Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electic Current Notes
Electic Current Notes
Uploaded by
naikkt240 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views6 pagesThis document contains notes on the topic of electric current and its effects for Class VII science. It includes fill-in-the-blank questions about how electric current is converted into other forms of energy by devices. True/false questions test understanding of heating effects, electromagnetism, and circuit safety. Multiple choice questions cover the workings of light bulbs, fuses, and electromagnets. Brief answer questions ask about circuit diagrams, practical applications of heating effects, characteristics of heating elements, definitions of short circuits and overloads, and uses of electromagnets. Detailed questions provide explanations of why only filaments glow and how brightness decreases with additional loads. An experiment demonstrating a fuse and a diagram of an electric bell are
Original Description:
Science class 7th DAV
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document contains notes on the topic of electric current and its effects for Class VII science. It includes fill-in-the-blank questions about how electric current is converted into other forms of energy by devices. True/false questions test understanding of heating effects, electromagnetism, and circuit safety. Multiple choice questions cover the workings of light bulbs, fuses, and electromagnets. Brief answer questions ask about circuit diagrams, practical applications of heating effects, characteristics of heating elements, definitions of short circuits and overloads, and uses of electromagnets. Detailed questions provide explanations of why only filaments glow and how brightness decreases with additional loads. An experiment demonstrating a fuse and a diagram of an electric bell are
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views6 pagesElectic Current Notes
Electic Current Notes
Uploaded by
naikkt24This document contains notes on the topic of electric current and its effects for Class VII science. It includes fill-in-the-blank questions about how electric current is converted into other forms of energy by devices. True/false questions test understanding of heating effects, electromagnetism, and circuit safety. Multiple choice questions cover the workings of light bulbs, fuses, and electromagnets. Brief answer questions ask about circuit diagrams, practical applications of heating effects, characteristics of heating elements, definitions of short circuits and overloads, and uses of electromagnets. Detailed questions provide explanations of why only filaments glow and how brightness decreases with additional loads. An experiment demonstrating a fuse and a diagram of an electric bell are
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 6
DAV PUBLIC SCHOOL, NERUL
CLASS – VII
SUBJECT – SCIENCE
TOPIC – Electric Current and its Effects
NOTES
A. Fill in the blanks
1. When current is switched on, an electric fan converts electric energy into
mechanical energy.
2. When current is switched on in a room heater, it converts electric energy
into heat energy.
3. We prefer a wire of nichrome for making the heating element in
domestic appliances like the electric iron, electric heater and the electric
toaster.
4. A safety device, based on the heating effect of current is fuse.
5. Electromagnet should show rapid magnetism when the current is
switched on.
B. Write True or False for the following statements.
1. An electric current can produce a heating effect but not a magnetic effect.
False.
2. The heating coils/elements of different electrical appliances are usually
made from copper or aluminum wires. False
3. When the current through a fuse wire exceeds its specified value, the fuse
wire melts and breaks. True.
4. Connecting many devices in a single socket is not likely to cause any
problem in a circuit. False
5. The strength of an electromagnet can be increased by decreasing the
number of turns of its coil. False.
C. Tick the correct option
1. When electric current flows through a filament of electric bulb, the
filament gives out – both heat and light energy.
2. A fuse wire is a wire of – high resistivity and low melting point.
3. We are more likely to observe a strong magnetic effect with a – current
carrying circular coil of many turns wound on a soft iron core.
4. A common house hold device, that uses an electromagnet in its working,
is – the electric bell.
5. A good electromagnet would – act like a magnet when the current is
on but would not do so when the current is off.
D. Answer the following questions in brief.
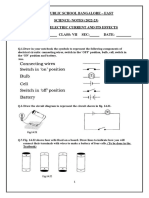
1. The bulb in the circuit shown in the figure does not glow. Why?
Redraw the circuit diagram by making the necessary changes in it, so
that the bulb starts glowing.
Ans. a) The two cells are not connected correctly.
b) And the switch is in the off position.
Because of these two reasons the bulb in the circuit is not glowing.
When the switch is in on position and the cells are connected properly, only
then the bulb will glow.
2. Name three practical devices based on the heating effect of current.
Ans. Electric toaster, geyser and electric iron, induction cooker, electric
kettle, electric heater etc.
3. Write two special characteristics of the wire needed for making the
element of an electric heater.
Ans. Element or heating coil is made up of nichrome because
a) It has a high melting point
b) It has a high resistivity
c) It can remain red hot for a long time without getting oxidized or burned
out.
4. Give the meaning of the terms ’short circuiting’ and ‘overloading’ in
an electric circuit.
Ans. Short circuiting – when hot wires touches conductive object its not
supposed to. It can lead to damage, electrical shock or even a fire.
Overloading – An overload occurs when your devices draw more electrical
power than a circuit can safely handle. i.e when more device is connected to
a socket.
5. Do you think an electromagnet can be used for separating plastic
bags from a garbage heap? Explain.
Ans. Electromagnets can be used only to pick up magnetic substance like
Iron, Nickel and Cobalt.
6. State any three applications of an electromagnet.
Ans. a) They are used in electric toys, electric bells, loudspeakers and
telephone diaphragms, MCB.
b) Giant electromagnets are used in mobile cranes to lift and transfer
heavy iron rods and machinery.
c) Doctors use tiny magnets to take out small devices of magnetic
materials that might have fallen in the eyes.
E. Answer the following questions.
1. The same amount of electric current flows through the connecting
wires and the bulb filament. However, it is only the filament that
glows. Why?
Ans. The filament of the bulb is made up of Tunsten which has some
special characteristics like
a) It has high melting point.
b) It becomes white –hot and glows brightly for a long time
c) Quiet stable and has a long life without getting burnt or oxidized.
The connecting wire do not have such characteristics. So it does not glow.
2. The brightness of light, emitted by a bulb, is observed to decrease
when an electric heater is connected in series with it. Suggest the likely
reason for this observation.
Ans. The voltage is divided into two parts, so the available voltage for the
bulb is less than 220V. The brightness of light emitted from the bulb will
decrease as some of the voltage will be cut off from the bulb in order to
provide full current to the heater. The heater needs more current to work
as compared to the bulb.
3. Suggest an experiment set up to illustrate the action of an electric
fuse.
Ans. To understand the working of
an electric fuse take a thin strip of
aluminum foil about 5 cm in length.
Fix its two ends on the tips of the
two nails placed vertically on the
table. Connect the two nails to a
battery through a plug key and a
small bulb. When the switch is put
on, the aluminum strip burns out
immediately. The circuit breaks and
current stops flowing. This is how an
electric fuse works using the heating
effect of current.
4. A novice electrician, while carrying out some repairs in Sumit’s house,
tried to put a piece of tungsten wire in a fuse. Sumits’s father on
noticing this, stopped him from doing so. Give reason as to why he did
that.
Ans. The role of the fuse wire is to melt and break the circuit when the
current exceeds a maximum safe value. If the wire get overheated or a
short circuit takes place, the device or gadget could get damaged and it can
also result in shock or fire as there is no fuse wire.
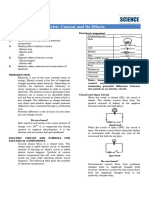
5. Draw a labelled diagram of an electric bell and explain its working.
Ans. Electric bell consists of a gong, an electromagnet, a soft iron rod or
armature and a contact screw.
WORKING:
• When current flows through the
electromagnet, it acquires
magnetism and attracts the
armature.
• As the armature bends towards the
electromagnet, the gong is struck.
At the same time, the contact
between the armature and the
contact screw breaks and the circuit
is switched off.
• The electromagnet loses its
magnetism and no longer attracts
the armature
• The armature gets pulled back to its original position by spring action
and circuit gets completed. The cycle repeats itself again and again and
the gong struck again and again
• Due to this alternate making and breaking of the circuit, the electric bell
keeps on ringing till the switch is pressed.
EXTRA QUESTIONS
Q1. Give reason
a) Filament in a bulb is made up of tungsten
Ans. The filament of the bulb is made up of tungsten because
d) It has high melting point.
e) It becomes white –hot and glows brightly for a long time
f) Quiet stable and has a long life without getting burnt or oxidized.
b) Fuse wire is made of an alloy of tin and lead.
• Ans. A fuse wire is made of an alloy of lead and tin because it has high
resistivity and low melting point. So when the wire gets overheated, the
fuse wire will melt and break the circuit preventing shock, fire or damage
to the appliances.
Q2. What is the heating effect of electric current called?
Ans. When electric current flows through electric devices, it produces heat
energy. This is known as Joule’s heating effect of electric current.
Q3. What is MCB? How does it work?
Ans. MCBs (Miniature circuit breakers) are electric switches which
automatically turn off when the current exceeds its safe limit. They work on
the basis of magnetic effect of current.
Q4. Differentiate between conductors and insulators.
Conductors Insulators
1.Materials that allow electricity to 1.Materials that do not allow
flow easily through them is called electricity to flow easily through
good conductors of electric current. them is called bad conductors of
2. These materials do not get electric current or insulators.
charged by rubbing. 2. These materials get charged by
3. Most of the metals are good rubbing.
conductors of electricity. 3. Most of the non-metals are bad
Ex. Iron, copper, Aluminum, silver, conductors of electricity.
Magnesium, Zinc, Ex. Plastic, rubber, wood, ebonite,
Q5.Write any two practical applications of electromagnet.
Ans. a) Electromagnets are used in electric toys, electric bells,
loudspeakers and telephone diaphragms, MCB.
b) Giant electromagnets are used in mobile cranes to lift and transfer
heavy iron rods and machinery.
You might also like
- Notes On Electricity For Grade 6Document4 pagesNotes On Electricity For Grade 6Robert Hooke100% (1)
- Science - 271020 - Electric Current Class 7 AssignmentDocument4 pagesScience - 271020 - Electric Current Class 7 AssignmentDeepak KansalNo ratings yet
- Ch-14 Electric Current and Its EffectsDocument5 pagesCh-14 Electric Current and Its Effectstanshikha dharNo ratings yet
- Electric Current and Its EffectsDocument4 pagesElectric Current and Its EffectsKunal SumukNo ratings yet
- Class Vii Notes For Electric Current and Its Effects-1.CleanedDocument5 pagesClass Vii Notes For Electric Current and Its Effects-1.CleanedarNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Circuits NotesDocument5 pagesElectricity and Circuits NotesThwayyiba PKNo ratings yet
- Electric Current & Its Heating EffectDocument6 pagesElectric Current & Its Heating EffectAshok SharmaNo ratings yet
- Electric Current & Its Effect HODocument7 pagesElectric Current & Its Effect HOchrisNo ratings yet
- Electric Current and Its EffectsDocument11 pagesElectric Current and Its EffectsRajeevSangam100% (1)
- G6 LM Science How Electric Energy Is ProducedDocument10 pagesG6 LM Science How Electric Energy Is ProducedJohniel BustamanteNo ratings yet
- Notes:: Electric Current & Its EffectsDocument2 pagesNotes:: Electric Current & Its EffectsJaynarayan HalderNo ratings yet
- Electric Current and Its EffectDocument21 pagesElectric Current and Its EffectPrisha SwamNo ratings yet
- Electric Current and Its Effects - NoteDocument6 pagesElectric Current and Its Effects - NoteToshit Kumar NaikNo ratings yet
- (Class 6) CH - Electricity and CircuitsDocument3 pages(Class 6) CH - Electricity and CircuitsSnigdha GoelNo ratings yet
- (Class 6th) Electricity and Circuits 2Document2 pages(Class 6th) Electricity and Circuits 2Snigdha GoelNo ratings yet
- Vi Physics WorksheetDocument4 pagesVi Physics WorksheetpodhigaifarmNo ratings yet
- Class 7 Electric Current and Its EffectsDocument3 pagesClass 7 Electric Current and Its EffectsNitesh KohliNo ratings yet
- 14 Electric Current and Its EffectsDocument10 pages14 Electric Current and Its EffectsSnehil VargheseNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 14: Electric Current and Its EffectsDocument10 pagesChapter - 14: Electric Current and Its EffectsDhruv GuptaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12: Electricity and Circuits: Manav Mangal School Class: VI Subject: ScienceDocument7 pagesChapter 12: Electricity and Circuits: Manav Mangal School Class: VI Subject: ScienceSAMAR PRATAP SINGHNo ratings yet
- 7th Physics, Lesson-7, Electricity and MagnetismDocument5 pages7th Physics, Lesson-7, Electricity and MagnetismmilliNo ratings yet
- Class 7 Science Electric Current and Its Effect-1 PDFDocument21 pagesClass 7 Science Electric Current and Its Effect-1 PDFMaya Munaiseche100% (4)
- Living Science Electric Current and Its Effects: AnswerDocument11 pagesLiving Science Electric Current and Its Effects: AnswerNaitik SinghNo ratings yet
- Grade-Vi Science - Worksheet Term-2 Ch-12-Electricity and CircuitsDocument4 pagesGrade-Vi Science - Worksheet Term-2 Ch-12-Electricity and CircuitsmohinderNo ratings yet
- c6bb1b6c 1666238234618Document7 pagesc6bb1b6c 1666238234618HarishNo ratings yet
- Extra Questions - Chapter 14Document3 pagesExtra Questions - Chapter 14rachna sharmaNo ratings yet
- Electricity and MagnetismDocument25 pagesElectricity and Magnetismdikshamachale.2549No ratings yet
- Learners' Packet Science 5 Week 7 - 8 NAME - GRADE/SECTIONDocument6 pagesLearners' Packet Science 5 Week 7 - 8 NAME - GRADE/SECTIONRosemarie Mañabo RamirezNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Circuits NotesDocument5 pagesElectricity and Circuits Noteskarthikkrishna12300No ratings yet
- Electricity and ElectromagnetsDocument27 pagesElectricity and ElectromagnetsVerniel Jason JimenezNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Circuits - Question and Answers: Answer The FollowingDocument5 pagesElectricity and Circuits - Question and Answers: Answer The FollowingkashviNo ratings yet
- G7 CBSE - Electric Current and Its Effects - ANAND KUMARDocument2 pagesG7 CBSE - Electric Current and Its Effects - ANAND KUMARAnandNo ratings yet
- Study Notes - Electricity and Circuits - Science Class 6 PDF DownloadDocument5 pagesStudy Notes - Electricity and Circuits - Science Class 6 PDF DownloadruchikaNo ratings yet
- Afe Babalola University: Name: Ogbapu Emmanuel UmefienDocument11 pagesAfe Babalola University: Name: Ogbapu Emmanuel UmefienTomi FapohundaNo ratings yet
- Notes - Electricity (Mick)Document10 pagesNotes - Electricity (Mick)SoniaNo ratings yet
- Household AppliancesDocument32 pagesHousehold Appliancesbhaskar51178No ratings yet
- Chapter 12. Electricity and Circuits: Very Short Q&ADocument8 pagesChapter 12. Electricity and Circuits: Very Short Q&ASubhojit MitraNo ratings yet
- CH 16 Electric Current and Simple CircuitsDocument3 pagesCH 16 Electric Current and Simple CircuitsLionel DsouzaNo ratings yet
- Science Grade 4 Unit 5 Making CircuitsDocument9 pagesScience Grade 4 Unit 5 Making CircuitsPhairouse Abdul SalamNo ratings yet
- Electric Current and Circuits NotesDocument9 pagesElectric Current and Circuits Notes13srivastava.nimishaNo ratings yet
- Electricity Class Notes Latest 21.10. 2019Document3 pagesElectricity Class Notes Latest 21.10. 2019bittuchintuNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 CHP 14 NotesDocument6 pagesGrade 7 CHP 14 Notesclass7science iisjNo ratings yet
- Electricity..class 7thDocument4 pagesElectricity..class 7thAyush Soni 7:- परिश्रम 3678No ratings yet
- Model Rocket Launch SystemsDocument18 pagesModel Rocket Launch SystemsAviation/Space History Library100% (1)
- Electricity and MagnetismDocument17 pagesElectricity and Magnetismaddy 05No ratings yet
- Electricity and MagnetismDocument42 pagesElectricity and Magnetismthunder32xNo ratings yet
- Electric Current and Its EffectsDocument22 pagesElectric Current and Its EffectsJatin GuptaNo ratings yet
- 2022 01 05 VI Science 1Document4 pages2022 01 05 VI Science 1KITE GLOBALNo ratings yet
- Project ReportDocument7 pagesProject ReportGaganpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Notes Electric Current and Its Effects GR 7Document9 pagesNotes Electric Current and Its Effects GR 7minecraftpriyansh232No ratings yet
- CLASS 7 Chapter 14-Electric Current and Its Effects HW1Document5 pagesCLASS 7 Chapter 14-Electric Current and Its Effects HW1shresthamajumdar9No ratings yet
- Class 7 Science Electric Current and Its EffectsDocument7 pagesClass 7 Science Electric Current and Its Effectsshanna_heenaNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 3 - Module 6: Factors Affecting The Strength of An ElectromagnetDocument12 pagesScience: Quarter 3 - Module 6: Factors Affecting The Strength of An ElectromagnetChester Allan EduriaNo ratings yet
- Learners' Packet Science 5 Week 7 - 8: Learning ActivitiesDocument4 pagesLearners' Packet Science 5 Week 7 - 8: Learning ActivitiesRosemarie Mañabo RamirezNo ratings yet
- ElectromagnetsDocument13 pagesElectromagnetsM Rameez Ul HassanNo ratings yet
- 3 Effects of Electric Current Physics ProjectDocument20 pages3 Effects of Electric Current Physics ProjectAkshatNo ratings yet
- Iron SteelDocument2 pagesIron SteelKira NguyễnNo ratings yet
- PPPPPPDocument3 pagesPPPPPPGOD OF GLITCH.No ratings yet
- Electric PowerDocument36 pagesElectric PowerfruqaiyahamzaNo ratings yet
- Motion Picture Operation, Stage Electrics and Illusions: A Practical Hand-book and Guide for Theater Electricians, Motion Picture Operators and Managers of Theaters and ProductionsFrom EverandMotion Picture Operation, Stage Electrics and Illusions: A Practical Hand-book and Guide for Theater Electricians, Motion Picture Operators and Managers of Theaters and ProductionsNo ratings yet