkenes, and CycloalkanesDocument27 pagesExp.5-Reaction of Alkanes, Alkenes, and CycloalkaneszazoNo ratings yet
- MIDTERMS CHEM - MazonDocument10 pagesMIDTERMS CHEM - MazonMazon, Dinah Melisse P.No ratings yet
- Angelica C. Anabe Bs Psy 2-1: AlkenesDocument12 pagesAngelica C. Anabe Bs Psy 2-1: Alkenesniela cruzNo ratings yet
- Alkanes: Hybridisation of OrbitalsDocument11 pagesAlkanes: Hybridisation of OrbitalsIsaa gabNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - 20210419Document38 pagesChapter 2 - 20210419firehywotNo ratings yet
- 1 Topic: 2.0 Carbon Compound: Homologous SeriesDocument22 pages1 Topic: 2.0 Carbon Compound: Homologous Seriesdr lailaNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons ChapterNotes-JEEMAIN - GURUDocument11 pagesHydrocarbons ChapterNotes-JEEMAIN - GURURaagNo ratings yet
- Assignment in Org ChemDocument25 pagesAssignment in Org ChemFrancine MaramagNo ratings yet
- Branch of Chemistry Dealing With Carbon MoleculesDocument31 pagesBranch of Chemistry Dealing With Carbon Moleculesedgardo mirandaNo ratings yet
- Lecture On Organic Chemistry Part 3Document7 pagesLecture On Organic Chemistry Part 3ARRIANE CYREL CAMACHONo ratings yet
- Alkenes and AlkynesDocument27 pagesAlkenes and AlkynesS:M:ENo ratings yet
- 10장Document37 pages10장sungyeon heoNo ratings yet
- Orgchem Lab M4Document7 pagesOrgchem Lab M4kieth marfilNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three Chem 130-1Document38 pagesChapter Three Chem 130-1hermanusjumaNo ratings yet
- AlkenesDocument5 pagesAlkenesSafa MarwanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document95 pagesChapter 6api-705775034No ratings yet
- XI Chem Ch13 Hydrocarbons ChapterNotesDocument11 pagesXI Chem Ch13 Hydrocarbons ChapterNotesAbhyuday BharatNo ratings yet
- C9 - Crude Oil and FuelsDocument3 pagesC9 - Crude Oil and FuelsAbdul-Muizz KhanNo ratings yet
- HydrocarbonsDocument27 pagesHydrocarbonsHoney MarquezNo ratings yet
- 3 Organic Chemistry - BenzeneDocument39 pages3 Organic Chemistry - BenzeneIsuriy AdasuriyaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Chapter 2 63-104Document42 pagesOrganic Chemistry Chapter 2 63-104mortemsondeathNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Alkenes and Alkynes PowerpointDocument61 pagesChapter 3 Alkenes and Alkynes PowerpointFreya An YbanezNo ratings yet
- Families of Organic CompoundsDocument8 pagesFamilies of Organic CompoundsJessa Mae LangcuyanNo ratings yet
- 4.1 - AlkenesDocument8 pages4.1 - Alkenesbecky.brownu746No ratings yet
- Module 4: Unsaturated HC (Reactions) and Aromatics (Properties)Document8 pagesModule 4: Unsaturated HC (Reactions) and Aromatics (Properties)back upNo ratings yet
- Bonding of Hydrocarbons: Presented by Rina Mae Manceras Benjamin BagayanDocument33 pagesBonding of Hydrocarbons: Presented by Rina Mae Manceras Benjamin BagayanIce BearNo ratings yet
- Unsaturated HydrocarbonsDocument12 pagesUnsaturated HydrocarbonsRielle JaliqueNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry,: AlkenesDocument35 pagesOrganic Chemistry,: AlkenesPayman SaidNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Laboratory Hydrocarbons: Group No. 6 NAME: Trishka Madeleine G. DelezDocument7 pagesOrganic Chemistry Laboratory Hydrocarbons: Group No. 6 NAME: Trishka Madeleine G. DelezKit GabrielNo ratings yet
- Alkenes Infrared Spectroscopy and Mass SpectrosDocument40 pagesAlkenes Infrared Spectroscopy and Mass Spectrosalexandra owNo ratings yet
- Biochem NotesDocument39 pagesBiochem NotesKaren May GarataNo ratings yet
- 1A Benzene and PhenolDocument13 pages1A Benzene and PhenolNicoleNo ratings yet
- IbchorganicDocument35 pagesIbchorganicapi-293306937100% (1)
- Daniel 2Document2 pagesDaniel 2Julio Cèsar GarcìaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding & Nomenclature of Hydrocarbons: Physical Science Week 4 HandoutsDocument2 pagesChemical Bonding & Nomenclature of Hydrocarbons: Physical Science Week 4 HandoutsBenj Jamieson DuagNo ratings yet
- Bahan Ajar AlkunaDocument28 pagesBahan Ajar Alkunakasma watiNo ratings yet
- A3 CosepeDocument4 pagesA3 CosepeSean Jodi CosepeNo ratings yet
- Edexcel IAL Chemistry A-Level: Topic 5: AlkenesDocument7 pagesEdexcel IAL Chemistry A-Level: Topic 5: AlkenesBara' HammadehNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem Organic Chemistry NotesDocument5 pagesGen Chem Organic Chemistry NotesVianneie Dominique BernadasNo ratings yet
- Alkanes, Alkenes, and AlkynesDocument2 pagesAlkanes, Alkenes, and AlkynesBacadon JerryNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry (Alkane, Alkene and Alkyne)Document7 pagesOrganic Chemistry (Alkane, Alkene and Alkyne)Dazell Varron100% (1)
- Hydrogen: Get The Power of Visual Impact On Your Side Log On ToDocument9 pagesHydrogen: Get The Power of Visual Impact On Your Side Log On ToShantam SinhaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry-I Reactive Intermeditate - Carbo Cation, Carbanion, Free Radicals and Carbenes.Document29 pagesOrganic Chemistry-I Reactive Intermeditate - Carbo Cation, Carbanion, Free Radicals and Carbenes.boopathi_chemist3628No ratings yet
- Review Organic ChemDocument49 pagesReview Organic ChemNihaya MulokNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 02 Sept 2023Document16 pagesAdobe Scan 02 Sept 2023Bhavya SomaiyaNo ratings yet
- 5.4 - Organic Independat OtesDocument5 pages5.4 - Organic Independat Otesvarda9877No ratings yet
- Ch03 Functional GroupsDocument37 pagesCh03 Functional GroupsSİNEM GÜVENNo ratings yet
- Alkenes and AlkynesDocument85 pagesAlkenes and AlkynesAdel M MalkawiNo ratings yet
- Alkanes and AlkenesDocument32 pagesAlkanes and AlkenesNicolás SerranoNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 13 Hydrocarbons Revision NotesDocument63 pagesCBSE Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 13 Hydrocarbons Revision NotesAjitesh KumarNo ratings yet
- 1 Review of Hydrocarbon Chemistry 2023Document5 pages1 Review of Hydrocarbon Chemistry 2023Clipped GamerNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Chemical BondingFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Chemical BondingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Chemical Bonding with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Chemical Bonding with AnswersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Dredge-Status February 2022Document8 pagesDredge-Status February 2022Berp OnrubiaNo ratings yet
- Pe Reviewer BadmintonDocument4 pagesPe Reviewer BadmintonRenmark MartinezNo ratings yet
- Genre Analysis EssayDocument8 pagesGenre Analysis Essayapi-339974812No ratings yet
- 10 1109@ice348803 2020 9122890Document3 pages10 1109@ice348803 2020 9122890Harsh SinghNo ratings yet
- Land Use Capability Classification Indicates The Suitability of Various Kinds of Soil ForDocument21 pagesLand Use Capability Classification Indicates The Suitability of Various Kinds of Soil Forcmindia2020No ratings yet
- DB en Macx MCR Ex SL Nam 2t SP 103752 en 02Document20 pagesDB en Macx MCR Ex SL Nam 2t SP 103752 en 02Seka Vilar SorucoNo ratings yet
- Hazards 28 Paper 37Document8 pagesHazards 28 Paper 37Abdeldjalil AchourNo ratings yet
- Kathrein Iot Portfolio Catalog 2021 enDocument33 pagesKathrein Iot Portfolio Catalog 2021 enUrdaNo ratings yet
- Conduct o Me TryDocument7 pagesConduct o Me Try19-28 Manan PopatNo ratings yet
- TWH27N TWH54N TWH120N TWH210N TWH430NDocument1 pageTWH27N TWH54N TWH120N TWH210N TWH430Nmohamed salahNo ratings yet
- 6.malnutrition inDocument129 pages6.malnutrition inCHALIE MEQU100% (1)
- Engineering MetallurgyDocument9 pagesEngineering MetallurgyDHANASEKAR K IV A 9023No ratings yet
- Kanker PayudaraDocument60 pagesKanker PayudaranoviNo ratings yet
- Toomay Radar Principles For Non-Specialist Chapter 3 Exercise SolutionsDocument12 pagesToomay Radar Principles For Non-Specialist Chapter 3 Exercise SolutionsJohanWNo ratings yet
- Espec Tecn XDM-500Document242 pagesEspec Tecn XDM-500Jose JaramilloNo ratings yet
- Monitoring of Tablet Coating Processes With Colored CoatingsDocument12 pagesMonitoring of Tablet Coating Processes With Colored CoatingsRong ZhaoNo ratings yet
- Abstract:: Home Automation Using Android AppDocument5 pagesAbstract:: Home Automation Using Android Appknb1990No ratings yet
- Gcse Landscape Project 12 Week Plan UpdatedDocument9 pagesGcse Landscape Project 12 Week Plan Updatedapi-442506422No ratings yet
- Anxiolytic DrugsDocument8 pagesAnxiolytic DrugsTony DawaNo ratings yet
- Learning Through StoriesDocument21 pagesLearning Through Storiesjeff talk talksNo ratings yet
- Kinematics Physics ProblemsDocument22 pagesKinematics Physics ProblemsAnup Navin78% (9)
- Construction Method Statement Car Lift: Debenham House, 8 Addison Road, W14 8DJ April 2016Document13 pagesConstruction Method Statement Car Lift: Debenham House, 8 Addison Road, W14 8DJ April 2016sahithasilvaNo ratings yet
- Rendering Trees From Precomputed Z-Buffer ViewsDocument10 pagesRendering Trees From Precomputed Z-Buffer ViewsLuis Enrique PulidoNo ratings yet
- LAB 8 - Compaction - LEVEL 2 - AINUR NASUHA BINTI MOHAMMAD RODZI-2019892466Document8 pagesLAB 8 - Compaction - LEVEL 2 - AINUR NASUHA BINTI MOHAMMAD RODZI-2019892466Ainur NasuhaNo ratings yet
- Transformer Room Ventilation CalculationDocument6 pagesTransformer Room Ventilation CalculationAryo Bayu TejokusumoNo ratings yet
- Remedial Exam - Gateway A2: Exclamativas, Imperativas, Declarativas)Document3 pagesRemedial Exam - Gateway A2: Exclamativas, Imperativas, Declarativas)Nga TrầnNo ratings yet
- Acer Iconia Tab 7 A1-713HD - Iconia Tab 7 User Guide English PDFDocument47 pagesAcer Iconia Tab 7 A1-713HD - Iconia Tab 7 User Guide English PDFBudi AjiNo ratings yet