Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bonding Summary Chart
Bonding Summary Chart
Uploaded by
Канат ТютеновOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bonding Summary Chart
Bonding Summary Chart
Uploaded by
Канат ТютеновCopyright:
Available Formats
Westminster H.S.
• AP Chemistry
8,9,10 · Bonding, IMFs, Liquids & Solids
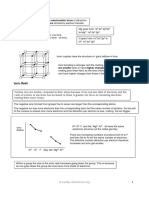
BIG PICTURE CHART
Electronegativity: how much an atom wants an electron from
ATOMS
another atom. (“TUG OF WAR”) [Noble Gases have no EN.)
Across period: increase protons, electrons more attracted to the
H He nucleus, increase EN
Li Be B C N O F Ne Down family: increase layers of electrons, electrons less
attracted to the nucleus, decrease EN
Na Mg Al Si P S Cl Ar
K Ca Sc Ti V Cr Mn Fe Co Ni Cu Zn Ga Ge As Se Br Kr Metals Non-Metals
Low EN; lose e- High EN; gain e-
Rb Sr Y Zr Nb Mo Tc Ru Rh Pd Ag Cd In Sn Sb Te I Xe
Form + ions Form – ions
Cs Ba La Hf Ta W Re Os Ir Pt Au Hg Tl Pb Bi Po At Rn “Strong Non-Metals” “Weak Non-
Fr Ra Ac Rf Db Sg Bh Hs Mt Ds Rg Cn Metals”
N, O, F, Cl All Others
COVALENT BONDS
BONDS Non-Polar Covalent Bond Polar Covalent Bond
IONIC BOND METALLIC BOND
δ+ δ– + – + +
Example Cl – Cl
H – Cl K – Cl K–K
Lewis
Structures
Electrons transferred;
Electrons shared equally Electrons shared unequally Metal cations surrounded by
Description Attraction between oppositely
between atoms. between atoms. “sea of electrons.”
charged ions.
Between non-metal atoms:
How do you Between non-metal atoms: Between cation and anion,
strong NM + strong NM Between metal atoms.
Know? strong NM + weak NM often M and NM.
weak NM + weak NM
COMPOUN
Non-Polar Compound Polar Compound
DS
Either:
(1) Compound has polar covalent
How do you (1) All non-polar covalent bonds
bonds, AND
Know? OR
(2) Polar bonds do not cancel out.
(2) Polar bonds cancel out.
SOLIDS Molecular Solid Network Solid Ionic Solid Metallic Solid
He, Kr, N2, F2, Br2, I2, P4, S8 Cdiamond, Cgraphite Ionic Compounds (cation + anion) Metals: Pb, Ag, Au, Cu, Fe, Zn
H2O, NH3, CO2, NO2, SiO2 (sand, glass, quartz) NaCl, KCl, KI, FeCl3, Alloys: Brass (Cu+Zn),
Examples
C6H12O6 CaCO3, CaCl2, MgSO4, Bronze (Cu+Sn),
Organic Compounds Fe2O3, AgNO3 Stainless Steel (Fe+Cr+C)
Molecules of covalent compounds All non-metal atoms connected Repeating lattice of A lattice of metal cations
Description
held by weak IMFs. with covalent bonds. cations and anions. in a sea of electrons.
Low MP and BP High MP and BP Brittle Lustrous / shiny
Poor Conductors Poor Conductors High MP and BP Malleable / Ductile
Properties
(except graphite) Dissolves in H2O Conducts heat + electricity
Conducts as (ℓ) , (aq), (g)
Inter-Particle Inter-Molecular Covalent Ionic Bonds Metallic
Forces Forces (IMFs) Bonds Bonds
IMFS London Dispersion Forces Dipole-Dipole Interactions Hydrogen Bonding
Examples CO2 HCl H2O
Attractions between temporary Special kind of Dipole-Dipole
Attractions between opposite
Description induced dipoles; main IMF in Interactions where H is tethered
charges of polar molecules.
non-polar compounds. between N, O, or F.
How do you Polar Compounds with
Non-Polar Compounds Polar Compounds
Know? H-N, H-O, or N-F
You might also like
- Analysis Questions: Part 1Document3 pagesAnalysis Questions: Part 1Celyn Millano50% (2)
- Redox MaterialDocument37 pagesRedox MaterialSuwahono, M.PdNo ratings yet
- Unit 10 HomeworkDocument10 pagesUnit 10 HomeworkKristen Leigh MarianoNo ratings yet
- Engineering MaterialsDocument51 pagesEngineering MaterialsSamer al sadikNo ratings yet
- BS Chemistry MCQsDocument6 pagesBS Chemistry MCQsRamsha saeedNo ratings yet
- Bonding Forces and Energies Al Francis Asuncion EE 3bDocument8 pagesBonding Forces and Energies Al Francis Asuncion EE 3bAce John OliverNo ratings yet
- Interatomic Bonds: Prof. H. K. Khaira Hod, Msme Deptt. Manit, BhopalDocument81 pagesInteratomic Bonds: Prof. H. K. Khaira Hod, Msme Deptt. Manit, Bhopalraj kumarNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Revision Guide Bonding AqaDocument3 pages1.3 Revision Guide Bonding AqaPragna AnanthNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding - Ionic BondDocument56 pagesChemical Bonding - Ionic BondFianna GalleroNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 02 NewDocument36 pagesChapter - 02 NewmaheshNo ratings yet
- Enlaces AtómicosDocument19 pagesEnlaces AtómicosJrjhf UeisNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Material ScienceDocument69 pagesChapter 1 Material ScienceFadhli JapryNo ratings yet
- Lecture TwoDocument27 pagesLecture TwoMohammed AliNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument29 pagesAtomic Structuremahmad123412374No ratings yet
- Metals and Non-Metals, Bonding: Ms. MatheisonDocument28 pagesMetals and Non-Metals, Bonding: Ms. MatheisonZae ZayNo ratings yet
- Principle: TypesDocument6 pagesPrinciple: TypeslilliaNo ratings yet
- Interatomic Bonding PDFDocument14 pagesInteratomic Bonding PDFFaysal Qadeer KhanNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 Bonding SL AnswersDocument48 pagesTopic 4 Bonding SL AnswersŁØNo ratings yet
- Ni Laterite Short Course 050512Document214 pagesNi Laterite Short Course 050512Totok GapuradianNo ratings yet
- ChembondDocument43 pagesChembondroziel A.mabitasanNo ratings yet
- ChembondDocument51 pagesChembondNovelynLozano-EdrosoNo ratings yet
- Ni Laterite Short Course 050512Document214 pagesNi Laterite Short Course 050512Slamet SetyowibowoNo ratings yet
- When Atoms Meet: Chemical BondingDocument88 pagesWhen Atoms Meet: Chemical BondingWilsonNo ratings yet
- 3 StructEngMatDocument43 pages3 StructEngMatM Thoriq BhadrikaNo ratings yet
- 11 S Block Revision Notes QuizrrDocument30 pages11 S Block Revision Notes QuizrrÃrjït ShûklãNo ratings yet
- 2 BondingDocument14 pages2 BondingRajasekar KrishnasamyNo ratings yet
- Bonding and Properties: Basics of Atomic StructureDocument13 pagesBonding and Properties: Basics of Atomic StructureAhsan AliNo ratings yet
- Mrs. Melendez-Beltran Pre-AICE ChemDocument98 pagesMrs. Melendez-Beltran Pre-AICE ChemTravel UnlimitedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Ionic and Metallic BondingDocument56 pagesChapter 7 Ionic and Metallic BondingCharles GibbsNo ratings yet
- ch02 0310Document26 pagesch02 0310pasternack2379No ratings yet
- Tema 3. Chemical BondingDocument68 pagesTema 3. Chemical Bondingkarthik tvkNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2021-22 BCHY101L TH VL2021220106627 Reference Material I 30-09-2021 EC Module 2 - MARDocument76 pagesFALLSEM2021-22 BCHY101L TH VL2021220106627 Reference Material I 30-09-2021 EC Module 2 - MARHarsh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- BondingDocument56 pagesBondingAngel Joy CATALAN (SHS)No ratings yet
- 12 SACE Start of Year Revision SOLUTIONSDocument6 pages12 SACE Start of Year Revision SOLUTIONSLydia LamNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4. Chemical BondDocument35 pagesLecture 4. Chemical BondВалентина ЮзьковаNo ratings yet
- ES 67 Lesson 2Document61 pagesES 67 Lesson 2nikkihipulanNo ratings yet
- 2 Physical Chemistry 18Document220 pages2 Physical Chemistry 18LaziNo ratings yet
- MINDMAP - Ionic BondingDocument1 pageMINDMAP - Ionic BondingalanchenyinNo ratings yet
- 02 BondingDocument24 pages02 Bondingiron_trNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Atomic BondingDocument23 pagesChapter 1 Atomic BondingLatisha AnthonyNo ratings yet
- Ionic BondDocument35 pagesIonic Bondirma.javashviliNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of Transition MetalsDocument56 pagesChemistry of Transition MetalsHamad Mohamad100% (1)
- G9 Science Q2-Week 2 - Types of CompoundsDocument79 pagesG9 Science Q2-Week 2 - Types of CompoundsKarina GentonNo ratings yet
- S-Block Class 11Document27 pagesS-Block Class 11sumitchauhan100000No ratings yet
- Conducting Properties of MaterialsDocument28 pagesConducting Properties of MaterialsMarzook JrNo ratings yet
- Continued:: More On Ionic BondingDocument37 pagesContinued:: More On Ionic BondingArdhy Biker'sNo ratings yet
- Ikatan KimiaDocument46 pagesIkatan KimiaFla Syafa SabitnaNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Revision Guide Bonding AqaDocument8 pages1.3 Revision Guide Bonding AqaRS JNo ratings yet
- 4.5 Metallic BondDocument22 pages4.5 Metallic BondDhevesh NishaNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument2 pagesElectrolysis Cheat Sheet: by Viaaziz ahmadNo ratings yet
- CH 02Document25 pagesCH 02usercmdmcNo ratings yet
- Summary Ch5-8 AtDocument7 pagesSummary Ch5-8 AtmtauNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10 &11 & 12 - 20240328Document107 pagesLecture 10 &11 & 12 - 20240328rohanom12No ratings yet
- Class01 Science G10 NotesDocument17 pagesClass01 Science G10 Notesemmazou18No ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument10 pagesChemical BondingseadiabaNo ratings yet
- PDF Document 5Document25 pagesPDF Document 5miriam harriottNo ratings yet
- 2 Chapter 02 Atomic BondingDocument17 pages2 Chapter 02 Atomic BondingZain FarhanNo ratings yet
- Ch2-Atomic Structure and Interatomic BondingDocument22 pagesCh2-Atomic Structure and Interatomic BondingSaif AlbaddawiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideFrom EverandChemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Quick Check 1 and 2Document2 pagesQuick Check 1 and 2Канат ТютеновNo ratings yet
- Station Review AnswersDocument5 pagesStation Review AnswersКанат ТютеновNo ratings yet
- Two Points AnswersDocument2 pagesTwo Points AnswersКанат ТютеновNo ratings yet
- Solution CompositionDocument2 pagesSolution CompositionКанат ТютеновNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 FULL PresentationDocument134 pagesChapter 7 FULL PresentationКанат ТютеновNo ratings yet
- IMF NotesDocument23 pagesIMF NotesКанат ТютеновNo ratings yet
- Quick Check 1Document1 pageQuick Check 1Канат ТютеновNo ratings yet
- Practice Test W AnswersDocument3 pagesPractice Test W AnswersКанат ТютеновNo ratings yet
- Le Chateliers Principle PracticeDocument1 pageLe Chateliers Principle PracticeКанат ТютеновNo ratings yet
- IMF WorksheetDocument3 pagesIMF WorksheetКанат ТютеновNo ratings yet
- Introduction To EnergyDocument2 pagesIntroduction To EnergyКанат ТютеновNo ratings yet
- Le Chateliers Principle Practice 2Document2 pagesLe Chateliers Principle Practice 2Канат ТютеновNo ratings yet
- Mole and Equation PracticeDocument1 pageMole and Equation PracticeКанат ТютеновNo ratings yet
- AP PPT CH 11Document68 pagesAP PPT CH 11Канат ТютеновNo ratings yet
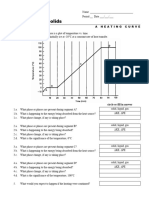
- Heating CurveDocument1 pageHeating CurveКанат ТютеновNo ratings yet
- Hess S Law NotesDocument2 pagesHess S Law NotesКанат ТютеновNo ratings yet
- Handwarmer Lab Write-Up SampleDocument1 pageHandwarmer Lab Write-Up SampleКанат ТютеновNo ratings yet
- Colligative Properties NotesDocument2 pagesColligative Properties NotesКанат ТютеновNo ratings yet
- IMF TrendsDocument1 pageIMF TrendsКанат ТютеновNo ratings yet
- Energies of Solution FormationDocument2 pagesEnergies of Solution FormationКанат ТютеновNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Quick Check 3Document1 pageChapter 7 Quick Check 3Канат ТютеновNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 AP PresentationDocument57 pagesChapter 7 AP PresentationКанат ТютеновNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Study QuestionsDocument2 pagesChapter 13 Study QuestionsКанат ТютеновNo ratings yet
- End Point Calculations AnswersDocument2 pagesEnd Point Calculations AnswersКанат ТютеновNo ratings yet
- End Point CalculationsDocument2 pagesEnd Point CalculationsКанат ТютеновNo ratings yet
- Ch14 Quick Check 3Document1 pageCh14 Quick Check 3Канат ТютеновNo ratings yet
- Ch14 PH CalculationsDocument1 pageCh14 PH CalculationsКанат ТютеновNo ratings yet
- AP PPT CH 9 AP OnlyDocument42 pagesAP PPT CH 9 AP OnlyКанат ТютеновNo ratings yet
- Buffer CalculationsDocument2 pagesBuffer CalculationsКанат ТютеновNo ratings yet
- AP Chem - Sections 1.2-1.3Document7 pagesAP Chem - Sections 1.2-1.3Канат ТютеновNo ratings yet
- Ch13 Attempt 3Document2 pagesCh13 Attempt 3Kelly TruongNo ratings yet
- Optimization of The Factors Affecting The Breakdown Voltage of The Transformer Oil Using Genetic AlgorithmDocument6 pagesOptimization of The Factors Affecting The Breakdown Voltage of The Transformer Oil Using Genetic AlgorithmMohsin ShahzadNo ratings yet
- XLPE Polyethylene Lifetime Detection PDFDocument120 pagesXLPE Polyethylene Lifetime Detection PDFconqiuNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Intermolecular Forces of AttractionDocument43 pagesLesson 3 - Intermolecular Forces of AttractionFreshieeNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Vibrational Frequenciesand IR Spectroscopy of HydrocarbonsDocument17 pagesFactors Affecting Vibrational Frequenciesand IR Spectroscopy of HydrocarbonsMuhammad HussnainNo ratings yet
- Chm142l - FR 1Document7 pagesChm142l - FR 1Adrian OblenaNo ratings yet
- Part 2 Physical ScienceDocument8 pagesPart 2 Physical Sciencejerick de veraNo ratings yet
- (B) (I) Protons: M1. (A) 1 / OneDocument16 pages(B) (I) Protons: M1. (A) 1 / OneAviBreezeNo ratings yet
- TestBank2 Funk GRP Intemol KRFT + SvarDocument9 pagesTestBank2 Funk GRP Intemol KRFT + SvarVictor HuangNo ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-02 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers)Document3 pagesCbse Test Paper-02 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers)Shreyash KolekarNo ratings yet
- Learners Academy: Chemistry - XI (Chap - 02, Test - 02 - Liquid)Document2 pagesLearners Academy: Chemistry - XI (Chap - 02, Test - 02 - Liquid)Umaid Ali KeerioNo ratings yet
- Ernest Rutherford and The Gold Foil Experiment: Image CC BY 4.0Document25 pagesErnest Rutherford and The Gold Foil Experiment: Image CC BY 4.0sohaib389892No ratings yet
- Module 7 POST-TASK Substance MP (Literature Value, ) Structure Main Intermolecular ForcesDocument2 pagesModule 7 POST-TASK Substance MP (Literature Value, ) Structure Main Intermolecular ForcesZHIARA MAE FACUNNo ratings yet
- 3.3.5 Bonding in Matter ChemDocument7 pages3.3.5 Bonding in Matter ChemCarina Silva-RomeroNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding PDFDocument14 pagesChemical Bonding PDFsiddhant shuklaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Chemistry 9701/12Document20 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: Chemistry 9701/12Tanzim RahmanNo ratings yet
- January 2018 MS - Paper 1C Edexcel Chemistry IGCSEDocument23 pagesJanuary 2018 MS - Paper 1C Edexcel Chemistry IGCSEVideesha AmunugamaNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Theory and Intermolecular Forces of Liquid and Solid PDFDocument70 pagesKinetic Theory and Intermolecular Forces of Liquid and Solid PDFMiguel RañadaNo ratings yet
- Partial Molar VolumeDocument8 pagesPartial Molar VolumeJansen KhoNo ratings yet
- Solids and Their PropertiesDocument31 pagesSolids and Their PropertiesTrexi Mag-asoNo ratings yet
- Assignment - States of MatterDocument14 pagesAssignment - States of MatterYash KumarNo ratings yet
- 4 PhysicochemicalPrinciples ofDrugAction PDFDocument29 pages4 PhysicochemicalPrinciples ofDrugAction PDFObagunwaTemitopeDamilareNo ratings yet
- GEN CHEM2 ExamDocument5 pagesGEN CHEM2 ExamMark Janssen dela FuenteNo ratings yet
- IMFA (Intermolecular Forces of Attraction) Surface TensionDocument27 pagesIMFA (Intermolecular Forces of Attraction) Surface TensionJoshua Gabriel Labaco100% (1)
- June 09 Mark Scheme OCR ChemistryDocument28 pagesJune 09 Mark Scheme OCR ChemistryrojersymondsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 NoPWDocument34 pagesChapter 10 NoPWArjun PatelNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Molecular Model of Liquids and Solids: Lesson 1Document28 pagesKinetic Molecular Model of Liquids and Solids: Lesson 1Fern Baldonaza100% (1)
- SAT II Chemistry Study Guide Pt. 1Document10 pagesSAT II Chemistry Study Guide Pt. 1Caryn Tran100% (4)
- Solu BilityDocument23 pagesSolu BilityVidya PasalkarNo ratings yet