Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
38 viewsGraph Skills 1: Hooke's Law: Mass (G) Load (N) Length (CM) Extension (CM)
Graph Skills 1: Hooke's Law: Mass (G) Load (N) Length (CM) Extension (CM)
Uploaded by
athenalavegaThis document provides data and instructions for an experiment on Hooke's law using a spring. It includes a table of mass, load, length, and extension measurements for various loads applied to a spring. A graph is plotted of load versus extension from the data. A line of best fit is drawn and its gradient calculated. The force constant of the spring is calculated as the reciprocal of the gradient.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Stephen Skinner - Sacred Geometry - Deciphering The Code (2006, Sterling Publishing) - Libgen - LiDocument168 pagesStephen Skinner - Sacred Geometry - Deciphering The Code (2006, Sterling Publishing) - Libgen - Lihminyvr100% (1)
- Oedemeter Consolidation TestDocument24 pagesOedemeter Consolidation Testyashas sNo ratings yet
- Cfroi HoltDocument7 pagesCfroi Holtamro_baryNo ratings yet
- CSEC Physics Jan 2012 P2Document16 pagesCSEC Physics Jan 2012 P2Clendon Donai0% (1)
- Tutorial SACS PDFDocument81 pagesTutorial SACS PDFRidho Ziska100% (1)
- Rules For DimensioningDocument2 pagesRules For DimensioningZakir Qureshi85% (13)
- CSC 472Document151 pagesCSC 472Han LinNo ratings yet
- TAILLOADDocument1 pageTAILLOADRuben Bartolome GarciaNo ratings yet
- Experiment Worksheet: Acceleration of Free Fall: A-Level Physics HQDocument4 pagesExperiment Worksheet: Acceleration of Free Fall: A-Level Physics HQPhatima Yadira Dimas LópezNo ratings yet
- Datos para Curvas Ifd: Curvas I.F.D ModalidadDocument4 pagesDatos para Curvas Ifd: Curvas I.F.D ModalidadFernanda SierraNo ratings yet
- Perhitungan Gaya Lateral Daerah Banda Aceh Tinggi 3.5Document2 pagesPerhitungan Gaya Lateral Daerah Banda Aceh Tinggi 3.5Jauhari Pras SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Group E Advanced Soil Mechanics CourseworkDocument21 pagesGroup E Advanced Soil Mechanics CourseworkJimmyNo ratings yet
- EXP: Spring Stiffness Test: Experiment GDocument13 pagesEXP: Spring Stiffness Test: Experiment GAditya KoutharapuNo ratings yet
- Producción Histórica (Cangallo, Huamanga, Huanta, Victor Fajardoy Parinacohas)Document4 pagesProducción Histórica (Cangallo, Huamanga, Huanta, Victor Fajardoy Parinacohas)Roly B GutierrezNo ratings yet
- EC340 DEC150 Assign1Document3 pagesEC340 DEC150 Assign1Cholwe Essau MbilimaNo ratings yet
- Calc SheetDocument69 pagesCalc SheetElda Adriani SimarmataNo ratings yet
- Chapter3 First Application Linear RegressionDocument8 pagesChapter3 First Application Linear RegressionPaterson NguepiNo ratings yet
- A Presentation ON "Fragility Analysis of RCC Building": Presented by Dinesh Sakhakarmi (ME/076/03)Document32 pagesA Presentation ON "Fragility Analysis of RCC Building": Presented by Dinesh Sakhakarmi (ME/076/03)Sarrows PrazzapatiNo ratings yet
- Investigation of Newton's Seocnd LawDocument5 pagesInvestigation of Newton's Seocnd Lawhellomeme11235No ratings yet
- Kami Export - Practice - Graphing Uniform AccelerationDocument5 pagesKami Export - Practice - Graphing Uniform AccelerationSantiago CastroNo ratings yet
- CV313 Assignment 2 - 2024Document2 pagesCV313 Assignment 2 - 2024nelsondeo111No ratings yet
- Form 3: Physics Paper 3 Marking SchemsDocument4 pagesForm 3: Physics Paper 3 Marking SchemsBenjamin mwanikiNo ratings yet
- Tutorial MaterialDocument12 pagesTutorial MaterialYamada Takeshi100% (2)
- 1-Way Slab Calc SheetDocument19 pages1-Way Slab Calc Sheetfeiz asgarNo ratings yet
- Highway Laboratory Civil Engineering Department: Practical 1: Elongation Index TestDocument2 pagesHighway Laboratory Civil Engineering Department: Practical 1: Elongation Index TestKayaNo ratings yet
- Force Vs Stretch of A Cylindrical Spring: Wwwwwwgraphical AnalysisDocument15 pagesForce Vs Stretch of A Cylindrical Spring: Wwwwwwgraphical AnalysisAlberto A.No ratings yet
- Informe de LaboratorioDocument12 pagesInforme de Laboratorioana palaciosNo ratings yet
- Practica N°08Document1 pagePractica N°08Juancho TusinNo ratings yet
- Principles of Foundation Engineering Ch03Document12 pagesPrinciples of Foundation Engineering Ch03Lee Jia HoeNo ratings yet
- ConsolidationDocument9 pagesConsolidationmouazam KhalidNo ratings yet
- Results & DiscussionDocument6 pagesResults & DiscussionSung Tze LauNo ratings yet
- Am2540 - Applied Mechanics Lab Solid Mechanics Lab ReportDocument13 pagesAm2540 - Applied Mechanics Lab Solid Mechanics Lab ReportAditya KoutharapuNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 Lab Report GuidanceDocument5 pagesExperiment 2 Lab Report GuidanceFatin FarwizahNo ratings yet
- Module D1 Strain Measurement in Bending System I. Data Computations A. Data ResultsDocument6 pagesModule D1 Strain Measurement in Bending System I. Data Computations A. Data ResultsAlifia T. OviningtyasNo ratings yet
- Second Mid-Term Examination (23%) Vii Sem, 2018 - 19Document2 pagesSecond Mid-Term Examination (23%) Vii Sem, 2018 - 19Kartik ModiNo ratings yet
- ANTAI Calculation 40m Per Second ASCE 7-10Document13 pagesANTAI Calculation 40m Per Second ASCE 7-10Yên BìnhNo ratings yet
- The Following Table Can Now Be Prepared.: SolutionDocument1 pageThe Following Table Can Now Be Prepared.: SolutionAdeel NizamiNo ratings yet
- CE 410 Final Exam (Hydrology) PDFDocument2 pagesCE 410 Final Exam (Hydrology) PDFKingwinston OmbionNo ratings yet
- Taller 4 GeotecniaDocument5 pagesTaller 4 GeotecniaJesus RedondoNo ratings yet
- Lab Thermal Free and Forced ConvectionDocument17 pagesLab Thermal Free and Forced ConvectionHAZMIERA AMRISYA HASLANNo ratings yet
- 15 PJ189 - Piling Form - 101122Document15 pages15 PJ189 - Piling Form - 101122Haritah HakimiNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 6Document4 pagesProblem Set 6PeaceNo ratings yet
- Earthwork For Proposed RoadDocument4 pagesEarthwork For Proposed RoadAh RashedNo ratings yet
- Soil Assign PDFDocument7 pagesSoil Assign PDFtilahun Mersha0% (1)
- 1) Background Information: Hooke's Law Experiment Data, Analysis and ConclusionsDocument5 pages1) Background Information: Hooke's Law Experiment Data, Analysis and ConclusionsEgedikilitasNo ratings yet
- Procedure: Fig.1: The Experimental ApparatusDocument3 pagesProcedure: Fig.1: The Experimental ApparatusFabeha KhanNo ratings yet
- Condition of The Atmosphere: StabilityDocument16 pagesCondition of The Atmosphere: StabilitysNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 3 - Edm Calibration: AbstractDocument2 pagesLab Report 3 - Edm Calibration: AbstractAman JainNo ratings yet
- Gaussian DispersionDocument17 pagesGaussian DispersionSaptarshi MajiNo ratings yet
- X52, X65 Weight ExtrapolationDocument4 pagesX52, X65 Weight ExtrapolationsivaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument6 pagesUntitled김서현 / 학생 / 기계공학부No ratings yet
- Heights With Time Taken To Hit The Ground (Line of Best Fit)Document2 pagesHeights With Time Taken To Hit The Ground (Line of Best Fit)Lee EnNo ratings yet
- Source: Jocelny Blink. Economics Course Companion, Second Edition. Oxford University Press 2011, 2012. P259 Figure 16.15Document13 pagesSource: Jocelny Blink. Economics Course Companion, Second Edition. Oxford University Press 2011, 2012. P259 Figure 16.15Esther WangNo ratings yet
- Stability Calculation of Abutment: ProjectDocument10 pagesStability Calculation of Abutment: ProjectJames McguireNo ratings yet
- GROUP 4 - Force and WorkDocument7 pagesGROUP 4 - Force and Workmeia quiderNo ratings yet
- Lampiran 2 Pile and Soil Capacity RevcDocument145 pagesLampiran 2 Pile and Soil Capacity RevcEndiarto Budi RaharjoNo ratings yet
- Column Load CalculationsDocument10 pagesColumn Load Calculationsatta-e-mustafaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document5 pagesAssignment 1s11197376No ratings yet
- TEK HIDROSTATIS MolanaDocument5 pagesTEK HIDROSTATIS MolanaHabib Al AhmadNo ratings yet
- Bombas MoodyDocument6 pagesBombas MoodyAlexCardoso1990No ratings yet
- 3FICADocument2 pages3FICAWilson Moises Perez RonzaNo ratings yet
- Driver Alert System Based On Eye RecognitionDocument20 pagesDriver Alert System Based On Eye Recognitionhostel boysNo ratings yet
- 2015 Call For Chapters IGI Global Handbook of ResearchDocument2 pages2015 Call For Chapters IGI Global Handbook of ResearchLaura JacksonNo ratings yet
- Syntax of 8086Document10 pagesSyntax of 8086ashashekarNo ratings yet
- Lab Activity 8 and 9 Class IxDocument4 pagesLab Activity 8 and 9 Class IxSiddhant NarayanNo ratings yet
- Maths IADocument10 pagesMaths IAkarenNo ratings yet
- Theory of Combustion PDFDocument9 pagesTheory of Combustion PDFMuthu Kumar100% (1)
- Assignment 2Document6 pagesAssignment 2gowricivilNo ratings yet
- Community Succession Simulation: Surviving Drought: 2023 Mcm/Icm Summary SheetDocument25 pagesCommunity Succession Simulation: Surviving Drought: 2023 Mcm/Icm Summary Sheet251513144No ratings yet
- NMAT Physics Guide: Topics and AnswersDocument5 pagesNMAT Physics Guide: Topics and AnswersCiullaeNo ratings yet
- Notes M1 MPG Unit 1Document21 pagesNotes M1 MPG Unit 1aishaNo ratings yet
- Laporan Modul 3Document12 pagesLaporan Modul 3IqbalNo ratings yet
- DequeDocument5 pagesDequeirinarmNo ratings yet
- Exam 2004Document20 pagesExam 2004kib6707No ratings yet
- Operating SystemDocument2 pagesOperating SystemNijin Vinod0% (1)
- C5-Equilibrium Part IIDocument11 pagesC5-Equilibrium Part IImaran.suguNo ratings yet
- Dissertation GaussDocument4 pagesDissertation GaussBuyCheapPapersSavannah100% (1)
- Ta ZC164 Ec-3r Second Sem 2015-2016Document3 pagesTa ZC164 Ec-3r Second Sem 2015-2016SatheeskumarNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics Chapter 6Document21 pagesMicroeconomics Chapter 6Fazila GirkarNo ratings yet
- Maths Y8 5Document2 pagesMaths Y8 5sNo ratings yet
- Jaime Sandoval Real EstateDocument3 pagesJaime Sandoval Real EstateJaime R. SandovalNo ratings yet
- Old FAA-9A PDFDocument551 pagesOld FAA-9A PDFzafarequbal686No ratings yet
- The Indexing or Dividing HeadDocument55 pagesThe Indexing or Dividing HeadShrinivas BhatNo ratings yet
- GRD 6 Maths Paper 1Document11 pagesGRD 6 Maths Paper 1addyNo ratings yet
- AsdDocument16 pagesAsdjossNo ratings yet
- Chap 4 - Digital Communication System For Communication EngineeringDocument47 pagesChap 4 - Digital Communication System For Communication Engineeringmiz_student9067% (3)
- Dynamic Programming:: Example 1: Assembly Line Scheduling. InstanceDocument14 pagesDynamic Programming:: Example 1: Assembly Line Scheduling. Instancekaustubh2008satputeNo ratings yet
- Math BDocument4 pagesMath BedylopezchangNo ratings yet
Graph Skills 1: Hooke's Law: Mass (G) Load (N) Length (CM) Extension (CM)
Graph Skills 1: Hooke's Law: Mass (G) Load (N) Length (CM) Extension (CM)
Uploaded by
athenalavega0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
38 views2 pagesThis document provides data and instructions for an experiment on Hooke's law using a spring. It includes a table of mass, load, length, and extension measurements for various loads applied to a spring. A graph is plotted of load versus extension from the data. A line of best fit is drawn and its gradient calculated. The force constant of the spring is calculated as the reciprocal of the gradient.
Original Description:
Original Title
ALevelPhysicsGraphSkills1Hookeslaw-2 (2)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides data and instructions for an experiment on Hooke's law using a spring. It includes a table of mass, load, length, and extension measurements for various loads applied to a spring. A graph is plotted of load versus extension from the data. A line of best fit is drawn and its gradient calculated. The force constant of the spring is calculated as the reciprocal of the gradient.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
38 views2 pagesGraph Skills 1: Hooke's Law: Mass (G) Load (N) Length (CM) Extension (CM)
Graph Skills 1: Hooke's Law: Mass (G) Load (N) Length (CM) Extension (CM)
Uploaded by
athenalavegaThis document provides data and instructions for an experiment on Hooke's law using a spring. It includes a table of mass, load, length, and extension measurements for various loads applied to a spring. A graph is plotted of load versus extension from the data. A line of best fit is drawn and its gradient calculated. The force constant of the spring is calculated as the reciprocal of the gradient.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
A-Level Physics HQ
Graph Skills 1 : Hooke’s Law
1. Complete this table of data and then plot the results onto the graph grid below by using an
appropriate set of scales on the axes.
Mass (g) Load (N) Length (cm) Extension (cm)
0 2.2
100 5.6
200 9.1
300 12.7
400 15.5
500 19.1
600 23.0
Load (y-axis) against Extension (x-axis)
Load = mass in kg × 9.81
Extension = length – original length (original length is length for load = 0 N)
2. Draw a straight line of best t.
3. Calculate the force constant of the spring (equal to the reciprocal of the gradient of the line).
–– © Daniel Wilson 2018 ––
fi
A-Level Physics HQ
Graph Skills 1 Solutions
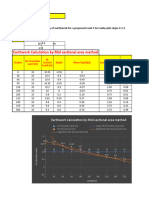
1. Table of data.
Mass (g) Load (N) Length (cm) Extension (cm)
0 0.0 2.2 0.0
100 1.0 5.6 3.4
200 2.0 9.1 6.9
300 2.9 12.7 10.5
400 3.9 15.5 13.3
500 4.9 19.1 16.9
600 5.9 23.0 20.8
2. Graph with line of best t.
25
(5.9,20.5)
20
15
Extension (cm)
10
Gradient triangle in pink
(0,0)
0
0.0 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0 6.0
Load (N)
3. Calculate gradient: gradient = (y2 – y1) ÷ (x2 – x1) = (20.5–0) ÷ (5.9–0) = 3.47
Force constant: k = 1 ÷ gradient = 0.29 N cm–1
–– © Daniel Wilson 2018 ––
fi
You might also like
- Stephen Skinner - Sacred Geometry - Deciphering The Code (2006, Sterling Publishing) - Libgen - LiDocument168 pagesStephen Skinner - Sacred Geometry - Deciphering The Code (2006, Sterling Publishing) - Libgen - Lihminyvr100% (1)
- Oedemeter Consolidation TestDocument24 pagesOedemeter Consolidation Testyashas sNo ratings yet
- Cfroi HoltDocument7 pagesCfroi Holtamro_baryNo ratings yet
- CSEC Physics Jan 2012 P2Document16 pagesCSEC Physics Jan 2012 P2Clendon Donai0% (1)
- Tutorial SACS PDFDocument81 pagesTutorial SACS PDFRidho Ziska100% (1)
- Rules For DimensioningDocument2 pagesRules For DimensioningZakir Qureshi85% (13)
- CSC 472Document151 pagesCSC 472Han LinNo ratings yet
- TAILLOADDocument1 pageTAILLOADRuben Bartolome GarciaNo ratings yet
- Experiment Worksheet: Acceleration of Free Fall: A-Level Physics HQDocument4 pagesExperiment Worksheet: Acceleration of Free Fall: A-Level Physics HQPhatima Yadira Dimas LópezNo ratings yet
- Datos para Curvas Ifd: Curvas I.F.D ModalidadDocument4 pagesDatos para Curvas Ifd: Curvas I.F.D ModalidadFernanda SierraNo ratings yet
- Perhitungan Gaya Lateral Daerah Banda Aceh Tinggi 3.5Document2 pagesPerhitungan Gaya Lateral Daerah Banda Aceh Tinggi 3.5Jauhari Pras SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Group E Advanced Soil Mechanics CourseworkDocument21 pagesGroup E Advanced Soil Mechanics CourseworkJimmyNo ratings yet
- EXP: Spring Stiffness Test: Experiment GDocument13 pagesEXP: Spring Stiffness Test: Experiment GAditya KoutharapuNo ratings yet
- Producción Histórica (Cangallo, Huamanga, Huanta, Victor Fajardoy Parinacohas)Document4 pagesProducción Histórica (Cangallo, Huamanga, Huanta, Victor Fajardoy Parinacohas)Roly B GutierrezNo ratings yet
- EC340 DEC150 Assign1Document3 pagesEC340 DEC150 Assign1Cholwe Essau MbilimaNo ratings yet
- Calc SheetDocument69 pagesCalc SheetElda Adriani SimarmataNo ratings yet
- Chapter3 First Application Linear RegressionDocument8 pagesChapter3 First Application Linear RegressionPaterson NguepiNo ratings yet
- A Presentation ON "Fragility Analysis of RCC Building": Presented by Dinesh Sakhakarmi (ME/076/03)Document32 pagesA Presentation ON "Fragility Analysis of RCC Building": Presented by Dinesh Sakhakarmi (ME/076/03)Sarrows PrazzapatiNo ratings yet
- Investigation of Newton's Seocnd LawDocument5 pagesInvestigation of Newton's Seocnd Lawhellomeme11235No ratings yet
- Kami Export - Practice - Graphing Uniform AccelerationDocument5 pagesKami Export - Practice - Graphing Uniform AccelerationSantiago CastroNo ratings yet
- CV313 Assignment 2 - 2024Document2 pagesCV313 Assignment 2 - 2024nelsondeo111No ratings yet
- Form 3: Physics Paper 3 Marking SchemsDocument4 pagesForm 3: Physics Paper 3 Marking SchemsBenjamin mwanikiNo ratings yet
- Tutorial MaterialDocument12 pagesTutorial MaterialYamada Takeshi100% (2)
- 1-Way Slab Calc SheetDocument19 pages1-Way Slab Calc Sheetfeiz asgarNo ratings yet
- Highway Laboratory Civil Engineering Department: Practical 1: Elongation Index TestDocument2 pagesHighway Laboratory Civil Engineering Department: Practical 1: Elongation Index TestKayaNo ratings yet
- Force Vs Stretch of A Cylindrical Spring: Wwwwwwgraphical AnalysisDocument15 pagesForce Vs Stretch of A Cylindrical Spring: Wwwwwwgraphical AnalysisAlberto A.No ratings yet
- Informe de LaboratorioDocument12 pagesInforme de Laboratorioana palaciosNo ratings yet
- Practica N°08Document1 pagePractica N°08Juancho TusinNo ratings yet
- Principles of Foundation Engineering Ch03Document12 pagesPrinciples of Foundation Engineering Ch03Lee Jia HoeNo ratings yet
- ConsolidationDocument9 pagesConsolidationmouazam KhalidNo ratings yet
- Results & DiscussionDocument6 pagesResults & DiscussionSung Tze LauNo ratings yet
- Am2540 - Applied Mechanics Lab Solid Mechanics Lab ReportDocument13 pagesAm2540 - Applied Mechanics Lab Solid Mechanics Lab ReportAditya KoutharapuNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 Lab Report GuidanceDocument5 pagesExperiment 2 Lab Report GuidanceFatin FarwizahNo ratings yet
- Module D1 Strain Measurement in Bending System I. Data Computations A. Data ResultsDocument6 pagesModule D1 Strain Measurement in Bending System I. Data Computations A. Data ResultsAlifia T. OviningtyasNo ratings yet
- Second Mid-Term Examination (23%) Vii Sem, 2018 - 19Document2 pagesSecond Mid-Term Examination (23%) Vii Sem, 2018 - 19Kartik ModiNo ratings yet
- ANTAI Calculation 40m Per Second ASCE 7-10Document13 pagesANTAI Calculation 40m Per Second ASCE 7-10Yên BìnhNo ratings yet
- The Following Table Can Now Be Prepared.: SolutionDocument1 pageThe Following Table Can Now Be Prepared.: SolutionAdeel NizamiNo ratings yet
- CE 410 Final Exam (Hydrology) PDFDocument2 pagesCE 410 Final Exam (Hydrology) PDFKingwinston OmbionNo ratings yet
- Taller 4 GeotecniaDocument5 pagesTaller 4 GeotecniaJesus RedondoNo ratings yet
- Lab Thermal Free and Forced ConvectionDocument17 pagesLab Thermal Free and Forced ConvectionHAZMIERA AMRISYA HASLANNo ratings yet
- 15 PJ189 - Piling Form - 101122Document15 pages15 PJ189 - Piling Form - 101122Haritah HakimiNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 6Document4 pagesProblem Set 6PeaceNo ratings yet
- Earthwork For Proposed RoadDocument4 pagesEarthwork For Proposed RoadAh RashedNo ratings yet
- Soil Assign PDFDocument7 pagesSoil Assign PDFtilahun Mersha0% (1)
- 1) Background Information: Hooke's Law Experiment Data, Analysis and ConclusionsDocument5 pages1) Background Information: Hooke's Law Experiment Data, Analysis and ConclusionsEgedikilitasNo ratings yet
- Procedure: Fig.1: The Experimental ApparatusDocument3 pagesProcedure: Fig.1: The Experimental ApparatusFabeha KhanNo ratings yet
- Condition of The Atmosphere: StabilityDocument16 pagesCondition of The Atmosphere: StabilitysNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 3 - Edm Calibration: AbstractDocument2 pagesLab Report 3 - Edm Calibration: AbstractAman JainNo ratings yet
- Gaussian DispersionDocument17 pagesGaussian DispersionSaptarshi MajiNo ratings yet
- X52, X65 Weight ExtrapolationDocument4 pagesX52, X65 Weight ExtrapolationsivaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument6 pagesUntitled김서현 / 학생 / 기계공학부No ratings yet
- Heights With Time Taken To Hit The Ground (Line of Best Fit)Document2 pagesHeights With Time Taken To Hit The Ground (Line of Best Fit)Lee EnNo ratings yet
- Source: Jocelny Blink. Economics Course Companion, Second Edition. Oxford University Press 2011, 2012. P259 Figure 16.15Document13 pagesSource: Jocelny Blink. Economics Course Companion, Second Edition. Oxford University Press 2011, 2012. P259 Figure 16.15Esther WangNo ratings yet
- Stability Calculation of Abutment: ProjectDocument10 pagesStability Calculation of Abutment: ProjectJames McguireNo ratings yet
- GROUP 4 - Force and WorkDocument7 pagesGROUP 4 - Force and Workmeia quiderNo ratings yet
- Lampiran 2 Pile and Soil Capacity RevcDocument145 pagesLampiran 2 Pile and Soil Capacity RevcEndiarto Budi RaharjoNo ratings yet
- Column Load CalculationsDocument10 pagesColumn Load Calculationsatta-e-mustafaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document5 pagesAssignment 1s11197376No ratings yet
- TEK HIDROSTATIS MolanaDocument5 pagesTEK HIDROSTATIS MolanaHabib Al AhmadNo ratings yet
- Bombas MoodyDocument6 pagesBombas MoodyAlexCardoso1990No ratings yet
- 3FICADocument2 pages3FICAWilson Moises Perez RonzaNo ratings yet
- Driver Alert System Based On Eye RecognitionDocument20 pagesDriver Alert System Based On Eye Recognitionhostel boysNo ratings yet
- 2015 Call For Chapters IGI Global Handbook of ResearchDocument2 pages2015 Call For Chapters IGI Global Handbook of ResearchLaura JacksonNo ratings yet
- Syntax of 8086Document10 pagesSyntax of 8086ashashekarNo ratings yet
- Lab Activity 8 and 9 Class IxDocument4 pagesLab Activity 8 and 9 Class IxSiddhant NarayanNo ratings yet
- Maths IADocument10 pagesMaths IAkarenNo ratings yet
- Theory of Combustion PDFDocument9 pagesTheory of Combustion PDFMuthu Kumar100% (1)
- Assignment 2Document6 pagesAssignment 2gowricivilNo ratings yet
- Community Succession Simulation: Surviving Drought: 2023 Mcm/Icm Summary SheetDocument25 pagesCommunity Succession Simulation: Surviving Drought: 2023 Mcm/Icm Summary Sheet251513144No ratings yet
- NMAT Physics Guide: Topics and AnswersDocument5 pagesNMAT Physics Guide: Topics and AnswersCiullaeNo ratings yet
- Notes M1 MPG Unit 1Document21 pagesNotes M1 MPG Unit 1aishaNo ratings yet
- Laporan Modul 3Document12 pagesLaporan Modul 3IqbalNo ratings yet
- DequeDocument5 pagesDequeirinarmNo ratings yet
- Exam 2004Document20 pagesExam 2004kib6707No ratings yet
- Operating SystemDocument2 pagesOperating SystemNijin Vinod0% (1)
- C5-Equilibrium Part IIDocument11 pagesC5-Equilibrium Part IImaran.suguNo ratings yet
- Dissertation GaussDocument4 pagesDissertation GaussBuyCheapPapersSavannah100% (1)
- Ta ZC164 Ec-3r Second Sem 2015-2016Document3 pagesTa ZC164 Ec-3r Second Sem 2015-2016SatheeskumarNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics Chapter 6Document21 pagesMicroeconomics Chapter 6Fazila GirkarNo ratings yet
- Maths Y8 5Document2 pagesMaths Y8 5sNo ratings yet
- Jaime Sandoval Real EstateDocument3 pagesJaime Sandoval Real EstateJaime R. SandovalNo ratings yet
- Old FAA-9A PDFDocument551 pagesOld FAA-9A PDFzafarequbal686No ratings yet
- The Indexing or Dividing HeadDocument55 pagesThe Indexing or Dividing HeadShrinivas BhatNo ratings yet
- GRD 6 Maths Paper 1Document11 pagesGRD 6 Maths Paper 1addyNo ratings yet
- AsdDocument16 pagesAsdjossNo ratings yet
- Chap 4 - Digital Communication System For Communication EngineeringDocument47 pagesChap 4 - Digital Communication System For Communication Engineeringmiz_student9067% (3)
- Dynamic Programming:: Example 1: Assembly Line Scheduling. InstanceDocument14 pagesDynamic Programming:: Example 1: Assembly Line Scheduling. Instancekaustubh2008satputeNo ratings yet
- Math BDocument4 pagesMath BedylopezchangNo ratings yet