Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CC Serum Protein Fractions
CC Serum Protein Fractions
Uploaded by
mendoxastar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views6 pagesSerum protein fractions serve specific functions and can indicate various health conditions. Prealbumin is the best indicator of malnutrition and transports thyroxine and vitamin A. Albumin contributes most to osmotic pressure and transports various substances; low levels occur in liver disease and nephrotic syndrome. Alpha-fetoprotein increases in amniotic fluid and hepatocellular carcinoma. Various proteins increase or decrease with inflammation and can reveal conditions like emphysema, cirrhosis, and Wilson's disease. Protein levels provide insights into nutritional, inflammatory, and disease states.
Original Description:
Original Title
Cc Serum Protein Fractions
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentSerum protein fractions serve specific functions and can indicate various health conditions. Prealbumin is the best indicator of malnutrition and transports thyroxine and vitamin A. Albumin contributes most to osmotic pressure and transports various substances; low levels occur in liver disease and nephrotic syndrome. Alpha-fetoprotein increases in amniotic fluid and hepatocellular carcinoma. Various proteins increase or decrease with inflammation and can reveal conditions like emphysema, cirrhosis, and Wilson's disease. Protein levels provide insights into nutritional, inflammatory, and disease states.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views6 pagesCC Serum Protein Fractions
CC Serum Protein Fractions
Uploaded by
mendoxastarSerum protein fractions serve specific functions and can indicate various health conditions. Prealbumin is the best indicator of malnutrition and transports thyroxine and vitamin A. Albumin contributes most to osmotic pressure and transports various substances; low levels occur in liver disease and nephrotic syndrome. Alpha-fetoprotein increases in amniotic fluid and hepatocellular carcinoma. Various proteins increase or decrease with inflammation and can reveal conditions like emphysema, cirrhosis, and Wilson's disease. Protein levels provide insights into nutritional, inflammatory, and disease states.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 6
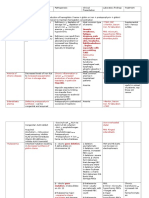
SERUM PROTEIN FRACTIONS
Specific Functions Other comments
Proteins
Prealbumin -Best indicator of Malnutrition -Most anodal
-Transport protein: -Forms a distinct band in
binds/transports T4 (transthyretin electrophoresis, thus, it is a
or Thyroxine binding Prealbumin [ landmark in identifying
TBPA]) unknown fluid CSF
-Involves in transport of Vit. A/
Retinol: forms a complex with
RBP [ Retinol Binding Complex]
Albumin -Major Contributor to osmotic/ -Osmotic pressure = Osmotic
oncotic pressure pressure
-General transport protein: - ↓ osmotic pressure will lead
transports bilirubin, fatty acids, to Edematous where water in
ions (Ca, Mg), and acidic drugs vascular wall goes to tissues
-Negative APR: ↓
inflammation
-↓ level in liver diease,
nephrotic syndrome, protein
losing enteropathy
α-Fetoprotein -↑ level in amniotic fluid: Neural -usually increase in
tube defect (Anencephaly or pregnancy
Spina Bifida) - Maternal serum as
screening, followed by
amniocentesis
-↑ level associated with
Hepatocellular carcinoma/
hepatoma/liver cancer (in
adult, not pregnant)
α1 -Antitrypsin -Positive APR: ↑ inflammation -“anti”- means an protease
-Protease inhibitor inhibitor
-90% of α1 band
-↓ level associated with
pulmonary emphysema and
Juvenile Hepatic Cirrhosis
(flat α-1)
α1- Acid -Positive APR: ↑ inflammation -aka. Orosomucoid
glycoprotein -Binds progesterone and some -Negatively charged even in
basic drugs acid pH
-very high carbohydrate
content
α1- -Protein inhibitor -Binds at prostate-specific
Antichymotrypsi -Mild Positive APR antigen
n -Essential in PSA assay
Gc-globulin -transport Vitamin D Binding -↓level may lead to abnormal
Protein [VBP] and in calcium calcium levels
homeostasis (intestinal absorption
and renal reabsorption)
Α2- -Negative APR -↑ten-fold in protein losing
Macroglobulin -Protease inhibitor conditions: Nephrotic
-largest non-Ig protein Syndrome, Protein losing
enteropathy
-Compensatory mechanism: ↑
synthesis of large proteins
which will be spared from
urinary and GI loss
Haptoglobin -Positive APR: ↑ inflammation -↓ level seen in hemolytic
-Binds to hemoglobin to preserve disorders (due to
iron consumption)
Ceruloplasmin -Positive APR: ↑ inflammation -Copper binding protein
-Has oxidase activity -↓ serum level in Wilson’s
Disease
-Wilson’s Disease: deposition
of coppers in tissue, thus ↓ in
serum
Transferrin -transport ferric iron -↑ level seen in Iron
Deficiency Anemia
-IDA: ↓ serum iron, ↑ TIBC,
↑transferrin (distinguish from
other anemia of chronic
disorders)
-measures/expressed/
reported as Total Iron Binding
Capacity [TIBC]
-Pseudoparaprotein:
mistaken for monoclonal
gammopathy [high peak:
severe IDA] due to proximity
to Immunoglobulin
C3 compliment -Immune response -Most abundant complement
-clearance of immune complexes, component (highest conc. In
as opsonin… serum)
-Convergence of classical
and alternative pathway
Hemopexin -Negative APR: ↓ inflammation -↓ level in intravascular
-Binds to heme hemolysis ( due to
consumption)
β2 -Microglobulin -component of MHC or HLA -Use to measure GFR
molecules - Serve as clearance
- Specifically, MHC Class I substance
-Clearance: removal from the
blood through filtration
-small protein with 11 800
Daltons (MW) [ 70 000
glomerular threshold]
-Unreliable in patients with
malignancies and
autoimmune disorders
(overestimation of GFR)
C-reactive -Positive APR: Most sensitive -Gamma migrating
protein -enhances phagocytosis in immunoglobulin
inflammatory disease ↑ up to 1000 times in
-Act as opsonin, a substance that inflammatory states
enhances phagocytosis -High Sensitivity CRP used
as a marker of Cardio
Vascular Disease
(immunoassay-based)
Immunoglobulins -Antibodies produced by plasma -Gamma globulins
cells (differentiated B- -Major classes/ isotypes: IgG,
lymphocytes) IgM, IgA, IgE, and IgD
-IgM- primary response
-IgG- anamnestic response
Extra bands will be seen if the specimen used is:
o Plasma: Fibrinogen in Beta-Gamma interzone
o Hemolyzed serum: Hemoglobin in A2-beta interzone or sometimes
contributes to beta band
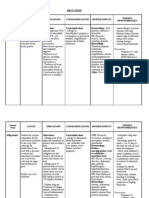
Type Pathologic conditions B1 B2
Pre-hepatic Hemolytic disorders ↑ N
Hepatic Gilbert syndrome Transport Defect
Lucey-Driscoll syndrome
Physiologic jaundice of Conjugation Defect
the newborn
Crigler-Najjar syndrome ↑ N
Viral hepatitis
Cirrhosis ↑ ↑
Hepatic carcinoma
Dubin- Johnson
syndrome N ↑ Secretory Defect
Rotor syndrome
Post Hepatic Biliary obstruction N ↑
Unconjugated Combined Conjugated
Hyperbilirubinemia Hyperbilirubinemia Hyperbilirubinemia
Enzymes of Clinical Importance
Start of Increase Peak Normalizes
CK-MB 4-6 hours 12-24 hours 48-72 hours (2-3 days)
LD (for MI) 12-24 hours 48-72 hours 10 days
AST (for MI) 6-8 hours 18-24 hours 4-5 days
You might also like
- Mechanism of Pain Generation For Endometriosis-Associated Pelvic PainDocument9 pagesMechanism of Pain Generation For Endometriosis-Associated Pelvic PainDwi CahyaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Main DrugsDocument14 pagesPharmacology Main DrugsSabir KhanNo ratings yet
- Gynecologic Problems of Childhood: Anne Margrette C. VelasquezDocument46 pagesGynecologic Problems of Childhood: Anne Margrette C. VelasquezAnne Margrette Velasquez100% (1)
- Experiment #15: Screening Test For Low Titer Group "O" BloodDocument5 pagesExperiment #15: Screening Test For Low Titer Group "O" BloodKriziaNo ratings yet
- Proteinele PlasmaticeDocument71 pagesProteinele PlasmaticeCiocarlan Mihai100% (1)
- LCC Notes - Specific ProteinsDocument2 pagesLCC Notes - Specific ProteinsLaurie Marie Caceres-CalupasNo ratings yet
- Week 11 TransDocument6 pagesWeek 11 Transchayiezen0301No ratings yet
- Decreased Levels of Iron by Diet or Hemorrhage Impaired Heme SynthesisDocument8 pagesDecreased Levels of Iron by Diet or Hemorrhage Impaired Heme SynthesisSamuel RothschildNo ratings yet
- Component Pancreatitis: PathophysiologyDocument1 pageComponent Pancreatitis: PathophysiologyEglNo ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry: Prepared By: Charizzemonique V. Daraug, RMTDocument22 pagesClinical Chemistry: Prepared By: Charizzemonique V. Daraug, RMTIsah SittiNo ratings yet
- Pharm Chemo Drugs SauldDocument6 pagesPharm Chemo Drugs Sauldneal100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Hepatitis B InfectionDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Hepatitis B InfectionSTORAGE FILENo ratings yet
- CC1 NPNDocument2 pagesCC1 NPNElijah Mae MundocNo ratings yet
- Ch2 Protein 2Document87 pagesCh2 Protein 2Loay Abu ZahraNo ratings yet
- Enzymes CC Part 2 PrintDocument6 pagesEnzymes CC Part 2 PrintKrystel Bea DinqueNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument22 pagesDrugsPAUL MICHAEL G. BAGUHINNo ratings yet
- Finals Topic 2 Clin Chem NpnsDocument6 pagesFinals Topic 2 Clin Chem NpnsErl Jerome CabayaoNo ratings yet
- 2 Lab Med Protein StudentDocument36 pages2 Lab Med Protein Studentkholoud220No ratings yet
- Additional Notes Hepatobilliary SystemDocument3 pagesAdditional Notes Hepatobilliary SystemShiela May FeriaNo ratings yet
- Pa ThoDocument4 pagesPa ThoErnest Genesis Mercado GuevaraNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis (Pediatrics)Document82 pagesHepatitis (Pediatrics)Hazel AsperaNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids and ProteinsDocument8 pagesAmino Acids and ProteinsathenasophiaabNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology NoteDocument3 pagesEndocrinology Notenistobdhoraat3No ratings yet
- Week 11 - Hema Lec Major Anticoagulants SystemDocument7 pagesWeek 11 - Hema Lec Major Anticoagulants SystemCzarina Mae IlaganNo ratings yet
- Ikd 10 Case 2Document11 pagesIkd 10 Case 2Senggol NgekNo ratings yet
- Differential Diagnosis ChartDocument2 pagesDifferential Diagnosis Chartaxmedfare138No ratings yet
- Cirrhosis Causative DiseasesDocument3 pagesCirrhosis Causative DiseasesMaryam FadahNo ratings yet
- Hematology System Lec. 2Document32 pagesHematology System Lec. 2xqfs2cd44sNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Hypoalbuminaemia.: Nephrotic SyndromeDocument4 pagesPathophysiology Hypoalbuminaemia.: Nephrotic SyndromegabyNo ratings yet
- LiverDocument20 pagesLiverasalizwa ludlalaNo ratings yet
- Ew Anu PDFDocument2 pagesEw Anu PDFrachel wongNo ratings yet
- Acute Renal Failure Introduction - : PrognosisDocument8 pagesAcute Renal Failure Introduction - : PrognosisHepsibaNo ratings yet
- PDF Anemia Concept Map0000Document1 pagePDF Anemia Concept Map0000alvianmerzaradiputraNo ratings yet
- EMD1 Pc1 PATOFISIOLOGI SEPSISDocument5 pagesEMD1 Pc1 PATOFISIOLOGI SEPSISRasyid RidhaNo ratings yet
- Cpliver 1Document4 pagesCpliver 1isahNo ratings yet
- AmlodipineDocument2 pagesAmlodipinejiglenssNo ratings yet
- Plasmatic Proteins. Protein ElectrophoresisDocument22 pagesPlasmatic Proteins. Protein ElectrophoresisIrina StamateNo ratings yet
- Renal DiseasesDocument1 pageRenal DiseasesRebecca BernalNo ratings yet
- AnemiaDocument10 pagesAnemiaBia Payawal100% (2)
- Drug Study: Proteus Mirabilis, Klebsiella Pneumoniae, Enterobacter Species, Distress, NauseaDocument6 pagesDrug Study: Proteus Mirabilis, Klebsiella Pneumoniae, Enterobacter Species, Distress, Nauseacsy123No ratings yet
- Anemia in SNDocument8 pagesAnemia in SNNurulSyaidahNo ratings yet
- OB Blood Transfusions PregnancyDocument37 pagesOB Blood Transfusions Pregnancykhadzx100% (2)
- HEMATOLOGY REVIEW Pt. 1Document6 pagesHEMATOLOGY REVIEW Pt. 1april jholynna garroNo ratings yet
- OS214 20060306 Grp10a Chronic Renal FailureDocument3 pagesOS214 20060306 Grp10a Chronic Renal Failureapi-3799593100% (5)
- 112 Lecture MidtermsDocument8 pages112 Lecture MidtermsRose Ann CammagayNo ratings yet
- 112 Lecture MidtermsDocument18 pages112 Lecture MidtermsRose Ann CammagayNo ratings yet
- Ascp StudyDocument18 pagesAscp StudyJamaica EstorninosNo ratings yet
- Babies Who Can't "Pee" in Utero Develop Potter Sequence. POTTER Sequence Associated WithDocument162 pagesBabies Who Can't "Pee" in Utero Develop Potter Sequence. POTTER Sequence Associated WithАндрей СырNo ratings yet
- Intravascular Extravascular: Fe Storage Tibc SerumDocument2 pagesIntravascular Extravascular: Fe Storage Tibc Serumazhar hussinNo ratings yet
- Proteins: Prepared By: Dayle Daniel G. Sorveto, RMT, MSMTDocument64 pagesProteins: Prepared By: Dayle Daniel G. Sorveto, RMT, MSMTDayledaniel SorvetoNo ratings yet
- 5 Drug Study, RLE DUTY CSV-shyDocument6 pages5 Drug Study, RLE DUTY CSV-shyShy Dela PuertaNo ratings yet
- Pharmaco - AntibioticsDocument4 pagesPharmaco - AntibioticsNashrah HusnaNo ratings yet
- Interpreting Liver Function TestsDocument1 pageInterpreting Liver Function TestskarenmstamNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Biochemistry Handout 2019Document15 pagesMetabolic Biochemistry Handout 2019Akashdeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Recall Questions-February 14, 2018 Wyne Brent M. Corpuz, RMTDocument4 pagesRecall Questions-February 14, 2018 Wyne Brent M. Corpuz, RMTRafael CayananNo ratings yet
- Chemical Urinalysis TransDocument8 pagesChemical Urinalysis TransIan Carlo B GalangNo ratings yet
- 2 Drug Study - PanganadamanDocument5 pages2 Drug Study - PanganadamanNornisah H. PangandamanNo ratings yet
- Drug Study2Document3 pagesDrug Study2Anjulie Austria SoNo ratings yet
- Non Protein Nitrogen CompoundsDocument2 pagesNon Protein Nitrogen Compoundsharith r donovanNo ratings yet
- Massive Blood Product Transfusion - Deranged PhysiologyDocument5 pagesMassive Blood Product Transfusion - Deranged Physiologyhnzzn2bymdNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyAkira Poscablo PiranteNo ratings yet
- Life Cycle of Babesia SPP.: Salivary Glands, DevelopingDocument1 pageLife Cycle of Babesia SPP.: Salivary Glands, DevelopingIrina AtudoreiNo ratings yet
- Poxviruses: Chapter 37: Herpesviruses, Poxviruses, & Human Papilloma VirusDocument4 pagesPoxviruses: Chapter 37: Herpesviruses, Poxviruses, & Human Papilloma Virustheodore_estradaNo ratings yet
- Measles Outbreak Response PlanDocument24 pagesMeasles Outbreak Response PlanveroniqueNo ratings yet
- Pathology Intro Part 1 PDFDocument13 pagesPathology Intro Part 1 PDFAmy LalringhluaniNo ratings yet
- 4 THROMBOLYTIC DRUGS by DR Azmat AliDocument90 pages4 THROMBOLYTIC DRUGS by DR Azmat AliAhmed YTNo ratings yet
- The Secret of Kimchi's Unique TasteDocument5 pagesThe Secret of Kimchi's Unique Tastetessar f gNo ratings yet
- Secondary Immunodeficiency in ChildrenDocument16 pagesSecondary Immunodeficiency in Childrenryan20eNo ratings yet
- COVID 19 em InglêsDocument6 pagesCOVID 19 em Inglêspallomabarbosa.biomedNo ratings yet
- Transfusion Medicine - RK SaranDocument80 pagesTransfusion Medicine - RK SaranAvinashNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Microbiology (PDFDrive) (001-018)Document18 pagesFundamentals of Microbiology (PDFDrive) (001-018)Nur FitrianaNo ratings yet
- Pfizer Pipeline 2023Document16 pagesPfizer Pipeline 2023sam.reinereineNo ratings yet
- 7.01-Medically Important Bacteria II (Part I)Document54 pages7.01-Medically Important Bacteria II (Part I)danNo ratings yet
- Jessica Le - Covid-19Document3 pagesJessica Le - Covid-19api-523306558No ratings yet
- TRANS BIO 024 Lecture 3 ProteinsDocument4 pagesTRANS BIO 024 Lecture 3 ProteinsMc AllenNo ratings yet
- Physiology Summary Chapter 32Document6 pagesPhysiology Summary Chapter 32gail018No ratings yet
- Presentation On Dysuria 1Document25 pagesPresentation On Dysuria 1ankur acharyaNo ratings yet
- Lecture III - Semi-FinalsDocument16 pagesLecture III - Semi-FinalsENGETS IT7No ratings yet
- 7.013 Pset 4 PDFDocument12 pages7.013 Pset 4 PDF15klaNo ratings yet
- Study Guide Protein Synthesis (KEY)Document2 pagesStudy Guide Protein Synthesis (KEY)owls_1102No ratings yet
- EndometritisDocument6 pagesEndometritisandriansyah2110% (1)
- Dengue and Chikungunya Infections in ChildrenDocument9 pagesDengue and Chikungunya Infections in ChildrenAl-Harits OctaNo ratings yet
- Production of Penicillin: A Review: International Journal of Research and Analytical Reviews (IJRAR)Document6 pagesProduction of Penicillin: A Review: International Journal of Research and Analytical Reviews (IJRAR)Kvc BioNo ratings yet
- Malay DnaDocument9 pagesMalay DnaEffandi Abu BakarNo ratings yet
- MCQ'S in Pharmacology Wid AnswersDocument18 pagesMCQ'S in Pharmacology Wid Answersapi-1991639975% (4)
- PdfText PDFDocument10 pagesPdfText PDFshakila banuNo ratings yet
- Notice: Agency Information Collection Activities Proposals, Submissions, and ApprovalsDocument2 pagesNotice: Agency Information Collection Activities Proposals, Submissions, and ApprovalsJustia.comNo ratings yet
- .Insecticidal Neem and Lemon Grass - 1637921960000Document50 pages.Insecticidal Neem and Lemon Grass - 1637921960000precious atakubiNo ratings yet