Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bee Unit 4 Important Questions
Bee Unit 4 Important Questions
Uploaded by
mangai.ece0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pageThis document contains 10 questions covering various topics in combinational logic circuits including:
1. Converting expressions to canonical SOP and POS forms, simplifying boolean expressions using K-maps, and converting between binary, decimal, octal, and hexadecimal number systems.
2. Explaining the significance of K-maps, Demorgan's theorem, combinational logic circuits, and the differences between SOP and POS forms.
3. Converting boolean functions to standard SOP and POS form, simplifying functions using 4-variable K-maps, and explaining half adders, full adders, half subtractors and full subtractors.
Original Description:
Original Title
bee unit 4 important questions
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document contains 10 questions covering various topics in combinational logic circuits including:
1. Converting expressions to canonical SOP and POS forms, simplifying boolean expressions using K-maps, and converting between binary, decimal, octal, and hexadecimal number systems.
2. Explaining the significance of K-maps, Demorgan's theorem, combinational logic circuits, and the differences between SOP and POS forms.
3. Converting boolean functions to standard SOP and POS form, simplifying functions using 4-variable K-maps, and explaining half adders, full adders, half subtractors and full subtractors.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pageBee Unit 4 Important Questions
Bee Unit 4 Important Questions
Uploaded by
mangai.eceThis document contains 10 questions covering various topics in combinational logic circuits including:
1. Converting expressions to canonical SOP and POS forms, simplifying boolean expressions using K-maps, and converting between binary, decimal, octal, and hexadecimal number systems.
2. Explaining the significance of K-maps, Demorgan's theorem, combinational logic circuits, and the differences between SOP and POS forms.
3. Converting boolean functions to standard SOP and POS form, simplifying functions using 4-variable K-maps, and explaining half adders, full adders, half subtractors and full subtractors.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
PART-A: UNIT IV
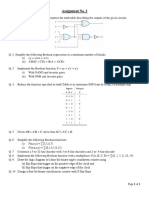
1. Convert the given expression in canonical SOP form Y=AC+AB+BC
2. Mention the signifiance of K-map .
3. State De-morgan’s theorem.
4. Simplify: AB+A(B+C)+B(B+C).
5. What is meant by combinational logic circuits ?Give example.
6. Explain about SOP and POS form.
7. Convert (342)10 to Hexa decimal.
8. Convert (436)8 to decimal.
9. What are the disadvantages of K-map?
10. Convert (25)10 to equivalent binary number.
UNIT IV:PART - B
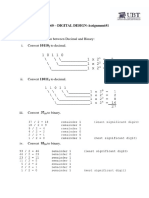
1 Convert following Decimal number to Binary,Octal and Hexadecimal
(i)(455)10 (ii))(256.22)10
2 Convert the following Binary to decimal,octal and Hexadecimal
(i)(11101)2 (ii))(100010.011)2
3 Express the following function using k-map.
F(w,x,y,z)=WX’Y’+WY+W’Y’Z’
4 Simplify the given boolean function using 4-variable k-map
f(A,B,C,D)=m(0,2,4,5,8,10,14,15)
5 Convert the given function into standard SOP
(i)F=AB’C+A’B’+ABC’D
(ii)F=AC’+B’D+A’CD+ABC’D
6 Convert the given function into standard POS
(i)Y=A+B’C
(ii)Y=(A’+B’D’)(A+B’+C’)(A’+B+D’)(B+C’+D’)
7 Explain in detail about Half Adder and Full adder.
8 Explain in detail about Half subtractor and Full subtractor.
9 Simplify the function F(A,B,C,D)= ∑m(2,4,6,10,12)+d(0,8,9,13) using k-map.
10 Simplify the Boolean expression using k-map in POS form.Y(A,B,C)=(A+B’+C)
(A’+B’+C)(A+B’+C’)(A’+B’+C’)
K1 – Remember; K2 – Understand; K3 – Apply; K4 – Analyze; K5 – Evaluate; K6 – Create
1
You might also like
- Question Bank Digital ElectronicsDocument12 pagesQuestion Bank Digital ElectronicsUrvin MistryNo ratings yet
- Question Bank AssignmentDocument3 pagesQuestion Bank AssignmentPavankumar MangavalliNo ratings yet
- Digital System Design Unit - 1 Boolean Algebra & Its Simplification Techniques 2 Marks QuestionsDocument1 pageDigital System Design Unit - 1 Boolean Algebra & Its Simplification Techniques 2 Marks QuestionsKeertanaNo ratings yet
- VL2021220504591 DaDocument2 pagesVL2021220504591 DaDattu GollapinniNo ratings yet
- Ece DLD Set IiDocument2 pagesEce DLD Set IikisnamohanNo ratings yet
- Digital Circuit 2.2Document1 pageDigital Circuit 2.2Utkarsh ShuklaNo ratings yet
- LOC Bca 1st YearDocument7 pagesLOC Bca 1st YearKhushbooNo ratings yet
- DCF AssignmentDocument1 pageDCF Assignmentrans_11No ratings yet
- DPSD QBDocument11 pagesDPSD QBHANISHA SAALIHNo ratings yet
- ECE20022 Assignment Module 1 2 3Document3 pagesECE20022 Assignment Module 1 2 3Nandini PandeyNo ratings yet
- Computer Organization & Architecture QPDocument3 pagesComputer Organization & Architecture QPShylesh PrabhuNo ratings yet
- KEE401 ASSIGNMENTS and QUESTION BANKDocument17 pagesKEE401 ASSIGNMENTS and QUESTION BANKPrince VermaNo ratings yet
- CT 02 Syllabus and Assignment OneDocument2 pagesCT 02 Syllabus and Assignment OneImran EmuNo ratings yet
- Obtain The 9's and 10's Complement ofDocument3 pagesObtain The 9's and 10's Complement ofNandha Kizor VNo ratings yet
- STLD QuestionsDocument2 pagesSTLD QuestionsVinod KumarNo ratings yet
- STLD Question Bank Unit I 1: (RR, R05, Nov 08SET II, III)Document16 pagesSTLD Question Bank Unit I 1: (RR, R05, Nov 08SET II, III)Harold WilsonNo ratings yet
- DCD DaDocument28 pagesDCD Dakathi50% (2)
- Convert Gray Code 101011 Into Its Binary Equivalent. Gray Code: 1 0 1 0 1 1 Binary Code: 1 1 0 0 1 0Document23 pagesConvert Gray Code 101011 Into Its Binary Equivalent. Gray Code: 1 0 1 0 1 1 Binary Code: 1 1 0 0 1 0khadarbasha.n nNo ratings yet
- STLD Question BankDocument18 pagesSTLD Question BankBattu DeepaNo ratings yet
- Btech 2-1 STLD QB Ece& DLD QB CseDocument8 pagesBtech 2-1 STLD QB Ece& DLD QB CseSateesh KunaNo ratings yet
- DLD Mid 1Document3 pagesDLD Mid 1lsrinivasamurthyNo ratings yet
- Assignment#02Document2 pagesAssignment#02sujan shresthaNo ratings yet
- Digital Logic Design TutorialDocument10 pagesDigital Logic Design TutorialShadab IrfanNo ratings yet
- Deld Insem QBDocument2 pagesDeld Insem QBUV New MoviesNo ratings yet
- BEE Assignment IVDocument1 pageBEE Assignment IVrajshrimohanksNo ratings yet
- DLD Question BankDocument1 pageDLD Question Banksanjanareddy.satti24No ratings yet
- Question Bank Subject Code: Ec6302 Subject: Digital Electronics Sem / Year: Iii / Ii-Ece Unit-I Minimization Techniques and Logic Gates Part-ADocument3 pagesQuestion Bank Subject Code: Ec6302 Subject: Digital Electronics Sem / Year: Iii / Ii-Ece Unit-I Minimization Techniques and Logic Gates Part-AmohanaNo ratings yet
- DCD Assignment QuestionsDocument5 pagesDCD Assignment QuestionsSYAMALANo ratings yet
- Ee 211 Assignment - 1 Ans KeyDocument5 pagesEe 211 Assignment - 1 Ans Keyabdulrahman abushanabNo ratings yet
- Assignment#1Document1 pageAssignment#1Subhan MûghåłNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4Document1 pageTutorial 4Sangam RanabhatNo ratings yet
- Demp Mid - 1 Question BankDocument3 pagesDemp Mid - 1 Question BankMᴀɴɪ TᴇᴊᴀNo ratings yet
- Digital Electronics QB 2015-RDocument8 pagesDigital Electronics QB 2015-RKeerthe VaasanNo ratings yet
- EEL2020 Assignment 01Document1 pageEEL2020 Assignment 01b22ee084No ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document1 pageAssignment 2anmol4242301No ratings yet
- 3630e772-7d45-4801-b968-a1864dbe8a4fDocument20 pages3630e772-7d45-4801-b968-a1864dbe8a4fMOHAMED IRREEF SNo ratings yet
- Computer System Architecture Question PaperDocument2 pagesComputer System Architecture Question PaperHimanshu AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Digital Electronics Assingement IDocument6 pagesDigital Electronics Assingement IAkshay GuptaNo ratings yet
- Questions of DFDocument5 pagesQuestions of DFUr MnNo ratings yet
- DLD GTU Question Bank: Chapter-1 Binary SystemDocument5 pagesDLD GTU Question Bank: Chapter-1 Binary Systemnirav34No ratings yet
- 9A04306 Digital Logic DesignDocument4 pages9A04306 Digital Logic DesignMahaboob SubahanNo ratings yet
- Digital Logic Design: Assignment 1 Due Date: 10.12.2020 (Thursday)Document3 pagesDigital Logic Design: Assignment 1 Due Date: 10.12.2020 (Thursday)muktikantaNo ratings yet
- Model ImpDocument3 pagesModel ImpjeevaNo ratings yet
- Rajagiri School of Engineering and Technology: Rajagiri Valley, Kakkanad. Third SemesterDocument37 pagesRajagiri School of Engineering and Technology: Rajagiri Valley, Kakkanad. Third SemesterAmrita VenkitaramaniNo ratings yet
- De (Unit-1) (Practice Sheet) PsitcoeDocument5 pagesDe (Unit-1) (Practice Sheet) PsitcoeA's Was UnlikedNo ratings yet
- DE For ECEDocument1 pageDE For ECEKarthick VijayanNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document7 pagesAssignment 1Ishmum Monjur NilockNo ratings yet
- DLD GTU Question Bank: Chapter-1 Binary SystemDocument129 pagesDLD GTU Question Bank: Chapter-1 Binary Systemnirav34No ratings yet
- DLD Assignment - 1Document2 pagesDLD Assignment - 1gokulNo ratings yet
- STLD Question BankDocument11 pagesSTLD Question BankSatish BojjawarNo ratings yet
- DLM - Digital Assignment 1Document1 pageDLM - Digital Assignment 1SamNo ratings yet
- DLD QBDocument5 pagesDLD QBSai Nath Reddy NerusupalliNo ratings yet
- DELD - Short Answer Questions and AnswersDocument23 pagesDELD - Short Answer Questions and AnswersPasupuleti Venkata RamanaNo ratings yet
- (WWW - Entrance-Exam - Net) - JNTU, B.tech, CSE, Digital Logic Design Sample Paper 1 PDFDocument2 pages(WWW - Entrance-Exam - Net) - JNTU, B.tech, CSE, Digital Logic Design Sample Paper 1 PDFpreethaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 - B Section EC1000Document1 pageAssignment 2 - B Section EC1000Rituraj TripathyNo ratings yet
- EC6302-Digital ElectronicsDocument14 pagesEC6302-Digital Electronicsmagy1989No ratings yet
- DLD 2nd Chapter KeyDocument15 pagesDLD 2nd Chapter KeyAnnas AfzalNo ratings yet
- Answers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesFrom EverandAnswers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesRating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (2)