Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Model Tom.1
Model Tom.1
Uploaded by
jamunaa83Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Model Tom.1
Model Tom.1
Uploaded by
jamunaa83Copyright:
Available Formats
Register No: _________________________
THE KAVERY ENGINEERING COLLEGE
DEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTURAL ENGINEERING
ME3491 Theory of Machines
2nd Year / 3rd Sem Duration :3 Hours
Date : Session: AN Model exam Max. Marks : 100
PART – A (ANSWER ALL QUESTIONS) 10*2=20
Q.No Questions BTL CO Marks
Classify kinematic pairs according to the type of relative motion
1. BL2 1 2
between the elements
2. Identify the Mechanism. BL1 1 2
3. Describe the factors consider in selection of belt drive BL2 2 2
4. Define Angle of Repose. BL1 2 2
5. Interpret the toothed wheels according to the type of gearing. BL2 3 2
6. Examine the module. BL1 3 2
7. State the principle of super position BL1 4 2
8. Define crank effort BL1 4 2
9. Why rotating masses are to be dynamically balanced? BL2 5 2
10. . Specify the importance of vibration isolation? BL2 5 2
PART – B Marks 5*13=65
Q.No Questions BTL CO Marks
1. a PQRS is a four bar chain with link PS fixed. The lengths of the BL4 1 13
links are PQ = 62.5 mm; QR = 175 mm; RS = 112.5 mm; and
PS = 200 mm. The crank PQ rotates at 10 rad/s clockwise. Draw
the velocity and acceleration diagram when angle QPS = 60°
and Q and R lie on the same side of PS. Find the angular
velocity and angular acceleration of
links QR and RS.
Or
b Explain the inversions of four bar chain with neat sketch and list BL4 1 13
out the practical applications of inversions.
2. a The mean diameter of a square threaded screw jack is 50 mm. BL5 2 13
The pitch of the thread is 10 mm. The coefficient of friction is
0.15. What force must be applied at the end of a 0.7 m long
lever, which is perpendicular
to the longitudinal axis of the screw to raise a load of 20 kN
Or
b A shaft rotating at 200 r.p.m. drives another shaft at 300 r.p.m. BL5 2 13
and transmits 6 kW through a belt. The belt is 100 mm wide and
10 mm thick. The distance between the shafts is 4m. The
smaller pulley is 0.5 m in diameter. Formulate the stress in the
Register No: _________________________
belt, if it is 1. An open belt
drive, and 2. A cross belt drive. Take μ = 0.3.
3. a A pair of gears, having 40 and 20 teeth respectively, are rotating BL5 3 13
in mesh, the speed of the smaller being 2000 r.p.m. Evaluate the
velocity of sliding between the gear teeth aces at the point of
engagement, at the pitch point, and at the point of
disengagement if the smaller gear is the driver. Assume that the
gear teeth are 20° involute form, addendum length is 5 mm and
the module is 5 mm. Also find the angle
through which the pinion turns while any pairs of teeth are in
contact
Or
b An epicyclic gear consists of three gears A, B and C as shown in BL5 3 13
Fig.4.1 The gear A has 72 internal teeth and gear C has 32
external teeth. The gear B meshes with both A and C and is
carried on an arm EF which rotates about the centre of A at 18
r.p.m. If the gear A is fixed, develop the speed of gears B and C.
4. a A single cylinder vertical engine has a bore of 100 mm and a BL3 4 13
stroke of 120 mm has a connecting rod of 250mm long. The
mass of the piston is 1.1kg. The speed is 2000rpm. On the
expansion stroke, with a crank at 20° from top dead center, the
gas pressure is 700kN/mm2. Determine (i) Net force acting on
the piston (ii) Resultant load on the gudgeon pin (iii) Thrust on
the cylinder walls, and (iv) Speed above which, other things
remaining the same, the gudgeon pin load would be reversed in
direction.
Or
b The lengths of crank and connecting rod of a horizontal BL3 4 13
reciprocating engine are 200 mm and 1 meter respectively. The
crank is rotating at 400 rpm.when the crank has turned through
30° from the inner dead centre. The difference of pressure
Register No: _________________________
between cover and piston rod is 0.4 N/mm2 .if the mass of the
reciprocating parts is 100 kg and cylinder bore is 0.4 meters,
then calculate: (i) inertia force, (ii) force on piston, (iii) piston
effort, (iv) thrust on the sides of the cylinder walls, (v) thrust in
the connecting rod, and (vi) crank effort
5. a A two cylinder uncoupled locomotive has inside cylinders 60 BL3 5 13
cm apart. The radius of each crank is 30 cm. The cranks are at
right angles. The weight of the revolving mass per cylinder is
2452.5 N and the weight of the reciprocating mass per cylinder
is 2943 N. The whole of the revolving and 2/3rd of the
reciprocating masses are to be balanced and the balanced
weights are placed, in the planes of rotation of the driving
wheels, at radius of 80 cm. The driving wheels are 2 m in
diameter and 1.5 m apart. If the speed of the engine is 80
km/hr., find the hammer blow, maximum variation of tractive
effort and maximum swaying couple
Or
b A shaft is simply supported at the ends and is of 20 mm in BL3 5 13
diameter and 600 mm in length. The shaft carries a load of
19.62 N at its centre. The weight of the shaft per metre length is
248.2 N. Find the critical speed of the shaft. Take Young’s
modulus as 200 GN/m2
PART – C (Compulsory Question)1*7=7
Q.No Questions BTL CO Marks
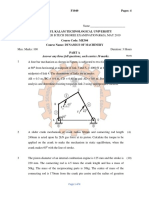
6. a The mechanism, as shown in Fig. 1.2, has the dimensions of BL6 1 15
various links as follows: AB = DE = 150 mm; BC = CD = 450
mm; EF = 375 mm. The crank AB makes an angle of 45° with
the horizontal and rotates about A in the clockwise direction at
a uniform speed of 120 r.p.m. The lever DC oscillates about the
fixed point D, which is connected to AB by the coupler BC.
The block F moves in the horizontal guides, being driven by
the link EF. Determine: 1. velocity of the block F, 2. angular
velocity of DC, and 3. rubbing speed at the pin C which is 50
mm in diameter.
Register No: _________________________
Or
b Construct the profile of a cam to suit the following BL6 1 15
specifications with the knife-edged follower
Cam shaft diameter = 40 mm; Least radius of cam = 25 mm;
Angle of lift = 120°; Angle of fall = 150°; Lift of the follower
= 40 mm; Number of pauses are two of equal interval between
motions. During the lift, the motion is S.H.M. During the fall
the motion is uniform acceleration and deceleration. The speed
of the cam shaft is uniform. The line of stroke of the follower is
off-set 12.5 mm from the centre of the cam
BL1-RememberBL2-Understand BL3-Apply BL4-Analyze BL5-EvaluateBL6-Create
Blooms
Marks Q.No CO Course Outcomes Marks
Level
BL1 10 1,2,11,16 I Discuss the basics of mechanism. 32
BTL2 10 3,4.12 II Solve problems on gears and gear trains 17
BTL3 26 5,6,13 III Examine friction in machine elements. 17
BTL4 13 7,8,14 IV Calculate static and dynamic forces of mechanisms. 17
BTL5 26 Calculate the balancing masses and their locations of
reciprocating and rotating masses. Computing the
9,10,15 V 17
BTL6 15 frequency of free vibration, forced vibration and
damping coefficient.
Subject Incharge Head of the Department IQAC
Coordinator
You might also like
- Wurlitzer Service Manual PDFDocument105 pagesWurlitzer Service Manual PDFISABELLA ISA100% (1)
- ISO/TC 164: Standards by Mechanical Testing of MetalsDocument7 pagesISO/TC 164: Standards by Mechanical Testing of Metalsjamunaa83No ratings yet
- Panasonic KV-S7077 - 7097 Service Manual PDFDocument217 pagesPanasonic KV-S7077 - 7097 Service Manual PDFАлександр Зыков100% (2)
- Labrie Optimizer Maintenance Manual PDFDocument81 pagesLabrie Optimizer Maintenance Manual PDFstainless31620039126100% (1)
- Cad and Tappet Full ReportDocument30 pagesCad and Tappet Full ReportRubaveeran GunasegaranNo ratings yet
- Model Tom.2Document4 pagesModel Tom.2jamunaa83No ratings yet
- Dom SyllabusDocument4 pagesDom SyllabusSreeraj S BabuNo ratings yet
- (W-19) Dynamics of MachinesDocument4 pages(W-19) Dynamics of MachinesNabeel KhanNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of Machines PDFDocument4 pagesDynamics of Machines PDFSunurvayu100% (1)
- P13ME51 BN AjanaDocument3 pagesP13ME51 BN AjanaRocky FxNo ratings yet
- ME8594-Dynamics of MachinesDocument29 pagesME8594-Dynamics of MachinesVinoth KumarNo ratings yet
- 2 - Dynamics of Machinery PDFDocument8 pages2 - Dynamics of Machinery PDFAkhil C KNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Checklist CT 1Document3 pagesQuestion Paper Checklist CT 1sar_tpgitNo ratings yet
- Ae3491 Mom Iat 1 Set 2Document4 pagesAe3491 Mom Iat 1 Set 2thandialNo ratings yet
- MET301 Dec 2021Document3 pagesMET301 Dec 2021Sudeesh SudevanNo ratings yet
- Dec 2019 ME304 - Dynamics of Machinery (S) - Ktu QbankDocument3 pagesDec 2019 ME304 - Dynamics of Machinery (S) - Ktu QbankMidhun SukumaranNo ratings yet
- 15A03402 Kinematics of MachinesDocument2 pages15A03402 Kinematics of Machinesrammohan reddyNo ratings yet
- WWW - Manaresults.co - In: (Mechanical Engineering)Document3 pagesWWW - Manaresults.co - In: (Mechanical Engineering)rajuNo ratings yet
- QUESTION PAPER CHECKLIST ModelDocument6 pagesQUESTION PAPER CHECKLIST Modelsar_tpgitNo ratings yet
- Design of Machine Elements-IiDocument2 pagesDesign of Machine Elements-IiAmal GangadharanNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Checklist CT 2Document3 pagesQuestion Paper Checklist CT 2sar_tpgitNo ratings yet
- Tom 7 JuneDocument3 pagesTom 7 JuneAnonymous mXicTi8hBNo ratings yet
- 161411-161901-Dynamics of MachineryDocument2 pages161411-161901-Dynamics of Machinerywind projectNo ratings yet
- MDSP Diag 3 and 4Document3 pagesMDSP Diag 3 and 4Tyron RebellonNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf - Merged - 2024-02-25T160505.161Document7 pagesIlovepdf - Merged - 2024-02-25T160505.161Aman SharmaNo ratings yet
- 07a60304 - Dynamics of MachineryDocument8 pages07a60304 - Dynamics of MachineryRajaganapathy GanaNo ratings yet
- Analysis OF Mechanisms GTU IMPDocument5 pagesAnalysis OF Mechanisms GTU IMPSwastik PanchalNo ratings yet
- Design of Machine Elements 2 Jan 2018 (2010 Scheme)Document2 pagesDesign of Machine Elements 2 Jan 2018 (2010 Scheme)KishoreNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.Document3 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: Reg. No.Tejaswi PilakaNo ratings yet
- Question Paper End Sem Old Syllabus 2010 1 280910Document3 pagesQuestion Paper End Sem Old Syllabus 2010 1 280910Vikrant HaribhaktaNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument3 pagesGujarat Technological UniversityKRISHI JANINo ratings yet
- Design of Machine Elements: B.E. Seventh Semester (Aeronautical Engineering) (C.B.S.)Document2 pagesDesign of Machine Elements: B.E. Seventh Semester (Aeronautical Engineering) (C.B.S.)Rohit RangariNo ratings yet
- AC3162 - Subject - Dynamics of Machines - 6 ME 02 - Year - B.E. Sixth Semester (Mechanical Engineering) (CBCS) Winter 2022Document4 pagesAC3162 - Subject - Dynamics of Machines - 6 ME 02 - Year - B.E. Sixth Semester (Mechanical Engineering) (CBCS) Winter 2022Gajanan SononeNo ratings yet
- r05310304 Kinematics of MachineryDocument10 pagesr05310304 Kinematics of MachinerySRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- ME6505-Dynamics of MachinesDocument17 pagesME6505-Dynamics of Machinesraja30gNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of MachineDocument4 pagesKinematics of MachineSumit KambleNo ratings yet
- Assignment Unit - 1: 2) .A Pair of Involute Gears Is in Mesh. The Application Restricts The Space To Accommodate TheseDocument4 pagesAssignment Unit - 1: 2) .A Pair of Involute Gears Is in Mesh. The Application Restricts The Space To Accommodate TheserahulNo ratings yet
- Ai 9202Document2 pagesAi 9202Pop EyeNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of MachineryDocument8 pagesDynamics of Machineryrajamutyala4uNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument3 pagesGujarat Technological Universityfeyayel990No ratings yet
- Fifth Semester B.Tech Degree Regular and Supplementary Examination December 2020Document2 pagesFifth Semester B.Tech Degree Regular and Supplementary Examination December 2020Nandagopan GNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of Machines-1Document4 pagesDynamics of Machines-1Akshay BondadeNo ratings yet
- MDDocument2 pagesMDAbhijeet PramanikNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Code:: (10×2 20 Marks)Document4 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: (10×2 20 Marks)Iyyappan SubramanianNo ratings yet
- PART-A (10 X 2 20 Marks)Document4 pagesPART-A (10 X 2 20 Marks)Arun R UNo ratings yet
- Au Qp-Me8594 PDFDocument18 pagesAu Qp-Me8594 PDFMariappan VNo ratings yet
- 16ME5DCDOMDocument3 pages16ME5DCDOMyyy 4uNo ratings yet
- 081B52EFAC704D5AB58072B74C443C48Document3 pages081B52EFAC704D5AB58072B74C443C48yashvantNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument3 pagesGujarat Technological UniversityKRISHI JANINo ratings yet
- DOM Question BankDocument4 pagesDOM Question BankGomish SharmaNo ratings yet
- 12 Me 5dcdm2Document3 pages12 Me 5dcdm2Abhyudaya SinghNo ratings yet
- QB Unit-3,4,5Document7 pagesQB Unit-3,4,5Agranshu BhardwajNo ratings yet
- 115DY122016Document3 pages115DY122016rohitchanakya76No ratings yet
- Tutorial-2 Kinematics of MachineryDocument2 pagesTutorial-2 Kinematics of MachineryInzamam Ul HaqueNo ratings yet
- PDDC Winter 2020Document2 pagesPDDC Winter 2020Bhavesh PatelNo ratings yet
- Question Paper-Theory of Machine - May 11 - (Mumbai University)Document2 pagesQuestion Paper-Theory of Machine - May 11 - (Mumbai University)learning.aatNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of MachineryDocument9 pagesKinematics of MachineryChinmay SahooNo ratings yet
- Machine Design Model PaperDocument2 pagesMachine Design Model Paperlalamramesh78No ratings yet
- Kinematics of Machinery November Am Rr222105Document12 pagesKinematics of Machinery November Am Rr222105Nizam Institute of Engineering and Technology LibraryNo ratings yet
- University QuestionsDocument4 pagesUniversity QuestionsMartin De Boras PragashNo ratings yet
- Cylindrical Compression Helix Springs For Suspension SystemsFrom EverandCylindrical Compression Helix Springs For Suspension SystemsNo ratings yet
- Electronic Control of Switched Reluctance MachinesFrom EverandElectronic Control of Switched Reluctance MachinesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Road Accident Survey - 2016Document37 pagesRoad Accident Survey - 2016jamunaa83No ratings yet
- Tom NotesDocument77 pagesTom Notesjamunaa83No ratings yet
- FRP PDFDocument3 pagesFRP PDFjamunaa83No ratings yet
- Multifactor RSM Tutorial (Part 3 - Advanced Topics) : Adding Propagation of Error (POE) To The OptimizationDocument10 pagesMultifactor RSM Tutorial (Part 3 - Advanced Topics) : Adding Propagation of Error (POE) To The Optimizationjamunaa83No ratings yet
- Combined Mixture-Process Tutorial: Experiments With Mixtures, 3Document20 pagesCombined Mixture-Process Tutorial: Experiments With Mixtures, 3jamunaa83No ratings yet
- Part - A (5x 2 10 MARKS) Answer All Questions: Academic Year 2020-21 ODD OML751 Testing of MaterialsDocument1 pagePart - A (5x 2 10 MARKS) Answer All Questions: Academic Year 2020-21 ODD OML751 Testing of Materialsjamunaa83No ratings yet
- Part - A (5x 2 10 MARKS) Answer All Questions: Academic Year 2020-21 ODD ME8594 Dynamics of MachinesDocument2 pagesPart - A (5x 2 10 MARKS) Answer All Questions: Academic Year 2020-21 ODD ME8594 Dynamics of Machinesjamunaa83No ratings yet
- Historical Data RSM Tutorial (Part 2 - Advanced Topics) : Design EvaluationDocument6 pagesHistorical Data RSM Tutorial (Part 2 - Advanced Topics) : Design Evaluationjamunaa83No ratings yet
- Model .10.A: Stiffness Matrix For One Dimension Conduction ElementDocument31 pagesModel .10.A: Stiffness Matrix For One Dimension Conduction Elementjamunaa83No ratings yet
- Model 3Document21 pagesModel 3jamunaa83No ratings yet
- W Wi 1 HMEYPonfc L8 MOAi I1588939613Document1 pageW Wi 1 HMEYPonfc L8 MOAi I1588939613jamunaa83No ratings yet
- Dynamics of Machines: Mr.S.Thanaga Kasi Rajan, M.E., (PH.D) ., & Mr.B.K.Parrthipan, M.E., M.B.A., (PH.D) .Document44 pagesDynamics of Machines: Mr.S.Thanaga Kasi Rajan, M.E., (PH.D) ., & Mr.B.K.Parrthipan, M.E., M.B.A., (PH.D) .jamunaa83No ratings yet
- Anna University:: Chennai - 600 025: Office of The Controller of ExaminationsDocument3 pagesAnna University:: Chennai - 600 025: Office of The Controller of Examinationsjamunaa83No ratings yet
- Fire Prevention and Fire Fighting in Plants/Working Places.: Presentation OnDocument97 pagesFire Prevention and Fire Fighting in Plants/Working Places.: Presentation Onjamunaa83No ratings yet
- Assignment 1 (18 08 2020)Document1 pageAssignment 1 (18 08 2020)jamunaa83No ratings yet
- Machine Hazards Fall1718Document47 pagesMachine Hazards Fall1718jamunaa83No ratings yet
- Unit I: - Finite Element Formulation of Boundary Value ProblemsDocument11 pagesUnit I: - Finite Element Formulation of Boundary Value Problemsjamunaa83No ratings yet
- OME754 Industrial SafetyDocument1 pageOME754 Industrial Safetyjamunaa8350% (12)
- ME 8594 Dynamics of MachinesDocument2 pagesME 8594 Dynamics of Machinesjamunaa83No ratings yet
- Anna University:: Chennai - 600 025: Office of The Controller of ExaminationsDocument3 pagesAnna University:: Chennai - 600 025: Office of The Controller of Examinationsjamunaa83No ratings yet
- Engineering Metallurgy Part.A Unit - IDocument4 pagesEngineering Metallurgy Part.A Unit - Ijamunaa83No ratings yet
- The Kavery Engineering CollegeDocument3 pagesThe Kavery Engineering Collegejamunaa83No ratings yet
- PT32 09 PDFDocument3 pagesPT32 09 PDFGrandhi Venkata Satya KiranNo ratings yet
- Tutorial ActuatorsDocument4 pagesTutorial ActuatorsImfarosha EmmaNo ratings yet
- DVC6200f Instruction ManualDocument340 pagesDVC6200f Instruction ManualEduardo Ulises Quevedo GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 MTDocument18 pagesUnit 4 MTMuthuvel M100% (1)
- Mechatronics (ME 71) 16 MarkDocument11 pagesMechatronics (ME 71) 16 MarkVignesh VickyNo ratings yet
- Service Manual: J Video Cassette RecorderDocument69 pagesService Manual: J Video Cassette Recordermzaq1No ratings yet
- Split Cavity and Side CoreDocument29 pagesSplit Cavity and Side CoreShubham ChoudhariNo ratings yet
- Cams Design & Kinematic Analysis: According To The Surface in ContactDocument13 pagesCams Design & Kinematic Analysis: According To The Surface in ContactFaisal MaqsoodNo ratings yet
- 0500-0750 Service ManualDocument24 pages0500-0750 Service ManualcgtottyNo ratings yet
- Cencon Atm Security Lock Installation InstructionsDocument24 pagesCencon Atm Security Lock Installation InstructionsbiggusxNo ratings yet
- HyperMILL 2016 2 enDocument16 pagesHyperMILL 2016 2 enPaul VeramendiNo ratings yet
- Basics of Weft KnittingDocument63 pagesBasics of Weft Knittinggovardhan6rao100% (2)
- JVC mx-gt80 gt90 SM No-Sch (ET)Document48 pagesJVC mx-gt80 gt90 SM No-Sch (ET)Cliffton FilipinoPrd ShraderNo ratings yet
- W - 8 - Mce 3513 - Lo3Document12 pagesW - 8 - Mce 3513 - Lo3Muhammed RazaNo ratings yet
- Functional Analysis and Mechatronic Design of A Cam Controlled MechanismDocument9 pagesFunctional Analysis and Mechatronic Design of A Cam Controlled MechanismDanieleNo ratings yet
- SQM10-20 Actuators For Air Dampers and Control Valves Oil Burners PDFDocument8 pagesSQM10-20 Actuators For Air Dampers and Control Valves Oil Burners PDFDimitry TIRANo ratings yet
- Rolls-Royce M250-C20R SERIES OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE 73-20-02Document20 pagesRolls-Royce M250-C20R SERIES OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE 73-20-02anony8103No ratings yet
- Wrap Spring ClutchesDocument44 pagesWrap Spring ClutchesWilfredy BPNo ratings yet
- A Novel Parallel-Kinematics Machine ToolDocument6 pagesA Novel Parallel-Kinematics Machine Toolbirdview champlainNo ratings yet
- What Is Crash Manoeuvring of Ship in Emergency Situation and WhatDocument1 pageWhat Is Crash Manoeuvring of Ship in Emergency Situation and Whatsuresh_marine20000% (1)
- Bre CS2684Document224 pagesBre CS2684awalmusmarNo ratings yet
- KTU BTech ME 2019scheme 2019Scheme-MinorsDocument114 pagesKTU BTech ME 2019scheme 2019Scheme-MinorsLearn Mechanical EngineeringNo ratings yet
- A11 ManualDocument68 pagesA11 ManualIvan KulicNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet Ramsey Pro Line EmeaDocument5 pagesData Sheet Ramsey Pro Line Emeadekyun49No ratings yet
- ME8651 Iq Design of Transmission SystemsDocument15 pagesME8651 Iq Design of Transmission SystemsJagannath CherkuNo ratings yet
- CVS 870 Limit Switch: Instruction ManualDocument4 pagesCVS 870 Limit Switch: Instruction ManualalexmontellNo ratings yet