Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Accounts Receivables
Accounts Receivables
Uploaded by
No NotreallyOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Accounts Receivables
Accounts Receivables
Uploaded by
No NotreallyCopyright:
Available Formats
TRADE AND NONTRADE RECEIVABLES
Trade Receivables
- claims arising from sale/ service from ordinary course of business
- includes accounts/notes receivable
- realized in one year or within the operating cycle whichever is longer
- current assets
Accounts Receivables
- open accounts arising from ordinary course of business
- customers’ accounts, trade debtors, and trade accounts receivable
Notes Receivables
- formal promise to pay(promissory note)
Nontrade Receivables
- claims arising from sources other than the ordinary course of business
- realized within one year, no matter the length of the operating cycle
PRESENTATION:
- current trade and nontrade shall be presented as a one line item “trade and other receivables” on
the face of the statement of financial position
- details are disclosed to notes to financial statements
EXAMPLES OF NONTRADE RECEIVABLES:
Current:
- advances/ receivables from shareholders/ members of the entity, classified as current/non
- advances to suppliers
- currently collectible subscription receivables
- creditors accounts with debit balance(customers with utang sa entity)
- dividends, accrued rent, accrued royalties, accrued interest receivable
- claims receivables: claims for losses or damages, rebates, tax refunds
Noncurrent:
- advances to affiliates
- special deposit on contracts bids, likely to remain outstanding for a long period of time
Customers’ credit balance
- results from overpayments, returns and allowances
- current liability
MEASUREMENT OF ACCOUNTS RECEIVABLES
- initially at face amount or original invoice amount plus directly attributable costs
- subsequently measured at amortized cost- net realizable value of a/r
Net realizable value
- initial amount reduced by adjustments, reduces the amount recoverable from the customer
Assets shall not be carried at above their recoverable amount
In estimating net value, ff deductions are made for allowances:
- freight charge
- Sales return
- Sales discount
- Doubtful accounts
METHODS OF RECORDING CREDIT SALES:
Gross method
- amounts are recorded without any deductions from discounts etc
- discounts are recorded when availed
Net method
- discount is recorded whether taken or not
ACCOUNTING FOR BAD DEBTS:
Allowance method
- requires allowance for doubtful accounts
- when considered as worthless, then it is written off
Direct writeoff
- recognizes loss when accounts prove to be worthless
- not permitted under IFRS
Recoveries of accounts written off
- recharge with the amount collected then record normally
- reverse the original entry written off
Entries:
Accounts receivable xx
Bad debts/Allow. For doubtful accounts xx
Cash xx
Accounts receivable xx
You might also like
- Property Management Proposal TemplateDocument10 pagesProperty Management Proposal Templatehossein100% (1)
- FABM 121 Week 11-20 (I Think)Document12 pagesFABM 121 Week 11-20 (I Think)Lymenson Boongaling75% (4)
- Financial Accounting Chapter 3Document5 pagesFinancial Accounting Chapter 3NiraniyaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Chapter 9 - Short-Term Operating Assets - Cash and ReceivablesDocument9 pagesLecture 2 - Chapter 9 - Short-Term Operating Assets - Cash and ReceivablesCorey VNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Financial Statements Project: GUL AHMAD Textile MillsDocument32 pagesAnalysis of Financial Statements Project: GUL AHMAD Textile MillsHanzala Asif100% (1)
- Far 2402 - ReceivablesDocument5 pagesFar 2402 - ReceivablesVangieNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 8 - Accounting For ReceivablesDocument41 pagesCHAPTER 8 - Accounting For ReceivablesVanessa BatallaNo ratings yet
- Presentation3.1 - Audit of Receivables, Revenue and Other Related AccountsDocument36 pagesPresentation3.1 - Audit of Receivables, Revenue and Other Related AccountsRoseanne Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Acctg Chap 5-7 PDFDocument16 pagesAcctg Chap 5-7 PDFAlexis B. BERTOLDONo ratings yet
- ACCOUNTINGDocument2 pagesACCOUNTINGtrixie manitoNo ratings yet
- Ypes of Fibers Such As Yarn or Fabric Are Produced and Processed Into Usable Products)Document4 pagesYpes of Fibers Such As Yarn or Fabric Are Produced and Processed Into Usable Products)Justine Ashley SavetNo ratings yet
- Share Accounting-WPS OfficeDocument5 pagesShare Accounting-WPS OfficeSurendra SharmaNo ratings yet
- ACT6146Document8 pagesACT6146coolleen101318No ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - Accounting For ReceivablesDocument10 pagesChapter 9 - Accounting For ReceivablesMajan Kaur100% (1)
- Fabm Q2 AnswersDocument15 pagesFabm Q2 AnswersminiriftyNo ratings yet
- BAT4M UniversityCollege Grade 12 Accounting Chapter 7 and 8 NotesDocument6 pagesBAT4M UniversityCollege Grade 12 Accounting Chapter 7 and 8 NotesBingyi Angela ZhouNo ratings yet
- Accounting Notes Chap 8-11Document20 pagesAccounting Notes Chap 8-11eemaanzhNo ratings yet
- Accounting VocabularyDocument4 pagesAccounting Vocabularyapi-526065196No ratings yet
- Accounting Chapter 5: Internal Control, Cash and Receivables 1. Accounts & Notes ReveivableDocument7 pagesAccounting Chapter 5: Internal Control, Cash and Receivables 1. Accounts & Notes ReveivableMarine De CocquéauNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting and ReportingDocument31 pagesFinancial Accounting and ReportingBer SchoolNo ratings yet
- Fa-I Chapter 7Document16 pagesFa-I Chapter 7Hussen AbdulkadirNo ratings yet
- Accounting 1Document4 pagesAccounting 1Shoaib YousufNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 ReceivablesDocument4 pagesChapter 3 ReceivablesRizia Feh EustaquioNo ratings yet
- Accounting Vocabulary (A To C)Document4 pagesAccounting Vocabulary (A To C)MARY GRACE VARGASNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Retailing: ©2020 John Wiley & Sons Australia LTDDocument42 pagesAccounting For Retailing: ©2020 John Wiley & Sons Australia LTDKristel Andrea100% (1)
- Accounts Receivable: By: Dr. Angeles A. de Guzman Dean, College of Business EducationDocument10 pagesAccounts Receivable: By: Dr. Angeles A. de Guzman Dean, College of Business EducationJay-L TanNo ratings yet
- Bullet Review On Cash and Cash Equivalents, Receivables and InventoriesDocument15 pagesBullet Review On Cash and Cash Equivalents, Receivables and InventoriesCrystal PanolNo ratings yet
- (ACCT 317) Chapter 8 - Reporting and Analyzing ReceivablesDocument1 page(ACCT 317) Chapter 8 - Reporting and Analyzing Receivablesp.a.No ratings yet
- Accnts 2021-22Document24 pagesAccnts 2021-22Hari RamNo ratings yet
- General Journal (Record) Check Voucher Trial Balance (Prepare) General Ledger (Post)Document10 pagesGeneral Journal (Record) Check Voucher Trial Balance (Prepare) General Ledger (Post)Teajay BautistaNo ratings yet
- Fabm 2 Reviewer 1Document7 pagesFabm 2 Reviewer 1lun3l1ght18No ratings yet
- Accounts ReceivableDocument41 pagesAccounts ReceivableTenshi ChanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Accounting: Concepts and PrinciplesDocument25 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To Accounting: Concepts and Principlesd_hambrettNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument3 pagesUntitled DocumentAlonethestic lyric/music videoNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes Accounting ADocument5 pagesRevision Notes Accounting AAndrewNo ratings yet
- Accts Rec Est of DADocument38 pagesAccts Rec Est of DAvanessasumagdon8No ratings yet
- Fabm 2 ReviewerDocument5 pagesFabm 2 Reviewerlun3l1ght18No ratings yet
- Cash, Accrual, and SingleDocument42 pagesCash, Accrual, and Singlejohn_domingo_3No ratings yet
- Accounting - Definition: American Institute of Certified Public AccountantsDocument37 pagesAccounting - Definition: American Institute of Certified Public AccountantsDuNo ratings yet
- Accounting Standard (AS) - 3: Cash Flow StatementsDocument26 pagesAccounting Standard (AS) - 3: Cash Flow StatementsJonathan BarretoNo ratings yet
- Week 6 - ACCY111 NotesDocument4 pagesWeek 6 - ACCY111 NotesDarcieNo ratings yet
- Accounts Receivable and Estimation of Doubtful Accounts PDFDocument21 pagesAccounts Receivable and Estimation of Doubtful Accounts PDFJamaica IndacNo ratings yet
- Accounting Equation and Double Entry SystemDocument52 pagesAccounting Equation and Double Entry SystemArmandoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - HandoutsDocument9 pagesChapter 2 - HandoutsKarysse Arielle Noel JalaoNo ratings yet
- Basic Accounting Terms: Name-Ritumbra Chilwal CLASS - 11 Subject - AccountancyDocument66 pagesBasic Accounting Terms: Name-Ritumbra Chilwal CLASS - 11 Subject - AccountancyAashray BehlNo ratings yet
- Cash To Inventory Reviewer 1Document15 pagesCash To Inventory Reviewer 1Patricia Camille AustriaNo ratings yet
- 7227 Bullet ReviewDocument8 pages7227 Bullet ReviewJohair BilaoNo ratings yet
- Elements of Financial Statements and Account Titles UsedDocument22 pagesElements of Financial Statements and Account Titles UsedJessa Beloy100% (3)
- Report Chapter 10Document39 pagesReport Chapter 10Erma CaseñasNo ratings yet
- Afm Research AssignmentDocument13 pagesAfm Research AssignmentNISHANo ratings yet
- Accounting For Non AccountantrDocument172 pagesAccounting For Non AccountantrCarlo Villanueva BeltranNo ratings yet
- Accounts ProjectDocument66 pagesAccounts ProjectAashray BehlNo ratings yet
- Sole TradersDocument12 pagesSole TradersWei WenNo ratings yet
- Trial Balance To Profit & Loss A/c and Balance Sheet For Corporate & Non-Corporate EntitiesDocument24 pagesTrial Balance To Profit & Loss A/c and Balance Sheet For Corporate & Non-Corporate EntitiesChintan PatelNo ratings yet
- Balance Sheets: The Basics: Balance Sheet Reporting - Who, When and Where?Document10 pagesBalance Sheets: The Basics: Balance Sheet Reporting - Who, When and Where?Rama KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Basic Elements of AccountingDocument19 pagesBasic Elements of AccountingMonique DanielleNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - Sci.1Document9 pagesModule 3 - Sci.1Anne MoralesNo ratings yet
- Accounting 101 MerchandisingDocument7 pagesAccounting 101 Merchandisingchristian talosig100% (2)
- AccountingDocument14 pagesAccountingSUNNY SIDE UPNo ratings yet
- PFS StudyDocument19 pagesPFS Studyigorwalczak321No ratings yet
- Financial Accounting - Want to Become Financial Accountant in 30 Days?From EverandFinancial Accounting - Want to Become Financial Accountant in 30 Days?Rating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
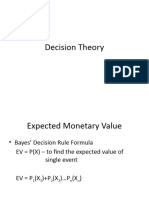
- Decision TheoryDocument5 pagesDecision TheoryNo NotreallyNo ratings yet
- Ex.3 AccountingDocument1 pageEx.3 AccountingNo NotreallyNo ratings yet
- Decision Theory LectureDocument9 pagesDecision Theory LectureNo NotreallyNo ratings yet
- Exercise 7 To 9Document4 pagesExercise 7 To 9No NotreallyNo ratings yet
- Periods of ArtDocument2 pagesPeriods of ArtNo NotreallyNo ratings yet
- LP Transportation Exercises 2Document1 pageLP Transportation Exercises 2No NotreallyNo ratings yet
- Questions C26Document2 pagesQuestions C26No NotreallyNo ratings yet
- Process CostingDocument5 pagesProcess CostingNo NotreallyNo ratings yet
- Course Intro Assignment 9112022Document2 pagesCourse Intro Assignment 9112022No NotreallyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 ExercisesDocument11 pagesChapter 3 ExercisesNo NotreallyNo ratings yet
- Question C27Document2 pagesQuestion C27No NotreallyNo ratings yet
- Merchandising Operations (Notes)Document9 pagesMerchandising Operations (Notes)No NotreallyNo ratings yet
- Chapter3 ExercisesDocument7 pagesChapter3 ExercisesNo NotreallyNo ratings yet
- Financial Asset: Non-Financial AssetDocument2 pagesFinancial Asset: Non-Financial AssetNo NotreallyNo ratings yet
- Adjusting EntryDocument3 pagesAdjusting EntryNo NotreallyNo ratings yet
- Questions C15Document2 pagesQuestions C15No NotreallyNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledNo NotreallyNo ratings yet
- Amanda EsquivelDocument2 pagesAmanda EsquivelNo NotreallyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2. Obligations of The AgentDocument9 pagesChapter 2. Obligations of The Agenteugenebriones27yahoo.comNo ratings yet
- Andhra Pradesh Money Lenders Act, 2000Document29 pagesAndhra Pradesh Money Lenders Act, 2000talktoravi8911No ratings yet
- Study Guide 1 ObliconDocument6 pagesStudy Guide 1 ObliconAudrey Gayle Castelo GervacioNo ratings yet
- Subscriber Agreement For Corporate Consumer With Turnover of Less Than R2MilDocument3 pagesSubscriber Agreement For Corporate Consumer With Turnover of Less Than R2MilanaisaNo ratings yet
- Garcia v. Thio, G.R. No. 154878, 16 March 2007, 518 SCRA 433.Document2 pagesGarcia v. Thio, G.R. No. 154878, 16 March 2007, 518 SCRA 433.JMae MagatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 IGCSEDocument74 pagesChapter 16 IGCSEtaj qaiserNo ratings yet
- Ryan International School Unit Test - I Class-Xi Sub.: Accounts (Paper-2) Time: 1 Hrs. MM: 32Document2 pagesRyan International School Unit Test - I Class-Xi Sub.: Accounts (Paper-2) Time: 1 Hrs. MM: 32RGN 11E 20 KHUSHI NAGARNo ratings yet
- Accounts Theory 21 Marks CTC ClassesDocument8 pagesAccounts Theory 21 Marks CTC Classeskhushalpareek8584No ratings yet
- Fiscal Deficit and Its ComponentDocument5 pagesFiscal Deficit and Its ComponentvishalNo ratings yet
- AST MidtermsDocument12 pagesAST MidtermsRica Regoris100% (1)
- Module 1 - Financial Statement Analysis - P1Document5 pagesModule 1 - Financial Statement Analysis - P1Jose Eduardo GumafelixNo ratings yet
- Accounting Final Mock 1 2023Document13 pagesAccounting Final Mock 1 2023diya pNo ratings yet
- Ca5101 Adjusting Entries La 1Document13 pagesCa5101 Adjusting Entries La 1Michael MagdaogNo ratings yet
- Castle Trust Direct PLC Fortress Bonds ProspectusDocument186 pagesCastle Trust Direct PLC Fortress Bonds ProspectushyenadogNo ratings yet
- CH 8 Sources of Business Finance Class 11 BSTDocument19 pagesCH 8 Sources of Business Finance Class 11 BSTRaman SachdevaNo ratings yet
- Security Bank and Trust Company vs. CuencaDocument14 pagesSecurity Bank and Trust Company vs. CuencaJoshua CuentoNo ratings yet
- Answer The Questions and Submit Thru Dropbox.: Case Analysis. (15 Points: 3 Items X 5 Points)Document2 pagesAnswer The Questions and Submit Thru Dropbox.: Case Analysis. (15 Points: 3 Items X 5 Points)Gabriel TantiongcoNo ratings yet
- Bachelor in Business Administration Semester 3: Prepared For: Lecturer's NameDocument3 pagesBachelor in Business Administration Semester 3: Prepared For: Lecturer's NameBrute1989No ratings yet
- FINMAR - Introduction To Financial Management and Financial MarketsDocument8 pagesFINMAR - Introduction To Financial Management and Financial MarketsLagcao Claire Ann M.No ratings yet
- Open MediaDocument8 pagesOpen MediaRajNo ratings yet
- Lembar Jawaban PD MITRADocument43 pagesLembar Jawaban PD MITRAIntanNo ratings yet
- Toaz - Info MCQ Nego PRDocument20 pagesToaz - Info MCQ Nego PRALCEDO KelvinnNo ratings yet
- Nishu Money Market 2Document102 pagesNishu Money Market 2kapil rastogiNo ratings yet
- What Does Billing in Arrears MeanDocument3 pagesWhat Does Billing in Arrears Meanmichelle dizonNo ratings yet
- Yucuico vs. Far East BankDocument15 pagesYucuico vs. Far East BankAmala Fay ChavezNo ratings yet
- Financial Performance of Commercial Banks in NepalDocument117 pagesFinancial Performance of Commercial Banks in NepalBee RazNo ratings yet
- G.R. No. 166884 June 13, 2012Document8 pagesG.R. No. 166884 June 13, 2012Lothy Ginipal RotellacNo ratings yet
- Fin 111 Final Quiz 1 Sy 2017 2018Document1 pageFin 111 Final Quiz 1 Sy 2017 2018Lanther Jaze AndrewsNo ratings yet