Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mechatronics
Mechatronics
Uploaded by
Jeslet JoyOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mechatronics
Mechatronics
Uploaded by
Jeslet JoyCopyright:
Available Formats
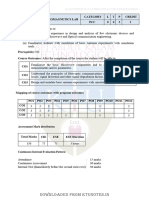
ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING
CATEGORY L T P CREDIT
ECT418 MECHATRONICS
PEC 2 1 0 3
Preamble: This course introduces students to the rapidly emerging, multi-disciplinary, and
exciting field of Mechatronics.
Prerequisite: Nil
Course Outcome: After the successful completion of the course the student will be able to
Understand the working principles of various sensors and actuators in Mechatronics
CO1
systems and be able to choose the suitable one for the real world application
CO2 Formulate and simulate models of mechatronics systems
CO3 Explain the implementation of PLC in mechatronics applications
CO4 Explain the standard fabrication techniques and principle of operation of MEMS devices
Design and Analysis of commonly encountered mechatronics systems for real time
CO5 applications
Mapping of course outcomes with program outcomes
PO1 PO2 PO3 PO4 PO5 PO6 PO7 PO8 PO9 PO10 PO11 PO12
CO1 3 3
CO2 3 3
CO3 3 3 2
CO4 3 3
CO5 3 3
Assessment Pattern
Bloom’s Continuous Assessment Tests End Semester
Category 1 2 Examination
Remember 10 10 20
Understand 30 30 60
Apply 10 10 20
Analyse
Evaluate
Create
Mark distribution
Total ESE
CIE ESE
Marks Duration
150 50 100 3 hours
Downloaded from Ktunotes.in
ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING
Continuous Internal Evaluation Pattern:
: 10 marks
Continuous Assessment Test (2 numbers)
: 25 marks
Assignment/Quiz/Course project
: 15 marks
End Semester Examination Pattern: There will be two parts; Part A and Part B. Part A contain
10 questions with 2 questions from each module, having 3 marks for each question. Students
should answer all questions. Part B contains 2 questions from each module of which student
should answer any one. Each question can have maximum 2 sub-divisions and carry 14 marks.
Course Level Assessment Questions
Course Outcome 1 (CO1):Understand the working principles of various sensors and actuators in
Mechatronics systems and be able to choose the suitable one for the real world application
1. Illustrate the working of a strain gauged load cell
2. Explain the working of any one non-contact temperature measurement system
3. Explain the principle of operation and suggest two applications of Hall effect sensor in
mechatronic systems.
4. With neat sketches explain the working of a double acting hydraulic actuator.
5. Design a hydraulic circuit to operate a winch fitted with a hydraulic motor. The
motor should be run clockwise, counter clockwise and stopped. Use a manually
operated valve.
6. Explain any two situations when pneumatic actuators are preferred over
hydraulic ones.
Course Outcome 2 (CO2): Formulate models of mechatronics systems
1. Derive the mathematical model of a general electrical system and draw its analogy with a
mechanical system.
2. Explain the working of a mechanical device using closed loop control system
with the help of a suitable example.
Course Outcome 3 (CO3): Explain the implementation of PLC in mechatronics applications
1. Explain ‘latching’ in PLC logic with an example.
2. Illustrate the significance of Internal Relays in PLC program
3. Consider a pneumatic system with single-solenoid controlled valves and
involving two cylinders A and B, with limit switches a–, a+, b–, b+ detecting
the limits of the piston rod movements. Design a ladder programme with the
requirement being when the start switch is triggered, the sequence A+, B+, A–,
10s time delay, B– occurs and stop at that point until the start switch is triggered
again.
Downloaded from Ktunotes.in
ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING
Course Outcome 4(CO4): Explain the standard fabrication techniques and principle of operation
of MEMS devices
1. Explain the steps involved in photolithography. State the chemicals used in each
of the stages along with the operating conditions.
2. Explain the criteria for choice of surface or bulk micromachining techniques in the design
of micro systems.
3. Explain with block diagram the steps in LIGA process. State two advantages of LIGA
process over other micro machining techniques.
Course Outcome 5 (CO5): Design and Analysis of commonly encountered mechatronics systems
for real time applications
1. With the help of a neat sketch explain the different mechatronics modules used
in automatic car park barrier system
2. Explain with a neat sketch the mechatronic implementation of a household weighing
machine
3. With a neat sketch, explain the physical system and working of a pick and place
robot.
SYLLABUS
MODULE I
Introduction to Mechatronics: Structure of Mechatronics system. Comparison between traditional
and mechatronics approach. Sensors - Characteristics -Temperature, flow, pressure sensors.
Displacement, position and proximity sensing by magnetic, optical, ultrasonic, inductive,
capacitive and eddy current methods. Encoders: incremental and absolute. Resolvers and
synchros. Piezoelectric sensors. Acoustic Emission sensors. vibration sensors.Force and tactile
sensors. Range finders: ultrasonic and light based range finders
MODULE II
Actuators: Hydraulic and Pneumatic actuators - Directional control valves,
pressure control valves, process control valves. Rotary actuators.
Development of simple hydraulic and pneumatic circuits using standard
Symbols. Electrical drives: DC, AC, brushless, servo and stepper motors. Harmonic
drive.Magnetostrictive actuators and piezoelectric actuators.
MODULE III
System modeling - Mathematical models and basic building blocks of general mechanical,
electrical, fluid and thermal systems. Typical elements of open and closed loop control systems.
Adaptive controllers for machine tools.
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC) –Basic structure, input/ output processing. Programming:
Timers, Internal Relays, Counters and Shift registers. Development of simple ladder programs for
specific purposes.
Downloaded from Ktunotes.in
ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING
MODULE IV
Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS): Fabrication: Deposition, Lithography,
Micromachining methods for MEMS -Surface and Bulk, Deep Reactive Ion Etching (DRIE) and
LIGA processes. Principle, fabrication and working of MEMS based pressure sensor,
accelerometer and gyroscope.
MODULE V
Mechatronics in Robotics- choice of Sensors and Actuators. Robotic vision system - Image
acquisition: Vidicon, charge coupled device (CCD) and charge injection device (CID) cameras.
Image processing techniques: histogram processing: sliding, stretching, equalization and
thresholding.
Case studies of Mechatronics systems: Automatic camera, bar code reader, simple weighing
machine, pick and place robot, automatic car park barrier system, automobileengine management
system.
Text Books:
1. Bolton W., Mechatronics: Electronic Control Systems in Mechanical and Electrical
Engineering, Person Education Limited, New Delhi, 2007
2. Ramachandran K. P., G. K. Vijayaraghavan, M. S. Balasundaram, Mechatronics:
IntegratedMechanical Electronic Systems, Wiley India Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi, 2008.
3. Saeed B. Niku, Introduction to Robotics: Analysis, Systems, Applications, Person
Education ,Inc., New Delhi, 2006.
4. Devdas Shetty, Richard A. Kolk, “Mechatronics System Design”, Thomson Learning
Publishing Company, Vikas publishing house, Second edition, 2001.
Reference Books:
1. David G. Aldatore, Michael B. Histand, Introduction to Mechatronics and Measurement
Systems, McGraw-Hill Inc., USA, 2003.
2. Gordon M. Mair, Industrial Robotics, Prentice Hall International, UK, 1998.
3. HMT, Mechatronics, Tata McGraw-Hill Publishing Company Ltd., New Delhi, 2004.
4. Vijay K. Varadan, K. J. Vinoy, S. Gopalakrishnan, Smart Material Systems and MEMS:
Design and Development Methodologies, John Wiley & Sons Ltd., England, 2006.
5. Bishop, Robert H. The Mechatronics Handbook-2 Volume Set. CRC press, 2002.
Downloaded from Ktunotes.in
ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING
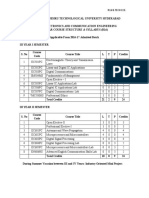
Course Plan Course Contents and Lecture Schedule
No Topic No. of
Lectures
Introduction to Mechatronics: Structure of Mechatronics system. 1
Comparison between traditional and mechatronics approach
Sensors - Characteristics -Temperature, flow, pressure sensors. 1
Displacement, position and proximity sensing by magnetic, 1
1 optical, ultrasonic, inductive, capacitive and eddy current methods
Encoders: incremental and absolute. Resolvers and synchros. 1
Piezoelectric sensors. Acoustic Emission sensors. vibration 1
sensors, Force and tactile sensors
Range finders: ultrasonic and light based range finders 1
Actuators: Hydraulic and Pneumatic actuators - Directional control 1
valves
pressure control valves, process control valves, 1
Rotary actuators. 1
2 Development of simple hydraulic and pneumatic circuits using 1
standard Symbols.
Electrical drives: DC, AC, and 1
brushless, servo 1
stepper motors. Harmonic drive. 1
System modeling - Mathematical models and basic building 2
blocks of general mechanical, electrical, fluid and thermal
systems.
Typical elements of open and closed loop control systems, 1
Adaptive controllers for machine tools
3
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC) –Basic structure, input/ 1
output processing.
Programming: Timers, Internal Relays, Counters and Shift 2
registers.
Development of simple ladder programs for specific purposes 1
Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS): Fabrication: 1
Deposition, Lithography
Micromachining methods for MEMS -Surface and Bulk, 2
4
Deep Reactive Ion Etching (DRIE) and LIGA processes. 1
Principle, fabrication and working of MEMS based pressure 3
sensor, accelerometer and gyroscope
Mechatronics in Robotics- choice of Sensors and Actuators. 1
5 Robotic vision system - Image acquisition: Vidicon, charge 2
coupled device (CCD) and charge injection device (CID) cameras.
Downloaded from Ktunotes.in
ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING
Image processing techniques: histogram processing: sliding, 2
stretching, equalization and thresholding.
Case studies of Mechatronics systems: Automatic camera, bar 2
code reader, simple weighing machine, picks and place robot,
Automatic car park barrier system, automobile engine 1
management system.
Model Question Paper
A P J ABDUL KALAM TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY
EIGHTH SEMESTER B TECH DEGREE EXAMINATION
COURSE: ECT418 MECHATRONICS
TIME: 3 HRS MAX. MARKS: 100
PART A
Answer All Questions
1 Differentiate between absolute and incremental encoders 3
2 List six examples of temperature sensors 3
3 Explain how cushioning is achieved in pneumatic actuators with a sketch. 3
4 Mention any two differences between finite position and infinite position 3
valves
5 List any 2 controlling factors in wet etching. 3
6 Sketch and label a MEMS based pressure sensor 3
7 What is latching? Draw a simple latched circuit 3
8 Write down the describing equations of basic mechanical building blocks 3
9 Illustrate the histogram processing technique for enhancing the image 3
contrast
10 Bring out any 3 difference between CCD and CID camera. 3
PART B
Answer one question from each module. Each question carries 14 marks.
Module I
11(A) Explain the working of an optical absolute encoder. How the number of 6
tracks and sectors of absolute encoder is related to the resolution of the
encoder?
11(B) Explain the structure of a mechatronics system. How is it different form 8
the traditional approach?
OR
12(A) Explain the sensor characteristics to be considered when choosing a 8
sensor for a mechatronics application
12(B) Compare the working of resolver and synchro 6
Downloaded from Ktunotes.in
ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING
Module II
13(A) Develop a pneumatic circuit with standard symbols, to operate two 8
cylinders in sequence. Explain its working.
13(B) Explain the constructional features and working of brushless DC motor 6
OR
14(A) Illustrate the working of Harmonic Drives with neat sketches 8
14(B) Design a hydraulic circuit to operate a winch fitted with a hydraulic 6
motor. The motor should be run clockwise, counter clockwise and
stopped. Use a manually operated valve.
Module III
15(A) Draw and explain the block diagram of a feedback control system. 4
15(B) Develop a PLC ladder program for the following sequence: Start a motor 10
with push switch, and then after a delay of 90s, start a pump. When the
motor is switched off, the pump will get switched off after a delay of 5s.
Mention the logic used for each rung in the program to substantiate your
answer.
OR
16(A) Explain how a PLC can be used to handle analog inputs? 4
16(B) Explain the model a fluid flow system with basic building blocks, clearly 10
mention all assumptions
Module IV
17(A) Explain the steps involved in photolithography. State the chemicals used 6
in each of the stages along with the operating conditions
17(B) Compare and contrast various micro manufacturing techniques 8
OR
18(A) Describe the various mechanical problems associated with surface 6
micromachining
18(B) Explain the LIGA process associated with MEMS fabrication 8
Module V
19(A) With the help of a neat sketch explain the different mechatronics modules 10
used in automatic car park barrier system
Downloaded from Ktunotes.in
ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING
19(B) List any fourapplications of robotic vision systems 4
OR
20(A) Explain the working of Barcode reader with reference to the coding 10
schemes. Mention the steps to process the digits in a barcode for a
particular product. Develop the steps in a program for reading the barcode.
20(B) List the steps in thresholding technique in image processing 4
Downloaded from Ktunotes.in
You might also like
- Components of Control PanelDocument17 pagesComponents of Control PanelHarish Padmanaban100% (1)
- A - Gray: C - Red B - GreenDocument4 pagesA - Gray: C - Red B - Greentigre1677100% (1)
- Jobber XLDocument4 pagesJobber XLDeva RajNo ratings yet
- ME407MECHATRONICSDocument2 pagesME407MECHATRONICScm.niveditha99No ratings yet
- CDM ME 407 Mechatronics - 2021Document15 pagesCDM ME 407 Mechatronics - 2021Tony K PaulNo ratings yet
- Course Code Course Name L-T-P-Credits Year of Introduction ME407 Mechatronics 3-0-0-3 2016 Prerequisite: Nil Course ObjectivesDocument2 pagesCourse Code Course Name L-T-P-Credits Year of Introduction ME407 Mechatronics 3-0-0-3 2016 Prerequisite: Nil Course ObjectivesVivek SivaramanNo ratings yet
- ME401 Design of Machine Elements - I.image - MarkedDocument2 pagesME401 Design of Machine Elements - I.image - MarkedShino BabuNo ratings yet
- Course Code Course Name L-T-P-Credits Year of Introduction ME407 Mechatronics 3-0-0-3 2016 Prerequisite: Nil Course ObjectivesDocument2 pagesCourse Code Course Name L-T-P-Credits Year of Introduction ME407 Mechatronics 3-0-0-3 2016 Prerequisite: Nil Course ObjectivesAnirudh Madhav KakkadNo ratings yet
- 1.unit 1 MechatronicsDocument63 pages1.unit 1 MechatronicsSolcastic SoulNo ratings yet
- BE Mechanical Syllabus FinalDocument2 pagesBE Mechanical Syllabus FinalsabnisnileshNo ratings yet
- 14MTGB0 Mechatronics: PreambleDocument6 pages14MTGB0 Mechatronics: PreambleManikandan SNo ratings yet
- Mechatronics Notes PDFDocument188 pagesMechatronics Notes PDFharish100% (1)
- KTU BTech MR 2019scheme 2019Scheme-MinorsDocument49 pagesKTU BTech MR 2019scheme 2019Scheme-Minorsregret0987654321098765No ratings yet
- M.Sc. I Electronics 2019-20Document12 pagesM.Sc. I Electronics 2019-20Hemant patilNo ratings yet
- SallyubusDocument61 pagesSallyubusravindra898233No ratings yet
- 7th Sem Syllabi - ECE (1) - 220718 - 184300Document11 pages7th Sem Syllabi - ECE (1) - 220718 - 184300vipul baggaNo ratings yet
- M.tech .Electronics071011Document49 pagesM.tech .Electronics071011John WilliamNo ratings yet
- ECE-2019-23-SYLLABUS III Year I SemesterDocument22 pagesECE-2019-23-SYLLABUS III Year I SemesterNani SaiNo ratings yet
- Mechatronics ME5007Document5 pagesMechatronics ME5007Kalum ChandraNo ratings yet
- SplitPDFFile 153 To 159Document7 pagesSplitPDFFile 153 To 159Sanjay DevNo ratings yet
- 1 HS05 Intellectual Property Rights 2 0 0 2.0 2 Ide Inter-Department Elective 4 0 0 4.0Document61 pages1 HS05 Intellectual Property Rights 2 0 0 2.0 2 Ide Inter-Department Elective 4 0 0 4.0Kushal BnNo ratings yet
- ME8791 Mechatronics 01 - by WWW - Learnengineering.inDocument125 pagesME8791 Mechatronics 01 - by WWW - Learnengineering.inLAKKANABOINA LAKSHMANARAONo ratings yet
- Syllabus - Electromagnetics LabDocument3 pagesSyllabus - Electromagnetics LabShakiraNo ratings yet
- Question Bank - 6thsem: Mission and Vision of The DepartmentDocument28 pagesQuestion Bank - 6thsem: Mission and Vision of The Department1232023No ratings yet
- Question Bank CIE-I and CO Wise Marks DistributionDocument4 pagesQuestion Bank CIE-I and CO Wise Marks DistributionbhargovkalitaaNo ratings yet
- Sensors and Actuators SyllabusDocument14 pagesSensors and Actuators SyllabusKeerthan R VarmaNo ratings yet
- ECT307 CS SyllabusDocument10 pagesECT307 CS Syllabusjinto0007No ratings yet
- GTU MechatronicsDocument2 pagesGTU MechatronicspmagrawalNo ratings yet
- 5th-6th Sem Detail Contents of Computer Engineering and IoTDocument80 pages5th-6th Sem Detail Contents of Computer Engineering and IoTLokender SinghNo ratings yet
- Mech SyllabusDocument2 pagesMech SyllabusprashanthattiNo ratings yet
- UG Syllabus 2019-23 (1) - 135-143Document9 pagesUG Syllabus 2019-23 (1) - 135-143Dark EnoughNo ratings yet
- Mtech ElectronicsDocument32 pagesMtech ElectronicsVikranth AmboreNo ratings yet
- Basic Elx Module-5 (2021-22)Document31 pagesBasic Elx Module-5 (2021-22)Mohammed MishaalNo ratings yet
- Professional Elective - IIdfdDocument13 pagesProfessional Elective - IIdfdsridharchandrasekarNo ratings yet
- Mechatronics - MODULE 1 - Yajnesha P ShettigarDocument35 pagesMechatronics - MODULE 1 - Yajnesha P ShettigarAYUSH CHANDRANo ratings yet
- Syllabus of OpjuDocument16 pagesSyllabus of OpjutarunNo ratings yet
- Syllabus MecveDocument44 pagesSyllabus MecveronpeterpNo ratings yet
- M.Tech. Programme in Mechatronics, IIT PatnaDocument13 pagesM.Tech. Programme in Mechatronics, IIT PatnaNPMYS23No ratings yet
- B.Tech. DEGREE Instrumentation and Control Engineering: Syllabus FOR Credit Based CurriculumDocument66 pagesB.Tech. DEGREE Instrumentation and Control Engineering: Syllabus FOR Credit Based CurriculumRajashree RaviNo ratings yet
- M.E. Mechatronics SyllabusDocument38 pagesM.E. Mechatronics SyllabusJoswa CaxtonNo ratings yet
- MechatronicsDocument2 pagesMechatronicsBharathi SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- 3rd Year SyllabusDocument7 pages3rd Year SyllabusMallikarjunNo ratings yet
- 4.68 M.E. InstrumentationDocument41 pages4.68 M.E. InstrumentationBhavesh DigeyNo ratings yet
- Ee404 Industrial Instrumentation and AutomationDocument3 pagesEe404 Industrial Instrumentation and AutomationArya RahulNo ratings yet
- Final Year BTech Electronics Syllabus 2022-23Document48 pagesFinal Year BTech Electronics Syllabus 2022-23SiddhantNo ratings yet
- E2 Sem2 CurriculumDocument21 pagesE2 Sem2 Curriculums180743 SUDHARANI INTINo ratings yet
- R18 B.tech Ii YearDocument29 pagesR18 B.tech Ii YearK SrinuNo ratings yet
- ECE SyllaubusDocument32 pagesECE SyllaubusAkhilesh UppulaNo ratings yet
- Unit1 - Introducation To MechatronicsDocument92 pagesUnit1 - Introducation To Mechatronicsguddu100% (3)
- M.E. Applied ElectronicsDocument39 pagesM.E. Applied ElectronicsVENKINo ratings yet
- Updated SyllabusDocument31 pagesUpdated SyllabusManish BisoiNo ratings yet
- Module Information Module Title Electric Drives and Control Module Code MMD2511Document4 pagesModule Information Module Title Electric Drives and Control Module Code MMD2511Ashley KaNo ratings yet
- Electronics Syllabus 1st SemesterDocument3 pagesElectronics Syllabus 1st SemesterLodhaNo ratings yet
- Course Syllabus Instrumentation Control Lab.Document3 pagesCourse Syllabus Instrumentation Control Lab.Monique OrugaNo ratings yet
- B.Tech 7th Sem ECE FinalDocument17 pagesB.Tech 7th Sem ECE FinalInvincible 2.0No ratings yet
- Instrumentation SyllabusDocument61 pagesInstrumentation SyllabusWilson dela FuenteNo ratings yet
- Ymca College 5 Sem Btech ElectricalDocument12 pagesYmca College 5 Sem Btech Electricalvinit kumarNo ratings yet
- Schaum's Outline of Electronic Devices and Circuits, Second EditionFrom EverandSchaum's Outline of Electronic Devices and Circuits, Second EditionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (6)
- Modern Anti-windup Synthesis: Control Augmentation for Actuator SaturationFrom EverandModern Anti-windup Synthesis: Control Augmentation for Actuator SaturationRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Introduction to Quantum Computing & Machine Learning Technologies: 1, #1From EverandIntroduction to Quantum Computing & Machine Learning Technologies: 1, #1No ratings yet
- New Sensors and Processing ChainFrom EverandNew Sensors and Processing ChainJean-Hugh ThomasNo ratings yet
- Electro Shear Brake BrochureDocument20 pagesElectro Shear Brake BrochureNatalio GarzonNo ratings yet
- Vumii Sii XR System SpecificationsDocument14 pagesVumii Sii XR System SpecificationsAHMED BOUMEDIANENo ratings yet
- De-je-Ar - Templet Letest PV2 - APDIYTID DecDocument121 pagesDe-je-Ar - Templet Letest PV2 - APDIYTID Decjohn jason bayudanNo ratings yet
- Optical Time Domain ReflectometerDocument4 pagesOptical Time Domain ReflectometerBinod Kumar BhagatNo ratings yet
- 888 97 387 G OrigDocument10 pages888 97 387 G Origrubberducky118811No ratings yet
- ABB Junction BoxDocument10 pagesABB Junction Boxjason chongNo ratings yet
- Manual IsDocument8 pagesManual IsJesús Torres YauriNo ratings yet
- Starline S9v2 InstallationDocument2 pagesStarline S9v2 InstallationHeyder HeyderovNo ratings yet
- Melfa: Industrial Robot Standard Specifications ManualDocument97 pagesMelfa: Industrial Robot Standard Specifications ManualMartin Minor EsparzaNo ratings yet
- Oventrop Kit Users GuideDocument6 pagesOventrop Kit Users Guidevatraxi1000No ratings yet
- InfraneoDocument134 pagesInfraneoJuan Carlos TolabaNo ratings yet
- Parveen: Technical ManualDocument16 pagesParveen: Technical ManualDEATH ASSASSIN GAMERNo ratings yet
- Symptom TroubleshootingDocument7 pagesSymptom TroubleshootingSebastian SirventNo ratings yet
- GT2500080 OH PresentationDocument33 pagesGT2500080 OH PresentationLaouini GhaithNo ratings yet
- Spare Parts Tool Ebook 2019Document239 pagesSpare Parts Tool Ebook 2019ravi_entertainfoNo ratings yet
- Overcurrent Protection of Transformer (NEC 450.3)Document10 pagesOvercurrent Protection of Transformer (NEC 450.3)Osama Shalaby100% (1)
- Din 14668 PDFDocument4 pagesDin 14668 PDFDorisjuarsa SmsNo ratings yet
- Manual Installation UnifiedValveAssembly enDocument2 pagesManual Installation UnifiedValveAssembly ennader0123No ratings yet
- 545 Znshine PDFDocument2 pages545 Znshine PDFDS INSTALAÇÕES ELÉTRICASNo ratings yet
- Catalog 120 Control Switches: CG, CH and CHR Type Up To 25 ADocument48 pagesCatalog 120 Control Switches: CG, CH and CHR Type Up To 25 AAceel FitchNo ratings yet
- CircuitsDocument41 pagesCircuitsriajulNo ratings yet
- Catalog Inverter Huawei SUN2000-100KTL-M1Document2 pagesCatalog Inverter Huawei SUN2000-100KTL-M1Nivet chanaiklangNo ratings yet
- Thermostat Thermo 091 - User'S Manual: Prog ProgDocument2 pagesThermostat Thermo 091 - User'S Manual: Prog ProgSnow White100% (1)
- Electro Procedure Test TestingDocument5 pagesElectro Procedure Test Testingjaime bernalesNo ratings yet
- PTW JHA Electrical Wiring Installation Work at Air Dryer RoomDocument4 pagesPTW JHA Electrical Wiring Installation Work at Air Dryer RoomPHH9834No ratings yet
- Vintage Lenses 20211124 153207Document6 pagesVintage Lenses 20211124 153207Jiang Hao (seiend)No ratings yet
- Technical SpecificationsDocument2 pagesTechnical SpecificationsHuanNo ratings yet