Professional Documents
Culture Documents
English Tenses 2023
English Tenses 2023
Uploaded by
erick robayoCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Sepedi Poetry Montshepetc5a1aboc5a1egoDocument106 pagesSepedi Poetry Montshepetc5a1aboc5a1egoTumi Shangwina100% (6)
- English Grammar Guide: 23 Grammar Rules You Must Know To Speak and Write English Like A NativeFrom EverandEnglish Grammar Guide: 23 Grammar Rules You Must Know To Speak and Write English Like A NativeRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (32)
- ESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideFrom EverandESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideNo ratings yet
- Class 3: Other Grammar Concepts Prepositions Exercises: 1. Choose The Correct PrepositionDocument2 pagesClass 3: Other Grammar Concepts Prepositions Exercises: 1. Choose The Correct PrepositionJeyson Patiño100% (1)
- Simple Present USE 1 Repeated ActionsDocument16 pagesSimple Present USE 1 Repeated ActionsGaram Esther GohNo ratings yet
- Simple Present: USE 1 Repeated ActionsDocument11 pagesSimple Present: USE 1 Repeated ActionsNicolás De los riosNo ratings yet
- Dosier AlvaroDocument22 pagesDosier AlvaroFernando Muñoz MontesinosNo ratings yet
- USE 1 Completed Action in The Past: Did You Have Dinner Last Night?Document25 pagesUSE 1 Completed Action in The Past: Did You Have Dinner Last Night?Dashrathsinh RathodNo ratings yet
- Verbs TensesDocument32 pagesVerbs TensesLucas Padrão100% (1)
- Grammar TensesDocument28 pagesGrammar TensesKoko AlayzaNo ratings yet
- Simple Present: Do You Speak English?Document27 pagesSimple Present: Do You Speak English?Andreea GîleaNo ratings yet
- Verb Tense Tutorial: Complete List of Simple Present FormsDocument43 pagesVerb Tense Tutorial: Complete List of Simple Present FormsRoxana TudoseNo ratings yet
- Tenses Oft He Verb QWDocument9 pagesTenses Oft He Verb QWvincentc84No ratings yet
- Simple Past: USE 1 Completed Action in The PastDocument7 pagesSimple Past: USE 1 Completed Action in The PastYsa YesoNo ratings yet
- Materi TensesDocument37 pagesMateri TensesNoviartiNo ratings yet
- Simple Past: USE 2 A Series of Completed ActionsDocument28 pagesSimple Past: USE 2 A Series of Completed ActionsDiamun FikriNo ratings yet
- Tense TheoryDocument33 pagesTense TheoryAnamaria Blajan-LazaNo ratings yet
- Eng Gram Mod 5 TensesDocument5 pagesEng Gram Mod 5 Tensesvikas1onlyNo ratings yet
- Tiempos InglésDocument43 pagesTiempos InglésFrancisca Ponce HilleNo ratings yet
- Past TenseDocument14 pagesPast Tensepandu MNo ratings yet
- Simple PastDocument8 pagesSimple Pastnavarreterobinson1No ratings yet
- Simple Past: EnglezaDocument21 pagesSimple Past: EnglezaLarissa TodeaNo ratings yet
- Simple Present: Do You Speak English?Document12 pagesSimple Present: Do You Speak English?aden_adennieNo ratings yet
- Present Simple: Does He Play Tennis?Document7 pagesPresent Simple: Does He Play Tennis?Marija MarkovićNo ratings yet
- Grammar TensesDocument27 pagesGrammar Tenseswendy nguNo ratings yet
- Simple Present: Do You Speak English?Document5 pagesSimple Present: Do You Speak English?roxanairimieaNo ratings yet
- English Club: Simple Present Tense & Present Continuous TenseDocument8 pagesEnglish Club: Simple Present Tense & Present Continuous TenseNailis SalamahNo ratings yet
- English On Line CourseDocument13 pagesEnglish On Line CourseDaniela Frediani RezendeNo ratings yet
- Simple PresentDocument38 pagesSimple PresentRohini SupramaniamNo ratings yet
- ContinuousDocument25 pagesContinuousLula KotulovaNo ratings yet
- Simple Past Past Continuous Past Perfect: Group 2: Abirami Tee Sha Ney Loh Jia Wei Tan Wei JianDocument37 pagesSimple Past Past Continuous Past Perfect: Group 2: Abirami Tee Sha Ney Loh Jia Wei Tan Wei JianAbirami SanmugumNo ratings yet
- Father Friends Mother Sons Sister Wife Brother I Love YouDocument66 pagesFather Friends Mother Sons Sister Wife Brother I Love YouAsemSalehNo ratings yet
- Grammar ReviewDocument35 pagesGrammar ReviewLuManNo ratings yet
- Simple Present: Do You Speak English?Document51 pagesSimple Present: Do You Speak English?Lorela Liliana TudorNo ratings yet
- Simple Present: USE 1 Repeated ActionsDocument38 pagesSimple Present: USE 1 Repeated Actionssabine111No ratings yet
- Unit 2, Lesson 6. The Passive Voice.: Sujeto + Verbo Auxiliar (To Be) + Participio PasadoDocument18 pagesUnit 2, Lesson 6. The Passive Voice.: Sujeto + Verbo Auxiliar (To Be) + Participio PasadoJuan Pablo CallejasNo ratings yet
- ×y ×y ×y ×y ×y ×yDocument23 pages×y ×y ×y ×y ×y ×yHealing SmileyNo ratings yet
- TenseDocument14 pagesTenseapi-214243994No ratings yet
- Simple Past, Past Cont, Past PerfectDocument14 pagesSimple Past, Past Cont, Past PerfectRe'ka Miha'lyNo ratings yet
- Past Simple Vs Past ContinuousDocument4 pagesPast Simple Vs Past ContinuousPaula DiazNo ratings yet
- Grammar EnglishDocument66 pagesGrammar EnglishChafik BerdjouhNo ratings yet
- TensesDocument9 pagesTensesSadiyah KaniNo ratings yet
- Farah Salma Nisrina - TensesDocument15 pagesFarah Salma Nisrina - TensesfarahNo ratings yet
- Past Simple Past ContinuousDocument13 pagesPast Simple Past ContinuousbiffinNo ratings yet
- The Past Continuous TenseDocument4 pagesThe Past Continuous TenseYeerina DebnathNo ratings yet
- WALKTHROUGH English Verb TensesDocument56 pagesWALKTHROUGH English Verb TensesLaurentiu IonescuNo ratings yet
- Past Continuous: Were You Studying When She Called?Document4 pagesPast Continuous: Were You Studying When She Called?SenaNo ratings yet
- Simple Past: USE 1 Completed Action in The PastDocument3 pagesSimple Past: USE 1 Completed Action in The PastAndreea LascuNo ratings yet
- Past ContinuousDocument4 pagesPast ContinuousILy SofiaNo ratings yet
- 04.past ContinuousDocument4 pages04.past ContinuousAdinaNo ratings yet
- Active / Passive Verb FormsDocument37 pagesActive / Passive Verb FormshusnaNo ratings yet
- Full Tenses PDFDocument40 pagesFull Tenses PDFsarief100% (2)
- English TaskDocument14 pagesEnglish TaskSitiaisyah Batusangkar100% (2)
- Simple PastDocument5 pagesSimple PastPonnya KhinNo ratings yet
- Rewiew GrammarDocument37 pagesRewiew GrammarFabricio Alberti Cervantes FalenNo ratings yet
- Past SimpleDocument4 pagesPast SimpleCamelia PleșaNo ratings yet
- T IS NOT Important That This Fact IS UntrueDocument20 pagesT IS NOT Important That This Fact IS UntrueURS_ANDRIANNo ratings yet
- Past Continuous Form: Were You Studying When She Called?Document4 pagesPast Continuous Form: Were You Studying When She Called?zvegaNo ratings yet
- Past Continuous: Were You Studying When She Called?Document4 pagesPast Continuous: Were You Studying When She Called?Philip KingNo ratings yet
- Complete List of Past Continuous FormsDocument2 pagesComplete List of Past Continuous FormsCristiana LapusanNo ratings yet
- Simple Present TenseDocument33 pagesSimple Present TensenorNo ratings yet
- B 2.3 - AajrDocument9 pagesB 2.3 - AajriTzDaxusProS7zZNo ratings yet
- Mediation Practice: Exam Tip: How To Write A Mediation SummaryDocument3 pagesMediation Practice: Exam Tip: How To Write A Mediation SummaryDavy EverhartNo ratings yet
- Language Biology and Cognition A Critical Perspective 1St Ed Edition Prakash Mondal Full ChapterDocument67 pagesLanguage Biology and Cognition A Critical Perspective 1St Ed Edition Prakash Mondal Full Chaptererin.soto657100% (13)
- American On Course Scope and SequenceDocument2 pagesAmerican On Course Scope and SequenceIgnacio50% (2)
- TA10-Unit 9Document65 pagesTA10-Unit 9Phan PhanNo ratings yet
- Schmieger Macedonian Language Greece PDFDocument32 pagesSchmieger Macedonian Language Greece PDFAlexandra Ioannidou-RallisNo ratings yet
- Regodo, Jerene (DLP English 2)Document4 pagesRegodo, Jerene (DLP English 2)Jerene RegodoNo ratings yet
- Upper Secondary Academy V Maps GSE 48 60 Relationships and SocialisingDocument1 pageUpper Secondary Academy V Maps GSE 48 60 Relationships and Socialisingkarely0226No ratings yet
- Five ELT Approaches OutlineDocument8 pagesFive ELT Approaches OutlineRaza ShahNo ratings yet
- Commonly Confused Words Week One-1Document6 pagesCommonly Confused Words Week One-1Zenobia AdonisNo ratings yet
- Suhaerin 03 11 2021Document25 pagesSuhaerin 03 11 2021SUHAERINNo ratings yet
- Samira CAPES Lesson Plan Waste Not Want NotDocument33 pagesSamira CAPES Lesson Plan Waste Not Want NotLarbi NadiaNo ratings yet
- Teaching Pronunciation - Pair Up WorkDocument7 pagesTeaching Pronunciation - Pair Up WorkJuan ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - Give Travel UpdatesDocument10 pagesLesson 4 - Give Travel Updatesalinaanton1980_73345No ratings yet
- ENGLISH PAPER2 28 JanDocument9 pagesENGLISH PAPER2 28 JanShreya DeyNo ratings yet
- Civil Service Reviewer PDFDocument65 pagesCivil Service Reviewer PDFTrixia Mae Batiancila100% (1)
- Korean VocabularyDocument106 pagesKorean VocabularyJu DNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect Continuous TenseDocument2 pagesPresent Perfect Continuous TenseABDUL GAFOOR MOHAMED ASFAKNo ratings yet
- Week 3 - The Danger of A Single StoryDocument15 pagesWeek 3 - The Danger of A Single StoryHiruni FernandoNo ratings yet
- Speaking Ae2Document77 pagesSpeaking Ae2Triet TruongNo ratings yet
- Development, Underdevelopment and Poverty: A Linguistic Study of Joseph Edoki'sDocument25 pagesDevelopment, Underdevelopment and Poverty: A Linguistic Study of Joseph Edoki'sMichael PreciousNo ratings yet
- Complete First For Schools - Test Unit Test 1 (PLUS)Document2 pagesComplete First For Schools - Test Unit Test 1 (PLUS)Mihai 1TAP50% (2)
- Assignment Eng 219Document8 pagesAssignment Eng 219Võ Hoàng Bảo NgọcNo ratings yet
- C1 C2 AdjectivesDocument7 pagesC1 C2 AdjectivesGvantsa mandzulashviliNo ratings yet
- The Writing Process (Revising Strategies) - (Literacy Strategy Guide)Document8 pagesThe Writing Process (Revising Strategies) - (Literacy Strategy Guide)Princejoy ManzanoNo ratings yet
- Unit 11 - Simple Past Written WorkDocument2 pagesUnit 11 - Simple Past Written WorkBLACUTT BALDIVIESO JULY ANDREANo ratings yet
- 'FUNCTIONS EXPONENTS AND CONTEXTS' ContigoDocument2 pages'FUNCTIONS EXPONENTS AND CONTEXTS' Contigobraian maxNo ratings yet
- Ef4e Beg Vocab 6b PCMDocument1 pageEf4e Beg Vocab 6b PCMmacarenasabao1994No ratings yet
English Tenses 2023
English Tenses 2023
Uploaded by
erick robayoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
English Tenses 2023
English Tenses 2023
Uploaded by
erick robayoCopyright:
Available Formats
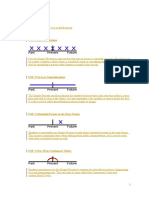
Simple Present
Uses
USE 1 Repeated Actions
Use the simple present to express the idea that an action is repeated or usual. The action can
be a habit, a hobby, a daily event, a scheduled event or something that often happens. It can
also be something a person often forgets or usually does not do.
Examples:
I play tennis.
She does not play tennis.
Does he play tennis?
USE 2 Facts or Generalizations
The simple present can also indicate the speaker believes that a fact was true before, is true
now, and will be true in the future. It is not important if the speaker is correct about the fact. It is
also used to make generalizations about people or things.
Examples:
Cats like milk.
Birds do not like milk.
Do pigs like milk?
USE 3 Scheduled Events in the Near Future
Speakers occasionally use simple present to talk about scheduled events in the near future.
This is most commonly done when talking about public transportation, but it can be used with
other scheduled events as well.
Examples:
The train leaves tonight at 6 PM.
The bus does not arrive at 11 AM, it arrives at 11 PM.
When do we board the plane?
USE 4 Now (Non-Continuous Verbs)
Speakers sometimes use the simple present to express the idea that an action is happening or
is not happening now. This can only be done with non-continuous verbs and certain mixed
verbs.
Examples:
I am here now.
She is not here now.
He needs help right now.
Present Continuous
Uses
USE 1 Now
Use the present continuous with normal verbs to express the idea that something
is happening now, at this very moment. It can also be used to show that something
is not happening now.
Examples:
You are learning English now.
You are not swimming now.
Are you sleeping?
USE 2 Longer Actions in Progress Now
In English, now can mean different things: this second, today, this month, this year,
this century, and so on. Sometimes, we use the present continuous to say that we
are in the process of doing a longer action which is in progress; however, we might
not be doing it at this exact second.
Examples: (All of these sentences can be said while eating dinner in a restaurant.)
I am studying to become a doctor.
I am not studying to become a dentist.
I am reading the book Tom Sawyer.
USE 3 Near Future
Sometimes, speakers use the present continuous to indicate that something will or
will not happen in the near future.
Examples:
I am meeting some friends after work.
I am not going to the party tonight.
USE 4 Repetition and Irritation with Always
The present continuous with words such as always or constantly expresses the
idea that something irritating or shocking often happens. Notice that the meaning is
like simple present, but with negative emotion. Remember to put the
words always or constantly between be and verb+ing.
Examples:
She is always coming to class late.
He is constantly talking. I wish he would shut up.
Simple Past
Uses
USE 1 Completed Action in the Past
Use the simple past to express the idea that an action started and finished at a specific time in
the past. Sometimes, the speaker may not actually mention the specific time, but they do have
one specific time in mind.
Examples:
I saw a movie yesterday.
I didn't see a play yesterday.
USE 2 A Series of Completed Actions
We use the simple past to list a series of completed actions in the past. These actions happen
1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th, and so on.
Examples:
I finished work, walked to the beach, and found a nice place to swim.
He arrived from the airport at 8:00, checked into the hotel at 9:00,
and met the others at 10:00.
USE 3 Duration in the Past
The simple past can be used with a duration which starts and stops in the past. A duration is a
longer action often indicated by expressions such as for two years, for five minutes, all day, all
year, etc.
Examples:
I lived in Brazil for two years.
Shauna studied Japanese for five years.
They sat at the beach all day.
USE 4 Habits in the Past
The simple past can also be used to describe a habit which stopped in the past. It
can have the same meaning as used to. To make it clear that we are talking about
a habit, we often add expressions such as always, often, usually, never, when I
was a child, when I was younger, etc.
Examples:
I studied French when I was a child.
He played the violin.
USE 5 Past Facts or Generalizations
The simple past can also be used to describe past facts or generalizations which
are no longer true. As in USE 4 above, this use of the simple past is quite similar to
the expression used to.
Examples:
She was shy as a child, but now she is very outgoing.
He didn't like tomatoes before.
Did you live in Texas when you were a kid?
Past Continuous
USE 1 Interrupted Action in the Past
Use the past continuous to indicate that a longer action in the past was interrupted.
The interruption is usually a shorter action in the simple past. Remember this can
be a real interruption or just an interruption in time.
Examples:
I was watching TV when she called.
When the phone rang, she was writing a letter.
While we were having the picnic, it started to rain.
USE 2 Specific Time as an Interruption
In USE 1, described above, the past continuous is interrupted by a shorter action in
the simple past. However, you can also use a specific time as an interruption.
Examples:
Last night at 6 PM, I was eating dinner.
At midnight, we were still driving through the desert.
Yesterday at this time, I was sitting at my desk at work.
USE 3 Parallel Actions
When you use the past continuous with two actions in the same sentence, it
expresses the idea that both actions were happening at the same time. The actions
are parallel.
Examples:
I was studying while he was making dinner.
While Ellen was reading, Tim was watching television.
Were you listening while he was talking?
USE 4 Atmosphere
In English, we often use a series of parallel actions to describe the atmosphere at a
particular time in the past.
Example:
When I walked into the office, several people were busily typing,
some were talking on the phones, the boss was yelling directions, and
customers were waiting to be helped. One customer was yelling at a
secretary and waving his hands. Others were complaining to each other
about the bad service.
USE 5 Repetition and Irritation with Always
The past continuous with words such as always or constantly expresses the idea
that something irritating or shocking often happened in the past. The concept is
very similar to the expression used to but with negative emotion. Remember to put
the words always or constantly between be and verb+ing.
Examples:
She was always coming to class late.
He was constantly talking. He annoyed everyone.
I didn't like them because they were always complaining.
You might also like
- Sepedi Poetry Montshepetc5a1aboc5a1egoDocument106 pagesSepedi Poetry Montshepetc5a1aboc5a1egoTumi Shangwina100% (6)
- English Grammar Guide: 23 Grammar Rules You Must Know To Speak and Write English Like A NativeFrom EverandEnglish Grammar Guide: 23 Grammar Rules You Must Know To Speak and Write English Like A NativeRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (32)
- ESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideFrom EverandESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideNo ratings yet
- Class 3: Other Grammar Concepts Prepositions Exercises: 1. Choose The Correct PrepositionDocument2 pagesClass 3: Other Grammar Concepts Prepositions Exercises: 1. Choose The Correct PrepositionJeyson Patiño100% (1)
- Simple Present USE 1 Repeated ActionsDocument16 pagesSimple Present USE 1 Repeated ActionsGaram Esther GohNo ratings yet
- Simple Present: USE 1 Repeated ActionsDocument11 pagesSimple Present: USE 1 Repeated ActionsNicolás De los riosNo ratings yet
- Dosier AlvaroDocument22 pagesDosier AlvaroFernando Muñoz MontesinosNo ratings yet
- USE 1 Completed Action in The Past: Did You Have Dinner Last Night?Document25 pagesUSE 1 Completed Action in The Past: Did You Have Dinner Last Night?Dashrathsinh RathodNo ratings yet
- Verbs TensesDocument32 pagesVerbs TensesLucas Padrão100% (1)
- Grammar TensesDocument28 pagesGrammar TensesKoko AlayzaNo ratings yet
- Simple Present: Do You Speak English?Document27 pagesSimple Present: Do You Speak English?Andreea GîleaNo ratings yet
- Verb Tense Tutorial: Complete List of Simple Present FormsDocument43 pagesVerb Tense Tutorial: Complete List of Simple Present FormsRoxana TudoseNo ratings yet
- Tenses Oft He Verb QWDocument9 pagesTenses Oft He Verb QWvincentc84No ratings yet
- Simple Past: USE 1 Completed Action in The PastDocument7 pagesSimple Past: USE 1 Completed Action in The PastYsa YesoNo ratings yet
- Materi TensesDocument37 pagesMateri TensesNoviartiNo ratings yet
- Simple Past: USE 2 A Series of Completed ActionsDocument28 pagesSimple Past: USE 2 A Series of Completed ActionsDiamun FikriNo ratings yet
- Tense TheoryDocument33 pagesTense TheoryAnamaria Blajan-LazaNo ratings yet
- Eng Gram Mod 5 TensesDocument5 pagesEng Gram Mod 5 Tensesvikas1onlyNo ratings yet
- Tiempos InglésDocument43 pagesTiempos InglésFrancisca Ponce HilleNo ratings yet
- Past TenseDocument14 pagesPast Tensepandu MNo ratings yet
- Simple PastDocument8 pagesSimple Pastnavarreterobinson1No ratings yet
- Simple Past: EnglezaDocument21 pagesSimple Past: EnglezaLarissa TodeaNo ratings yet
- Simple Present: Do You Speak English?Document12 pagesSimple Present: Do You Speak English?aden_adennieNo ratings yet
- Present Simple: Does He Play Tennis?Document7 pagesPresent Simple: Does He Play Tennis?Marija MarkovićNo ratings yet
- Grammar TensesDocument27 pagesGrammar Tenseswendy nguNo ratings yet
- Simple Present: Do You Speak English?Document5 pagesSimple Present: Do You Speak English?roxanairimieaNo ratings yet
- English Club: Simple Present Tense & Present Continuous TenseDocument8 pagesEnglish Club: Simple Present Tense & Present Continuous TenseNailis SalamahNo ratings yet
- English On Line CourseDocument13 pagesEnglish On Line CourseDaniela Frediani RezendeNo ratings yet
- Simple PresentDocument38 pagesSimple PresentRohini SupramaniamNo ratings yet
- ContinuousDocument25 pagesContinuousLula KotulovaNo ratings yet
- Simple Past Past Continuous Past Perfect: Group 2: Abirami Tee Sha Ney Loh Jia Wei Tan Wei JianDocument37 pagesSimple Past Past Continuous Past Perfect: Group 2: Abirami Tee Sha Ney Loh Jia Wei Tan Wei JianAbirami SanmugumNo ratings yet
- Father Friends Mother Sons Sister Wife Brother I Love YouDocument66 pagesFather Friends Mother Sons Sister Wife Brother I Love YouAsemSalehNo ratings yet
- Grammar ReviewDocument35 pagesGrammar ReviewLuManNo ratings yet
- Simple Present: Do You Speak English?Document51 pagesSimple Present: Do You Speak English?Lorela Liliana TudorNo ratings yet
- Simple Present: USE 1 Repeated ActionsDocument38 pagesSimple Present: USE 1 Repeated Actionssabine111No ratings yet
- Unit 2, Lesson 6. The Passive Voice.: Sujeto + Verbo Auxiliar (To Be) + Participio PasadoDocument18 pagesUnit 2, Lesson 6. The Passive Voice.: Sujeto + Verbo Auxiliar (To Be) + Participio PasadoJuan Pablo CallejasNo ratings yet
- ×y ×y ×y ×y ×y ×yDocument23 pages×y ×y ×y ×y ×y ×yHealing SmileyNo ratings yet
- TenseDocument14 pagesTenseapi-214243994No ratings yet
- Simple Past, Past Cont, Past PerfectDocument14 pagesSimple Past, Past Cont, Past PerfectRe'ka Miha'lyNo ratings yet
- Past Simple Vs Past ContinuousDocument4 pagesPast Simple Vs Past ContinuousPaula DiazNo ratings yet
- Grammar EnglishDocument66 pagesGrammar EnglishChafik BerdjouhNo ratings yet
- TensesDocument9 pagesTensesSadiyah KaniNo ratings yet
- Farah Salma Nisrina - TensesDocument15 pagesFarah Salma Nisrina - TensesfarahNo ratings yet
- Past Simple Past ContinuousDocument13 pagesPast Simple Past ContinuousbiffinNo ratings yet
- The Past Continuous TenseDocument4 pagesThe Past Continuous TenseYeerina DebnathNo ratings yet
- WALKTHROUGH English Verb TensesDocument56 pagesWALKTHROUGH English Verb TensesLaurentiu IonescuNo ratings yet
- Past Continuous: Were You Studying When She Called?Document4 pagesPast Continuous: Were You Studying When She Called?SenaNo ratings yet
- Simple Past: USE 1 Completed Action in The PastDocument3 pagesSimple Past: USE 1 Completed Action in The PastAndreea LascuNo ratings yet
- Past ContinuousDocument4 pagesPast ContinuousILy SofiaNo ratings yet
- 04.past ContinuousDocument4 pages04.past ContinuousAdinaNo ratings yet
- Active / Passive Verb FormsDocument37 pagesActive / Passive Verb FormshusnaNo ratings yet
- Full Tenses PDFDocument40 pagesFull Tenses PDFsarief100% (2)
- English TaskDocument14 pagesEnglish TaskSitiaisyah Batusangkar100% (2)
- Simple PastDocument5 pagesSimple PastPonnya KhinNo ratings yet
- Rewiew GrammarDocument37 pagesRewiew GrammarFabricio Alberti Cervantes FalenNo ratings yet
- Past SimpleDocument4 pagesPast SimpleCamelia PleșaNo ratings yet
- T IS NOT Important That This Fact IS UntrueDocument20 pagesT IS NOT Important That This Fact IS UntrueURS_ANDRIANNo ratings yet
- Past Continuous Form: Were You Studying When She Called?Document4 pagesPast Continuous Form: Were You Studying When She Called?zvegaNo ratings yet
- Past Continuous: Were You Studying When She Called?Document4 pagesPast Continuous: Were You Studying When She Called?Philip KingNo ratings yet
- Complete List of Past Continuous FormsDocument2 pagesComplete List of Past Continuous FormsCristiana LapusanNo ratings yet
- Simple Present TenseDocument33 pagesSimple Present TensenorNo ratings yet
- B 2.3 - AajrDocument9 pagesB 2.3 - AajriTzDaxusProS7zZNo ratings yet
- Mediation Practice: Exam Tip: How To Write A Mediation SummaryDocument3 pagesMediation Practice: Exam Tip: How To Write A Mediation SummaryDavy EverhartNo ratings yet
- Language Biology and Cognition A Critical Perspective 1St Ed Edition Prakash Mondal Full ChapterDocument67 pagesLanguage Biology and Cognition A Critical Perspective 1St Ed Edition Prakash Mondal Full Chaptererin.soto657100% (13)
- American On Course Scope and SequenceDocument2 pagesAmerican On Course Scope and SequenceIgnacio50% (2)
- TA10-Unit 9Document65 pagesTA10-Unit 9Phan PhanNo ratings yet
- Schmieger Macedonian Language Greece PDFDocument32 pagesSchmieger Macedonian Language Greece PDFAlexandra Ioannidou-RallisNo ratings yet
- Regodo, Jerene (DLP English 2)Document4 pagesRegodo, Jerene (DLP English 2)Jerene RegodoNo ratings yet
- Upper Secondary Academy V Maps GSE 48 60 Relationships and SocialisingDocument1 pageUpper Secondary Academy V Maps GSE 48 60 Relationships and Socialisingkarely0226No ratings yet
- Five ELT Approaches OutlineDocument8 pagesFive ELT Approaches OutlineRaza ShahNo ratings yet
- Commonly Confused Words Week One-1Document6 pagesCommonly Confused Words Week One-1Zenobia AdonisNo ratings yet
- Suhaerin 03 11 2021Document25 pagesSuhaerin 03 11 2021SUHAERINNo ratings yet
- Samira CAPES Lesson Plan Waste Not Want NotDocument33 pagesSamira CAPES Lesson Plan Waste Not Want NotLarbi NadiaNo ratings yet
- Teaching Pronunciation - Pair Up WorkDocument7 pagesTeaching Pronunciation - Pair Up WorkJuan ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - Give Travel UpdatesDocument10 pagesLesson 4 - Give Travel Updatesalinaanton1980_73345No ratings yet
- ENGLISH PAPER2 28 JanDocument9 pagesENGLISH PAPER2 28 JanShreya DeyNo ratings yet
- Civil Service Reviewer PDFDocument65 pagesCivil Service Reviewer PDFTrixia Mae Batiancila100% (1)
- Korean VocabularyDocument106 pagesKorean VocabularyJu DNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect Continuous TenseDocument2 pagesPresent Perfect Continuous TenseABDUL GAFOOR MOHAMED ASFAKNo ratings yet
- Week 3 - The Danger of A Single StoryDocument15 pagesWeek 3 - The Danger of A Single StoryHiruni FernandoNo ratings yet
- Speaking Ae2Document77 pagesSpeaking Ae2Triet TruongNo ratings yet
- Development, Underdevelopment and Poverty: A Linguistic Study of Joseph Edoki'sDocument25 pagesDevelopment, Underdevelopment and Poverty: A Linguistic Study of Joseph Edoki'sMichael PreciousNo ratings yet
- Complete First For Schools - Test Unit Test 1 (PLUS)Document2 pagesComplete First For Schools - Test Unit Test 1 (PLUS)Mihai 1TAP50% (2)
- Assignment Eng 219Document8 pagesAssignment Eng 219Võ Hoàng Bảo NgọcNo ratings yet
- C1 C2 AdjectivesDocument7 pagesC1 C2 AdjectivesGvantsa mandzulashviliNo ratings yet
- The Writing Process (Revising Strategies) - (Literacy Strategy Guide)Document8 pagesThe Writing Process (Revising Strategies) - (Literacy Strategy Guide)Princejoy ManzanoNo ratings yet
- Unit 11 - Simple Past Written WorkDocument2 pagesUnit 11 - Simple Past Written WorkBLACUTT BALDIVIESO JULY ANDREANo ratings yet
- 'FUNCTIONS EXPONENTS AND CONTEXTS' ContigoDocument2 pages'FUNCTIONS EXPONENTS AND CONTEXTS' Contigobraian maxNo ratings yet
- Ef4e Beg Vocab 6b PCMDocument1 pageEf4e Beg Vocab 6b PCMmacarenasabao1994No ratings yet