Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gi Bleed
Gi Bleed
Uploaded by
praveenbhavniOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Gi Bleed
Gi Bleed
Uploaded by
praveenbhavniCopyright:
Available Formats
6/4/2017 www.gastroenterologybook.com/images/page_images/452.
SVG
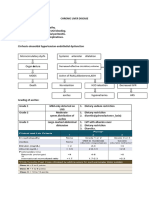
Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding Management
Rockall Score (predicts rebleeding and death) Forrest classification
Cause of bleeding: Relative frequency
0 1 2 3
Age >60 6079 >80
(Endoscopic score)
Peptic ulcer. 44 Shock Not Tachycardia Hypotension
1A spurting
Oesophagitis. shocked Active bleeding during endoscopy 90 % recurrence
28 CHF/ IHD/ Renal failure/ liver failure/ 1B oozing
Comorbidity None
Gastritis/ erosions. 26 any major disseminated malignancy 2A visible vessel Visible vessel 50 % recurrence
Erosive duodenitis. 15 Diagnosis 2B clots
Varices. 2C Black spot at base An adherent clot 25 to 30 % recurrence
13 Black or red spot at base negligeable rebleed rate
Portal hypertensive gastropathy. 7 Major stigmata of recent None or dark Blood in upper GI tract/ 3 clean
haemorrhage spot only adherent clot, visible or
Malignancy. 5 spurting vessel
Mallory Weiss Tear. 5
Vascular Malformation. 3
If the initial (preendoscopic) score > 0 then
significant mortality (score 1: 2.4%; score 2: 5.6%)
Indications for Endoscopy Within 24 hours:
Active bleeding.
Haematemesis ongoing.
Fresh melaena ongoing.
Hypotension or sinus tachycardia not responsive to resuscitation.
Persistently low Hb despite transfusion.
Resuscitation Endoscopy Acid Suppression Repeat Endoscopy
Repeat if difficult endoscopy or rebleed likely to be life
threatening.
Repeat OGD can reduce rebleeding rates but doesnt
Indications For Endoscopic Therapy: Acid Suppression confer survival benefit.
Active bleeding. PPI reduces risk of rebleeding .
Visible vessel. iv PPI Before endoscopy reduces
Adherent clot if technically possible snare adherent clots if bleeding signs but no effect on mortality. Rebleed
cant be removed with suctioning/ irrigation. H2 No good really for ulcers. Gastric ulcers along the lesser curvature and duodenal
Clas s I Clas s II Clas s III Clas s IV
Oral PPI for bleeding. bulbar ulcers in the posterior wall appeared to be at
Blood los s
volume (ml)
<750 7501500 15002000 >2000 Endoscopic Therapy High dose of oral omeprazole (40 mg PO greater risk for severe bleeding or rebleeding compared
The use of combination therapy (adrenaline + one other BID) was associated with a decreased risk with ulcers in other locations because of their proximity to
Blood los s (%
of circulating 015 1530 3040 >40
therapy) reduces the mortality from 5.6% to 2.6%. of recurrent bleeding in patients who had large underlying arteries (left gastric and posterior
blood)
Sys tolic blood No change Normal Reduced Very reduced/ Clips are more effective than epinephrine alone, but not ulcers with a visible vessel or adherent gastroduodenal arteries, respectively).Options:
pres s ure unrecordable
different than other therapies. clots who did not undergo endoscopic
Dias tolic blood No change Rais ed Reduced Very reduced/ The efficacy of endoscopic therapies for clots was uncertain. therapy.
pres s ure unrecordable
Puls e (beats Slight 100200 120 (thready) <120 (very
Thermal coagulation has the same efficacy as adrenaline if
per minute) tachycardia thready) used alone. SOMATOSTATIN AND OCTREOTIDE
Res piratory rate Normal Normal Rais ed Rais ed
(>20/min) (>20/min) Thermal coagulation should be used until area is blackened Repeat Angiogra Sur
M ental s tate Alert, thirs ty Anxious or Anxious , Drows y,
and cavitated. Somatostatin or octreotide can be used as
aggres s ive aggres s ive or confus ed or OGD phy gery
drows y uncons cious
If Injection therapy with adrenaline is given alone, the adjunctive therapy before endoscopy, or
Adapted from Bas kett, PJ F. ABC of major trauma. M anagement of Hypovolaemic Shock.BM J 1990;
300: 14531457
rebleeding rate is high (18 %). when endoscopy is unsuccessful, contrain
dicated, or unavailable due to its splanchnic Surgery and transcatheter
Use 13ml 1:10,000 adrenaline.
vasoconstrictive effects arteriography/intervention (TAI) are equally
Mechanical Therapy is more effective than adrenaline alone
Typical dose of somatostatin is 250 mcg effective following failed therapeutic
Argon plasma coagulation can be effective although it
then hourly for 37d while a typical dose of endoscopy, but TAI should be considered
doesnt involve tamponade.
octreotide was 50 to 100mcg then particularly in patients at high risk for surgery.
25mcg/hr for up to 3 days. TAI is less likely to be successful in patients with
impaired coagulation.
TAI is the best technique for treatment of
bleeding into the biliary tree or pancreatic duct.
http://www.gastroenterologybook.com/images/page_images/452.SVG 1/1
You might also like
- Mechanical Ventilation Made EasyDocument5 pagesMechanical Ventilation Made EasypraveenbhavniNo ratings yet
- Esophageal Varices Concept MapDocument2 pagesEsophageal Varices Concept MapSureen Regular100% (1)
- STUDENT-Sepsis - Fundamental - Reasoning Fillable-1Document5 pagesSTUDENT-Sepsis - Fundamental - Reasoning Fillable-1Laura PoultneyNo ratings yet
- Case Study 3Document5 pagesCase Study 3api-644492588100% (1)
- IPD - Kelas AC - Perdarahan Sal. Cerna - Dr. Hery Djagat - 28 Agustus 2018Document75 pagesIPD - Kelas AC - Perdarahan Sal. Cerna - Dr. Hery Djagat - 28 Agustus 2018evanoNo ratings yet
- Body Fluid Analysis Table-2017Document2 pagesBody Fluid Analysis Table-2017Afrasiab KhanNo ratings yet
- Complications of Cirrhosis: Update 2015: M.pinzani@ucl - Ac.ukDocument24 pagesComplications of Cirrhosis: Update 2015: M.pinzani@ucl - Ac.ukNovita ApramadhaNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure: Peter A. Mccullough, MD, MPH, Facc, Facp, Faha, FCCPDocument54 pagesHeart Failure: Peter A. Mccullough, MD, MPH, Facc, Facp, Faha, FCCPDenisse Tinajero SánchezNo ratings yet
- Peptic Ulcer Disease UpdatedDocument19 pagesPeptic Ulcer Disease UpdatedKiara GovenderNo ratings yet
- Approach To Lower GI BleedingDocument86 pagesApproach To Lower GI BleedingwassupporamaNo ratings yet
- SYOK - Desi Surya IniDocument40 pagesSYOK - Desi Surya IniDesi Suryani DewiNo ratings yet
- IMS All Seminars FinalDocument21 pagesIMS All Seminars Finaljwxxi11No ratings yet
- Neurology SummaryDocument57 pagesNeurology SummaryMajed AlamiNo ratings yet
- Syndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuresis From Pathophysiology To ManagementDocument43 pagesSyndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuresis From Pathophysiology To ManagementArley SuarezNo ratings yet
- SPARCtoolDocument1 pageSPARCtoolqerat88No ratings yet
- Syndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuresis: From Pathophysiology To ManagementDocument43 pagesSyndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuresis: From Pathophysiology To ManagementDanny VarjãoNo ratings yet
- Wednesday HarvardDocument61 pagesWednesday HarvardNational Press FoundationNo ratings yet
- UGI BLEED-OfficeDocument24 pagesUGI BLEED-OfficeVishal PNo ratings yet
- Congenital Valvular StenosisDocument46 pagesCongenital Valvular StenosisInsan IlmanNo ratings yet
- MIS-C: Clinic-Diagnostic/Dispo Recs For Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in ChildrenDocument8 pagesMIS-C: Clinic-Diagnostic/Dispo Recs For Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in ChildrenJosselle Sempio CalientaNo ratings yet
- AK Tripathi, Kamal Sawlani - Essentials of Medicine For Dental Students - 2nd Edition - WWW - Thedentalhub.org - inDocument302 pagesAK Tripathi, Kamal Sawlani - Essentials of Medicine For Dental Students - 2nd Edition - WWW - Thedentalhub.org - inemanNo ratings yet
- 3 Abses SerebelumDocument3 pages3 Abses SerebelumseruniallisaaslimNo ratings yet
- ACC Anticoagulation For AFib in CLL Patients Interactive V05 GoldDocument22 pagesACC Anticoagulation For AFib in CLL Patients Interactive V05 GoldhibaNo ratings yet
- Vascular CatastropheDocument3 pagesVascular CatastropheJesily JoyNo ratings yet
- CCS Heart Failure Guidelines: 2014 Update On New Therapies, Biomarkers, Anemia Management, and Complex CasesDocument88 pagesCCS Heart Failure Guidelines: 2014 Update On New Therapies, Biomarkers, Anemia Management, and Complex CaseseliasNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Studies: FecalysisDocument2 pagesLaboratory Studies: FecalysisKris TejereroNo ratings yet
- Retinal Vein OcclusionDocument1 pageRetinal Vein Occlusionmart0830No ratings yet
- DR Sutarmawan Acute Presentation of Valve SletnosisDocument33 pagesDR Sutarmawan Acute Presentation of Valve SletnosisArniNo ratings yet
- Week 13 Disorders of Secondary Hemostasis LecDocument8 pagesWeek 13 Disorders of Secondary Hemostasis LecCzarina Mae IlaganNo ratings yet
- Cardiac SurgeryDocument110 pagesCardiac SurgeryChristopher McAndrew100% (1)
- OPTO 309 Other Retinal Vascular DisordersDocument5 pagesOPTO 309 Other Retinal Vascular DisorderscaponsharranerizaNo ratings yet
- Abd Distension & Ascites-1, All NewDocument34 pagesAbd Distension & Ascites-1, All NewANENA RHODANo ratings yet
- Upper Gi BleedDocument12 pagesUpper Gi BleedTaha KamranNo ratings yet
- Hemolytic Anemia's Thalassemia (REZAMAGHAMI)Document57 pagesHemolytic Anemia's Thalassemia (REZAMAGHAMI)Siavash HosseinjanzadehNo ratings yet
- Severe Aortic Stenosis and TavrDocument67 pagesSevere Aortic Stenosis and TavrnaimNo ratings yet
- AMLS Mobile Reference GuideDocument6 pagesAMLS Mobile Reference GuideLim Jun Bin100% (1)
- Aortic Stenosis BY ISRARDocument50 pagesAortic Stenosis BY ISRARAkramNo ratings yet
- Diabetic RetinopathyDocument1 pageDiabetic RetinopathyshakyaNo ratings yet
- K9. Penyakit Kardiovaskuler BawaanDocument70 pagesK9. Penyakit Kardiovaskuler Bawaanjulis muharamNo ratings yet
- Arrythmia Management in Primary CareDocument51 pagesArrythmia Management in Primary CarecelinamannaNo ratings yet
- AnemiaDocument2 pagesAnemiaRed DiggerNo ratings yet
- Handout StudentsDocument2 pagesHandout Studentsapi-588254706No ratings yet
- Epidemiology Clinical Features Diagnosis Treatment EndocarditisDocument1 pageEpidemiology Clinical Features Diagnosis Treatment EndocarditisSolomon Seth SallforsNo ratings yet
- 20.guidelines AnaemiaDocument5 pages20.guidelines AnaemiaRed DevilNo ratings yet
- Syok Hipovolemik (1) SalinanDocument34 pagesSyok Hipovolemik (1) SalinanyusufNo ratings yet
- UWORLDDocument1 pageUWORLDmerontesfaye51No ratings yet
- Acute and Chronic Gastrointestinal BleedingDocument7 pagesAcute and Chronic Gastrointestinal BleedingMarwan M.100% (1)
- Abd Distension & Ascites-2, All You NeedDocument36 pagesAbd Distension & Ascites-2, All You NeedANENA RHODANo ratings yet
- Int - med.Fet.3.EGRTACOS-Manejo Retraso Crecimiento Intrauterino.Document11 pagesInt - med.Fet.3.EGRTACOS-Manejo Retraso Crecimiento Intrauterino.zaaaidaNo ratings yet
- Abnormal FBC 1.16 Feb 2016Document5 pagesAbnormal FBC 1.16 Feb 2016jyothi vallabhaneniNo ratings yet
- Novine U Lecenju HTA Ber HemiDocument62 pagesNovine U Lecenju HTA Ber HemispalemaxNo ratings yet
- Acute Myeloid Leukemia (Drug Study)Document3 pagesAcute Myeloid Leukemia (Drug Study)Krisianne Mae Lorenzo FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Giant Cell Arteritis: Basic InformationDocument3 pagesGiant Cell Arteritis: Basic Informationjenny grovesNo ratings yet
- Kawasaki - Lab&drug, NCPDocument18 pagesKawasaki - Lab&drug, NCPJayzee ServantesNo ratings yet
- AULIA AHMAD G2A009130 Bab8KTI PDFDocument11 pagesAULIA AHMAD G2A009130 Bab8KTI PDFMargotNo ratings yet
- Mahmood Care BlanDocument5 pagesMahmood Care Blanmahmood asafraNo ratings yet
- Anticoag Peri Op ManagementDocument16 pagesAnticoag Peri Op Managementlokeswara reddyNo ratings yet
- HaemorrhageDocument19 pagesHaemorrhageSrishti SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- UPPER GASTROINTESTINAL BLEEDING Simp HemoroidDocument44 pagesUPPER GASTROINTESTINAL BLEEDING Simp HemoroidKomang YudaNo ratings yet
- LeukemiaDocument1 pageLeukemiaFabshkieee 3No ratings yet
- Anticoagulation TherapyFrom EverandAnticoagulation TherapyJoe F. LauNo ratings yet
- Biomarkers in Various DiseasesDocument3 pagesBiomarkers in Various DiseasespraveenbhavniNo ratings yet
- Chronic Liver DiseaseDocument6 pagesChronic Liver DiseasepraveenbhavniNo ratings yet
- Bed Idden Format For PatientsDocument1 pageBed Idden Format For PatientspraveenbhavniNo ratings yet
- Programme Schedule Workshop-1Document4 pagesProgramme Schedule Workshop-1Ram PattnaikNo ratings yet
- Ortho Final ExamDocument40 pagesOrtho Final ExamMariane GumbanNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2473952921007515 MainDocument10 pages1 s2.0 S2473952921007515 MainAndreea RacovitaNo ratings yet
- Pash Syndrome Co-Existing With Rheumatic Heart Disease and Severe Mitral Valve Regurgitation: A Rare Case ReportDocument3 pagesPash Syndrome Co-Existing With Rheumatic Heart Disease and Severe Mitral Valve Regurgitation: A Rare Case ReportIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- ACLS MedicationsDocument31 pagesACLS MedicationsDrNorNo ratings yet
- How To Write A Research Paper On Prostate CancerDocument4 pagesHow To Write A Research Paper On Prostate Cancertus0zaz1b1g3No ratings yet
- Diploma in DiabetologyDocument8 pagesDiploma in Diabetologydawood260No ratings yet
- Pap SmearDocument24 pagesPap SmearAavash PradhanNo ratings yet
- Autogenic TrainingDocument5 pagesAutogenic Trainingking.fahmie23100% (1)
- E Scleroderma Ye Scleroderma LikeDocument31 pagesE Scleroderma Ye Scleroderma LikeHmn07No ratings yet
- Physical, Leisure, and Daily Living Activities In.3Document11 pagesPhysical, Leisure, and Daily Living Activities In.3yogithajeganathan5197No ratings yet
- Interstitial Lung Diseases2Document186 pagesInterstitial Lung Diseases2Mohamed HefnyNo ratings yet
- Neck Trauma DR Hauwa Shitu 1Document40 pagesNeck Trauma DR Hauwa Shitu 1Hauwa shitu.B100% (1)
- Health Ass.Document6 pagesHealth Ass.Rashmi Devrani VyasNo ratings yet
- (Diabetes) PresentationDocument13 pages(Diabetes) Presentationsabanayyar56No ratings yet
- ATI MedSurg Respiratory System Practice QuestionsDocument19 pagesATI MedSurg Respiratory System Practice QuestionsHHNo ratings yet
- Domestic Violence and AbuseDocument7 pagesDomestic Violence and AbuseKate20100% (1)
- HEALTH 8: Communicable DiseaseDocument31 pagesHEALTH 8: Communicable DiseaseElissah S PabilonaNo ratings yet
- Epiglottitis - AMBOSSDocument10 pagesEpiglottitis - AMBOSSSadikNo ratings yet
- Jain (2003) - Fibromyalgia Syndrome Canadian Clinical Working Case Definition, Diagnostic and Treatment Protocols - A Consensus DocumentDocument106 pagesJain (2003) - Fibromyalgia Syndrome Canadian Clinical Working Case Definition, Diagnostic and Treatment Protocols - A Consensus DocumentLuciana AraújoNo ratings yet
- Mineral, Vitamin, and Herbal SupplementsDocument18 pagesMineral, Vitamin, and Herbal SupplementsismailcemNo ratings yet
- HePatic AbscessDocument67 pagesHePatic AbscessCharlie Mignonette BalaNo ratings yet
- PHAR 233 - Pathophysiology of Infectious DiseasesDocument89 pagesPHAR 233 - Pathophysiology of Infectious DiseasesLina RamojNo ratings yet
- IIRP IG Result 22112023Document11 pagesIIRP IG Result 22112023icmrbharthNo ratings yet
- Medicare GuideDocument3 pagesMedicare GuideyigaplusoneNo ratings yet
- Pivotmed Webinar - Dyspnea in Adult - Approach and Early Management by Dr. Irandi Putra P, PHD, SPP (K), FAPSRDocument36 pagesPivotmed Webinar - Dyspnea in Adult - Approach and Early Management by Dr. Irandi Putra P, PHD, SPP (K), FAPSRMochamad Fadel AuliaNo ratings yet
- NCM 101A 13 Areas of AssessmentDocument4 pagesNCM 101A 13 Areas of AssessmentGladys JhayeNo ratings yet
- Indicador Gabs AtualizadoDocument2 pagesIndicador Gabs AtualizadoBiXus Estrategas EmpresarialesNo ratings yet