Professional Documents
Culture Documents
GDE Gr.11 Life Sciences ATP Term 1 2024
GDE Gr.11 Life Sciences ATP Term 1 2024
Uploaded by
destineemande07Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
GDE Gr.11 Life Sciences ATP Term 1 2024
GDE Gr.11 Life Sciences ATP Term 1 2024
Uploaded by
destineemande07Copyright:
Available Formats
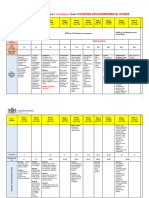
Annual Teaching Plan 2024
Term 1: LIFE SCIENCES: Grade 11
Week 9
Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Week 5 Week 6 Week 7 Week 8 Week 10
TERM 1 (5
(46 days)
(3 days) (5 days) (5 days) (5 days) (5 days) (5 days) (5 days) (5 days) (3 days)
17/1 – 19/1 22/1 – 26/1 29/1 – 2/2 5/2 - 9/2 12/2 – 16/2 19/2 – 23/2 26/2- 1/3 4/3 – 8/3 days) 18/3 –20/3
11/3 –15/3
CAPS Topics Orientation (CAPS p 39) Biodiversity and classification of microorganisms (CAPS p 40) Biodiversity of plants (CAPS p 41) Biodiversity of animals
SBA Part 2
SBA Practical SBA Part 1 21/2
ATP
3% 7% 10% 14% 17% 21% 24% 28% 31%
coverage
Date & DH
signature
Baseline Micro-organisms: Symbiotic Immunity, including plants Grouping of Bryophytes Asexual and Flowers as The concept of a phylum.
assessment basic structure relationships of and animals’ immune and Pteridophytes sexual reproductive
based on and general bacteria such as responses against the Grouping of reproduction, structures Relationship between body plan and grouping of animals in phyla.
Grade 10 Gymnosperms and name Adaptations for Six animal Phyla:
characteristics of nitrogen fixing infecting micro-organisms.
topics needed Angiosperms advantages pollination - Porifera,
for Term 1 e.g., the following bacteria in plants and through (different - Cnidaria,
classification groups and E. coli in the The use of drugs e.g., Use simple diagrams to disadvantages pollinators) wind, - Platyhelminthes,
schemes, the viruses human intestine antibiotics; effect on micro- identify an example of of each. insects and birds - Annelida,
nitrogen cycle. bacteria organisms each group and a Removed: The (South African - Arthropoda
Revise comparative table to significance of examples only) - Chordata
Core Concepts, Skills and Values
Protista The effect and Vaccinations (discuss
scientific skills. fungi management of one briefly) demonstrate the seeds differences and Use simple diagrams to identify an example of each phylum and a
presence/absence of seed banks similarities. comparative table to demonstrate the following in the six phyla:
disease from each
following in the four -seeds as a
The roles that of the four groups: The use of micro-organisms groups: food source Key features in respect of body plans:
these groups play - viruses (rabies, to produce medicines (e.g., and - symmetry and cephalisation
in maintaining HIV/AIDS, insulin and antibiotics) vascular tissue (xylem -endemic - the number of tissue layers
balance in the influenza) and phloem) species in developed from embryo
environment and - bacteria (blight, Traditional technology to true leaves and roots South Africa - the number of openings in the gut
web of life cholera, produce, e.g., beer, wine seeds or spores - coelom and blood systems.
and cheese. fruit.
tuberculosis,
decreasing dependence The role of invertebrates in agriculture and ecosystems
anthrax) on water for
- protists (malaria) reproduction from
- fungi (rust, thrush, Bryophytes to
ringworm, athlete’s Angiosperm
foot)
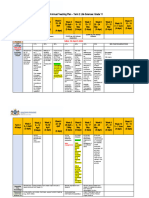
TV Lessons 1-5 6-9 10 11-14 15 16 17- 20
RELAB Booklet 4-18 19 24 25-30 31-37 38 - 44 45 - 53
pg.
Pre- BIODIVERSITY, CLASSIFICATION & ECOSYSTEMS GRADE 10
Knowledge
Week 9
Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Week 5 Week 6 Week 7 Week 8 Week 10
TERM 1 (5
(46 days)
(3 days) (5 days) (5 days) (5 days) (5 days) (5 days) (5 days) (5 days) (3 days)
17/1 – 19/1 22/1 – 26/1 29/1 – 2/2 5/2 - 9/2 12/2 – 16/2 19/2 – 23/2 26/2- 1/3 4/3 – 8/3 days) 18/3 –20/3
11/3 –15/3
Watch Activity Activity Activity Activity Activity Activity Activity Activity
Telematics Table on micro- Symbiotic Immunity, vaccinations Phylogenetic trees and Table Calculate Construct a The role of invertebrates in
video on organisms: relationships of using articles cladograms showing the indicating the approxima comparative table agriculture and ecosystems
names, basic nitrogen fixing evolutionary history of differences of these four k e y
scientific te surface
structures, bacteria in plants Activity the four plant groups and between area to features in the six
method at: characteristics and E. coli in the Effect of antibiotics on major structural changes asexual and selected phyla
https://bit.ly/2 volume
and diagrams. human intestine. micro-organisms; use of in their history of sexual ratios of and indicate the
VOLuhj micro-organisms to produce development reproduction mode of living of
selected
Activity medicine; traditional showing examples each phyla.
https:// A table of ONE technology to produce e.g. Activity advantages Include as many
Examples of informal/daily activities
of different
youtu.be/ disease from each beer, wine and cheese. Table indicating the and diagrams or
animals of
oKhS30j_vQo group indicating differences between disadvantages. pictures as
the six
effect and Bryophytes, phyla. possible.
management Pteridophytes,
Gymnosperms and
Angiosperms in terms of
vascular tissue, leaves
and roots, seeds or
spores and fruit also
including drawings of the
macroscopic parts:
bryophytes: moss plant
pteridophytes: rhizome,
frond with sori
gymnosperms: needles,
cones and seeds; and
Angiosperms: flower, fruit
and seeds.
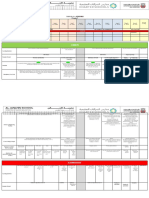
INVESTIGATION Prac 1, Worksheets 2-4 INVESTIGATION INVESTIGATION
Growing cultures Dissect an Select one
on agar plates, or example of each phylum and
bread mould of the following
Investigations/Experiments
design a poster
(fungus) on types of flowers: to show diversity
bread. wind pollinated, in that phylum in
Prac 1, insect pollinated South Africa.
Worksheet 1 and
bird pollinated
Record
observations in a
comparative
table.
Prac 1,
Worksheets 5A, 6
Informal Tests Topic Test Topic Test Topic Test
SBA (Formal TASK 1: PRACTICAL TASK (minimum 30 marks) - SBA Weighting: 10% TASK 2: FORMAL TEST (minimum 50 marks) - SBA Weighting: 20%
Assessment) TERM WEIGHTING: 25% TERM WEIGHTING: 75%
SBA completion: 1 task completed = 17%
2 tasks completed = 33%
You might also like
- 2021 Chapter 7 Diversity in Living Organism MCQsDocument6 pages2021 Chapter 7 Diversity in Living Organism MCQsGauravNo ratings yet
- GDE Gr.11 Life Sciences ATP Term 1 2024Document3 pagesGDE Gr.11 Life Sciences ATP Term 1 2024Mpho MashediNo ratings yet
- 1 2023 ATP Gr.10 Term 1 Gauteng CorrectedDocument4 pages1 2023 ATP Gr.10 Term 1 Gauteng CorrectedpholoshomalahleNo ratings yet
- 2021 Life SciencesDocument4 pages2021 Life SciencesNelly KhondloNo ratings yet
- GDE Gr.10 Life Sciences ATP Term 1 2024Document3 pagesGDE Gr.10 Life Sciences ATP Term 1 2024lukhuludumoNo ratings yet
- GDE Gr.11 Life Sciences ATP Term 2 2024Document4 pagesGDE Gr.11 Life Sciences ATP Term 2 2024Samukelisiwe ndlovuNo ratings yet
- LTP Term 1 Grade 1-3Document8 pagesLTP Term 1 Grade 1-3mahra alshamsiNo ratings yet
- Oridi 1Document273 pagesOridi 1Sandesh MavliyaNo ratings yet
- Notification ScienceDocument273 pagesNotification ScienceSeema SainiNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2024-01-06 at 9.47.25 AMDocument32 pagesScreenshot 2024-01-06 at 9.47.25 AMGungun GuptaNo ratings yet
- Biof214 1920Document3 pagesBiof214 1920Anurag KadkolNo ratings yet
- Yr 7 WB EditedDocument62 pagesYr 7 WB Editedolive mayanjaNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences Grade 11 ATP 2024Document14 pagesLife Sciences Grade 11 ATP 2024isiphombau33No ratings yet
- Exploring Creation With Biology Schedule For 2013-2014Document17 pagesExploring Creation With Biology Schedule For 2013-2014karen100% (2)
- 2024 ATP Gr.10 Term 2 GautengDocument10 pages2024 ATP Gr.10 Term 2 GautengOxford Da SoulNo ratings yet
- Neet-Biology For NSEBDocument23 pagesNeet-Biology For NSEBshruti.fedbankNo ratings yet
- Hasanuddin University: Semester Learning PlanDocument7 pagesHasanuddin University: Semester Learning PlanHafiedz FahreziNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Orientation To Life SciencesDocument31 pagesChapter 1 Orientation To Life SciencesHappy Monamaladi Sibahle MoepyaNo ratings yet
- LEARNING-GUIDE-for AGSC 55Document7 pagesLEARNING-GUIDE-for AGSC 55Rozele RomNo ratings yet
- entomology HandbookDocument97 pagesentomology HandbookPeter MwauraNo ratings yet
- 11th Bio-Botany-EM - SampleDocument30 pages11th Bio-Botany-EM - Samplemidhunkumarg0545No ratings yet
- Ramniranjan Jhunjhunwala College: of Arts, Science & Commerce (Autonomous College)Document21 pagesRamniranjan Jhunjhunwala College: of Arts, Science & Commerce (Autonomous College)Bobby MatNo ratings yet
- ISC Biology 2026Document21 pagesISC Biology 2026Vikram SinghNo ratings yet
- ISC BiologyDocument21 pagesISC Biologytuhinbose370No ratings yet
- 1122 - B.sc. Botany Semester-I, IIDocument16 pages1122 - B.sc. Botany Semester-I, IIgungunjain132005No ratings yet
- 20 ISC Biology SyllabusDocument23 pages20 ISC Biology SyllabusDebdutta PanditNo ratings yet
- Biology Textbook - NOUNDocument427 pagesBiology Textbook - NOUNamodusofiat77No ratings yet
- BIO F111 General Biology I Sem 23-24 HODocument3 pagesBIO F111 General Biology I Sem 23-24 HOobettajohnson6No ratings yet
- ISC Biology XI RevisedDocument9 pagesISC Biology XI RevisedSreerupa BandyopadhyayNo ratings yet
- Cprot 100 SyllabusDocument6 pagesCprot 100 Syllabusjan ray aribuaboNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Fall 2017 - Biology 336: Parasitology: Deburoni@cofc - EduDocument2 pagesSyllabus Fall 2017 - Biology 336: Parasitology: Deburoni@cofc - EduCristina AmaranteNo ratings yet
- B.Sc. B.Ed. Part II, 2020Document37 pagesB.Sc. B.Ed. Part II, 2020dinesh ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Table of Specification Item Location: Sta. Cruz National High SchoolDocument1 pageTable of Specification Item Location: Sta. Cruz National High SchoolGrace TiongsonNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument362 pagesUntitledshifaNo ratings yet
- B.SC Botany Sem 1 To 6 2017Document72 pagesB.SC Botany Sem 1 To 6 2017Jay ShethNo ratings yet
- SBTS Schedule (Revised Syllabus) - 07-10-2023 - Jyoti Ma'mDocument16 pagesSBTS Schedule (Revised Syllabus) - 07-10-2023 - Jyoti Ma'maltmshansriNo ratings yet
- 2023/24 Annual Teaching Plans: Life Sciences: Grade 11 (Term 1)Document7 pages2023/24 Annual Teaching Plans: Life Sciences: Grade 11 (Term 1)NokwandaNo ratings yet
- 2024 ATP Gr.10 Term 2 GautengDocument2 pages2024 ATP Gr.10 Term 2 GautengSamukelisiwe ndlovuNo ratings yet
- Biology XI Revised - 020424 - ISC2026Document9 pagesBiology XI Revised - 020424 - ISC2026tapanmukhopadhyay066No ratings yet
- Aiats Syllabus 12th StudyingDocument1 pageAiats Syllabus 12th Studyingravi1967ranjanNo ratings yet
- ISC Class 11 Biology Syllabus 2023 24Document10 pagesISC Class 11 Biology Syllabus 2023 24bohnibajpayiNo ratings yet
- ISC BiologyDocument21 pagesISC BiologyDebasish NayakNo ratings yet
- ISC 11th - Biology 2023-24 Council Syllabus-1-10Document10 pagesISC 11th - Biology 2023-24 Council Syllabus-1-10R HarryNo ratings yet
- 36 Year Pyq Biology PW PDFDocument368 pages36 Year Pyq Biology PW PDFpradnyakalseNo ratings yet
- Field of Study and Research Plan - Adrian TriandiDocument3 pagesField of Study and Research Plan - Adrian TriandiMaysixth92No ratings yet
- 20 ISC BiologyDocument22 pages20 ISC BiologyBran strongNo ratings yet
- Emmanuel College Planning Document - Semester One 2016 VCE - Biology Unit 1Document2 pagesEmmanuel College Planning Document - Semester One 2016 VCE - Biology Unit 1Doan Chan PhongNo ratings yet
- JAC 11th Biology Syllabus 2023-24Document8 pagesJAC 11th Biology Syllabus 2023-24Akanksha KumariNo ratings yet
- Term - I: (Code No. 044)Document6 pagesTerm - I: (Code No. 044)Hitesh YadavNo ratings yet
- Internal Assement XIDocument5 pagesInternal Assement XIJaysukh yt (Jay)No ratings yet
- TOS Second Prelim 19 20Document2 pagesTOS Second Prelim 19 20Chinitz ChanNo ratings yet
- EntomologyDocument7 pagesEntomologyNani MarapelliNo ratings yet
- Biologiýa Gollonma EnglishDocument568 pagesBiologiýa Gollonma EnglishAmangeldi BayrammamedowNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Biology Syllabus PDFDocument6 pagesCBSE Class 11 Biology Syllabus PDFKhushi PanjgotraNo ratings yet
- Neet 2024 BiologyDocument18 pagesNeet 2024 Biologydassrestha73No ratings yet
- Bio F111 1002Document4 pagesBio F111 1002ANo ratings yet
- Optimization of Protoplast Isolation From The Gametophytes of Brown Alga Undaria Pinnatifida Using Response Surface MethodologyDocument13 pagesOptimization of Protoplast Isolation From The Gametophytes of Brown Alga Undaria Pinnatifida Using Response Surface MethodologyJo CynthiaNo ratings yet
- ISC BiologyDocument23 pagesISC BiologyMr FeaRYTNo ratings yet
- 205-Article Text-1338-1-10-20230505Document8 pages205-Article Text-1338-1-10-20230505shrikant.teewaryNo ratings yet
- 69 Science FacultyDocument300 pages69 Science FacultyMedha KaushikNo ratings yet
- Table WorksheetDocument10 pagesTable WorksheetJuju ZenemijNo ratings yet
- Ncert Page Wise Q Plant KingdomDocument17 pagesNcert Page Wise Q Plant KingdomSagarNo ratings yet
- Plant Kingdom PDFDocument24 pagesPlant Kingdom PDFAdhil MusthafaNo ratings yet
- Leaves Can Also Store Food and WaterDocument5 pagesLeaves Can Also Store Food and WaterMaximos ManiatisNo ratings yet
- MCQ Class 11 Chapter 3Document5 pagesMCQ Class 11 Chapter 3Ashok KumarNo ratings yet
- Plant Kingdom 1Document7 pagesPlant Kingdom 1YoNo ratings yet
- Bio Midterm Last YearDocument8 pagesBio Midterm Last YearYun JiNo ratings yet
- HBBV-IX Practical-Module Biology Lab ManualDocument49 pagesHBBV-IX Practical-Module Biology Lab ManualAindri SinghNo ratings yet
- KVS TGT PGT PRT Previuous PepersDocument113 pagesKVS TGT PGT PRT Previuous PepersKaushik Sharma67% (3)
- 5 Kingdom ClassificationDocument36 pages5 Kingdom ClassificationMichelle Arienza100% (2)
- Desiccation and Survival in Plants, Drying Without DyingDocument422 pagesDesiccation and Survival in Plants, Drying Without DyingalejandroNo ratings yet
- MossesDocument8 pagesMossesValentinoDullSatinNo ratings yet
- BryophyteDocument71 pagesBryophyteSuci Hidayati Dwi LestariNo ratings yet
- Bio102 General Biology II SummaryDocument47 pagesBio102 General Biology II SummaryIkenna Okpala100% (1)
- KVS PGT Question PaperDocument117 pagesKVS PGT Question Papergauravhchavda100% (2)
- Sb025 1. BiodiversityDocument60 pagesSb025 1. BiodiversityazizrafeeqNo ratings yet
- Kebo 103Document14 pagesKebo 103Cedrickk AlforooNo ratings yet
- NSEB 2022-23 - (Question & Answers)Document19 pagesNSEB 2022-23 - (Question & Answers)Aditya RaiNo ratings yet
- Gurumantra of Biology Final File GurashDocument61 pagesGurumantra of Biology Final File GurashSaurav YadavNo ratings yet
- Lab 12: Bryophytes: Mosses and Liverworts (And Hornworts)Document28 pagesLab 12: Bryophytes: Mosses and Liverworts (And Hornworts)marcNo ratings yet
- Basic Concept of Alage - Bryophyte - Pteridophyte & GymnospermDocument19 pagesBasic Concept of Alage - Bryophyte - Pteridophyte & GymnospermDivyansha Sharma100% (1)
- Evolutionary Relationship in Kingdom Plantae: Dependence of Gametophyte and Sporophyte Water Dependence in FertilizationDocument4 pagesEvolutionary Relationship in Kingdom Plantae: Dependence of Gametophyte and Sporophyte Water Dependence in FertilizationAida AisyahNo ratings yet
- Major: Pre-Pharmacy: Nther: IsDocument7 pagesMajor: Pre-Pharmacy: Nther: IsFatima Al SayyedNo ratings yet
- Algae and BryophytaDocument25 pagesAlgae and BryophytaswischrisNo ratings yet
- Unit 11Document64 pagesUnit 11Lighto RyusakiNo ratings yet
- DLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W7Document8 pagesDLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W7clyde alfarasNo ratings yet
- Long Questions (5 Marks) : MSC-BOTANY, Model QuestionsDocument4 pagesLong Questions (5 Marks) : MSC-BOTANY, Model QuestionsCDB 1st Semester 2077No ratings yet
- Menti Quiz - 3rd Plant KingdomDocument32 pagesMenti Quiz - 3rd Plant KingdomUpal PramanickNo ratings yet
- BRYOPHYTESDocument13 pagesBRYOPHYTESHaneefullahNo ratings yet