Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Exponent Properties
Exponent Properties
Uploaded by
nkatekodawn72Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Exponent Properties
Exponent Properties
Uploaded by
nkatekodawn72Copyright:
Available Formats
Exponent Properties
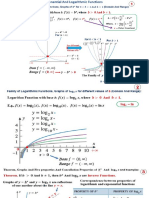
1. Product of like bases: a m a n a m n
To multiply powers with the same base, add the exponents and keep the common base.
Example:
am
2. Quotient of like bases: a m n
an
To divide powers with the same base, subtract the exponents and keep the common base.
Example:
3. Power to a power: (a m ) n a mn
To raise a power to a power, keep the base and multiply the exponents.
Example:
4. Product to a power: (ab) m a mb m
To raise a product to a power, raise each factor to the power.
Example:
an an
5. Quotient to a power n
b b
To raise a quotient to a power, raise the numerator and the denominator to the power.
Example: ( )
6. Zero Exponent: a0 1
Any number raised to the zero power is equal to “1”.
Examples:
1
7. Negative exponent: a n
an
Unhappy (negative) exponents will become happy (positive) by having the base/exponent pair “switch
floors”. Another way to interpret this: negative exponents mean to write the reciprocal of the original,
making the exponent positive.
Examples: ( ) ( )
You might also like
- Autocad Subassembly Composer ExpressionsDocument17 pagesAutocad Subassembly Composer ExpressionsMervin Bocatcat67% (3)
- Laws of ExponentsDocument13 pagesLaws of ExponentsEdralyn SegubienseNo ratings yet
- Exponents ReviewDocument2 pagesExponents Reviewapi-375918702No ratings yet
- TNR BIA Lecture Notes 5.3Document4 pagesTNR BIA Lecture Notes 5.3madridamayaeNo ratings yet
- Power and ExponentsDocument9 pagesPower and ExponentsPranav GirheNo ratings yet
- Exponents Radicals and Radical EquationsDocument38 pagesExponents Radicals and Radical EquationsBrent Harvey MagnoNo ratings yet
- Probs On Equivalent ForcesDocument20 pagesProbs On Equivalent Forcesvat007No ratings yet
- Properties of Exponents in Multiplication Expressions CK-12 Foundation 2Document1 pageProperties of Exponents in Multiplication Expressions CK-12 Foundation 2Ace Jaypee TorralbaNo ratings yet
- 7.2 - Exponents and Logarithms - Blank NotesDocument30 pages7.2 - Exponents and Logarithms - Blank Notesld745150No ratings yet
- 1.3 - Axioms For The Real NumbersDocument38 pages1.3 - Axioms For The Real NumbersAnkur TiwariNo ratings yet
- Elementary AlgebraDocument9 pagesElementary AlgebraSrikant AcharyNo ratings yet
- Rational ExponentDocument7 pagesRational ExponentAmiel Marie M. CalpitoNo ratings yet
- Net Force Worksheet: Name - DateDocument3 pagesNet Force Worksheet: Name - DateNubar MammadovaNo ratings yet
- Exponents and RadicalsDocument27 pagesExponents and RadicalsLeonessa CortesNo ratings yet
- HSC Maths NotesDocument1 pageHSC Maths NotesAri GoldNo ratings yet
- Debremarkos University Burie Campus: Logic in Computer ScienceDocument44 pagesDebremarkos University Burie Campus: Logic in Computer ScienceGebrekidane WalleNo ratings yet
- R P, I, L: Atio and Roportion Ndices OgarithmsDocument56 pagesR P, I, L: Atio and Roportion Ndices OgarithmsdbNo ratings yet
- Exponent Rules NotesDocument3 pagesExponent Rules Notesenhlentshangase3008No ratings yet
- Powers: Engr. Annalyn D. Soria LecturerDocument17 pagesPowers: Engr. Annalyn D. Soria LecturerAnnalyn Duculan SoriaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 - Couples Changing The Line of Action of A Force (Equivalent Force-Couple System) PDFDocument48 pagesLecture 8 - Couples Changing The Line of Action of A Force (Equivalent Force-Couple System) PDFMichael Jeawel AlabanNo ratings yet
- Laws of ExponentsDocument10 pagesLaws of ExponentsPriya N Ashu100% (1)
- Unit 2. Powers and RootsDocument6 pagesUnit 2. Powers and RootsmariacaballerocobosNo ratings yet
- Fluid p11Document3 pagesFluid p11fisehadinku74No ratings yet
- Laws of ExponentDocument2 pagesLaws of Exponentapi-722103421No ratings yet
- Bes 121Document17 pagesBes 121Mariyah LykhaNo ratings yet
- CH - 2 - DEFINITIONS and-AXIOMSDocument52 pagesCH - 2 - DEFINITIONS and-AXIOMSeeffefef100% (1)
- MPM2D Self AssessmentDocument11 pagesMPM2D Self AssessmentRudrashish JassalNo ratings yet
- Q 1: Define Like and Unlike Parallel Forces?: A B OA AB OB AB B OB OA AB R A BDocument3 pagesQ 1: Define Like and Unlike Parallel Forces?: A B OA AB OB AB B OB OA AB R A BRiaz Hussain LaghariNo ratings yet
- Geom. TermsDocument2 pagesGeom. Termsayshasarip13No ratings yet
- Exponents: Mary Danielle M. Alcantara Mathematics Instructor Malcantara@nagahope - Edu.ph Elective 10: CalculusDocument26 pagesExponents: Mary Danielle M. Alcantara Mathematics Instructor Malcantara@nagahope - Edu.ph Elective 10: CalculusMary Danielle AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Exponents HandoutDocument2 pagesExponents Handoutapi-250789865No ratings yet
- Exponents HandoutDocument2 pagesExponents HandoutMia SaysNo ratings yet
- Exponents HandoutDocument2 pagesExponents Handoutapi-313311184No ratings yet
- Laws of Exponents Part 2Document11 pagesLaws of Exponents Part 2Michelle MendozaNo ratings yet
- Solving Linear EqualitiesDocument12 pagesSolving Linear EqualitiesKatherine Ilac BravoNo ratings yet
- 7.1 Completed NotesDocument10 pages7.1 Completed NotesThi KieuNo ratings yet
- Math, Q1 ReviewerDocument8 pagesMath, Q1 ReviewerPrime JavateNo ratings yet
- 5 2020 02 13!12 40 35 AmDocument10 pages5 2020 02 13!12 40 35 AmRaafa AliankaNo ratings yet
- Conditional StatementDocument5 pagesConditional StatementDon CelladorNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 0.5 Exponential and Logarithmic Function of Mat 120 of MTMDocument10 pagesLecture 4 0.5 Exponential and Logarithmic Function of Mat 120 of MTMABU MASROOR AHMEDNo ratings yet
- The Zero Power ExplainedDocument4 pagesThe Zero Power ExplainedCrónicasNo ratings yet
- Example On Calculation of Principal Stresses andDocument10 pagesExample On Calculation of Principal Stresses andNambiyanna DavanagereNo ratings yet
- CH 7 Sec 2Document17 pagesCH 7 Sec 2Louie jay UrsuaNo ratings yet
- Law of Exponents Presentation by RossanaDocument20 pagesLaw of Exponents Presentation by Rossanahadji montanoNo ratings yet
- Struct Tire: Axaxqxaxaa5Document49 pagesStruct Tire: Axaxqxaxaa5Wasif HossainNo ratings yet
- Fields Worksheet3Document4 pagesFields Worksheet3VINOD CHACKONo ratings yet
- 4 Work Energy PowerDocument7 pages4 Work Energy PowerAdam JrNo ratings yet
- Sketchup Ruby CodeCamp - FinalDocument88 pagesSketchup Ruby CodeCamp - Finalagliekaje100% (1)
- Math 101 Unit 2 Lesson 1.Document31 pagesMath 101 Unit 2 Lesson 1.Paul John PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Law of EcponentDocument5 pagesLaw of EcponentAmiel Marie M. CalpitoNo ratings yet
- Power of A QoutientDocument6 pagesPower of A Qoutientalyssa suyatNo ratings yet
- Propositional LogicDocument9 pagesPropositional LogicVikash DubeyNo ratings yet
- College Algebra Tutorial 2: Integer Exponents: (Back To The College Algebra Homepage) (Back To The GRE Math Help Page)Document16 pagesCollege Algebra Tutorial 2: Integer Exponents: (Back To The College Algebra Homepage) (Back To The GRE Math Help Page)salman saeedNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7Document111 pagesLecture 7Bilal AlderbashiNo ratings yet
- Power Method: Eigenvalue & Eigenvector: MPHYCC-05 Unit-IV Semester-IIDocument9 pagesPower Method: Eigenvalue & Eigenvector: MPHYCC-05 Unit-IV Semester-IISargi BeepumohanNo ratings yet
- Negative Exponents: Product of Powers PropertyDocument1 pageNegative Exponents: Product of Powers PropertyDarylMalihanNo ratings yet
- ELECTRONICS Grade10 Quarter1 Module5 Week5 PDFDocument8 pagesELECTRONICS Grade10 Quarter1 Module5 Week5 PDFxander isonNo ratings yet
- 1-Elastic, Kinetic & Potential (2019)Document22 pages1-Elastic, Kinetic & Potential (2019)Autumn SmithNo ratings yet
- EC English HL Grade 11 June 2024 P1 OnlyDocument13 pagesEC English HL Grade 11 June 2024 P1 Onlynkatekodawn72No ratings yet
- Acc Grade 10 Nov 2019 P2 MemoDocument10 pagesAcc Grade 10 Nov 2019 P2 Memonkatekodawn72No ratings yet
- MP Economics Grade 12 September 2023 P1 and MemoDocument32 pagesMP Economics Grade 12 September 2023 P1 and Memonkatekodawn72No ratings yet
- I Grade 11 2018 June Maths Paper 1 SolutionsDocument6 pagesI Grade 11 2018 June Maths Paper 1 Solutionsnkatekodawn72No ratings yet
- LP EAST Economics Grade 12 Pre JUNE 2024 P1 and MemoDocument31 pagesLP EAST Economics Grade 12 Pre JUNE 2024 P1 and Memonkatekodawn72No ratings yet
- J Grade 11 2018 June Maths Paper 2Document8 pagesJ Grade 11 2018 June Maths Paper 2nkatekodawn72No ratings yet
- Gr10 t2 Maths Exam Paper 1 and Paper 2 Questions Answer SeriesDocument5 pagesGr10 t2 Maths Exam Paper 1 and Paper 2 Questions Answer Seriesnkatekodawn72No ratings yet
- Phy P1 Nov QpmemoDocument32 pagesPhy P1 Nov Qpmemonkatekodawn72No ratings yet
- Limpopo Capricorn North Physical Science Grade 11 September 2023 QP and MemoDocument17 pagesLimpopo Capricorn North Physical Science Grade 11 September 2023 QP and Memonkatekodawn72No ratings yet
- Physical Science Grade 12 SEPT 2022 P1 and MemoDocument33 pagesPhysical Science Grade 12 SEPT 2022 P1 and Memonkatekodawn72No ratings yet
- Nov P1 QpmemoDocument14 pagesNov P1 Qpmemonkatekodawn72No ratings yet
- JHB Physical Science Grade 11 September 2023 QP OnlyDocument11 pagesJHB Physical Science Grade 11 September 2023 QP Onlynkatekodawn72No ratings yet
- Maths Grade 12 SEPT 2022 P2 and MemoDocument30 pagesMaths Grade 12 SEPT 2022 P2 and Memonkatekodawn72No ratings yet
- Accounting GR 11 MEMO P2Document11 pagesAccounting GR 11 MEMO P2nkatekodawn72No ratings yet
- NSC Physical Science Grade 12 November 2022 P1 and MemoDocument53 pagesNSC Physical Science Grade 12 November 2022 P1 and Memonkatekodawn72No ratings yet
- FS Maths Grade 12 June 2022 P2 and MemoDocument26 pagesFS Maths Grade 12 June 2022 P2 and Memonkatekodawn72No ratings yet
- Grade 11 Year Note - 2024Document116 pagesGrade 11 Year Note - 2024nkatekodawn72100% (1)
- NW NSC GR 10 Life Sciences P2 Eng Nov 2019Document13 pagesNW NSC GR 10 Life Sciences P2 Eng Nov 2019nkatekodawn72No ratings yet
- G10 - History of Life On Earth - DR RossDocument14 pagesG10 - History of Life On Earth - DR Rossnkatekodawn72No ratings yet
- 1 Grade 10 TestDocument6 pages1 Grade 10 Testnkatekodawn72No ratings yet
- 2019 NAT PhySci GR 10 Nov Exam P2 MemoDocument10 pages2019 NAT PhySci GR 10 Nov Exam P2 Memonkatekodawn72No ratings yet
- My Wife's BossDocument1,589 pagesMy Wife's Bossnkatekodawn72100% (1)