Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chemistry Mid Term Terminology Yr10
Chemistry Mid Term Terminology Yr10
Uploaded by
Chloe WOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chemistry Mid Term Terminology Yr10
Chemistry Mid Term Terminology Yr10
Uploaded by
Chloe WCopyright:
Available Formats
Chemistry Revision Sheet Science Extension Year 10 2023
KEY CONCEPTS Understand Have done
concept practise
questions
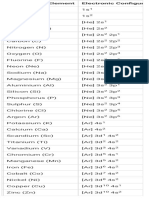
Atomic structure
Electron configuration, valence electrons and the
periodic table
Formation of ions and the periodic table
Ionic bonding -transfer of electrons
Writing chemical formulas for simple ionic substances
Writing and naming ionic substances with polyatomic
ions
Formation of covalent bonds
Writing and naming for covalent molecules and ions
Writing and balancing chemical equations – context
acid-base reactions
- Further practise other equations
Precipitation reactions, solubility
Mole concept and ratio
`
Knowledge Review Pearson Science 10 (pp 189 – 192)
Atom Module 5.1 Q 2 – 8, 10
Structure: electrons, neutrons, protons Introductory Chemistry (pp 1 – 5)
Atomic number, mass number and isotopes Q 1.1, 1.2 and Set 1
Elements
Pearson Activity Book
Revision: Symbols of common elements 5.1 (pp 69 – 70)
Arranging the elements Pearson Science 10 (pp 196 – 197)
The Periodic Table – periods and groups Pearson Science 10 p 206 – ‘Similar but different’
(Group 1 -14: Chemistry is optional)
Teacher Demo: Activity of sodium metal (Group
1) in water.
Electrons and the Periodic Table Pearson Science 10; p 216 only (Role of electrons &
Electron shells)
Role of electrons – valence electrons take part in
chemical reactions
Electron configuration exercises - Write electron Periodic table template for electron configuration for Gp 1,
configuration for first 20 elements 2, 13 to 18)
Identify the pattern of valence electrons in the Introductory Chemistry (pp 6 – 11)
periodic table for Gp 1,2, 13 to 18, ie Gp 1 has Q 2.1 - 2.6
one electron, Gp 2 has 2 electrons
Revision & Consolidation Pearson Science 10 (pp 223 – 226)
Understanding Q 4 – 8
Applying Q 9 – 11
Thinking scientifically Q 1 – 3
Exam-style Q 1 – 3
Formation of ions On top of periodic table write the valencies when valence
Positive and negative ions, show students electrons are removed.
pattern on periodic table for removal and gain of
electrons- Gp 1,2: 13-18 Valency table – handed out to students.
Valency Table (monoatomic & polyatomic ions)
Symbols & names of simple monoatomic ions
(Note: Names and symbols MUST be
memorised as Valency
Table will NOT be provided in the end-of-topic
test).
Formation of ionic bonds Introductory Chemistry pp 14 – 15
Transfer of electrons, balancing of positive and Formation of ionic bonds
negative charges
Set 3: Q 1 – 5 (p 18)
Chemical formula -ionic bonds Set 4: Q 1, 4 (p 19)
Naming & Writing Chemical Formula of ionic
compounds consisting of monoatomic ions.
Identification of common cations: Science Aspects 4
Laboratory: Identification of metal ions using Focus 4.1 (p146)
Flame Tests Pearson Science 10
or Practical Investigation
Laboratory: Firework colours
Ionic compounds (cont.) Introductory Chemistry pp 24 - 26
Naming & Writing Chemical Formula of ionic Q 4.7 – 4.9
compounds consisting of polyatomic ions. Set 3: Q 5
Set 6: Q 1 – 5 (p 28)
Covalent compounds Naming & Writing Chemical Formula of covalent
What is a molecule and how are they formed? compounds
Sharing of electrons Science Aspects 4 p 147 – 149 (theory only)
Writing and naming of covalent molecular Introductory Chemistry pp 20 – 21
compounds Q 4.1 – 4.3
Q 1, 2 (p 27)
Introduction to Chemistry Calculations pp 19 – 20
Exercises 19 – 21
Science Aspects 4 Homework Book (p 90)
Q1-2
Revision Ionic and Covalent Naming Introductory Chemistry pp 27 – 28
Chemical formula writing and naming for both ionic and Sets 5, 6
covalent compounds.
CHEMICAL SCIENCE VOCABULARY LIST - YEAR
10
Words Meaning
Ions An electrically charged atom or group of atoms formed by the loss
or gain of one or more electrons
An acid is a molecule or ion capable of either donating a proton or
forming a covalent bond with an electronic pair
Acid
Compounds that form hydrogen ions when dissolved in water
(Arrhenius)
A base is any substance that in water solution is
slippery to the touch, tastes bitter, changes the colour
Base
of indicators ( e.g., turns red litmus paper blue), reacts
with acids to form salts, and promotes certain chemical
reactions (base catalysis).
compounds that form hydroxide ions when dissolved in water
(Arrhenius)
Process in which one or more substances, the reactants, are
converted to one or more different substances, the product.
Chemical reaction
A chemical equation is the symbolic representation of a chemical
Chemical equation A written representation, using numbers and symbols, of the
process that occurs during a chemical reaction.
Reactants are the starting materials in a chemical reaction. They
undergo a chemical change in which chemical bonds are broken
Reactants and new ones are formed to make products
Substances that start a chemical reaction and are used up in the
process.
Products New substances that are formed from a chemical reaction.
Neutralisation A chemical reaction between an acid and a base
Precipitation An insoluble substance that emerges from a liquid solution mixture
Reaction rate A measure of how fast a chemical reaction happens over time
Concentration Amount of dissolved solute in a solution at a temperature
Catalyst A substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction but is
not consumed in the process.
Temperature A measure of average kinetic energy of particles in a matter.
You might also like
- Chapter 1-Introduction To Organic Chemistry - ODLDocument48 pagesChapter 1-Introduction To Organic Chemistry - ODLNURUL BALQIS DZULKIFLINo ratings yet
- Chemistry Schemes of Work Grade 11Document6 pagesChemistry Schemes of Work Grade 11Rodgers Principle100% (2)
- CAGI Compresed Air HandbookDocument757 pagesCAGI Compresed Air Handbookhidrastar123100% (8)
- Electrochemical Rehabilitation Methods For Reinforced Concrete StructuresDocument61 pagesElectrochemical Rehabilitation Methods For Reinforced Concrete StructuresCarlos RomeroNo ratings yet
- Che101 Chap 8Document68 pagesChe101 Chap 8Ruhi AfsaraNo ratings yet
- (2103) Lecture Notes Chemical Bonding eDocument69 pages(2103) Lecture Notes Chemical Bonding erennyabhaskaran_4560100% (1)
- B.Sc. Chemistry (With Physics/ Life Sciences)Document31 pagesB.Sc. Chemistry (With Physics/ Life Sciences)Gaming SisbroNo ratings yet
- 10 Chemistry Student OutlineDocument3 pages10 Chemistry Student OutlinejasNo ratings yet
- Check List For Inorganic ChemistryDocument1 pageCheck List For Inorganic ChemistrySRK laptopNo ratings yet
- Chemistry IGCSE SpecificationDocument14 pagesChemistry IGCSE SpecificationStudent Marc Sanchis VilaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Year 8 Scheme 2012Document6 pagesChemistry Year 8 Scheme 2012Maoga2013No ratings yet
- CS CHM1203Document5 pagesCS CHM1203Ariful IslamNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Year10 EoS1 LO BookletDocument62 pagesChemistry Year10 EoS1 LO Booklet29x4rk8pgfNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Engineering ChemistryDocument64 pagesIntroduction To Engineering ChemistryMegha VermaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Paper SyllabusDocument6 pagesChemistry Paper SyllabusAAKASH FACTSNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Check List To Score ADocument11 pagesChemistry - Check List To Score AMC KsyNo ratings yet
- 11 Chem Syllabus Term1Document3 pages11 Chem Syllabus Term1gNo ratings yet
- Chemistry WorksheetDocument4 pagesChemistry WorksheetLIYA ASKARNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument14 pagesChemistryANUSHKA SUBHASH HANDENo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument14 pagesChemistryANUSHKA SUBHASH HANDENo ratings yet
- Content: Name of The Books: NCERT Name of The Publisher: (Term-1)Document3 pagesContent: Name of The Books: NCERT Name of The Publisher: (Term-1)AbabeeNo ratings yet
- Chemical Compund NotesDocument16 pagesChemical Compund NotesAlbert Benjamin LeeNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument14 pagesChemistryAnupam DixitNo ratings yet
- Summarised Yearly Teaching Plan F4Document14 pagesSummarised Yearly Teaching Plan F4FatimahHishamuddinNo ratings yet
- Analysis Past Year Chemistry SPM Question (2003-2017)Document7 pagesAnalysis Past Year Chemistry SPM Question (2003-2017)Ting TCNo ratings yet
- Class 11 ChemistryDocument21 pagesClass 11 ChemistrypravinmoharilNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Chem Eqns Tables ChartsDocument9 pagesClass 11 Chem Eqns Tables ChartstisaNo ratings yet
- B.Sc. (Hons.) Science / Life Sciences / Home Science: (A) EnglishDocument15 pagesB.Sc. (Hons.) Science / Life Sciences / Home Science: (A) Englishshadab ansariNo ratings yet
- Notes From The Chemistry Director 2023-2024Document5 pagesNotes From The Chemistry Director 2023-2024gaminginsane372No ratings yet
- Unit I, Module 3, Tutorial 1Document1 pageUnit I, Module 3, Tutorial 1Jays WorldNo ratings yet
- Subject: Chemistry Code: 34 Class: Second PuDocument8 pagesSubject: Chemistry Code: 34 Class: Second PuDarshan GowdaNo ratings yet
- 1a Syllabus Periodic Table EquationsDocument1 page1a Syllabus Periodic Table EquationsKarina LeungNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Inorganic Chemistry For Competitive Exams Ananya Ganguly Full ChapterDocument51 pagesFundamentals of Inorganic Chemistry For Competitive Exams Ananya Ganguly Full Chapterdavid.brown418100% (15)
- B.SC - Chemistry Syllabus CompleteDocument15 pagesB.SC - Chemistry Syllabus CompleteAnurag YadavNo ratings yet
- Self Study Revision Plan For JEE Mains Jan 2023Document7 pagesSelf Study Revision Plan For JEE Mains Jan 2023Yakshit JunejaNo ratings yet
- ACADEMIC YEAR 2020-2021 70% Content Intermediate 1 Year Chemistry SyllabusDocument2 pagesACADEMIC YEAR 2020-2021 70% Content Intermediate 1 Year Chemistry SyllabusSyed abdul raqeebNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class 9 Chemistry Ch1 NotesDocument6 pagesICSE Class 9 Chemistry Ch1 NotesNetriderTheThechieNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2021-06-23 at 1.22.22 AMDocument1 pageScreenshot 2021-06-23 at 1.22.22 AMJustin LingNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Course 1P - PreparationDocument13 pagesChemistry Course 1P - PreparationAlfieNo ratings yet
- Pakistan International School (English Section) : Scheme of Studies (1 Term) Session 2022-2023Document2 pagesPakistan International School (English Section) : Scheme of Studies (1 Term) Session 2022-2023Nazim Ehsan MalikNo ratings yet
- Shestakov 2018Document3 pagesShestakov 2018Nyau NyauNo ratings yet
- Mastering Organic Chemistry and INORGANICDocument11 pagesMastering Organic Chemistry and INORGANICsatyag24No ratings yet
- BSC Bed 2 Year Chemistry SyllabusDocument6 pagesBSC Bed 2 Year Chemistry Syllabuslelico724No ratings yet
- Literature For Canvas Tests ChemistryDocument24 pagesLiterature For Canvas Tests Chemistryrio kurniaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 5070 ChecklistDocument5 pagesChemistry 5070 ChecklistObby-GiftMwambaKachecheNo ratings yet
- Paper-Iv (Iv Sem Final Copy)Document5 pagesPaper-Iv (Iv Sem Final Copy)RAKESH KUMAR'SNo ratings yet
- KLB Chem FORM 2Document170 pagesKLB Chem FORM 2Job Makori OmbuiNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class 9 Chemistry Ch1 NotesDocument6 pagesICSE Class 9 Chemistry Ch1 NotesNetriderTheThechieNo ratings yet
- Chem516-17 (SingYin)Document5 pagesChem516-17 (SingYin)endickhkNo ratings yet
- Chemistry BSC 1 Samester PDFDocument4 pagesChemistry BSC 1 Samester PDFMax TNo ratings yet
- 2018SU B.SC Chemistry SyllabusDocument22 pages2018SU B.SC Chemistry Syllabussachin81185No ratings yet
- BS ChemistryDocument73 pagesBS Chemistryawais gujjarNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class 10 Chemistry Syllabus 2023 24Document7 pagesICSE Class 10 Chemistry Syllabus 2023 24bindyasri16No ratings yet
- Chapterwise Topicwise Solved Papers Chem ArihantDocument960 pagesChapterwise Topicwise Solved Papers Chem Arihantstuti mishraNo ratings yet
- Edexcel IGCSE ChemistryDocument11 pagesEdexcel IGCSE ChemistrySamuel Muabia Plānet0% (1)
- Chemistry Class XIDocument5 pagesChemistry Class XILuciefer 0035No ratings yet
- Handout - 2021 - CHEM F111Document2 pagesHandout - 2021 - CHEM F111vishnuNo ratings yet
- XI Yearly Examination NoticeDocument3 pagesXI Yearly Examination Noticesubikshansubikshan28No ratings yet
- Syllabus Chemistry Goa University CBCSDocument95 pagesSyllabus Chemistry Goa University CBCSVishnu ChariNo ratings yet
- Lec 4 23-10-2022Document113 pagesLec 4 23-10-2022mohamed1hassan_2No ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Biology The Dynamic Science 4th EditionDocument36 pagesSolution Manual For Biology The Dynamic Science 4th Editioncabecadrawable.sxfi2c100% (58)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Periodic Table with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Periodic Table with AnswersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- October 2023 MsDocument38 pagesOctober 2023 MsNourNo ratings yet
- KR10150 Rev02Document2 pagesKR10150 Rev02KOUAME EDYMAIN FRANCISNo ratings yet
- Cy1101 Chemistry I 3 0 0 100Document1 pageCy1101 Chemistry I 3 0 0 100Rajeshkannan VasinathanNo ratings yet
- BE210S97W7R01Document33 pagesBE210S97W7R01Ahmad HoteitNo ratings yet
- Basic Nomenclature AlkanesDocument12 pagesBasic Nomenclature AlkanesPsychoPak OfficialNo ratings yet
- 40 Austrian Chemistry Olympiad National CompetitionDocument9 pages40 Austrian Chemistry Olympiad National CompetitionMuhammad TanveerNo ratings yet
- Iron Gall Ink Bibliography - Subject Breakdown - 2017Document14 pagesIron Gall Ink Bibliography - Subject Breakdown - 2017mm857No ratings yet
- 31-3-2 ScienceDocument15 pages31-3-2 Sciencepriyanshusingh7797No ratings yet
- Forensics Lab 8.2 - Revealing Latent Fingerprints Using Iodine Fuming - Make - DIY Projects and Ideas For MakersDocument6 pagesForensics Lab 8.2 - Revealing Latent Fingerprints Using Iodine Fuming - Make - DIY Projects and Ideas For MakersPortia HermosaNo ratings yet
- HV-EHV Cables Synthetic Isolation DegassingDocument16 pagesHV-EHV Cables Synthetic Isolation DegassingAmina Malek AyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document25 pagesChapter 7andrew.gregory978No ratings yet
- Chapter9 - WSDOT - BEARINGS & EXPANSION JOINTSDocument40 pagesChapter9 - WSDOT - BEARINGS & EXPANSION JOINTSmabuhamdNo ratings yet
- A 624 PDFDocument5 pagesA 624 PDFTri-Sure More Than ClosuresNo ratings yet
- What Is Physical Chemistry?Document6 pagesWhat Is Physical Chemistry?kiny81No ratings yet
- 0620 w23 QP 22 MergedDocument30 pages0620 w23 QP 22 MergedMaram MohanNo ratings yet
- Proximate, Phytochemical and Antioxidant Activity of Amla Powder and Amla CandyDocument5 pagesProximate, Phytochemical and Antioxidant Activity of Amla Powder and Amla CandySajib RezaNo ratings yet
- Roles of Double Salt FormationDocument8 pagesRoles of Double Salt FormationAmer AlkalaifhNo ratings yet
- Metal Structure and Bonding in MaterialsDocument95 pagesMetal Structure and Bonding in MaterialsTeptep GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Tesa Folder HafDocument5 pagesTesa Folder Hafgökhan tanrıseverNo ratings yet
- RodsealsDocument186 pagesRodsealsMarti caradagianNo ratings yet
- Arthrobacter AK19Document8 pagesArthrobacter AK19k200219 Muhammad Ferdeen BakhtNo ratings yet
- Techno Commercial Part IIDocument9 pagesTechno Commercial Part IImalaya tripathyNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates: Mubashra Gul LecturerDocument41 pagesCarbohydrates: Mubashra Gul LecturerNauman ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Operating Instructions Instrucciones de Operación: AC/Rechargeable Beard/Hair TrimmerDocument10 pagesOperating Instructions Instrucciones de Operación: AC/Rechargeable Beard/Hair TrimmerCJRCNo ratings yet
- Chem2521 W5 DistillationDocument4 pagesChem2521 W5 DistillationWiwit Zuriati UnoNo ratings yet
- Air-Source Hybrid Absorption-Compression Heat Pumps With Three-StageDocument16 pagesAir-Source Hybrid Absorption-Compression Heat Pumps With Three-StageDaniel DimaNo ratings yet
- MICROENCAPSULATION of PROPOLIS With Gum Arabic and MaltodextrinDocument17 pagesMICROENCAPSULATION of PROPOLIS With Gum Arabic and MaltodextrinDiah Kartika PratamiNo ratings yet
- Adv Funct Materials - 2021 - Collins - Scaffold Fabrication Technologies and Structure Function Properties in Bone TissueDocument23 pagesAdv Funct Materials - 2021 - Collins - Scaffold Fabrication Technologies and Structure Function Properties in Bone TissueIsworo RukmiNo ratings yet