Professional Documents
Culture Documents
IB Physics - Topic 2-2 - Determining G Using Atwoods Machine
IB Physics - Topic 2-2 - Determining G Using Atwoods Machine
Uploaded by
ROldfordCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Danielson Pre-Observation Form 409Document2 pagesDanielson Pre-Observation Form 409api-28624516150% (2)
- Atwood Machine LQ CC NGSS PDFDocument4 pagesAtwood Machine LQ CC NGSS PDFGrace KimNo ratings yet
- 19 Impulse and Momentum LQ - ModifiedDocument6 pages19 Impulse and Momentum LQ - ModifiedRaymond Zheng100% (1)
- Rectilinear Motion LabDocument3 pagesRectilinear Motion LabAbbey EzedonmwenNo ratings yet
- Physics 133 Experiment No. 3 AccelerationDocument3 pagesPhysics 133 Experiment No. 3 AccelerationGiovanniDaltonNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 Acceleration-1Document3 pagesLab 1 Acceleration-1Grace KimNo ratings yet
- A-level Physics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Physics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (10)
- Instructions:: FINA 6216 ASSIGNMENT 1: Asset Allocation (25 Points)Document8 pagesInstructions:: FINA 6216 ASSIGNMENT 1: Asset Allocation (25 Points)Mathew SawyerNo ratings yet
- Lab 3: The Measurement of "G" Using An Atwood's Machine: Type: CookbookDocument3 pagesLab 3: The Measurement of "G" Using An Atwood's Machine: Type: Cookbookaayush tomarNo ratings yet
- SampSample Formal Laboratory Report For Physics On The Picket Fence Lab Without The Parachutele Formal Lab ReportDocument5 pagesSampSample Formal Laboratory Report For Physics On The Picket Fence Lab Without The Parachutele Formal Lab ReportKhatri NasrullahNo ratings yet
- Atwood'S Machine: LabquestDocument4 pagesAtwood'S Machine: LabquestGrace KimNo ratings yet
- Atwoods MachineDocument4 pagesAtwoods MachineMarianoNo ratings yet
- 04 AtwoodDocument8 pages04 Atwoodunregistered000No ratings yet
- Movimiento Armonico SimpleDocument6 pagesMovimiento Armonico SimpleFrancisco Manuel Ugarte PalacinNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Different Inclines of The Ramp On The Force of The CartDocument10 pagesThe Impact of Different Inclines of The Ramp On The Force of The CartNguyenNo ratings yet
- UPM Lab Manual 29.07.15 RevisedDocument19 pagesUPM Lab Manual 29.07.15 RevisedAbhisikta MishraNo ratings yet
- 2A Lab 5 Atwood's MachineDocument3 pages2A Lab 5 Atwood's MachineDita PramidaNo ratings yet
- Vernier Act16 PicketfenceDocument7 pagesVernier Act16 Picketfencefoureyed0_00% (1)
- PWV 10 COMP Atwoods MachineDocument5 pagesPWV 10 COMP Atwoods MachineSandi WiarsanaNo ratings yet
- 15 Simple Harmonic MotionDocument4 pages15 Simple Harmonic Motionjohnhwang940% (1)
- Atwoods MachineDocument4 pagesAtwoods MachineMelissa Smith0% (1)
- AtwoodDocument3 pagesAtwoodBahril IlmiwanNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument3 pagesLab ReportTom DonohueNo ratings yet
- Picket Fence LabDocument3 pagesPicket Fence Labapi-236349398No ratings yet
- Aqa A Level Physics - Required Practicals: JUNE 2017Document33 pagesAqa A Level Physics - Required Practicals: JUNE 2017LouisNo ratings yet
- Lab Picket Fence Free FallDocument4 pagesLab Picket Fence Free FallKurt PreyNo ratings yet
- AP Lab-Atwoods MachineDocument4 pagesAP Lab-Atwoods Machinernguyen7007No ratings yet
- Atwood's MachineDocument22 pagesAtwood's MachineDebora Tresia PurbaNo ratings yet
- Physics Labreport Free FallDocument6 pagesPhysics Labreport Free Fallapi-257070591No ratings yet
- Lab 7 - Simple Harmonic MotionDocument6 pagesLab 7 - Simple Harmonic MotionCanjiCanji50% (2)
- DynamicDocument6 pagesDynamicAbdla DoskiNo ratings yet
- IA ParachuteDocument4 pagesIA ParachuteJoshua KurniawanNo ratings yet
- 05 Picket Fence Free Fall LQDocument4 pages05 Picket Fence Free Fall LQNayeli CarrascoNo ratings yet
- Atwood's MachineDocument22 pagesAtwood's MachineagnesNo ratings yet
- Acceleration On An Air TrackDocument7 pagesAcceleration On An Air TrackSandra SaviromoNo ratings yet
- Acc BtaDocument4 pagesAcc BtaSharon JoseNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Report - Simple Atwood MachineDocument8 pagesLaboratory Report - Simple Atwood MachineAlthea DumabokNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Aurora State College of Technology Zabali Baler, Aurora Physics LaboratoryDocument5 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Aurora State College of Technology Zabali Baler, Aurora Physics LaboratoryChristopher PaladioNo ratings yet
- Lab 2a Dynamic Response of A Mass-Spring System With DampingDocument5 pagesLab 2a Dynamic Response of A Mass-Spring System With DampingPrashant AshishNo ratings yet
- Lesson 08 Acceleration RPDocument15 pagesLesson 08 Acceleration RPAlya Defa AnindaNo ratings yet
- Picket FencingDocument3 pagesPicket FencingKitkatNo ratings yet
- Accceleration Due To GravityDocument7 pagesAccceleration Due To Gravityapi-3759956No ratings yet
- PHY Unit 6Document276 pagesPHY Unit 6Ugly TwitterNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Inquiry Free Fall: Time Alloted: 3 Lab PeriodsDocument5 pagesLaboratory Inquiry Free Fall: Time Alloted: 3 Lab PeriodsSandi BerginNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3.5.3 Picket Fence LabDocument3 pagesLesson 3.5.3 Picket Fence LabnassNo ratings yet
- Experiment 102Document5 pagesExperiment 102Romulus BloodNo ratings yet
- Newton Second LawDocument4 pagesNewton Second LawLester ParadilloNo ratings yet
- SGDE3Document4 pagesSGDE3SCVLifeNo ratings yet
- Murciano A 2Document5 pagesMurciano A 2AaronNo ratings yet
- 21d Simple Harmonic Motion-RGC 03-03-09Document6 pages21d Simple Harmonic Motion-RGC 03-03-09Raymond KipkoechNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 CombinedDocument24 pagesUnit 6 Combinedbhuvanharish25No ratings yet
- Name: Ahammad Nadendla Roll No: B19BB030Document12 pagesName: Ahammad Nadendla Roll No: B19BB030Ankur BorkarNo ratings yet
- Centripetal Acceleration Lab ReportDocument7 pagesCentripetal Acceleration Lab Reportapi-263389150No ratings yet
- 201 Lab 7. Work and EnergyDocument9 pages201 Lab 7. Work and EnergydermaNo ratings yet
- Strain GaugeDocument3 pagesStrain GaugeManthan SinghNo ratings yet
- Experimental ReportDocument11 pagesExperimental Reportapi-319119669No ratings yet
- Picket Fence Freefall LabDocument4 pagesPicket Fence Freefall Labasdf100% (1)
- Lab Report 2Document3 pagesLab Report 2api-263411981100% (1)
- Bundle Adjustment: Optimizing Visual Data for Precise ReconstructionFrom EverandBundle Adjustment: Optimizing Visual Data for Precise ReconstructionNo ratings yet
- STEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10From EverandSTEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10No ratings yet
- M1T1-2 Group3 BEEd201 EdTech1Document5 pagesM1T1-2 Group3 BEEd201 EdTech1Regina Vera Lisondra OracionNo ratings yet
- Essential Statistics 2E: William Navidi and Barry MonkDocument23 pagesEssential Statistics 2E: William Navidi and Barry Monkkaled1971No ratings yet
- HW 106-2 ColorDocument24 pagesHW 106-2 Colormonktheop1155No ratings yet
- Resume - Ricky - VivancoDocument1 pageResume - Ricky - VivancoRicky VivancoNo ratings yet
- Gabriel Zarzycki - Portfolio Assignment #1 - Intro EssayDocument2 pagesGabriel Zarzycki - Portfolio Assignment #1 - Intro EssayGabriel ZarzyckiNo ratings yet
- The First Term English Exam Level: 3am Duration:1h30 TextDocument2 pagesThe First Term English Exam Level: 3am Duration:1h30 Textaicha yayoucheNo ratings yet
- 1992 - Worlds of Consciousness and The Structure of ConsciousnessDocument43 pages1992 - Worlds of Consciousness and The Structure of ConsciousnessKátharsisNo ratings yet
- Human Eye and EarDocument2 pagesHuman Eye and Earshathurjanan.jana5No ratings yet
- Kleij-Leukfeldt2020 Chapter CyberResilientBehaviorIntegratDocument13 pagesKleij-Leukfeldt2020 Chapter CyberResilientBehaviorIntegratThanh MonNo ratings yet
- Renewal of Notarial Commission 2022-2023 For UploadDocument3 pagesRenewal of Notarial Commission 2022-2023 For UploadmacrosalNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 The Teaching ProfessionDocument7 pagesAssignment 2 The Teaching ProfessionRholynne Ghie Anne EstebanNo ratings yet
- Tekin Iftar2017 PDFDocument21 pagesTekin Iftar2017 PDFVictor Martin CobosNo ratings yet
- How To Write A Geotechnical Investigation Report - CivilblogDocument12 pagesHow To Write A Geotechnical Investigation Report - CivilblogOladunni AfolabiNo ratings yet
- Turkey and Azerbaijan: Passion, Principle, or Pragmatism?Document4 pagesTurkey and Azerbaijan: Passion, Principle, or Pragmatism?German Marshall Fund of the United StatesNo ratings yet
- Certainty Equivalent FactorDocument2 pagesCertainty Equivalent FactorParth SahniNo ratings yet
- Lavendia Portfolio PR2 ABM12 4Document28 pagesLavendia Portfolio PR2 ABM12 4PresydenteNo ratings yet
- College of Health & Allied Sciences: Review of Related LiteratureDocument20 pagesCollege of Health & Allied Sciences: Review of Related LiteratureAngela V. De LunaNo ratings yet
- Pima Unofficial TranscriptDocument9 pagesPima Unofficial Transcriptapi-301121897No ratings yet
- Republic Act 3019Document8 pagesRepublic Act 3019Isha SorianoNo ratings yet
- December 06Document36 pagesDecember 06Quy DangNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Test: Make Circle Around A), B), C) or D) According To The Asked QuestionDocument2 pagesDiagnostic Test: Make Circle Around A), B), C) or D) According To The Asked QuestionAtif LiaqatNo ratings yet
- Value Education Presentation (203-065Document9 pagesValue Education Presentation (203-065ANISH PATIL (RA2111029010064)No ratings yet
- A Feminist Analysis of A Doll HouseDocument6 pagesA Feminist Analysis of A Doll HouseMaida Khan100% (1)
- Research ProposalDocument4 pagesResearch ProposalMax Odeh100% (1)
- Vehicle Dynamics Prof. R. Krishnakumar Department of Engineering Design Indian Institute of Technology - Madras Lecture - 12 Lateral Force GenerationDocument17 pagesVehicle Dynamics Prof. R. Krishnakumar Department of Engineering Design Indian Institute of Technology - Madras Lecture - 12 Lateral Force Generationgauraang singh baghelNo ratings yet
- Unified Power Quality Conditioner (Upqc) With Pi and Hysteresis Controller For Power Quality Improvement in Distribution SystemsDocument7 pagesUnified Power Quality Conditioner (Upqc) With Pi and Hysteresis Controller For Power Quality Improvement in Distribution SystemsKANNAN MANINo ratings yet
- Nonhuman PhotographyDocument21 pagesNonhuman PhotographySNo ratings yet
- Ge Lit1 PrelimDocument13 pagesGe Lit1 PrelimJovelle ConahapNo ratings yet
IB Physics - Topic 2-2 - Determining G Using Atwoods Machine
IB Physics - Topic 2-2 - Determining G Using Atwoods Machine
Uploaded by
ROldfordOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
IB Physics - Topic 2-2 - Determining G Using Atwoods Machine
IB Physics - Topic 2-2 - Determining G Using Atwoods Machine
Uploaded by
ROldfordCopyright:
Available Formats
Lab Investigation Topic 2.
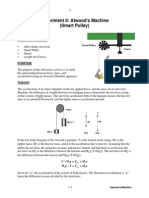
2 Forces and Dynamics Determining g using Atwoods Machine DCP, CE Purpose: To determine the acceleration due to gravity, g, using Atwoods Machine.
Introduction Atwoods Machine is a simple machine, where a string connecting 2 different masses is looped over a pulley. This setup is similar to an elevator and counterweight system. Since the two masses are connected, their accelerations will be equal, but will have opposite directions. The larger mass will be accelerated down, while the smaller mass will be accelerated up. Since the tension force must be the same for each mass, we can create a net force equation for each mass. Larger mass: T - Mg = - Ma Smaller mass: T - mg = ma Subtracting the two equations, then simplifying, we derive the equation M- m a=g M +m In our lab investigation, we will keep the total mass constant and vary the difference in masses. If we replace M+m with mtotal, and M-m with m, we can rearrange our equation into g a= Dm mtotal Since this is a linear equation, we can graph m vs. a, and use the line of best fits slope to find an experimental value for g. To find acceleration, we will use Logger Pros video analysis software. This will allow us to track the motion of the masses over time and analyze it to find the acceleration. Materials: Lab stand and clamp Pulley Set of masses String 30 cm scale
Procedure:
Set up the Atwoods Machine as shown below. Start with 50g on the left and 70g on the right. Make sure your laptop only has Photo Booth running. Point your laptop camera directly at the Atwoods Machine. Make sure that the 30 cm scale is placed the same distance away from the camera as the Atwoods Machine. Begin recording your video. Move the larger mass up towards the pulley, then let go. Stop recording, and check that your video was recorded properly. Repeat these steps with the following masses on either side of the Atwoods Machine. Left Side Right Side 40 g 80 g 30 g 90 g 20 g 100 g 10 g 110 g Data Processing and Analysis: Import each video into Logger Pro. Using the video analysis tools, track the motion of the larger mass in each trial. Use the y position data to determine the vertical acceleration, a, of the larger mass in each trial. Record the acceleration for each m, and the uncertainties. Make a graph of a vs. m, including error bars. Make a line of best fit on that graph, and show the best fit lines equation. Using the error bars, find the uncertainty in the slope of the line of best fit. Using the slope of the line of best fit, find your experimental value for g. Find the percent error in your value for g. Using the error bars, find the uncertainty in the slope of the line of best fit. Make a conclusion about your experimental value for g using the percent error and percent uncertainty.
You might also like
- Danielson Pre-Observation Form 409Document2 pagesDanielson Pre-Observation Form 409api-28624516150% (2)
- Atwood Machine LQ CC NGSS PDFDocument4 pagesAtwood Machine LQ CC NGSS PDFGrace KimNo ratings yet
- 19 Impulse and Momentum LQ - ModifiedDocument6 pages19 Impulse and Momentum LQ - ModifiedRaymond Zheng100% (1)
- Rectilinear Motion LabDocument3 pagesRectilinear Motion LabAbbey EzedonmwenNo ratings yet
- Physics 133 Experiment No. 3 AccelerationDocument3 pagesPhysics 133 Experiment No. 3 AccelerationGiovanniDaltonNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 Acceleration-1Document3 pagesLab 1 Acceleration-1Grace KimNo ratings yet
- A-level Physics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Physics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (10)
- Instructions:: FINA 6216 ASSIGNMENT 1: Asset Allocation (25 Points)Document8 pagesInstructions:: FINA 6216 ASSIGNMENT 1: Asset Allocation (25 Points)Mathew SawyerNo ratings yet
- Lab 3: The Measurement of "G" Using An Atwood's Machine: Type: CookbookDocument3 pagesLab 3: The Measurement of "G" Using An Atwood's Machine: Type: Cookbookaayush tomarNo ratings yet
- SampSample Formal Laboratory Report For Physics On The Picket Fence Lab Without The Parachutele Formal Lab ReportDocument5 pagesSampSample Formal Laboratory Report For Physics On The Picket Fence Lab Without The Parachutele Formal Lab ReportKhatri NasrullahNo ratings yet
- Atwood'S Machine: LabquestDocument4 pagesAtwood'S Machine: LabquestGrace KimNo ratings yet
- Atwoods MachineDocument4 pagesAtwoods MachineMarianoNo ratings yet
- 04 AtwoodDocument8 pages04 Atwoodunregistered000No ratings yet
- Movimiento Armonico SimpleDocument6 pagesMovimiento Armonico SimpleFrancisco Manuel Ugarte PalacinNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Different Inclines of The Ramp On The Force of The CartDocument10 pagesThe Impact of Different Inclines of The Ramp On The Force of The CartNguyenNo ratings yet
- UPM Lab Manual 29.07.15 RevisedDocument19 pagesUPM Lab Manual 29.07.15 RevisedAbhisikta MishraNo ratings yet
- 2A Lab 5 Atwood's MachineDocument3 pages2A Lab 5 Atwood's MachineDita PramidaNo ratings yet
- Vernier Act16 PicketfenceDocument7 pagesVernier Act16 Picketfencefoureyed0_00% (1)
- PWV 10 COMP Atwoods MachineDocument5 pagesPWV 10 COMP Atwoods MachineSandi WiarsanaNo ratings yet
- 15 Simple Harmonic MotionDocument4 pages15 Simple Harmonic Motionjohnhwang940% (1)
- Atwoods MachineDocument4 pagesAtwoods MachineMelissa Smith0% (1)
- AtwoodDocument3 pagesAtwoodBahril IlmiwanNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument3 pagesLab ReportTom DonohueNo ratings yet
- Picket Fence LabDocument3 pagesPicket Fence Labapi-236349398No ratings yet
- Aqa A Level Physics - Required Practicals: JUNE 2017Document33 pagesAqa A Level Physics - Required Practicals: JUNE 2017LouisNo ratings yet
- Lab Picket Fence Free FallDocument4 pagesLab Picket Fence Free FallKurt PreyNo ratings yet
- AP Lab-Atwoods MachineDocument4 pagesAP Lab-Atwoods Machinernguyen7007No ratings yet
- Atwood's MachineDocument22 pagesAtwood's MachineDebora Tresia PurbaNo ratings yet
- Physics Labreport Free FallDocument6 pagesPhysics Labreport Free Fallapi-257070591No ratings yet
- Lab 7 - Simple Harmonic MotionDocument6 pagesLab 7 - Simple Harmonic MotionCanjiCanji50% (2)
- DynamicDocument6 pagesDynamicAbdla DoskiNo ratings yet
- IA ParachuteDocument4 pagesIA ParachuteJoshua KurniawanNo ratings yet
- 05 Picket Fence Free Fall LQDocument4 pages05 Picket Fence Free Fall LQNayeli CarrascoNo ratings yet
- Atwood's MachineDocument22 pagesAtwood's MachineagnesNo ratings yet
- Acceleration On An Air TrackDocument7 pagesAcceleration On An Air TrackSandra SaviromoNo ratings yet
- Acc BtaDocument4 pagesAcc BtaSharon JoseNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Report - Simple Atwood MachineDocument8 pagesLaboratory Report - Simple Atwood MachineAlthea DumabokNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Aurora State College of Technology Zabali Baler, Aurora Physics LaboratoryDocument5 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Aurora State College of Technology Zabali Baler, Aurora Physics LaboratoryChristopher PaladioNo ratings yet
- Lab 2a Dynamic Response of A Mass-Spring System With DampingDocument5 pagesLab 2a Dynamic Response of A Mass-Spring System With DampingPrashant AshishNo ratings yet
- Lesson 08 Acceleration RPDocument15 pagesLesson 08 Acceleration RPAlya Defa AnindaNo ratings yet
- Picket FencingDocument3 pagesPicket FencingKitkatNo ratings yet
- Accceleration Due To GravityDocument7 pagesAccceleration Due To Gravityapi-3759956No ratings yet
- PHY Unit 6Document276 pagesPHY Unit 6Ugly TwitterNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Inquiry Free Fall: Time Alloted: 3 Lab PeriodsDocument5 pagesLaboratory Inquiry Free Fall: Time Alloted: 3 Lab PeriodsSandi BerginNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3.5.3 Picket Fence LabDocument3 pagesLesson 3.5.3 Picket Fence LabnassNo ratings yet
- Experiment 102Document5 pagesExperiment 102Romulus BloodNo ratings yet
- Newton Second LawDocument4 pagesNewton Second LawLester ParadilloNo ratings yet
- SGDE3Document4 pagesSGDE3SCVLifeNo ratings yet
- Murciano A 2Document5 pagesMurciano A 2AaronNo ratings yet
- 21d Simple Harmonic Motion-RGC 03-03-09Document6 pages21d Simple Harmonic Motion-RGC 03-03-09Raymond KipkoechNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 CombinedDocument24 pagesUnit 6 Combinedbhuvanharish25No ratings yet
- Name: Ahammad Nadendla Roll No: B19BB030Document12 pagesName: Ahammad Nadendla Roll No: B19BB030Ankur BorkarNo ratings yet
- Centripetal Acceleration Lab ReportDocument7 pagesCentripetal Acceleration Lab Reportapi-263389150No ratings yet
- 201 Lab 7. Work and EnergyDocument9 pages201 Lab 7. Work and EnergydermaNo ratings yet
- Strain GaugeDocument3 pagesStrain GaugeManthan SinghNo ratings yet
- Experimental ReportDocument11 pagesExperimental Reportapi-319119669No ratings yet
- Picket Fence Freefall LabDocument4 pagesPicket Fence Freefall Labasdf100% (1)
- Lab Report 2Document3 pagesLab Report 2api-263411981100% (1)
- Bundle Adjustment: Optimizing Visual Data for Precise ReconstructionFrom EverandBundle Adjustment: Optimizing Visual Data for Precise ReconstructionNo ratings yet
- STEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10From EverandSTEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10No ratings yet
- M1T1-2 Group3 BEEd201 EdTech1Document5 pagesM1T1-2 Group3 BEEd201 EdTech1Regina Vera Lisondra OracionNo ratings yet
- Essential Statistics 2E: William Navidi and Barry MonkDocument23 pagesEssential Statistics 2E: William Navidi and Barry Monkkaled1971No ratings yet
- HW 106-2 ColorDocument24 pagesHW 106-2 Colormonktheop1155No ratings yet
- Resume - Ricky - VivancoDocument1 pageResume - Ricky - VivancoRicky VivancoNo ratings yet
- Gabriel Zarzycki - Portfolio Assignment #1 - Intro EssayDocument2 pagesGabriel Zarzycki - Portfolio Assignment #1 - Intro EssayGabriel ZarzyckiNo ratings yet
- The First Term English Exam Level: 3am Duration:1h30 TextDocument2 pagesThe First Term English Exam Level: 3am Duration:1h30 Textaicha yayoucheNo ratings yet
- 1992 - Worlds of Consciousness and The Structure of ConsciousnessDocument43 pages1992 - Worlds of Consciousness and The Structure of ConsciousnessKátharsisNo ratings yet
- Human Eye and EarDocument2 pagesHuman Eye and Earshathurjanan.jana5No ratings yet
- Kleij-Leukfeldt2020 Chapter CyberResilientBehaviorIntegratDocument13 pagesKleij-Leukfeldt2020 Chapter CyberResilientBehaviorIntegratThanh MonNo ratings yet
- Renewal of Notarial Commission 2022-2023 For UploadDocument3 pagesRenewal of Notarial Commission 2022-2023 For UploadmacrosalNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 The Teaching ProfessionDocument7 pagesAssignment 2 The Teaching ProfessionRholynne Ghie Anne EstebanNo ratings yet
- Tekin Iftar2017 PDFDocument21 pagesTekin Iftar2017 PDFVictor Martin CobosNo ratings yet
- How To Write A Geotechnical Investigation Report - CivilblogDocument12 pagesHow To Write A Geotechnical Investigation Report - CivilblogOladunni AfolabiNo ratings yet
- Turkey and Azerbaijan: Passion, Principle, or Pragmatism?Document4 pagesTurkey and Azerbaijan: Passion, Principle, or Pragmatism?German Marshall Fund of the United StatesNo ratings yet
- Certainty Equivalent FactorDocument2 pagesCertainty Equivalent FactorParth SahniNo ratings yet
- Lavendia Portfolio PR2 ABM12 4Document28 pagesLavendia Portfolio PR2 ABM12 4PresydenteNo ratings yet
- College of Health & Allied Sciences: Review of Related LiteratureDocument20 pagesCollege of Health & Allied Sciences: Review of Related LiteratureAngela V. De LunaNo ratings yet
- Pima Unofficial TranscriptDocument9 pagesPima Unofficial Transcriptapi-301121897No ratings yet
- Republic Act 3019Document8 pagesRepublic Act 3019Isha SorianoNo ratings yet
- December 06Document36 pagesDecember 06Quy DangNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Test: Make Circle Around A), B), C) or D) According To The Asked QuestionDocument2 pagesDiagnostic Test: Make Circle Around A), B), C) or D) According To The Asked QuestionAtif LiaqatNo ratings yet
- Value Education Presentation (203-065Document9 pagesValue Education Presentation (203-065ANISH PATIL (RA2111029010064)No ratings yet
- A Feminist Analysis of A Doll HouseDocument6 pagesA Feminist Analysis of A Doll HouseMaida Khan100% (1)
- Research ProposalDocument4 pagesResearch ProposalMax Odeh100% (1)
- Vehicle Dynamics Prof. R. Krishnakumar Department of Engineering Design Indian Institute of Technology - Madras Lecture - 12 Lateral Force GenerationDocument17 pagesVehicle Dynamics Prof. R. Krishnakumar Department of Engineering Design Indian Institute of Technology - Madras Lecture - 12 Lateral Force Generationgauraang singh baghelNo ratings yet
- Unified Power Quality Conditioner (Upqc) With Pi and Hysteresis Controller For Power Quality Improvement in Distribution SystemsDocument7 pagesUnified Power Quality Conditioner (Upqc) With Pi and Hysteresis Controller For Power Quality Improvement in Distribution SystemsKANNAN MANINo ratings yet
- Nonhuman PhotographyDocument21 pagesNonhuman PhotographySNo ratings yet
- Ge Lit1 PrelimDocument13 pagesGe Lit1 PrelimJovelle ConahapNo ratings yet