Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 viewsCh05 Customer Relationship Management
Ch05 Customer Relationship Management
Uploaded by
kkyran727Customer relationship management (CRM) is the process of managing detailed customer information to maximize customer loyalty. It involves identifying and differentiating customers, interacting to improve knowledge of customers, and customizing for each customer. Key aspects of CRM include building loyalty programs, measuring satisfaction, creating brand communities, and maximizing customer lifetime value through retention strategies. The goal is to reduce defection rates, increase customer longevity, and enhance how much each customer spends.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Creating Customer Value, Satisfaction, and LoyaltyDocument30 pagesCreating Customer Value, Satisfaction, and Loyaltyajit75% (4)
- Creating Customer Value, Satisfaction, and Loyalty: Source: Marketing Management, 13Document20 pagesCreating Customer Value, Satisfaction, and Loyalty: Source: Marketing Management, 13Rohit ChourasiaNo ratings yet
- Kotler Customer Satisfaction CRMDocument19 pagesKotler Customer Satisfaction CRMsumit7137No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Creating Customer Value - Satisfaction and Loyalty - W QDocument24 pagesChapter 4 - Creating Customer Value - Satisfaction and Loyalty - W QH. V.No ratings yet
- Creating Customer Value and Customer RelationshipDocument26 pagesCreating Customer Value and Customer RelationshipmeghkknaNo ratings yet
- Creating Customer Value, Satisfaction and Loyalty 2022Document37 pagesCreating Customer Value, Satisfaction and Loyalty 2022Tanmay MandaliyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document27 pagesChapter 4Pooja SuranaNo ratings yet
- Section 3Document9 pagesSection 3Jatin AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Creating Customer Value, Satisfaction, and LoyaltyDocument26 pagesCreating Customer Value, Satisfaction, and LoyaltyPratik RajNo ratings yet
- Creating Customer Value, Satisfaction, and Loyalty: Marketing Management, 13 EdDocument24 pagesCreating Customer Value, Satisfaction, and Loyalty: Marketing Management, 13 Edsumaira sarwarNo ratings yet
- Consumer Value PropositionDocument19 pagesConsumer Value PropositionKrishi PatelNo ratings yet
- Creating Customer Value, Satisfaction & LoyaltyDocument26 pagesCreating Customer Value, Satisfaction & Loyaltydrlov_20037767No ratings yet
- Creating Customer Value and LoyaltyDocument29 pagesCreating Customer Value and LoyaltybakshikamyNo ratings yet
- Cust Value, Satisfaction & LoyaltyDocument30 pagesCust Value, Satisfaction & Loyaltyprabhu dasNo ratings yet
- Customer Value, Satisfaction and LoyaltyDocument21 pagesCustomer Value, Satisfaction and LoyaltyJahnavi JallepalliNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document50 pagesLecture 3Mehak SinghNo ratings yet
- Creating Customer Value, Satisfaction & LoyaltyDocument21 pagesCreating Customer Value, Satisfaction & Loyaltydrlov_20037767No ratings yet
- Marketing 5Document23 pagesMarketing 5Bilal TasleemNo ratings yet
- CRM - Unit 2Document26 pagesCRM - Unit 2Toshini BarhateNo ratings yet
- Slides CRM-VVR (Master)Document28 pagesSlides CRM-VVR (Master)Ram KrishnaNo ratings yet
- CRM & Creating CustomerDocument17 pagesCRM & Creating CustomerPuneet SrivastavNo ratings yet
- Managing RelationshipsDocument18 pagesManaging RelationshipsDEEPALI SINGHNo ratings yet
- Building Customer RelationshipDocument21 pagesBuilding Customer RelationshipJoeNo ratings yet
- Capturing Customer Value and CRMDocument19 pagesCapturing Customer Value and CRMDanzo ShahNo ratings yet
- Creating Customer Value, Satisfaction, and LoyaltyDocument13 pagesCreating Customer Value, Satisfaction, and LoyaltyRhythdm MalhotraNo ratings yet
- Loyalty & Co Branding: Bank Card & Epayment 2005 26 October 2005Document22 pagesLoyalty & Co Branding: Bank Card & Epayment 2005 26 October 2005sdj32No ratings yet
- Marketing Management: MKT 402 Section O Credit Hours 3Document49 pagesMarketing Management: MKT 402 Section O Credit Hours 3RaffayNo ratings yet
- Ch#05Document36 pagesCh#05ahmed amiraliNo ratings yet
- Class 5 - Customer LifecycleDocument22 pagesClass 5 - Customer LifecycleAneesh SasidharanNo ratings yet
- Customer Relationship Management StrategiesDocument22 pagesCustomer Relationship Management Strategiesbhawna kaushikNo ratings yet
- Customer Life Time ValueDocument24 pagesCustomer Life Time ValuelogeshNo ratings yet
- Kotler 05Document16 pagesKotler 05Nafees Hasan ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 PPT - Kotler & Keller - Creating Longterm Customer Loyalty and RelationshipsDocument20 pagesChapter 3 PPT - Kotler & Keller - Creating Longterm Customer Loyalty and Relationshipsram kesavanNo ratings yet
- CRM IntroDocument48 pagesCRM Introdivyansha RajNo ratings yet
- Customer SatisfactionDocument21 pagesCustomer SatisfactionRavindra GoyalNo ratings yet
- CRM 1Document31 pagesCRM 1Swati TiwariNo ratings yet
- How To Win Over CustomerDocument14 pagesHow To Win Over Customershrenikjc7121No ratings yet
- Service PrestnDocument23 pagesService Prestnniraj3handeNo ratings yet
- Customer Service ManagementDocument10 pagesCustomer Service ManagementKeith Rose LictawaNo ratings yet
- Customer Relationship Management: Naveen Kumar J P Sathish Kumar KDocument19 pagesCustomer Relationship Management: Naveen Kumar J P Sathish Kumar Ksridevi gopalakrishnanNo ratings yet
- CRM Unit 3Document50 pagesCRM Unit 3divyansha RajNo ratings yet
- 03 Session Concepts 5&6Document9 pages03 Session Concepts 5&6SHREYASI SAHANo ratings yet
- In-SIDE Group: Presented byDocument109 pagesIn-SIDE Group: Presented bymeor shahifulNo ratings yet
- L5a Creating Customer Loyalties & SatisfactionDocument38 pagesL5a Creating Customer Loyalties & SatisfactionAshish kumar ThapaNo ratings yet
- Customer Relationship Management: Instructor: Diamond TaiDocument58 pagesCustomer Relationship Management: Instructor: Diamond TaiDiamond MC TaiNo ratings yet
- Markma Chapter 5 2023Document34 pagesMarkma Chapter 5 2023Gabriel Jose ReyesNo ratings yet
- CRM 1Document71 pagesCRM 1Anonymous GVWIlk3ZNo ratings yet
- Building Customer RelationshipDocument38 pagesBuilding Customer RelationshipDepankan DasNo ratings yet
- Loyalty ApproachDocument22 pagesLoyalty Approachlogan143No ratings yet
- W 11 Building Customer LoyaltyDocument21 pagesW 11 Building Customer LoyaltyKania HansdinataNo ratings yet
- The Cost of Service Quality Unit 4Document25 pagesThe Cost of Service Quality Unit 4feelnknowNo ratings yet
- Brand Loyalty and Customer Loyalty, Loyalty Segmentation, Concept of Relationship MarketingDocument23 pagesBrand Loyalty and Customer Loyalty, Loyalty Segmentation, Concept of Relationship Marketingsneha2129No ratings yet
- Creating Long-Term Loyalty RelationshipsDocument21 pagesCreating Long-Term Loyalty RelationshipsSachi JoshiNo ratings yet
- CRM - Part 1 - Conceptual FoundationDocument45 pagesCRM - Part 1 - Conceptual FoundationGia Hân PhạmNo ratings yet
- CH 4 Creating Customer Value & Customer RelationshipsDocument11 pagesCH 4 Creating Customer Value & Customer RelationshipsMuhammad Tahmid HossainNo ratings yet
- Understanding Customer Requirements-CrmDocument47 pagesUnderstanding Customer Requirements-CrmBenedict MuringakumweNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document19 pagesLecture 3farooquisharineNo ratings yet
- CRM - Part 1 - Conceptual FoundationDocument47 pagesCRM - Part 1 - Conceptual FoundationNhuY BuiThiNo ratings yet
- Customer Relationship Management: Lecturer: Đinh Thu Qu NHDocument164 pagesCustomer Relationship Management: Lecturer: Đinh Thu Qu NHLưu Thị Thu Hà100% (1)
- CUSTOMER CENTRICITY & GLOBALISATION: PROJECT MANAGEMENT: MANUFACTURING & IT SERVICESFrom EverandCUSTOMER CENTRICITY & GLOBALISATION: PROJECT MANAGEMENT: MANUFACTURING & IT SERVICESNo ratings yet
Ch05 Customer Relationship Management
Ch05 Customer Relationship Management
Uploaded by
kkyran7270 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views21 pagesCustomer relationship management (CRM) is the process of managing detailed customer information to maximize customer loyalty. It involves identifying and differentiating customers, interacting to improve knowledge of customers, and customizing for each customer. Key aspects of CRM include building loyalty programs, measuring satisfaction, creating brand communities, and maximizing customer lifetime value through retention strategies. The goal is to reduce defection rates, increase customer longevity, and enhance how much each customer spends.
Original Description:
Business Marketing Guide
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCustomer relationship management (CRM) is the process of managing detailed customer information to maximize customer loyalty. It involves identifying and differentiating customers, interacting to improve knowledge of customers, and customizing for each customer. Key aspects of CRM include building loyalty programs, measuring satisfaction, creating brand communities, and maximizing customer lifetime value through retention strategies. The goal is to reduce defection rates, increase customer longevity, and enhance how much each customer spends.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views21 pagesCh05 Customer Relationship Management
Ch05 Customer Relationship Management
Uploaded by
kkyran727Customer relationship management (CRM) is the process of managing detailed customer information to maximize customer loyalty. It involves identifying and differentiating customers, interacting to improve knowledge of customers, and customizing for each customer. Key aspects of CRM include building loyalty programs, measuring satisfaction, creating brand communities, and maximizing customer lifetime value through retention strategies. The goal is to reduce defection rates, increase customer longevity, and enhance how much each customer spends.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 21
CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP
MANAGEMENT
By
Prof. Krairit Boonyakiat
Building Customer Value,
Satisfaction and Loyalty
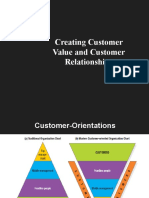
(a) Traditional Organization Chart (b) Modern Customer-Oriented
Organization Chart
Customer-Perceived-Value
(CPV)
• The difference between the
prospective customer’s
evaluation of all the benefits
and costs of an offering and
the perceived alternatives
Total customer benefit VS.
Total customer cost
Total customer benefit Total customer cost
• Product benefit • Monetary cost
• Services benefit • Time cost
• Personal benefit • Energy cost
• Image benefit • Psychological cost
Steps in a Customer Value Analysis
• Identify major attributes and benefits
that customers value
• Assess the qualitative importance of
different attributes and benefits
• Assess the company’s and competitor's
performances on the different
customer values against rated
importance
• Examine ratings of specific segments
• Monitor customer values over time
What is Loyalty?
• Loyalty is a deeply held
commitment to re-buy or re-
patronize a preferred product
or service in the future
despite situational influences
and marketing efforts having
the potential to cause
switching behavior.
Building loyalty
Interact closely with
customers
Develop loyalty
programs
Create institutional ties
Measuring Satisfaction
• Periodic surveys
• Customer loss rate
• Mystery shoppers
• Monitor competitive performance
What is Quality?
• Product and service quality
- Quality is the totality of features and
characteristics of a product or service
that bear on its ability to satisfy stated
or implied needs.
- Conformance quality vs. Performance
quality
- Impact of quality
Brand communities
• A specialized community of
consumers and employees whose
identification and activities
focus around the brand
Maximizing Customer
Lifetime Value
•Customer profitability
•Customer equity
•Lifetime value
What is Customer
Relationship Management?
• CRM is the process of
carefully managing detailed
information about individual
customers and all customer
touchpoints to maximize
customer loyalty.
Framework for CRM
• Identify prospects and
customers
• Differentiate customers by
needs and value to company
• Interact to improve
knowledge
• Customize for each customer
CRM Strategies
• Reduce the rate of defection
• Increase longevity
• Enhance “share of wallet”
• Terminate low-profit customers
• Focus more effort on high-profit customers
Value Creation Practices
• Social networking • Community engagement
- Welcoming, - Staking, mile-stoning,
empathizing, badging, documenting
governing • Brand use
• Impression management
- Grooming, customizing,
- Evangelizing,
commoditizing
justifying
Customer Retention
• Acquisition of customers can
cost 5 times more than retaining
current customers.
• The average customer loses 10%
of its customers each year.
• A 5% reduction to the customer
defection rate can increase
profits by 25% to 85%
• The customer profit rate
increases over the life of a
retained customer.
Steps for Creating Customer Evangelists
• Customer plus-delta
• Build the buzz
• Create community
• Make bite-size chunks
• Create a cause
Database Key Concepts
• Customer database
• Database marketing
• Mailing list
• Business database
• Data warehouse
• Data mining
Using the Database
• To identify prospects
• To target offers
• To deepen loyalty
• To reactivate customers
• To avoid mistakes
Don’t Build a Database When
• The product is a once-in-a-lifetime purchase
• Customers do not show loyalty
• The unit sale is very small
• The cost of gathering information is too high
Perils of CRM
• Implementing CRM before creating a
customer strategy
• Rolling our CRM before changing the
organization to match
• Assuming more CRM technology is better
• Stalking, not wooing, customers
You might also like
- Creating Customer Value, Satisfaction, and LoyaltyDocument30 pagesCreating Customer Value, Satisfaction, and Loyaltyajit75% (4)
- Creating Customer Value, Satisfaction, and Loyalty: Source: Marketing Management, 13Document20 pagesCreating Customer Value, Satisfaction, and Loyalty: Source: Marketing Management, 13Rohit ChourasiaNo ratings yet
- Kotler Customer Satisfaction CRMDocument19 pagesKotler Customer Satisfaction CRMsumit7137No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Creating Customer Value - Satisfaction and Loyalty - W QDocument24 pagesChapter 4 - Creating Customer Value - Satisfaction and Loyalty - W QH. V.No ratings yet
- Creating Customer Value and Customer RelationshipDocument26 pagesCreating Customer Value and Customer RelationshipmeghkknaNo ratings yet
- Creating Customer Value, Satisfaction and Loyalty 2022Document37 pagesCreating Customer Value, Satisfaction and Loyalty 2022Tanmay MandaliyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document27 pagesChapter 4Pooja SuranaNo ratings yet
- Section 3Document9 pagesSection 3Jatin AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Creating Customer Value, Satisfaction, and LoyaltyDocument26 pagesCreating Customer Value, Satisfaction, and LoyaltyPratik RajNo ratings yet
- Creating Customer Value, Satisfaction, and Loyalty: Marketing Management, 13 EdDocument24 pagesCreating Customer Value, Satisfaction, and Loyalty: Marketing Management, 13 Edsumaira sarwarNo ratings yet
- Consumer Value PropositionDocument19 pagesConsumer Value PropositionKrishi PatelNo ratings yet
- Creating Customer Value, Satisfaction & LoyaltyDocument26 pagesCreating Customer Value, Satisfaction & Loyaltydrlov_20037767No ratings yet
- Creating Customer Value and LoyaltyDocument29 pagesCreating Customer Value and LoyaltybakshikamyNo ratings yet
- Cust Value, Satisfaction & LoyaltyDocument30 pagesCust Value, Satisfaction & Loyaltyprabhu dasNo ratings yet
- Customer Value, Satisfaction and LoyaltyDocument21 pagesCustomer Value, Satisfaction and LoyaltyJahnavi JallepalliNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document50 pagesLecture 3Mehak SinghNo ratings yet
- Creating Customer Value, Satisfaction & LoyaltyDocument21 pagesCreating Customer Value, Satisfaction & Loyaltydrlov_20037767No ratings yet
- Marketing 5Document23 pagesMarketing 5Bilal TasleemNo ratings yet
- CRM - Unit 2Document26 pagesCRM - Unit 2Toshini BarhateNo ratings yet
- Slides CRM-VVR (Master)Document28 pagesSlides CRM-VVR (Master)Ram KrishnaNo ratings yet
- CRM & Creating CustomerDocument17 pagesCRM & Creating CustomerPuneet SrivastavNo ratings yet
- Managing RelationshipsDocument18 pagesManaging RelationshipsDEEPALI SINGHNo ratings yet
- Building Customer RelationshipDocument21 pagesBuilding Customer RelationshipJoeNo ratings yet
- Capturing Customer Value and CRMDocument19 pagesCapturing Customer Value and CRMDanzo ShahNo ratings yet
- Creating Customer Value, Satisfaction, and LoyaltyDocument13 pagesCreating Customer Value, Satisfaction, and LoyaltyRhythdm MalhotraNo ratings yet
- Loyalty & Co Branding: Bank Card & Epayment 2005 26 October 2005Document22 pagesLoyalty & Co Branding: Bank Card & Epayment 2005 26 October 2005sdj32No ratings yet
- Marketing Management: MKT 402 Section O Credit Hours 3Document49 pagesMarketing Management: MKT 402 Section O Credit Hours 3RaffayNo ratings yet
- Ch#05Document36 pagesCh#05ahmed amiraliNo ratings yet
- Class 5 - Customer LifecycleDocument22 pagesClass 5 - Customer LifecycleAneesh SasidharanNo ratings yet
- Customer Relationship Management StrategiesDocument22 pagesCustomer Relationship Management Strategiesbhawna kaushikNo ratings yet
- Customer Life Time ValueDocument24 pagesCustomer Life Time ValuelogeshNo ratings yet
- Kotler 05Document16 pagesKotler 05Nafees Hasan ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 PPT - Kotler & Keller - Creating Longterm Customer Loyalty and RelationshipsDocument20 pagesChapter 3 PPT - Kotler & Keller - Creating Longterm Customer Loyalty and Relationshipsram kesavanNo ratings yet
- CRM IntroDocument48 pagesCRM Introdivyansha RajNo ratings yet
- Customer SatisfactionDocument21 pagesCustomer SatisfactionRavindra GoyalNo ratings yet
- CRM 1Document31 pagesCRM 1Swati TiwariNo ratings yet
- How To Win Over CustomerDocument14 pagesHow To Win Over Customershrenikjc7121No ratings yet
- Service PrestnDocument23 pagesService Prestnniraj3handeNo ratings yet
- Customer Service ManagementDocument10 pagesCustomer Service ManagementKeith Rose LictawaNo ratings yet
- Customer Relationship Management: Naveen Kumar J P Sathish Kumar KDocument19 pagesCustomer Relationship Management: Naveen Kumar J P Sathish Kumar Ksridevi gopalakrishnanNo ratings yet
- CRM Unit 3Document50 pagesCRM Unit 3divyansha RajNo ratings yet
- 03 Session Concepts 5&6Document9 pages03 Session Concepts 5&6SHREYASI SAHANo ratings yet
- In-SIDE Group: Presented byDocument109 pagesIn-SIDE Group: Presented bymeor shahifulNo ratings yet
- L5a Creating Customer Loyalties & SatisfactionDocument38 pagesL5a Creating Customer Loyalties & SatisfactionAshish kumar ThapaNo ratings yet
- Customer Relationship Management: Instructor: Diamond TaiDocument58 pagesCustomer Relationship Management: Instructor: Diamond TaiDiamond MC TaiNo ratings yet
- Markma Chapter 5 2023Document34 pagesMarkma Chapter 5 2023Gabriel Jose ReyesNo ratings yet
- CRM 1Document71 pagesCRM 1Anonymous GVWIlk3ZNo ratings yet
- Building Customer RelationshipDocument38 pagesBuilding Customer RelationshipDepankan DasNo ratings yet
- Loyalty ApproachDocument22 pagesLoyalty Approachlogan143No ratings yet
- W 11 Building Customer LoyaltyDocument21 pagesW 11 Building Customer LoyaltyKania HansdinataNo ratings yet
- The Cost of Service Quality Unit 4Document25 pagesThe Cost of Service Quality Unit 4feelnknowNo ratings yet
- Brand Loyalty and Customer Loyalty, Loyalty Segmentation, Concept of Relationship MarketingDocument23 pagesBrand Loyalty and Customer Loyalty, Loyalty Segmentation, Concept of Relationship Marketingsneha2129No ratings yet
- Creating Long-Term Loyalty RelationshipsDocument21 pagesCreating Long-Term Loyalty RelationshipsSachi JoshiNo ratings yet
- CRM - Part 1 - Conceptual FoundationDocument45 pagesCRM - Part 1 - Conceptual FoundationGia Hân PhạmNo ratings yet
- CH 4 Creating Customer Value & Customer RelationshipsDocument11 pagesCH 4 Creating Customer Value & Customer RelationshipsMuhammad Tahmid HossainNo ratings yet
- Understanding Customer Requirements-CrmDocument47 pagesUnderstanding Customer Requirements-CrmBenedict MuringakumweNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document19 pagesLecture 3farooquisharineNo ratings yet
- CRM - Part 1 - Conceptual FoundationDocument47 pagesCRM - Part 1 - Conceptual FoundationNhuY BuiThiNo ratings yet
- Customer Relationship Management: Lecturer: Đinh Thu Qu NHDocument164 pagesCustomer Relationship Management: Lecturer: Đinh Thu Qu NHLưu Thị Thu Hà100% (1)
- CUSTOMER CENTRICITY & GLOBALISATION: PROJECT MANAGEMENT: MANUFACTURING & IT SERVICESFrom EverandCUSTOMER CENTRICITY & GLOBALISATION: PROJECT MANAGEMENT: MANUFACTURING & IT SERVICESNo ratings yet