Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Greek Alphabet Letters & Symbols - Greek Gods & Goddesses
Greek Alphabet Letters & Symbols - Greek Gods & Goddesses
Uploaded by
XtiviaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- AfrikaansDocument6 pagesAfrikaansJanaNo ratings yet
- Uzbek OriginalDocument225 pagesUzbek Originalgeneup3587No ratings yet
- 4 575973715896959125 PDFDocument481 pages4 575973715896959125 PDFAinul Luthfi100% (2)
- NATA Act SinhalaDocument28 pagesNATA Act SinhalaaclghambantotaNo ratings yet
- Arabian NightsDocument24 pagesArabian NightsnwytgNo ratings yet
- Alphabet YunaniDocument2 pagesAlphabet YunaniMark HenryNo ratings yet
- A Table of Greek LettersDocument1 pageA Table of Greek LettersmalparoneNo ratings yet
- Table of Greek Letters PDFDocument1 pageTable of Greek Letters PDFGaidaa HeakalNo ratings yet
- Greek SymbolsDocument2 pagesGreek SymbolsC.Mahesh Assistant Professor, ME DepartmentNo ratings yet
- Appendix 10 Greek AlphabetDocument2 pagesAppendix 10 Greek AlphabetNguyen Van QuyenNo ratings yet
- Mathmatical SymbolsDocument1 pageMathmatical SymbolsdevsharmaNo ratings yet
- Independent Learning 4Document9 pagesIndependent Learning 4novitaNo ratings yet
- Greek AlphabetsDocument1 pageGreek Alphabetsrajeevup2004No ratings yet
- Grčka SlovaDocument2 pagesGrčka SlovatricenNo ratings yet
- Greek I: Dr. C Mkombe Lecture 1: The Greek Language (PG 128 - 129 Vocabulary List)Document68 pagesGreek I: Dr. C Mkombe Lecture 1: The Greek Language (PG 128 - 129 Vocabulary List)Justice MachiwanaNo ratings yet
- Greek AlphabetsDocument1 pageGreek AlphabetsSupadej KorsrisuwanNo ratings yet
- 123Document1 page123koyenabasak13No ratings yet
- Greek Alphabet LettersDocument3 pagesGreek Alphabet LettersAmmarNo ratings yet
- The Greek AlphabetDocument1 pageThe Greek AlphabethtcnrkmrcNo ratings yet
- GreekalphDocument1 pageGreekalphpankajkhatak8069No ratings yet
- Greek AlphabetDocument1 pageGreek Alphabetyoavram0% (1)
- John Lucian Pronunciation ChartDocument3 pagesJohn Lucian Pronunciation ChartDomingos SávioNo ratings yet
- Greek Alphabet ListDocument1 pageGreek Alphabet ListgoldflackNo ratings yet
- Latin-Script AlphabetDocument4 pagesLatin-Script AlphabetqhwhwgzxNo ratings yet
- 數學課程慣用術語符號表Document2 pages數學課程慣用術語符號表h34121240No ratings yet
- Alfabeto GregoDocument1 pageAlfabeto GregoGiovani PicheliNo ratings yet
- Math Sym N NamesDocument1 pageMath Sym N NamesarunaradhiNo ratings yet
- Name Lower Case Upper Case Pronunciation/Equivalent English LetterDocument3 pagesName Lower Case Upper Case Pronunciation/Equivalent English Letterbobmacbob5No ratings yet
- Greek Alphabet Letters & Symbols (α,β,γ,δ,ε,..Document2 pagesGreek Alphabet Letters & Symbols (α,β,γ,δ,ε,..kumarNo ratings yet
- السيميوزيس البورسية في منظومة إيكو السيميائيةDocument19 pagesالسيميوزيس البورسية في منظومة إيكو السيميائيةأحمد بن عبد الكريمNo ratings yet
- Updated Lesson 1Document8 pagesUpdated Lesson 1Rjay MedenillaNo ratings yet
- Greek A01 StudentDocument6 pagesGreek A01 StudentGeorge AgungaNo ratings yet
- Bloodborne Collectors Edition ArtbookDocument52 pagesBloodborne Collectors Edition ArtbookSAAVEDRA WAXLIGHT100% (1)
- Latin-Script Alphabet: Encoding Key Types of Differences PropertiesDocument4 pagesLatin-Script Alphabet: Encoding Key Types of Differences PropertiesMaxwell MoralesNo ratings yet
- Classical Greek AlphabetDocument2 pagesClassical Greek AlphabetAjayi Akinoluwa OluwafemiNo ratings yet
- A AlphabetDocument15 pagesA AlphabetfadelNo ratings yet
- Alphabet Minibooks 1 Puzzle GamesDocument1 pageAlphabet Minibooks 1 Puzzle GamesSheana leeNo ratings yet
- Greek AlphabetDocument1 pageGreek AlphabetUnver OzkolNo ratings yet
- Learning Hebrew: Other NikkudimDocument18 pagesLearning Hebrew: Other NikkudimAndrew Morgan50% (2)
- Pronunciation PDFDocument20 pagesPronunciation PDFkronyer upNo ratings yet
- Greek Alphabet Letters & SymbolsDocument3 pagesGreek Alphabet Letters & SymbolsJane LeaNo ratings yet
- Greek AlphabetDocument2 pagesGreek AlphabetMadhu BediguthuNo ratings yet
- Hakka-Chinese - Illustrations of The IpaDocument5 pagesHakka-Chinese - Illustrations of The IpaarmenNo ratings yet
- Romanian AlphabetDocument6 pagesRomanian Alphabetcatalin catalinNo ratings yet
- Using Qedavian ScriptDocument5 pagesUsing Qedavian ScriptAraya AnantaghulNo ratings yet
- Six Years OldDocument28 pagesSix Years Oldmelissa.jthrNo ratings yet
- Curs Greaca An 1Document25 pagesCurs Greaca An 1MihaitaStiulete100% (1)
- Greek Alphabet List: Upper Case Letter Lower Case Letter Greek Letter Name English Equivalent Letter Name PronounceDocument1 pageGreek Alphabet List: Upper Case Letter Lower Case Letter Greek Letter Name English Equivalent Letter Name PronounceMona YunitaNo ratings yet
- Hebrew Characters 1.Document5 pagesHebrew Characters 1.ScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Symbols PDFDocument2 pagesSymbols PDFRight LeftNo ratings yet
- Romanian Alphabet: WorksheetDocument6 pagesRomanian Alphabet: WorksheetCyrus ChanNo ratings yet
- AlfabetoDocument1 pageAlfabetoGiovanni TosoNo ratings yet
- French Alphabet: WorksheetDocument5 pagesFrench Alphabet: WorksheetLasya S0% (1)
- The Greek Alphabet For WordDocument1 pageThe Greek Alphabet For WordjbrossiNo ratings yet
- HebrewAlphabet 1Document1 pageHebrewAlphabet 1Dr Nicholas Baruch ChiNo ratings yet
- Approximate Reflexes of PIE ConsonantsDocument2 pagesApproximate Reflexes of PIE ConsonantsMorgoth BauglirNo ratings yet
- English Grammar For All LevelsDocument21 pagesEnglish Grammar For All Levelsnagi zomrawiNo ratings yet
- PhoneticsDocument1 pagePhoneticsLinh Đỗ Ngọc ThùyNo ratings yet
- TurkishDocument5 pagesTurkishGuzel TmNo ratings yet
- The Willow Song: Anonymous (1616 or Earlier)Document4 pagesThe Willow Song: Anonymous (1616 or Earlier)JB TaylorNo ratings yet
- A Reading Course in Homeric GreekDocument80 pagesA Reading Course in Homeric GreekEiichiro Tani100% (2)
- Mathcad Keyboard ShortcutsDocument6 pagesMathcad Keyboard ShortcutsjayalakshmiNo ratings yet
- LaTeX SymbolsDocument4 pagesLaTeX SymbolsMarciana_2013No ratings yet
- Introduction To The Study of Latin InscriptionsDocument492 pagesIntroduction To The Study of Latin Inscriptionslonnnet7380No ratings yet
- MRC-107 RADIO PALLET TM Veis.s SV2IPWDocument158 pagesMRC-107 RADIO PALLET TM Veis.s SV2IPWΒΕΗΣ ΣΤΕΛΙΟΣ Veis SteliosNo ratings yet
- Oral Presentations Ormrod 2015 06Document23 pagesOral Presentations Ormrod 2015 06Miguel GonzalezNo ratings yet
- LotusDocument9 pagesLotusNora ButarbutarNo ratings yet
- The Correct Methodology To Re-Establish The Islamic State (Urdu PDFDocument89 pagesThe Correct Methodology To Re-Establish The Islamic State (Urdu PDFapi-3712897No ratings yet
- Qadyani Djal Ki Thriri GstakhyanDocument33 pagesQadyani Djal Ki Thriri GstakhyanIslamic Reserch Center (IRC)No ratings yet
- Introduction To Russian Alphabet (Cyrillic)Document2 pagesIntroduction To Russian Alphabet (Cyrillic)sblee.saferwithNo ratings yet
- RunesDocument19 pagesRunesGray Bohnen100% (1)
- Capital LettersDocument39 pagesCapital LettersValarmathi VeerasenanNo ratings yet
- Kylver StoneDocument3 pagesKylver StoneJ.B. BuiNo ratings yet
- Wikipedia - LaTeX Symbols - WikipediaDocument6 pagesWikipedia - LaTeX Symbols - WikipediaNikhil VidhaniNo ratings yet
- Batha Urdu MonthlyDocument47 pagesBatha Urdu MonthlySalman AhmedNo ratings yet
- AP LAWCET 2010 Question Paper With Answers DownloadDocument13 pagesAP LAWCET 2010 Question Paper With Answers DownloadgayathriNo ratings yet
- Mathschallenge 1 Star PDFDocument127 pagesMathschallenge 1 Star PDFSushma RaniNo ratings yet
- NeutrafaceDocument11 pagesNeutrafacealaintheloneNo ratings yet
- Gematria of GodDocument10 pagesGematria of GodEDUARDO BRANDÃO100% (2)
- LemegetonDocument132 pagesLemegetonFrater Alastor100% (2)
- Manual 98 ADocument53 pagesManual 98 AAndreiNo ratings yet
- Ivana Stefanovic-Mala OtkrovenjaDocument9 pagesIvana Stefanovic-Mala OtkrovenjaNada KolundzijaNo ratings yet
- The Weird and Wonderful Chemistry of Audio Active Decay Conway 1987Document16 pagesThe Weird and Wonderful Chemistry of Audio Active Decay Conway 1987mkozturk100% (1)
- Squirrel All-Parts PDFDocument5 pagesSquirrel All-Parts PDFSaraGonzalezNo ratings yet
- English Alphabet PronunciationDocument3 pagesEnglish Alphabet PronunciationDomingos Tolentino Saide DtsNo ratings yet
- Ahkam Ahle ZimmaDocument27 pagesAhkam Ahle ZimmaAbdulAzizSuraqahNo ratings yet
- Kemet Writing PDFDocument2 pagesKemet Writing PDFJacen BondsNo ratings yet
Greek Alphabet Letters & Symbols - Greek Gods & Goddesses
Greek Alphabet Letters & Symbols - Greek Gods & Goddesses
Uploaded by
XtiviaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Greek Alphabet Letters & Symbols - Greek Gods & Goddesses
Greek Alphabet Letters & Symbols - Greek Gods & Goddesses
Uploaded by
XtiviaCopyright:
Available Formats
Greek Gods &
Goddesses
HOME » SITEMAP » SYMBOLS » GREEK
ALPHABET LETTERS & SYMBOLS
Greek Alphabet Letters &
Symbols
The Greek alphabet in an ancient writing
system first developed around 1000 BCE.
However, its letters remain prevalent today.
Throughout history, letters of the Greek
alphabet evolved to represent many things.
The alphabet is a staple in the “Greek
System” of American universities, scientific
naming schemes, modern military
communications, and more.
The alphabet holds great significance. Not
only is it commonly used in many forms today,
but it either directly or indirectly influenced all
modern European alphabets. That includes
the Latin alphabet of the Western world.
The origins of the Greek alphabet come from
the North Semitic alphabet. The Phoenicians
took inspiration from the North Semitic
alphabet to create their own writing system.
The Greeks then modified the Phoenician
alphabet to make writing a non-Semitic
language more efficient and accurate. Greeks
did this by adding new letters and removing
others.
For example, the Greek alphabet turned
Semitic symbols representing consonants into
those denoted vowel sounds. The introduction
of vowels was a game-changer increasing the
overall legibility of the new non-Semitic writing
system.
Greeks separated the new alphabet into two
branches during the early stages of adoption.
Around the 5th century BCE, there was the
Ionic Greek alphabet and the Chalcidian
Greek Alphabet. The branches belonged to
eastern and western Greece, respectively.
The Chalcidian Greek alphabet of the west
paved the way for the Etruscan alphabet of
Italy. As a result, it’s considered an indirect
ancestor of the Latin alphabet.
The Ionic Greek alphabet became the official
writing system for Athens in 403 BCE. During
the next five decades, its adoption spread. It
replaced all other versions, including
Chalcidian. Thus, the Ionic script became the
classical Greek alphabet.
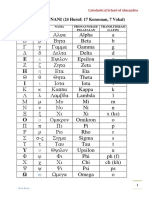
The Greek alphabet consists of 24 letters.
Seven of the 24 letters are vowels. Ancient
Greeks also had lowercase and uppercase
characters. Furthermore, the alphabet had
different scripts. These included uncial,
cursive, and minuscule. Uncial dropped out of
favor, allowing the modern Greek handwriting
form to prominence.
The Classical Greek
Alphabet In Order
Below is a table that indicates the Classical
Greek alphabet in order.
GREEK
UPPERCASE LOWERCASE ENGLISH
LETTER
LETTER LETTER EQUIVALENT
NAME
Alpha Α α a
Beta Β β b
Gamma Γ γ g
Delta Δ δ d
Epsilon Ε ε e
Zeta Ζ ζ z
Eta Η η h
Theta Θ θ th
Iota Ι ι i
Kappa Κ κ k
Lambda Λ λ l
Mu Μ μ m
Nu Ν ν n
Xi Ξ ξ x
Omicron Ο ο o
Pi Π π p
Rho Ρ ρ r
Sigma Σ σ/ς s
Tau Τ τ t
Upsilon Υ υ u
Phi Φ φ ph
Chi Χ χ ch
Psi Ψ ψ ps
Omega Ω ω o
Classical Greek Numerals
Below is a table that indicates the Classical
Greek numerals.
Show 10 entries
Search:
GREEK ARABIC
α′ 1
β′ 2
γ′ 3
δ′ 4
ε′ 5
ζ′ 6
ξ′ 7
η′ 8
θ′ 9
ι′ 10
Showing 1 to 10 of 41 entries
PREVIOUS
NEXT
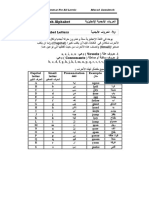
Modern Greek Alphabet
Below is a table that indicates the modern
Greek alphabet
Take a 2-Min
ADHD Test
···
Getting an ADHD diagnosis doesn’t
have to cost thousands of dollars in
Ontario.
··· Frida
LOWER ENGLISH
CAPITAL COMBINATIONS NAME
CASE EQUIVALENTS
A α, α* álfa a
αι e
αï ai
αυ av/af
αϋ ai
Β β víta v
Γ γ ghámma gh before α, ο,
ου, ω, and
consonants
other than γ, ξ,
and χ, y before
αι, ε, ει, η, ι,
οι, υ, υι; n
before γ, ξ, and
γκ initial, g;
medial, ng
Δ δ, ∂* dhélta dh; d between
ν and ρ
Ε ε épsilon e
ει i
εï eï
ευ ev/ef
Ζ ζ zíta z
Η η íta i
ηυ iv/if
Θ θ, ϑ* thíta th
Ι ι ióta i
Κ κ káppa k
Λ λ lámbdha l
Μ μ mi m
μπ initial, b;
medial, mb
Ν ν ni n
ντ initial, d;
medial, nd
ντζ ntz
Ξ ξ xi x
Ο ο ómikron o
οι i
οï oi
ου u
Π π pi p
Ρ ρ ro r
Σ σ*** sígma s
Τ τ taf t
Υ υ ípsilon i initially and
between
consonants
υι i
Φ , * fi f
Χ χ khi kh
Ψ ψ psi ps
Ω ω oméga o
Alpha – Α α
The first letter of the Greek alphabet is Alpha.
Because it starts the entire writing system,
Alpha often signifies the first or the best in a
group.
···
For example, game and software developers
use it to represent the first testing stage. It’s
also common in science and medicine. You
might see it used to describe the first variant of
a virus or the most essential element of a
scientific concept.
Alpha even appears in different faiths across
the world. In the bible, God is referred to as
the “Alpha and the Omega.” Generally, the
interpretation is that God is both the beginning
and end of all things.
···
Beta – Β β
Beta is the second letter of the Greek
alphabet. It has a numerical value of two and
often represents an item that’s second in a line
of concession. The term “Beta” is often used in
slang to represent someone less than an
Alpha. It may also describe second versions of
concepts in science. For example, a Beta
variant of a virus will come after the Alpha.
In software development, Beta is a term that
represents the second stage of testing after
the Alpha. You might also hear the letter used
in physics, aerodynamics, and even finance.
Gamma – Γ γ
Gamma has a numerical value of three. The
approximate Western equivalent of Gamma is
a hard “G” sound. It can also take the place of
the “ng” sound that end words like “sing” or
“belong.”
···
Once again, this letter is frequently utilized in
science and physics. The most popular use
describes the smallest wavelengths in the
electromagnetic spectrum: Gamma rays. The
lowercase Gamma letter is also the symbol for
photon particles, motor neurons, and more. It
represents many concepts, including the
active coefficient in thermodynamics, the
gyromagnetic ratio in electromagnetism, and
the Lorentz factor in the Theory of Relativity.
Delta – Δ δ
The fourth letter in the Greek alphabet is
Delta. The capital Delta symbol is a triangle.
As a result, the term “Delta” was used to
describe many phenomena with a similar
shape. The most recognizable is a river delta.
In the realm of mathematics, Delta plays a big
part in calculus. It’s an auxiliary function and
represents the change of a variable value. In
chemistry, Delta is predominantly used to
show the shift of nuclear magnetic resonance.
···
Delta also appears in writing. Proofreaders
typically use the uppercase Delta symbol to
indicate text that needs deletion.
Epsilon – Ε ε
Epsilon in the Greek alphabet is the equivalent
of the letter “E” in Western European
alphabets. Both the uppercase and the
lowercase symbols even look like the letter
“E.”
There are many uses of the Epsilon letter. In
computer science, the lowercase symbol
represents an empty string. Meanwhile, it’s
used for the degree of error in statistics.
Epsilon is important in astronomy, too. The
letter lends its name to the most visible ring of
Uranus. It also indicates the axial tilt of
planetary bodies in space.
Zeta – Ζ ζ
The sixth letter of the Greek alphabet is Zeta,
but it has a numeric value of seven. The
modern pronunciation is similar to the letter
“Z.” The same goes for its uppercase symbol
appearance. However, the ancient
pronunciation of Zeta is closer to the sound of
“sd.” For example, the middle of the word
“wisdom.”
···
Zeta is most often used to represent the
damping ratio in physics and engineering. It’s
also the symbol of equilibrium computations.
For mathematics, Zeta is a prominent symbol
in the Riemann Zeta function and the
Weierstrass Zeta function.
Like other letters, Zeta is also used in many
naming conventions. One famous example
was the tropical storm Zeta in 2005. It became
the 30th storm of the season.
Eta – Η η
Next is Eta. It has a numerical value of eight
and is the seventh letter of the Greek
alphabet. The original Greek alphabet had a
different letter in Eta’s position, but it was
phased out in the transition to Ionic script
across Greece.
···
You might also like
- AfrikaansDocument6 pagesAfrikaansJanaNo ratings yet
- Uzbek OriginalDocument225 pagesUzbek Originalgeneup3587No ratings yet
- 4 575973715896959125 PDFDocument481 pages4 575973715896959125 PDFAinul Luthfi100% (2)
- NATA Act SinhalaDocument28 pagesNATA Act SinhalaaclghambantotaNo ratings yet
- Arabian NightsDocument24 pagesArabian NightsnwytgNo ratings yet
- Alphabet YunaniDocument2 pagesAlphabet YunaniMark HenryNo ratings yet
- A Table of Greek LettersDocument1 pageA Table of Greek LettersmalparoneNo ratings yet
- Table of Greek Letters PDFDocument1 pageTable of Greek Letters PDFGaidaa HeakalNo ratings yet
- Greek SymbolsDocument2 pagesGreek SymbolsC.Mahesh Assistant Professor, ME DepartmentNo ratings yet
- Appendix 10 Greek AlphabetDocument2 pagesAppendix 10 Greek AlphabetNguyen Van QuyenNo ratings yet
- Mathmatical SymbolsDocument1 pageMathmatical SymbolsdevsharmaNo ratings yet
- Independent Learning 4Document9 pagesIndependent Learning 4novitaNo ratings yet
- Greek AlphabetsDocument1 pageGreek Alphabetsrajeevup2004No ratings yet
- Grčka SlovaDocument2 pagesGrčka SlovatricenNo ratings yet
- Greek I: Dr. C Mkombe Lecture 1: The Greek Language (PG 128 - 129 Vocabulary List)Document68 pagesGreek I: Dr. C Mkombe Lecture 1: The Greek Language (PG 128 - 129 Vocabulary List)Justice MachiwanaNo ratings yet
- Greek AlphabetsDocument1 pageGreek AlphabetsSupadej KorsrisuwanNo ratings yet
- 123Document1 page123koyenabasak13No ratings yet
- Greek Alphabet LettersDocument3 pagesGreek Alphabet LettersAmmarNo ratings yet
- The Greek AlphabetDocument1 pageThe Greek AlphabethtcnrkmrcNo ratings yet
- GreekalphDocument1 pageGreekalphpankajkhatak8069No ratings yet
- Greek AlphabetDocument1 pageGreek Alphabetyoavram0% (1)
- John Lucian Pronunciation ChartDocument3 pagesJohn Lucian Pronunciation ChartDomingos SávioNo ratings yet
- Greek Alphabet ListDocument1 pageGreek Alphabet ListgoldflackNo ratings yet
- Latin-Script AlphabetDocument4 pagesLatin-Script AlphabetqhwhwgzxNo ratings yet
- 數學課程慣用術語符號表Document2 pages數學課程慣用術語符號表h34121240No ratings yet
- Alfabeto GregoDocument1 pageAlfabeto GregoGiovani PicheliNo ratings yet
- Math Sym N NamesDocument1 pageMath Sym N NamesarunaradhiNo ratings yet
- Name Lower Case Upper Case Pronunciation/Equivalent English LetterDocument3 pagesName Lower Case Upper Case Pronunciation/Equivalent English Letterbobmacbob5No ratings yet
- Greek Alphabet Letters & Symbols (α,β,γ,δ,ε,..Document2 pagesGreek Alphabet Letters & Symbols (α,β,γ,δ,ε,..kumarNo ratings yet
- السيميوزيس البورسية في منظومة إيكو السيميائيةDocument19 pagesالسيميوزيس البورسية في منظومة إيكو السيميائيةأحمد بن عبد الكريمNo ratings yet
- Updated Lesson 1Document8 pagesUpdated Lesson 1Rjay MedenillaNo ratings yet
- Greek A01 StudentDocument6 pagesGreek A01 StudentGeorge AgungaNo ratings yet
- Bloodborne Collectors Edition ArtbookDocument52 pagesBloodborne Collectors Edition ArtbookSAAVEDRA WAXLIGHT100% (1)
- Latin-Script Alphabet: Encoding Key Types of Differences PropertiesDocument4 pagesLatin-Script Alphabet: Encoding Key Types of Differences PropertiesMaxwell MoralesNo ratings yet
- Classical Greek AlphabetDocument2 pagesClassical Greek AlphabetAjayi Akinoluwa OluwafemiNo ratings yet
- A AlphabetDocument15 pagesA AlphabetfadelNo ratings yet
- Alphabet Minibooks 1 Puzzle GamesDocument1 pageAlphabet Minibooks 1 Puzzle GamesSheana leeNo ratings yet
- Greek AlphabetDocument1 pageGreek AlphabetUnver OzkolNo ratings yet
- Learning Hebrew: Other NikkudimDocument18 pagesLearning Hebrew: Other NikkudimAndrew Morgan50% (2)
- Pronunciation PDFDocument20 pagesPronunciation PDFkronyer upNo ratings yet
- Greek Alphabet Letters & SymbolsDocument3 pagesGreek Alphabet Letters & SymbolsJane LeaNo ratings yet
- Greek AlphabetDocument2 pagesGreek AlphabetMadhu BediguthuNo ratings yet
- Hakka-Chinese - Illustrations of The IpaDocument5 pagesHakka-Chinese - Illustrations of The IpaarmenNo ratings yet
- Romanian AlphabetDocument6 pagesRomanian Alphabetcatalin catalinNo ratings yet
- Using Qedavian ScriptDocument5 pagesUsing Qedavian ScriptAraya AnantaghulNo ratings yet
- Six Years OldDocument28 pagesSix Years Oldmelissa.jthrNo ratings yet
- Curs Greaca An 1Document25 pagesCurs Greaca An 1MihaitaStiulete100% (1)
- Greek Alphabet List: Upper Case Letter Lower Case Letter Greek Letter Name English Equivalent Letter Name PronounceDocument1 pageGreek Alphabet List: Upper Case Letter Lower Case Letter Greek Letter Name English Equivalent Letter Name PronounceMona YunitaNo ratings yet
- Hebrew Characters 1.Document5 pagesHebrew Characters 1.ScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Symbols PDFDocument2 pagesSymbols PDFRight LeftNo ratings yet
- Romanian Alphabet: WorksheetDocument6 pagesRomanian Alphabet: WorksheetCyrus ChanNo ratings yet
- AlfabetoDocument1 pageAlfabetoGiovanni TosoNo ratings yet
- French Alphabet: WorksheetDocument5 pagesFrench Alphabet: WorksheetLasya S0% (1)
- The Greek Alphabet For WordDocument1 pageThe Greek Alphabet For WordjbrossiNo ratings yet
- HebrewAlphabet 1Document1 pageHebrewAlphabet 1Dr Nicholas Baruch ChiNo ratings yet
- Approximate Reflexes of PIE ConsonantsDocument2 pagesApproximate Reflexes of PIE ConsonantsMorgoth BauglirNo ratings yet
- English Grammar For All LevelsDocument21 pagesEnglish Grammar For All Levelsnagi zomrawiNo ratings yet
- PhoneticsDocument1 pagePhoneticsLinh Đỗ Ngọc ThùyNo ratings yet
- TurkishDocument5 pagesTurkishGuzel TmNo ratings yet
- The Willow Song: Anonymous (1616 or Earlier)Document4 pagesThe Willow Song: Anonymous (1616 or Earlier)JB TaylorNo ratings yet
- A Reading Course in Homeric GreekDocument80 pagesA Reading Course in Homeric GreekEiichiro Tani100% (2)
- Mathcad Keyboard ShortcutsDocument6 pagesMathcad Keyboard ShortcutsjayalakshmiNo ratings yet
- LaTeX SymbolsDocument4 pagesLaTeX SymbolsMarciana_2013No ratings yet
- Introduction To The Study of Latin InscriptionsDocument492 pagesIntroduction To The Study of Latin Inscriptionslonnnet7380No ratings yet
- MRC-107 RADIO PALLET TM Veis.s SV2IPWDocument158 pagesMRC-107 RADIO PALLET TM Veis.s SV2IPWΒΕΗΣ ΣΤΕΛΙΟΣ Veis SteliosNo ratings yet
- Oral Presentations Ormrod 2015 06Document23 pagesOral Presentations Ormrod 2015 06Miguel GonzalezNo ratings yet
- LotusDocument9 pagesLotusNora ButarbutarNo ratings yet
- The Correct Methodology To Re-Establish The Islamic State (Urdu PDFDocument89 pagesThe Correct Methodology To Re-Establish The Islamic State (Urdu PDFapi-3712897No ratings yet
- Qadyani Djal Ki Thriri GstakhyanDocument33 pagesQadyani Djal Ki Thriri GstakhyanIslamic Reserch Center (IRC)No ratings yet
- Introduction To Russian Alphabet (Cyrillic)Document2 pagesIntroduction To Russian Alphabet (Cyrillic)sblee.saferwithNo ratings yet
- RunesDocument19 pagesRunesGray Bohnen100% (1)
- Capital LettersDocument39 pagesCapital LettersValarmathi VeerasenanNo ratings yet
- Kylver StoneDocument3 pagesKylver StoneJ.B. BuiNo ratings yet
- Wikipedia - LaTeX Symbols - WikipediaDocument6 pagesWikipedia - LaTeX Symbols - WikipediaNikhil VidhaniNo ratings yet
- Batha Urdu MonthlyDocument47 pagesBatha Urdu MonthlySalman AhmedNo ratings yet
- AP LAWCET 2010 Question Paper With Answers DownloadDocument13 pagesAP LAWCET 2010 Question Paper With Answers DownloadgayathriNo ratings yet
- Mathschallenge 1 Star PDFDocument127 pagesMathschallenge 1 Star PDFSushma RaniNo ratings yet
- NeutrafaceDocument11 pagesNeutrafacealaintheloneNo ratings yet
- Gematria of GodDocument10 pagesGematria of GodEDUARDO BRANDÃO100% (2)
- LemegetonDocument132 pagesLemegetonFrater Alastor100% (2)
- Manual 98 ADocument53 pagesManual 98 AAndreiNo ratings yet
- Ivana Stefanovic-Mala OtkrovenjaDocument9 pagesIvana Stefanovic-Mala OtkrovenjaNada KolundzijaNo ratings yet
- The Weird and Wonderful Chemistry of Audio Active Decay Conway 1987Document16 pagesThe Weird and Wonderful Chemistry of Audio Active Decay Conway 1987mkozturk100% (1)
- Squirrel All-Parts PDFDocument5 pagesSquirrel All-Parts PDFSaraGonzalezNo ratings yet
- English Alphabet PronunciationDocument3 pagesEnglish Alphabet PronunciationDomingos Tolentino Saide DtsNo ratings yet
- Ahkam Ahle ZimmaDocument27 pagesAhkam Ahle ZimmaAbdulAzizSuraqahNo ratings yet
- Kemet Writing PDFDocument2 pagesKemet Writing PDFJacen BondsNo ratings yet