Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views1506231856511463
1506231856511463
Uploaded by
chikenbiriyanieater1. The document provides instructions for an experiment to identify the different parts of a dicot seed embryo, including the radicle, plumule, cotyledons, and their functions.
2. Students are asked to soak dicot seeds such as peas, beans, or chickpeas overnight, remove the seed coat, and observe the embryo axis under a microscope to identify the radicle, plumule, and cotyledons, recording their observations.
3. The aim is to learn that the radicle is the embryonic root, plumule the shoot, and cotyledons store food for the embryo.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Avocado ProductionDocument82 pagesAvocado ProductionDr.Eswara Reddy Siddareddy100% (2)
- Plant HybridizationDocument23 pagesPlant HybridizationMyla Santiago33% (3)
- KOlomi 65 e 8 B Ve CEt JES1Document11 pagesKOlomi 65 e 8 B Ve CEt JES1mahender106yoNo ratings yet
- Agr122 Lab Report 4Document8 pagesAgr122 Lab Report 4Nur AthirahNo ratings yet
- Plant Dissection LabDocument9 pagesPlant Dissection Labmischa.noelleNo ratings yet
- Parts of The Seed: ObjectiveDocument4 pagesParts of The Seed: ObjectiveJoan Rayos PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Final SLM OA11, Quarter 3, Week2Document2 pagesFinal SLM OA11, Quarter 3, Week2l.a. lopezNo ratings yet
- The Structure of Dicot Seed:: Icse Class:9 Biology GerminationDocument3 pagesThe Structure of Dicot Seed:: Icse Class:9 Biology GerminationjaswanthNo ratings yet
- Science Book 1 Chapter 6Document49 pagesScience Book 1 Chapter 624 Jefferson Κoh JingNo ratings yet
- Ex 5-9 DevbiolabDocument27 pagesEx 5-9 DevbiolabPrezyNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument9 pagesAnatomymomina tayyabNo ratings yet
- GerminationDocument14 pagesGerminationPhoo Pyae Pyae KyawNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 14Document2 pagesExperiment No. 14mayankroy9431No ratings yet
- Reproduction Handout For Feb 19 23Document10 pagesReproduction Handout For Feb 19 23cykg4qkbtqNo ratings yet
- Daryl GuinayenDocument9 pagesDaryl GuinayenEmmanuel GallidoNo ratings yet
- DLP in Scince 4Document8 pagesDLP in Scince 4Rosemarie GaringNo ratings yet
- SeedsDocument6 pagesSeedsLawrence KasambaNo ratings yet
- PARTS OF A SEED - PartiDocument6 pagesPARTS OF A SEED - Partichristian capunongNo ratings yet
- GR 9 CH 6 and 7 Question and AnswerDocument18 pagesGR 9 CH 6 and 7 Question and AnswerlegendarychampionthorNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and MorphologyDocument8 pagesAnatomy and MorphologyminichelNo ratings yet
- Botafun SeedsDocument22 pagesBotafun SeedsstephaniealmendralNo ratings yet
- Seed Antatomy and Germination Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesSeed Antatomy and Germination Lesson Planapi-600991950No ratings yet
- Anatomy of SeedDocument15 pagesAnatomy of Seedujam5378No ratings yet
- Seeds: Strategic Intervention Materials in Science by Dr. AaaDocument9 pagesSeeds: Strategic Intervention Materials in Science by Dr. AaajoseNo ratings yet
- 6.3 Pollination and Fertilisation, 6.4 Development of Seeds and Fruits and 6.5 Importance of Seeds For SurvivalDocument56 pages6.3 Pollination and Fertilisation, 6.4 Development of Seeds and Fruits and 6.5 Importance of Seeds For Survivalwickedbiology101No ratings yet
- 3.6.1 Plant Reproduction H 3.6.3 - 3.6.5Document12 pages3.6.1 Plant Reproduction H 3.6.3 - 3.6.5George Oswald Junior CarringtonNo ratings yet
- Sexual ReproductionDocument41 pagesSexual Reproductionapi-406307933No ratings yet
- Class 12 Biology Chapter 2 Revision NotesDocument25 pagesClass 12 Biology Chapter 2 Revision NotesSrushti BhagitNo ratings yet
- G5 Plant Notes 1Document1 pageG5 Plant Notes 1Hi ByeNo ratings yet
- NoteDocument26 pagesNoteRajnish KumarNo ratings yet
- Flowering Plants Forms and Functions (BOT 102) - 2 2023-1Document23 pagesFlowering Plants Forms and Functions (BOT 102) - 2 2023-1faborodeharyomideNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of SeedsDocument3 pagesCharacteristics of SeedsMaria Fe GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Biology 6th ClassDocument4 pagesLesson Plan Biology 6th ClassManju kotturNo ratings yet
- Morfologi BijiDocument48 pagesMorfologi BijiSt. Lailatul RizqiNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 01 Nov 2022Document2 pagesAdobe Scan 01 Nov 2022Sauri ChaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Reproduction & Growth: 4.5 - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument25 pagesReproduction & Growth: 4.5 - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsSanthiya MadhavanNo ratings yet
- Aaua SIWES Report Compiled by OLATUNJI ODocument51 pagesAaua SIWES Report Compiled by OLATUNJI OAyodeleNo ratings yet
- Parts of SeedDocument1 pageParts of SeedScarlet Danielle CASASNo ratings yet
- Reproduction & Growth: 4.5 - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument25 pagesReproduction & Growth: 4.5 - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsZainurain Zainal AbidinNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument26 pagesSexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsMauz KhanNo ratings yet
- Botany Lab Module 8Document7 pagesBotany Lab Module 8annaNo ratings yet
- Seed Appendages and Dispersal MechanismsDocument25 pagesSeed Appendages and Dispersal MechanismsPremNo ratings yet
- The SeedDocument4 pagesThe SeedAnonymous fe9UIiNo ratings yet
- Biology AssignmentDocument15 pagesBiology AssignmentTAHRIM FATIMA0% (1)
- Sexual Reproduction in PlantsDocument13 pagesSexual Reproduction in Plantsshikaanara8686No ratings yet
- 1 - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument22 pages1 - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plantssakeenasiddik22No ratings yet
- Lab Rep 9Document8 pagesLab Rep 9Reign RosadaNo ratings yet
- Exercise 5Document4 pagesExercise 5Cindy jabilloNo ratings yet
- Seeds: DispersalDocument33 pagesSeeds: Dispersalyoussefsamir991No ratings yet
- Sevilla, Joyce Anne C - CASNS 1a - Laboratory Module 10Document4 pagesSevilla, Joyce Anne C - CASNS 1a - Laboratory Module 10Joyce SevillaNo ratings yet
- Seedstructure 130129220104 Phpapp01Document16 pagesSeedstructure 130129220104 Phpapp01Rehana PillayNo ratings yet
- Seed TechnologyDocument11 pagesSeed TechnologyristiyaadiwiratamaNo ratings yet
- 5ad43b99e4b0fa8be1f4fe4f 5e9a092ba8446510cc99fb5a 1615282586341Document28 pages5ad43b99e4b0fa8be1f4fe4f 5e9a092ba8446510cc99fb5a 1615282586341seaid zahidNo ratings yet
- Embryo Development: Seedling Development - A Typical Seed Consists ofDocument3 pagesEmbryo Development: Seedling Development - A Typical Seed Consists ofMelody LolupNo ratings yet
- Seeds Laboratory ActivityDocument3 pagesSeeds Laboratory ActivityDaryl Boldios LoterteNo ratings yet
- Plant Reproduction 2015Document46 pagesPlant Reproduction 2015Jodd Ardee TorresNo ratings yet
- QTR 2 Module 4 ReproductionDocument10 pagesQTR 2 Module 4 ReproductionNick BantoloNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Lower and Higher PlantsDocument89 pagesReproduction in Lower and Higher Plantsmohdyasir6643No ratings yet
- Terms in Biology: Oleh Wirda Taufik 16031071Document25 pagesTerms in Biology: Oleh Wirda Taufik 16031071Bintang MatahariNo ratings yet
- Parts of The Seeds and Its GerminationDocument18 pagesParts of The Seeds and Its GerminationNova Estrada KionisalaNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Bio CH 1Document6 pagesClass 12 Bio CH 1AbhishekDwivediNo ratings yet
- Gardener's Guide to Seed Catalogs: Gardener's Guide Series, #3From EverandGardener's Guide to Seed Catalogs: Gardener's Guide Series, #3No ratings yet
- Sollutions To Water PollutionDocument9 pagesSollutions To Water Pollutionslychn100% (1)
- Vision IAS Mains 365 2019 Social Issues PDFDocument71 pagesVision IAS Mains 365 2019 Social Issues PDFVishnuvardhanreddy PalvaiNo ratings yet
- KissanPro - Deck - Feb (3) - CompressedDocument27 pagesKissanPro - Deck - Feb (3) - CompressedSanjay Kumar100% (1)
- WD 3-October ProjectsDocument2 pagesWD 3-October Projectsfake nameNo ratings yet
- Manalocon Farm Structures ReportDocument54 pagesManalocon Farm Structures ReportNasif ManaloconNo ratings yet
- Hoja de Practica Noun PhraseDocument2 pagesHoja de Practica Noun Phrasedante jesus barrios vilcahuamanNo ratings yet
- Journal of Geographical Research - Vol.6, Iss.1 January 2023Document73 pagesJournal of Geographical Research - Vol.6, Iss.1 January 2023Bilingual PublishingNo ratings yet
- CSP 4Document43 pagesCSP 4nagasuri lavanyaNo ratings yet
- PD 1144Document10 pagesPD 1144Wendell Leigh OasanNo ratings yet
- Hill Horticulture (JHA)Document11 pagesHill Horticulture (JHA)Vijay Rakesh Reddy SanikommuNo ratings yet
- PSF Presentation From Elaine 110817Document30 pagesPSF Presentation From Elaine 110817Jayson VillezaNo ratings yet
- Crop ScienceDocument17 pagesCrop ScienceMary Andrea Sumalde DioNo ratings yet
- Globalization in Historical PerspectiveDocument22 pagesGlobalization in Historical PerspectiveSandhya BossNo ratings yet
- Process Technology BooksDocument7 pagesProcess Technology BookseiribooksNo ratings yet
- Blueberries in Romania: Past, Present and Future PerspectiveDocument1 pageBlueberries in Romania: Past, Present and Future PerspectiveGina FelyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Industrialisation and Food ProductionDocument26 pagesChapter 4 - Industrialisation and Food Productionapi-349195282No ratings yet
- Sample Business Plan CoverDocument4 pagesSample Business Plan CoverYared YaddaNo ratings yet
- Food EnquiriesreportDocument44 pagesFood Enquiriesreportkalpana lahamageNo ratings yet
- PDD Moldova Community Forestry Development ProjectDocument99 pagesPDD Moldova Community Forestry Development ProjectFitzgerald BillyNo ratings yet
- Plano Analitico 9 Classe - Inglês 2024Document2 pagesPlano Analitico 9 Classe - Inglês 2024teixeiradeinacio849No ratings yet
- Effect of Soil Tillage System On Soil Properties and Yield in Some Arable CropsDocument5 pagesEffect of Soil Tillage System On Soil Properties and Yield in Some Arable CropsLiv CBNo ratings yet
- ICARDocument111 pagesICARAa2323aANo ratings yet
- Corrected TLE 6 Agri Module 3 v.01 CCDocument31 pagesCorrected TLE 6 Agri Module 3 v.01 CCJunaliza Mansalay Daquio100% (6)
- ConfirmedDocument18 pagesConfirmedashisharun100% (2)
- Daily Lesson Log DLL TLE 7 Week 1 June 3 - 7, 2019Document4 pagesDaily Lesson Log DLL TLE 7 Week 1 June 3 - 7, 2019LEANDRO BOTALON100% (2)
- Bonsai - CotoneasterDocument3 pagesBonsai - CotoneasterKoula IslayNo ratings yet
- Kaingin-Destroyed Ipo Forest and Watershed - A Powerpoint PresentationDocument39 pagesKaingin-Destroyed Ipo Forest and Watershed - A Powerpoint PresentationIan Martinez100% (1)
- Nestle Cocoa PlanDocument8 pagesNestle Cocoa PlanmetaslaNo ratings yet
1506231856511463
1506231856511463
Uploaded by
chikenbiriyanieater0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views3 pages1. The document provides instructions for an experiment to identify the different parts of a dicot seed embryo, including the radicle, plumule, cotyledons, and their functions.
2. Students are asked to soak dicot seeds such as peas, beans, or chickpeas overnight, remove the seed coat, and observe the embryo axis under a microscope to identify the radicle, plumule, and cotyledons, recording their observations.
3. The aim is to learn that the radicle is the embryonic root, plumule the shoot, and cotyledons store food for the embryo.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. The document provides instructions for an experiment to identify the different parts of a dicot seed embryo, including the radicle, plumule, cotyledons, and their functions.
2. Students are asked to soak dicot seeds such as peas, beans, or chickpeas overnight, remove the seed coat, and observe the embryo axis under a microscope to identify the radicle, plumule, and cotyledons, recording their observations.
3. The aim is to learn that the radicle is the embryonic root, plumule the shoot, and cotyledons store food for the embryo.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views3 pages1506231856511463
1506231856511463
Uploaded by
chikenbiriyanieater1. The document provides instructions for an experiment to identify the different parts of a dicot seed embryo, including the radicle, plumule, cotyledons, and their functions.
2. Students are asked to soak dicot seeds such as peas, beans, or chickpeas overnight, remove the seed coat, and observe the embryo axis under a microscope to identify the radicle, plumule, and cotyledons, recording their observations.
3. The aim is to learn that the radicle is the embryonic root, plumule the shoot, and cotyledons store food for the embryo.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 3
LOYOLA INTERNATIONAL SCHOOLS
Qatar
ACADEMIC SESSION 2023-2024
Biology Practical
NAME: __________________________ CLASS: X
Experiment No. 4
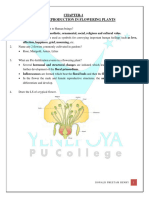
Identification of the different parts of an embryo of a dicot seed
Aim
To identify the different parts of an embryo of a dicot seed (pea, gram or
red kidney bean).
Theory
• Seed: Seed is a small embryonic plant present in a safe coating of seed
coat, it stores food.
• Seed formation: The male gamete of plant, i.e., pollen grains and
female gamete of a plant, i.e., ovules fuse together to form seed. The
seed formation takes place due to fertilization, and it is the product of
reproduction in plants. The embryo of seed is formed from the zygote.
• Food in seed: The food is stored in the cotyledons of embryo in some
plants and in the endosperm, a special tissue outside the embryo in
other plants.
• Three basic parts of a seed:
1. An embryo
2. Nutrient for embryo
3. Seed coat.
• Embryo: The embryo of seed is an immature plant from which a new
plant can grow.
• The radicle that comes out of the embryo is the embryonic root. The
plumule is the embryonic shoot.
• Cotyledons: It is the seed leaf present in seed. If the embryo has one
seed leaf it is monocotyledon and if it has two seed leaves it is
dicotyledon.
• Epicotyl: The part of the embryonic stem above the point of
attachment of the cotyledon is the epicotyl.
• Hypocotyl: The area between the radicle and the place of origin of
cotyledons is termed as hypocotyl.
• Nutrients for the Embryo: Seed stores nutrients for the growth of an
embryo during germination. The nutrients/ stored food is in the form
of oil, fat and protein.
• Seed Coat: The seed coat protects the embryo from mechanical
injury and from drying out. It can be a paper thin as in case of peanut
or may be very thick e.g. coconut.
Materials Required
Water soaked seeds of pea, gram or red kidney beans, petridish, forcep,
needle, brush and simple microscope and slide.
Procedure
1. Take 8-10 soaked seeds of pea/gram/red kidney beans, place them on
wet cotton in petridish overnight. The seed coat becomes soft which
helps in the opening of the seeds.
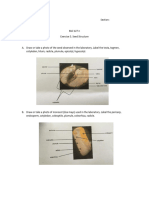
2. With the help of forceps, slowly remove the seed coat and study
different parts of seed embryo.
3. Now, slowly remove the embryo axis with needle and place it on the
slide.
4. Observe these three parts of the seed obtained, record your
observations and draw diagrams.
Observations
1. The seed has a small pore called micropyle.
2. It is a dicot seed, i.e., the seed has two cotyledons.
3. The embryo axis shows radicle and plumule, (as shown in the figure),
the radicle is future root and the plumule is future shoot.
4. The food is stored in cotyledons.
Conclusion
The different parts of an embryo of a dicot seed were identified as plumule
(future shoot), radicle (future root), seed coat (outer covering) and
cotyledons (food store)
Precautions
1. The best quality seeds should be used for study.
2. Soak the seeds overnight to make the seed coat soft.
3. Observe the parts under simple microscope/lens and record your
observations.
4. Remove the seed coat very gently.
You might also like
- Avocado ProductionDocument82 pagesAvocado ProductionDr.Eswara Reddy Siddareddy100% (2)
- Plant HybridizationDocument23 pagesPlant HybridizationMyla Santiago33% (3)
- KOlomi 65 e 8 B Ve CEt JES1Document11 pagesKOlomi 65 e 8 B Ve CEt JES1mahender106yoNo ratings yet
- Agr122 Lab Report 4Document8 pagesAgr122 Lab Report 4Nur AthirahNo ratings yet
- Plant Dissection LabDocument9 pagesPlant Dissection Labmischa.noelleNo ratings yet
- Parts of The Seed: ObjectiveDocument4 pagesParts of The Seed: ObjectiveJoan Rayos PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Final SLM OA11, Quarter 3, Week2Document2 pagesFinal SLM OA11, Quarter 3, Week2l.a. lopezNo ratings yet
- The Structure of Dicot Seed:: Icse Class:9 Biology GerminationDocument3 pagesThe Structure of Dicot Seed:: Icse Class:9 Biology GerminationjaswanthNo ratings yet
- Science Book 1 Chapter 6Document49 pagesScience Book 1 Chapter 624 Jefferson Κoh JingNo ratings yet
- Ex 5-9 DevbiolabDocument27 pagesEx 5-9 DevbiolabPrezyNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument9 pagesAnatomymomina tayyabNo ratings yet
- GerminationDocument14 pagesGerminationPhoo Pyae Pyae KyawNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 14Document2 pagesExperiment No. 14mayankroy9431No ratings yet
- Reproduction Handout For Feb 19 23Document10 pagesReproduction Handout For Feb 19 23cykg4qkbtqNo ratings yet
- Daryl GuinayenDocument9 pagesDaryl GuinayenEmmanuel GallidoNo ratings yet
- DLP in Scince 4Document8 pagesDLP in Scince 4Rosemarie GaringNo ratings yet
- SeedsDocument6 pagesSeedsLawrence KasambaNo ratings yet
- PARTS OF A SEED - PartiDocument6 pagesPARTS OF A SEED - Partichristian capunongNo ratings yet
- GR 9 CH 6 and 7 Question and AnswerDocument18 pagesGR 9 CH 6 and 7 Question and AnswerlegendarychampionthorNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and MorphologyDocument8 pagesAnatomy and MorphologyminichelNo ratings yet
- Botafun SeedsDocument22 pagesBotafun SeedsstephaniealmendralNo ratings yet
- Seed Antatomy and Germination Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesSeed Antatomy and Germination Lesson Planapi-600991950No ratings yet
- Anatomy of SeedDocument15 pagesAnatomy of Seedujam5378No ratings yet
- Seeds: Strategic Intervention Materials in Science by Dr. AaaDocument9 pagesSeeds: Strategic Intervention Materials in Science by Dr. AaajoseNo ratings yet
- 6.3 Pollination and Fertilisation, 6.4 Development of Seeds and Fruits and 6.5 Importance of Seeds For SurvivalDocument56 pages6.3 Pollination and Fertilisation, 6.4 Development of Seeds and Fruits and 6.5 Importance of Seeds For Survivalwickedbiology101No ratings yet
- 3.6.1 Plant Reproduction H 3.6.3 - 3.6.5Document12 pages3.6.1 Plant Reproduction H 3.6.3 - 3.6.5George Oswald Junior CarringtonNo ratings yet
- Sexual ReproductionDocument41 pagesSexual Reproductionapi-406307933No ratings yet
- Class 12 Biology Chapter 2 Revision NotesDocument25 pagesClass 12 Biology Chapter 2 Revision NotesSrushti BhagitNo ratings yet
- G5 Plant Notes 1Document1 pageG5 Plant Notes 1Hi ByeNo ratings yet
- NoteDocument26 pagesNoteRajnish KumarNo ratings yet
- Flowering Plants Forms and Functions (BOT 102) - 2 2023-1Document23 pagesFlowering Plants Forms and Functions (BOT 102) - 2 2023-1faborodeharyomideNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of SeedsDocument3 pagesCharacteristics of SeedsMaria Fe GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Biology 6th ClassDocument4 pagesLesson Plan Biology 6th ClassManju kotturNo ratings yet
- Morfologi BijiDocument48 pagesMorfologi BijiSt. Lailatul RizqiNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 01 Nov 2022Document2 pagesAdobe Scan 01 Nov 2022Sauri ChaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Reproduction & Growth: 4.5 - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument25 pagesReproduction & Growth: 4.5 - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsSanthiya MadhavanNo ratings yet
- Aaua SIWES Report Compiled by OLATUNJI ODocument51 pagesAaua SIWES Report Compiled by OLATUNJI OAyodeleNo ratings yet
- Parts of SeedDocument1 pageParts of SeedScarlet Danielle CASASNo ratings yet
- Reproduction & Growth: 4.5 - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument25 pagesReproduction & Growth: 4.5 - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsZainurain Zainal AbidinNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument26 pagesSexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsMauz KhanNo ratings yet
- Botany Lab Module 8Document7 pagesBotany Lab Module 8annaNo ratings yet
- Seed Appendages and Dispersal MechanismsDocument25 pagesSeed Appendages and Dispersal MechanismsPremNo ratings yet
- The SeedDocument4 pagesThe SeedAnonymous fe9UIiNo ratings yet
- Biology AssignmentDocument15 pagesBiology AssignmentTAHRIM FATIMA0% (1)
- Sexual Reproduction in PlantsDocument13 pagesSexual Reproduction in Plantsshikaanara8686No ratings yet
- 1 - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument22 pages1 - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plantssakeenasiddik22No ratings yet
- Lab Rep 9Document8 pagesLab Rep 9Reign RosadaNo ratings yet
- Exercise 5Document4 pagesExercise 5Cindy jabilloNo ratings yet
- Seeds: DispersalDocument33 pagesSeeds: Dispersalyoussefsamir991No ratings yet
- Sevilla, Joyce Anne C - CASNS 1a - Laboratory Module 10Document4 pagesSevilla, Joyce Anne C - CASNS 1a - Laboratory Module 10Joyce SevillaNo ratings yet
- Seedstructure 130129220104 Phpapp01Document16 pagesSeedstructure 130129220104 Phpapp01Rehana PillayNo ratings yet
- Seed TechnologyDocument11 pagesSeed TechnologyristiyaadiwiratamaNo ratings yet
- 5ad43b99e4b0fa8be1f4fe4f 5e9a092ba8446510cc99fb5a 1615282586341Document28 pages5ad43b99e4b0fa8be1f4fe4f 5e9a092ba8446510cc99fb5a 1615282586341seaid zahidNo ratings yet
- Embryo Development: Seedling Development - A Typical Seed Consists ofDocument3 pagesEmbryo Development: Seedling Development - A Typical Seed Consists ofMelody LolupNo ratings yet
- Seeds Laboratory ActivityDocument3 pagesSeeds Laboratory ActivityDaryl Boldios LoterteNo ratings yet
- Plant Reproduction 2015Document46 pagesPlant Reproduction 2015Jodd Ardee TorresNo ratings yet
- QTR 2 Module 4 ReproductionDocument10 pagesQTR 2 Module 4 ReproductionNick BantoloNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Lower and Higher PlantsDocument89 pagesReproduction in Lower and Higher Plantsmohdyasir6643No ratings yet
- Terms in Biology: Oleh Wirda Taufik 16031071Document25 pagesTerms in Biology: Oleh Wirda Taufik 16031071Bintang MatahariNo ratings yet
- Parts of The Seeds and Its GerminationDocument18 pagesParts of The Seeds and Its GerminationNova Estrada KionisalaNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Bio CH 1Document6 pagesClass 12 Bio CH 1AbhishekDwivediNo ratings yet
- Gardener's Guide to Seed Catalogs: Gardener's Guide Series, #3From EverandGardener's Guide to Seed Catalogs: Gardener's Guide Series, #3No ratings yet
- Sollutions To Water PollutionDocument9 pagesSollutions To Water Pollutionslychn100% (1)
- Vision IAS Mains 365 2019 Social Issues PDFDocument71 pagesVision IAS Mains 365 2019 Social Issues PDFVishnuvardhanreddy PalvaiNo ratings yet
- KissanPro - Deck - Feb (3) - CompressedDocument27 pagesKissanPro - Deck - Feb (3) - CompressedSanjay Kumar100% (1)
- WD 3-October ProjectsDocument2 pagesWD 3-October Projectsfake nameNo ratings yet
- Manalocon Farm Structures ReportDocument54 pagesManalocon Farm Structures ReportNasif ManaloconNo ratings yet
- Hoja de Practica Noun PhraseDocument2 pagesHoja de Practica Noun Phrasedante jesus barrios vilcahuamanNo ratings yet
- Journal of Geographical Research - Vol.6, Iss.1 January 2023Document73 pagesJournal of Geographical Research - Vol.6, Iss.1 January 2023Bilingual PublishingNo ratings yet
- CSP 4Document43 pagesCSP 4nagasuri lavanyaNo ratings yet
- PD 1144Document10 pagesPD 1144Wendell Leigh OasanNo ratings yet
- Hill Horticulture (JHA)Document11 pagesHill Horticulture (JHA)Vijay Rakesh Reddy SanikommuNo ratings yet
- PSF Presentation From Elaine 110817Document30 pagesPSF Presentation From Elaine 110817Jayson VillezaNo ratings yet
- Crop ScienceDocument17 pagesCrop ScienceMary Andrea Sumalde DioNo ratings yet
- Globalization in Historical PerspectiveDocument22 pagesGlobalization in Historical PerspectiveSandhya BossNo ratings yet
- Process Technology BooksDocument7 pagesProcess Technology BookseiribooksNo ratings yet
- Blueberries in Romania: Past, Present and Future PerspectiveDocument1 pageBlueberries in Romania: Past, Present and Future PerspectiveGina FelyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Industrialisation and Food ProductionDocument26 pagesChapter 4 - Industrialisation and Food Productionapi-349195282No ratings yet
- Sample Business Plan CoverDocument4 pagesSample Business Plan CoverYared YaddaNo ratings yet
- Food EnquiriesreportDocument44 pagesFood Enquiriesreportkalpana lahamageNo ratings yet
- PDD Moldova Community Forestry Development ProjectDocument99 pagesPDD Moldova Community Forestry Development ProjectFitzgerald BillyNo ratings yet
- Plano Analitico 9 Classe - Inglês 2024Document2 pagesPlano Analitico 9 Classe - Inglês 2024teixeiradeinacio849No ratings yet
- Effect of Soil Tillage System On Soil Properties and Yield in Some Arable CropsDocument5 pagesEffect of Soil Tillage System On Soil Properties and Yield in Some Arable CropsLiv CBNo ratings yet
- ICARDocument111 pagesICARAa2323aANo ratings yet
- Corrected TLE 6 Agri Module 3 v.01 CCDocument31 pagesCorrected TLE 6 Agri Module 3 v.01 CCJunaliza Mansalay Daquio100% (6)
- ConfirmedDocument18 pagesConfirmedashisharun100% (2)
- Daily Lesson Log DLL TLE 7 Week 1 June 3 - 7, 2019Document4 pagesDaily Lesson Log DLL TLE 7 Week 1 June 3 - 7, 2019LEANDRO BOTALON100% (2)
- Bonsai - CotoneasterDocument3 pagesBonsai - CotoneasterKoula IslayNo ratings yet
- Kaingin-Destroyed Ipo Forest and Watershed - A Powerpoint PresentationDocument39 pagesKaingin-Destroyed Ipo Forest and Watershed - A Powerpoint PresentationIan Martinez100% (1)
- Nestle Cocoa PlanDocument8 pagesNestle Cocoa PlanmetaslaNo ratings yet