Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Physics
Physics
Uploaded by
yebin0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views3 pagesThis document contains physics notes on various topics:
1. It defines mass and weight, and distinguishes between scalar and vector quantities. Weight is a force measured in Newtons, while mass is a measure of the amount of matter.
2. Forces are defined as vector quantities that have both magnitude and direction. Resultant force determines the direction and magnitude of motion as well as if a force is balanced or unbalanced.
3. Newton's laws of motion are summarized, relating force, mass and acceleration. Hooke's law relating the extension of springs to applied force is also introduced.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document contains physics notes on various topics:
1. It defines mass and weight, and distinguishes between scalar and vector quantities. Weight is a force measured in Newtons, while mass is a measure of the amount of matter.
2. Forces are defined as vector quantities that have both magnitude and direction. Resultant force determines the direction and magnitude of motion as well as if a force is balanced or unbalanced.
3. Newton's laws of motion are summarized, relating force, mass and acceleration. Hooke's law relating the extension of springs to applied force is also introduced.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views3 pagesPhysics
Physics
Uploaded by
yebinThis document contains physics notes on various topics:
1. It defines mass and weight, and distinguishes between scalar and vector quantities. Weight is a force measured in Newtons, while mass is a measure of the amount of matter.
2. Forces are defined as vector quantities that have both magnitude and direction. Resultant force determines the direction and magnitude of motion as well as if a force is balanced or unbalanced.
3. Newton's laws of motion are summarized, relating force, mass and acceleration. Hooke's law relating the extension of springs to applied force is also introduced.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
[0654] Physics Notes GRAD24
Mass and Weight 220920 TUES
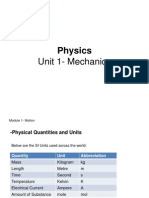
Mass- quantity of matter in an object // Is constant everywhere // Is measured in Kilogram or
Gram.
Weight- Measure of gravity on an object // Not constant everywhere // Is measured in Newtons
// Uses spring balance
Difference between a vector and a scalar quantity:
Scalar quantity- Magnitude only
Vector quantity- Has direction // Earth and Mass
Weight= Mass x gravitational pull
Gravitational pull= Weight / Mass
Mass= Weight / Gravitational pull
Forces 220921 WED
Forces + Effects of force
Vector quantity- Quantity with magnitude and directions.
Force is a Vector quantity.
Length of an arrow corresponds to the magnitude. Arrows pointing in different directions imply
different signs [positive or negative].
Resultant Force [Net Force]- A single force that describes all forces acting on a body.
[ex. Left force 50, Right Force 100; Resultant Force is 50 forces to the right]
Resultant Force determines:
- Direction of motion
- Magnitude of the final force
- Balanced force: Resultant force is 0 [No Motion]
- Unbalanced force: There is a net force [object moves in the
direction of the Net Force]
Newton’s First Law of Motion:
- No force applied = Object stays in fixed position.
- Objects will remain at rest or move with a constant velocity
unless acted on by a resultant force.
- [ex. Lima did some online research and found out that the
moon orbits the earth at a constant speed of 2000mph. She
says that this is not an example of Newton’s First Law of
Motion. Lima’s research is wrong because the velocity isn’t
constant; an object in a circular path keeps on changing the
direction so there is no way that the speed wouldn’t change.]
Newton’s Second Law of Motion:
- Force= Mass * Acceleration
Newton’s Law + Test Revision 220922 THURS
Newton’s First Law of Motion:
- Objects will remain at rest or move with a constant velocity
unless acted on by a resultant force.
- a=net force/mass
- Net force / Resultant force is responsible for acceleration.
Newton’s Second Law of Motion:
- The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the
resultant/net force.
- Acceleration is inversely proportional to the mass and directly
proportional to the force. The bigger the force, the bigger the
acceleration.
- A is directly proportional to F/M
Test Revision 220923 FRI
Gravitational field strength- Force acting on a unit mass in the field. [Gravitational field
strength= Force / Mass]
Hooke’s Law 220928 WED
Introduction to the Hooke’s Law and Moments:
- Force is directly proportional to extension. [F=kx; k=spring
constant]
- Extension of a spring is directly proportional to the applied
force as long as the elastic limit is not exceeded.
- The spring obeys Hooke’s Law as long as the elastic limit is not
exceeded.
- The letter k determines the spring constant and is the
measure of how stiff the spring is.
- Moment= Force*Perpendicular distance from the point of
support (pivot)= FD
- The principle of moments states that at equilibrium (balance),
the sum of clockwise moments about a pivot equals the sum
of anticlockwise moments about the same point.
Pressure 221010 MON
Pressure- Force per unit area.
Work 221020 THURS
Work done= Force * Distance (moved in the direction of the applied force.)
(ex. If a shelf is not moving, no work is being done.)
(ex2. A man is shoveling. He does 600J of work, therefore he loses 600J of energy.
The substance being shoveled gains the energy, but not the full 600J of energy
because some energy is wasted as a form of heat and sound.)
Formula & key information for work, force, and direction:
- W= FD
- F= W/D
- D= W/F
- Nm is also known as Joules (J).
- Work is done when a force makes something move.
- The greater the force, and the greater the distance moved, the
more work is done.
- When work is done energy is transferred from one form into
another.
- Delta E is another way to say Delta W.
Energy 221024 MON
Energy- Work in transport/reservoir for work. The ability of an object to do work. Energy is a
scalar quantity.
The standard unit for energy is Joule (J) or Newton-meter (Nm).
Work done= Energy transferred.
Forms of Energy/Types of Energy:
- There are two forms of energy. Kinetic energy and Potential
energy.
- For something to have kinetic energy, it has to be in motion.
- If an object is not moving, the object has potential energy.
(ex. If a battery is sitting on the floor not moving, then it has
potential energy. An object not moving doesn’t mean that
there is no energy!)
(ex. A spring has elastic potential energy)
Matter 221202 FRI
Melting- Solid -> Liquid
Evaporation- Liquid -> Gas
Freezing- Liquid -> Solid
Condensation- Gas -> Liquid
Boiling Point- At constant temperature (100C)
Latent Heat- Hidden Heat; Heat absorbed (evaporation) or released (condensation) during
change on state.
Latent Heat of Vaporization- Liquid to Gas
Latent Heat of Fusion- Gas to Liquid
Heat (Thermal Energy) can be either absorbed or released (lost) during the changes of state.
At 100C
If you blow hot water, the rate of evaporation speeds up.
Gas is the easiest to compress because they have the largest inter-molecular distance.
You might also like
- PipingDocument739 pagesPipingAnonymous ieWpd823Lg95% (40)
- Science 8 Reviewer (Physics) : A. Forces and MotionDocument5 pagesScience 8 Reviewer (Physics) : A. Forces and Motionp r i n c e s s i t a88% (8)
- Paramahamsa Tewari - Conceptual Error On The Fundamental Nature of Light-Phenomenon in Classical Electrodynamics, Led To The Complexities in Quantum PhysicsDocument15 pagesParamahamsa Tewari - Conceptual Error On The Fundamental Nature of Light-Phenomenon in Classical Electrodynamics, Led To The Complexities in Quantum PhysicsKluff5878No ratings yet
- 21 Golden Safety Rules. PortfolioDocument2 pages21 Golden Safety Rules. PortfolioPaul Bugeja100% (2)
- Work and EnegyDocument8 pagesWork and Enegysohan.gspatilNo ratings yet
- Work (Physics) : Etymology Units Work and Energy Constraint Forces Mathematical CalculationDocument14 pagesWork (Physics) : Etymology Units Work and Energy Constraint Forces Mathematical CalculationBenjamin KonjicijaNo ratings yet
- Work (Physics)Document15 pagesWork (Physics)Alfredo RomeroNo ratings yet
- Forces, Vectors, Work, Energy, PowerDocument43 pagesForces, Vectors, Work, Energy, Poweranwar9602020100% (1)
- Science Midterm ReviewerDocument4 pagesScience Midterm ReviewerRoseNo ratings yet
- Work and EnergyDocument28 pagesWork and Energymasuma.bvbvnird21No ratings yet
- Science NotesDocument4 pagesScience NotesKenneth Jacob Ong (Bowenss)No ratings yet
- 11 Work EnergyDocument2 pages11 Work Energytara tuition100% (1)
- Newtons LawsDocument46 pagesNewtons LawsNelita MalinaoNo ratings yet
- Force and Motion Before Newton: - GalileoDocument24 pagesForce and Motion Before Newton: - GalileotommyNo ratings yet
- Force, Motion & EnergyDocument10 pagesForce, Motion & EnergyShelin GaziNo ratings yet
- IB PhysicsDocument25 pagesIB Physicssamuthiram771198100% (1)
- Affiliated To Central Board of Secondary Education - New DelhiDocument4 pagesAffiliated To Central Board of Secondary Education - New Delhideetchu10No ratings yet
- Kinetic and Potential Energy/Conservation of Energy IntroDocument4 pagesKinetic and Potential Energy/Conservation of Energy IntroRenz MaguilaNo ratings yet
- DLR-Fizik Konu AnlatımıDocument18 pagesDLR-Fizik Konu Anlatımıugurhan96No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - 2Document25 pagesChapter 5 - 2Qassem MohaidatNo ratings yet
- Disha - Publication - AFCAT - GK - General Science PDFDocument53 pagesDisha - Publication - AFCAT - GK - General Science PDFRajeev RanjanNo ratings yet
- Physics Lesson ReviewsDocument9 pagesPhysics Lesson ReviewsРубабе ХалиловаNo ratings yet
- Forces and MotionDocument37 pagesForces and MotionRachel Navarro RicafrenteNo ratings yet
- Forces and Motion: Reference: Prentice Hall Physical Science: Concepts in ActionDocument37 pagesForces and Motion: Reference: Prentice Hall Physical Science: Concepts in ActionKeshawn SutherlandNo ratings yet
- Forces and MotionDocument37 pagesForces and MotionMhai AndersonNo ratings yet
- 4-1 - Work and EnergyDocument11 pages4-1 - Work and Energycarlos51952No ratings yet
- AP B Chapter 4 Newtons Laws PDFDocument19 pagesAP B Chapter 4 Newtons Laws PDFAbcNo ratings yet
- Gce o Level Physics MatterDocument8 pagesGce o Level Physics MatterBakhita Maryam100% (1)
- SCIENCE Reviewer 2nd MonthlyDocument2 pagesSCIENCE Reviewer 2nd MonthlyRaizza Mae NovelaNo ratings yet
- Physics ReviewerDocument4 pagesPhysics ReviewerROEB AIREE MUEGANo ratings yet
- Revieww QTR 1Document19 pagesRevieww QTR 1Jyrisa Laine MalimataNo ratings yet
- Forces and Motion PDFDocument36 pagesForces and Motion PDFJezreel BuenoNo ratings yet
- Newtons Laws GR 10Document31 pagesNewtons Laws GR 10Jonathan ThomasNo ratings yet
- LM5 - Newton's Laws of Motion and Applications - GPHYS1Document53 pagesLM5 - Newton's Laws of Motion and Applications - GPHYS1burner accNo ratings yet
- 9 Application of Forces & Transfer of Energy - 2023Document83 pages9 Application of Forces & Transfer of Energy - 2023Tarun Rana Rajdevar (Victoriasch)No ratings yet
- Module 3 PhysciDocument124 pagesModule 3 Physciburner accNo ratings yet
- Applied Physics Lecture 1Document61 pagesApplied Physics Lecture 1omerNo ratings yet
- IX Force and Laws of Motion 1Document9 pagesIX Force and Laws of Motion 1smi_santhoshNo ratings yet
- Laporan Praktikum TBKDocument19 pagesLaporan Praktikum TBKRizki FatmawatiNo ratings yet
- Newtons Law of MotionDocument44 pagesNewtons Law of MotionAgustin L. IdausosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 NotespdfDocument4 pagesChapter 6 NotespdfVincent JosephNo ratings yet
- Physics Notes Chapter 3-7Document16 pagesPhysics Notes Chapter 3-7Esther Chua100% (1)
- Forces: Free Body DiagramsDocument45 pagesForces: Free Body DiagramsAsad SamiNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer q4.Document3 pagesScience Reviewer q4.souichiisoeNo ratings yet
- ForceDocument11 pagesForceAnastasia LarasatiNo ratings yet
- Gce o Level Physics MatterDocument9 pagesGce o Level Physics MatterirmaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1-Different Types of ForcesDocument56 pagesLesson 1-Different Types of Forcesclyde domingoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Newton's Laws of Motion - OkDocument14 pagesChapter 4 Newton's Laws of Motion - Okzzz munaNo ratings yet
- Physics Unit 1 MechanicsDocument49 pagesPhysics Unit 1 Mechanicsamir hamza100% (1)
- Physics Tutorial: Andalas UniversityDocument26 pagesPhysics Tutorial: Andalas UniversityMiranda Febriani TanjungNo ratings yet
- 2.1 - Force and LawDocument45 pages2.1 - Force and LawsanthiyaperemelNo ratings yet
- Linear Mechanics: Motion in A LineDocument19 pagesLinear Mechanics: Motion in A LineDilla DefayanaNo ratings yet
- Calculated Moves: Physical Science Week 8 HandoutsDocument2 pagesCalculated Moves: Physical Science Week 8 HandoutsBenj Jamieson DuagNo ratings yet
- Acceleration Due To Gravity ForcesDocument28 pagesAcceleration Due To Gravity Forcesfelipee20No ratings yet
- Work and Energy: Work Done by A Constant ForceDocument22 pagesWork and Energy: Work Done by A Constant ForceLindokunhle MabuzaNo ratings yet
- DynamicsDocument11 pagesDynamicsBLESSIE ARCENIO0% (1)
- Kinetic Energy and WorkDocument15 pagesKinetic Energy and WorkMahesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Work and EnergyDocument5 pagesChapter 6 - Work and EnergyDatu Sarip Azeemkhan Ampatuan-BernanNo ratings yet
- Dynamics Newton'S Laws of Motion Intended Learning Outcomes (Ilo) 2. Field ForcesDocument5 pagesDynamics Newton'S Laws of Motion Intended Learning Outcomes (Ilo) 2. Field ForcesRALPH ANDREW ESPERONNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Work & EnergyDocument51 pagesChapter 2 - Work & EnergyiitrboyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2:forceDocument74 pagesChapter 2:forceTing CheongNo ratings yet
- Overcurrent Protection: of Transmission LineDocument19 pagesOvercurrent Protection: of Transmission LinePratham VaghelaNo ratings yet
- Question 984176Document10 pagesQuestion 984176Sudharsan AjayNo ratings yet
- Elechome QuestionsDocument22 pagesElechome QuestionsasifshahanaNo ratings yet
- To use a multimeter to (a) identify base of a multimeter (b) distinguish between non and pop type transistors (c) see the unidirectional flow of current in case of a diode and an LED (d) check whether a given electronic component (ex- diode, transistor, or IC) is in working orderDocument5 pagesTo use a multimeter to (a) identify base of a multimeter (b) distinguish between non and pop type transistors (c) see the unidirectional flow of current in case of a diode and an LED (d) check whether a given electronic component (ex- diode, transistor, or IC) is in working orderAurora Aurealis67% (3)
- SAL A0 0 - TechDocument11 pagesSAL A0 0 - TechRacu TudorNo ratings yet
- Sol Assign 1Document2 pagesSol Assign 1Jerome MagnoNo ratings yet
- Week 7 GeothermalDocument104 pagesWeek 7 GeothermalMikeNo ratings yet
- Impulse-And-Momentum Cutnell PPT Ch07Document26 pagesImpulse-And-Momentum Cutnell PPT Ch07REY ADRIAN MARTINNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document16 pagesChapter 7Pyae Sone KyawNo ratings yet
- DatasheetDocument2 pagesDatasheetStuxnetNo ratings yet
- Support STR & FDN Design Calculation For 66kV PT - R0 - SinghikDocument20 pagesSupport STR & FDN Design Calculation For 66kV PT - R0 - SinghikKRKA EngineersNo ratings yet
- Electricity Web Quest 5 11 17Document4 pagesElectricity Web Quest 5 11 17api-2625864460% (1)
- 2020 - 21 Session Full SyllabusDocument167 pages2020 - 21 Session Full Syllabuskec.abhishek463No ratings yet
- 10kV and 15kV MEGOHMMETERS: User ManualDocument72 pages10kV and 15kV MEGOHMMETERS: User ManualMartin NNo ratings yet
- Edid041521 (FTKC15-35PVM4)Document92 pagesEdid041521 (FTKC15-35PVM4)yoga pNo ratings yet
- Si Units: Nsci-6100 Physics For Engineers 1Document8 pagesSi Units: Nsci-6100 Physics For Engineers 1Yoo JungNo ratings yet
- Xtra Power Solar Products Off Grid 2022 11Document5 pagesXtra Power Solar Products Off Grid 2022 11Prinkatelo SarahgeNo ratings yet
- Electrical EquipmentDocument21 pagesElectrical EquipmentRajad ShakyaNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument5 pagesIntroductionjayantabhbasuNo ratings yet
- BX1S-KV-BT212M80 P40 P52 P52 LP52N BT212M81 BT212N40 BT212N50Document11 pagesBX1S-KV-BT212M80 P40 P52 P52 LP52N BT212M81 BT212N40 BT212N50Jomasando10No ratings yet
- 179 92 02 TM100Document2 pages179 92 02 TM100jiwani87No ratings yet
- Experiment No - 14Document8 pagesExperiment No - 14Konem SolutionsNo ratings yet
- Derivation of The Heat Equation in One Dimension: Homework 11/11/21 Irene Pascual-Heranz Bronchalo (100452087)Document3 pagesDerivation of The Heat Equation in One Dimension: Homework 11/11/21 Irene Pascual-Heranz Bronchalo (100452087)Irene Pascual-Heranz BronchaloNo ratings yet
- Jee Advanced 2 Paper 2Document13 pagesJee Advanced 2 Paper 2egoistic dumboNo ratings yet
- 09 Science Notes Ch11 WorkDocument8 pages09 Science Notes Ch11 WorkHarshJangidNo ratings yet
- Soneloid FailureDocument2 pagesSoneloid FailureIago SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Safety (IEC) Report ZK-D3180S ZK-D2180S ZK-D1065SDocument72 pagesSafety (IEC) Report ZK-D3180S ZK-D2180S ZK-D1065SOscar Danilo Erazo Pecillo100% (1)