Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tiger Notes
Tiger Notes
Uploaded by
michaela.deleon07Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tiger Notes
Tiger Notes
Uploaded by
michaela.deleon07Copyright:
Available Formats
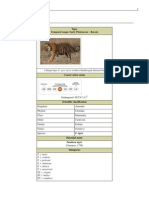
The tiger (Panthera tigris) is the largest living cat species and a member of the genus Panthera.
It
is most recognisable for its dark vertical stripes on orange fur with a white underside. An apex
predator, it primarily preys on ungulates, such as deer and wild boar. It is territorial and generally a
solitary but social predator, requiring large contiguous areas of habitat to support its requirements for
prey and rearing of its offspring. Tiger cubs stay with their mother for about two years and then
become independent, leaving their mother's home range to establish their own.
The tiger was first scientifically described in 1758. It once ranged widely from the Eastern Anatolia
Region in the west to the Amur River basin in the east, and in the south from the foothills of the
Himalayas to Bali in the Sunda Islands. Since the early 20th century, tiger populations have lost at
least 93% of their historic range and have been extirpated from Western and Central Asia, the
islands of Java and Bali, and in large areas of Southeastand South Asia and China. What remains of
the range where tigers still roam free is fragmented, stretching in spots from Siberian temperate
forests to subtropical and tropical forests on the Indian subcontinent, Indochinaand a single
Indonesian island, Sumatra.
The tiger is listed as Endangered on the IUCN Red List. As of 2023, the global wild tiger population
[5]
is estimated to number 5,574 individuals, with most populations living in small isolated pockets.
India hosts the largest tiger population. Major reasons for population decline are habitat destruction,
habitat fragmentation and poaching. Tigers are also victims of human–wildlife conflict, due to
encroachment in countries with a high human population density.
The tiger is among the most recognisable and popular of the world's charismatic megafauna. It
featured prominently in the ancient mythology and folklore of cultures throughout its historic range
and continues to be depicted in modern films and literature, appearing on many flags, coats of arms
and as mascots for sporting teams. The tiger is the national animal of India, Bangladesh, Malaysia
and South Korea.
Etymology
The Middle English tigre and Old English tigras derive from Old French tigre, from Latin tigris. This
was a borrowing of Classical Greek τίγρις 'tigris', a foreign borrowing of unknown origin meaning
[6]
'tiger' and the river Tigris. The generic name Panthera is derived from the Latin word panthera and
[7]
the Ancient Greek word πάνθηρ pánthēr.
Taxonomy
In 1758, Carl Linnaeus described the tiger in his work Systema Naturae and gave it the scientific
[2]
name Felis tigris. In 1929, the British taxonomist Reginald Innes Pocock subordinated the species
[8][9]
under the genus Panthera using the scientific name Panthera tigris.
You might also like
- Tabby MctatDocument40 pagesTabby MctatVijayan TVNo ratings yet
- Tigers: Revered Around The World, But Persecuted Throughout Its RangeDocument4 pagesTigers: Revered Around The World, But Persecuted Throughout Its RangedharshanaNo ratings yet
- Cat Show MagelangDocument15 pagesCat Show MagelangMydesign IdNo ratings yet
- The TigerDocument1 pageThe TigerJan PrcekNo ratings yet
- Panthera: EtymologyDocument2 pagesPanthera: EtymologyAzreen Anis azmiNo ratings yet
- FRRTTTTDocument36 pagesFRRTTTTMarie MythosNo ratings yet
- Tiger - WikipediaDocument36 pagesTiger - WikipediaRobxn GrciaNo ratings yet
- All The Tiger 1231213123121Document3 pagesAll The Tiger 1231213123121Vigu CristianNo ratings yet
- Tiger - WikipediaDocument34 pagesTiger - WikipediaOmoishiro NamikazeNo ratings yet
- Tiger: PantheraDocument10 pagesTiger: PantheraacatoptenNo ratings yet
- TigerDocument6 pagesTigerAnonymous J70OQBprUSNo ratings yet
- TigerDocument27 pagesTigerMsKarolyNo ratings yet
- Etymology: PantheraDocument4 pagesEtymology: PantheraMaximos ManiatisNo ratings yet
- Le TigerDocument1 pageLe TigerlolNo ratings yet
- TigerDocument5 pagesTigertrianaNo ratings yet
- TigerDocument1 pageTigerASHVIN YADAVNo ratings yet
- Tiger: "Tigress" Redirects Here. For Other Uses, See andDocument19 pagesTiger: "Tigress" Redirects Here. For Other Uses, See andtukuNo ratings yet
- TigerDocument44 pagesTigerMustafa DildarNo ratings yet
- TigerDocument1 pageTigerSanduNo ratings yet
- Tiger 12Document24 pagesTiger 12nilebhalNo ratings yet
- Tiger: This Article Is About The Feline. For Other Uses, See - "Tigress" Redirects Here. For Other Uses, SeeDocument6 pagesTiger: This Article Is About The Feline. For Other Uses, See - "Tigress" Redirects Here. For Other Uses, SeeSiddesh BhagatNo ratings yet
- Three Thousand Wild TigersDocument2 pagesThree Thousand Wild TigersHugo Rodriguez AguilarNo ratings yet
- ScribdDocument2 pagesScribdSuhas SuhaasNo ratings yet
- Tiger: This Article Is About The Big Cat. For Other Uses, See - "Tigress" Redirects Here. For Other Uses, SeeDocument39 pagesTiger: This Article Is About The Big Cat. For Other Uses, See - "Tigress" Redirects Here. For Other Uses, SeeSharmistha Talukder KhastagirNo ratings yet
- Extant Cat Species Genus Apex Predator Ungulates Deer Wild Boar Solitary But Social Habitat Prey Home RangeDocument2 pagesExtant Cat Species Genus Apex Predator Ungulates Deer Wild Boar Solitary But Social Habitat Prey Home RangeHazel GocelaNo ratings yet
- File: Unsaved Document 1 Page 1 of 1Document1 pageFile: Unsaved Document 1 Page 1 of 1adarshNo ratings yet
- Tiger: Navigation Search Tiger (Disambiguation) Tigress (Disambiguation)Document45 pagesTiger: Navigation Search Tiger (Disambiguation) Tigress (Disambiguation)manoj kumarNo ratings yet
- TigerDocument1 pageTigerserena mNo ratings yet
- Tiger of Bengal With PhotoDocument30 pagesTiger of Bengal With PhotoVikas SainiNo ratings yet
- TigerDocument4 pagesTigeradith arulNo ratings yet
- Felidae: Navigation Search Felidae (Disambiguation)Document12 pagesFelidae: Navigation Search Felidae (Disambiguation)ari_ariesgurl94No ratings yet
- The Magnificent World of TigersDocument6 pagesThe Magnificent World of TigersHeir_Of_DoomNo ratings yet
- Crows (: L. Cyclotis Respectively) - Elephants Are Scattered ThroughoutDocument7 pagesCrows (: L. Cyclotis Respectively) - Elephants Are Scattered ThroughoutAmitVyavahareNo ratings yet
- Panther, The: Linnaeus Scientific Name Reginald Innes PocockDocument1 pagePanther, The: Linnaeus Scientific Name Reginald Innes PocockRind Bergh DevelosNo ratings yet
- Etymology: SubspeciesDocument2 pagesEtymology: Subspecieskomal patelNo ratings yet
- Bengal Tiger: Panthera Tigris TigrisDocument1 pageBengal Tiger: Panthera Tigris TigrisavncntnNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument2 pagesDocumentaabankhanjmiNo ratings yet
- TigersDocument15 pagesTigersChinna MuthuNo ratings yet
- SquirrelDocument18 pagesSquirrelLitzy estefany Morales cortesNo ratings yet
- Presentation: Alviant Sadad Al FariziDocument2 pagesPresentation: Alviant Sadad Al FariziXXDRA 35No ratings yet
- 20-Endangered and Extinct AnimalsDocument31 pages20-Endangered and Extinct AnimalsAubreyNo ratings yet
- The TigerDocument1 pageThe TigerRPH SETAHUN SK & SMKNo ratings yet
- TigerDocument31 pagesTigerrNo ratings yet
- 1 Horned RhinoDocument12 pages1 Horned RhinoPrachi NikhadeNo ratings yet
- Recount Animal Kelas 10Document5 pagesRecount Animal Kelas 10Febrian FadilahNo ratings yet
- Science Essay Q3Document2 pagesScience Essay Q3racyfiloteo11No ratings yet
- The TigerDocument4 pagesThe TigerArnav BamoriaNo ratings yet
- AnimalDocument5 pagesAnimalShunk ScraperNo ratings yet
- CheetahDocument1 pageCheetahserena mNo ratings yet
- Biodiversiti TapirDocument1 pageBiodiversiti TapirZul NazrieNo ratings yet
- Tiger An Endangered SpeciesDocument25 pagesTiger An Endangered Speciesmonika_waghmareNo ratings yet
- Source:NDTV Source:NDTVDocument10 pagesSource:NDTV Source:NDTVAddy JainNo ratings yet
- Dangerous Species of The Word: World Wildlife FundDocument5 pagesDangerous Species of The Word: World Wildlife FundEshita RoyNo ratings yet
- English ProjectDocument14 pagesEnglish ProjectVaibhav KadriNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Article (S) Used For The SpeechDocument5 pages1.1 Article (S) Used For The SpeechMOHD AZAMNo ratings yet
- Tigers The Ultimate Tiger Book for Kids: 100+ Amazing Tiger Facts, Photos, Quiz & MoreFrom EverandTigers The Ultimate Tiger Book for Kids: 100+ Amazing Tiger Facts, Photos, Quiz & MoreNo ratings yet
- TigerDocument1 pageTigerBrundyNo ratings yet
- Tiger FactsDocument6 pagesTiger FactsTanNo ratings yet
- Tigers: A Species in Danger of ExtinctionDocument23 pagesTigers: A Species in Danger of ExtinctionSergio B. Flores RamírezNo ratings yet
- Módulo 6Document1 pageMódulo 6Rafael Quitandala Baia NogueiraNo ratings yet
- Red Data Book 2.0Document12 pagesRed Data Book 2.0MOULIK MITTALNo ratings yet
- Liger: Ligre CachorroDocument2 pagesLiger: Ligre CachorroJénner Martín Fernández LópezNo ratings yet
- Valvert Et Al 2014 Body Size East African LionDocument2 pagesValvert Et Al 2014 Body Size East African LionMuhammed-YusufNo ratings yet
- Barbary Lions and Cape LionsDocument5 pagesBarbary Lions and Cape LionsRudrodip MajumdarNo ratings yet
- British ShorthairsDocument4 pagesBritish ShorthairsCristiana TemelieNo ratings yet
- Sunda Leopard Cat Classification ChartDocument1 pageSunda Leopard Cat Classification ChartSmail ADJOUNo ratings yet
- Balinese-Javanese Cat Breed: TemperamentDocument2 pagesBalinese-Javanese Cat Breed: TemperamentAdelaNo ratings yet
- Feline Behavioral Evaluation FormDocument3 pagesFeline Behavioral Evaluation FormWalter Peres BiazottoNo ratings yet
- Large Cats: Anther May Refer ToDocument8 pagesLarge Cats: Anther May Refer Tofatima ezzahra FAKIR100% (1)
- Tiger FactsDocument6 pagesTiger FactsTanNo ratings yet
- Services Invoice With Tax Calculation1Document1 pageServices Invoice With Tax Calculation1Hanane HadriNo ratings yet
- Nomenclature and Etymology: GatoDocument3 pagesNomenclature and Etymology: GatoAnonymous JOOQkGbwoRNo ratings yet
- Persian Cat - Google SearchbDocument1 pagePersian Cat - Google Searchbimtiaz AhmefNo ratings yet
- Descriptive TextDocument7 pagesDescriptive TextMila RNo ratings yet
- Trabajo Final de InglesDocument4 pagesTrabajo Final de InglesAaron ChuquirayNo ratings yet
- Zoogeography of FieldsDocument18 pagesZoogeography of FieldsKhadija IkramNo ratings yet
- Article I. Manx Cat: Did You Know?Document2 pagesArticle I. Manx Cat: Did You Know?prosvetiteljNo ratings yet
- Zoo Standards For Keeping Small Felids in CaptivityDocument6 pagesZoo Standards For Keeping Small Felids in CaptivityKai KhanNo ratings yet
- Wild Cat! Wild Cat!Document15 pagesWild Cat! Wild Cat!PrabhakarReddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Cat Breeds: Dr.D.Anil Pavan Kumar M.V.SC.,PH.DDocument55 pagesCat Breeds: Dr.D.Anil Pavan Kumar M.V.SC.,PH.DNaveen BasudeNo ratings yet
- Two White Lions L2Document2 pagesTwo White Lions L2antoniomoncadaNo ratings yet
- 1000 Words of ArticlesDocument6 pages1000 Words of ArticlesKakaNo ratings yet
- Ocicat: Cat Breed Profile: Characteristics, History, Care Tips, and Helpful Information For Pet OwnersDocument17 pagesOcicat: Cat Breed Profile: Characteristics, History, Care Tips, and Helpful Information For Pet OwnersprosvetiteljNo ratings yet
- Maine CoonDocument10 pagesMaine CoonRyan HoganNo ratings yet
- Fun Cat Facts For Kids - Interesting Facts About Cats & KittensDocument2 pagesFun Cat Facts For Kids - Interesting Facts About Cats & Kittenskamarb31No ratings yet
- Felidae Is The Biological Family of The CatsDocument3 pagesFelidae Is The Biological Family of The Catsapi-3799296No ratings yet
- Hndout Test 9comparatives-SuperlativesDocument1 pageHndout Test 9comparatives-Superlativesraffaello3No ratings yet
- For Other Uses, See .: Lion (Disambiguation)Document34 pagesFor Other Uses, See .: Lion (Disambiguation)James CapellanNo ratings yet
- 09 Vet Clinic Patients Solution 2Document6 pages09 Vet Clinic Patients Solution 2Mila Mercado100% (1)
- Cat PDFDocument6 pagesCat PDFAnonymous GxMazRCNo ratings yet