Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1.2 Mass Spectrometry of Elements
1.2 Mass Spectrometry of Elements
Uploaded by
Hilary K0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views1 pageMass spectrometry is a technique used to determine the mass-to-charge ratio of ions by separating them based on their mass and charge. It is used to determine the isotopic composition of elements by distinguishing between isotopes based on their mass-to-charge ratios. Applications include isotopic analysis to determine elemental composition in samples, and elemental analysis to determine the elemental composition of a sample. Mass spectrometers consist of ion sources, mass analyzers, and detectors, and mass spectra provide information about ion mass and abundance through peaks representing specific mass-to-charge ratios.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentMass spectrometry is a technique used to determine the mass-to-charge ratio of ions by separating them based on their mass and charge. It is used to determine the isotopic composition of elements by distinguishing between isotopes based on their mass-to-charge ratios. Applications include isotopic analysis to determine elemental composition in samples, and elemental analysis to determine the elemental composition of a sample. Mass spectrometers consist of ion sources, mass analyzers, and detectors, and mass spectra provide information about ion mass and abundance through peaks representing specific mass-to-charge ratios.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views1 page1.2 Mass Spectrometry of Elements
1.2 Mass Spectrometry of Elements
Uploaded by
Hilary KMass spectrometry is a technique used to determine the mass-to-charge ratio of ions by separating them based on their mass and charge. It is used to determine the isotopic composition of elements by distinguishing between isotopes based on their mass-to-charge ratios. Applications include isotopic analysis to determine elemental composition in samples, and elemental analysis to determine the elemental composition of a sample. Mass spectrometers consist of ion sources, mass analyzers, and detectors, and mass spectra provide information about ion mass and abundance through peaks representing specific mass-to-charge ratios.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
1.
2 Mass Spectrometry of Elements
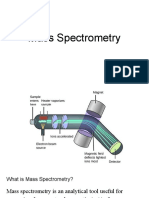
Principle of Mass Spectrometry:
● Technique used to determine the mass-to-charge ratio of ions
● Separates ions based on their mass & charge
● Involves ionizing the sample to form ions, accelerating the ions, & then passing
them through a magnetic field where they are separated based on their mass-to-
charge ratio
Mass Spectrometry of Elements:
● Used to determine the isotopic composition of elements
● Isotopes of an element have different masses due to variations in the number of
neutrons in their nuclei
● Mass spectrometry can distinguish between isotopes based on their mass-to-
charge ratios, allowing the determination of the relative abundance of different
isotopes in a sample
Applications of Mass Spectrometry of Elements:
● Isotopic analysis: mass spectrometry is used to determine the isotopic
composition of elements in various samples, such as geological samples,
environmental samples, and forensic evidence
● Elemental analysis: mass spectrometry can be used to determine the elemental
composition of a sample by measuring the masses of the ions produced from the
sample
Instrumentation:
● Consist of ion sources, mass analyzers, and detectors.
● Ion source ionizes the sample
● Mass analyzer separates the ions based on their mass-to-charge ratios
● Detector measures the ions to determine their abundance.
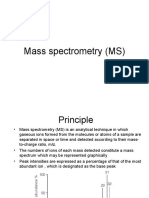
Interpretation of Mass Spectra:
● Produced by mass spectrometry
● Provide information about the mass and abundance of ions in the sample.
● Peaks in the mass spectrum represent ions with specific mass-to-charge ratios
● Relative heights of the peaks correspond to the relative abundances of the ions.
You might also like
- Untitled PresentationDocument17 pagesUntitled Presentationvnitya0630No ratings yet
- Mass Spectrometry InstrumentationDocument3 pagesMass Spectrometry InstrumentationSangeetha priya SNo ratings yet
- Mass SpectrometryDocument1 pageMass SpectrometryAnanda VijayasarathyNo ratings yet
- Principle: Analytical Chemistry and Abundance of Gas-Phase IonsDocument6 pagesPrinciple: Analytical Chemistry and Abundance of Gas-Phase IonsEngr Abuzar KhanNo ratings yet
- MassSpectrometry (MS)Document33 pagesMassSpectrometry (MS)KassimNo ratings yet
- Mass Spectroscopy 2Document25 pagesMass Spectroscopy 2AamirNo ratings yet
- Mass SpectrometryDocument19 pagesMass SpectrometryArchieNo ratings yet
- Mass SpectrosDocument33 pagesMass Spectrosboyapati venupriyaNo ratings yet
- NAME: Mahnoor Kamran Roll Number: 22-80052: Submitted To: DR - Laiba ArshadDocument29 pagesNAME: Mahnoor Kamran Roll Number: 22-80052: Submitted To: DR - Laiba Arshadtayyab malikNo ratings yet
- Mass SpectrosDocument19 pagesMass SpectrosArghya MishraNo ratings yet
- Mass Spectrometry 1Document10 pagesMass Spectrometry 1saymaNo ratings yet
- Mass SpectrometryDocument12 pagesMass Spectrometrypako ramaphaneNo ratings yet
- QQ MS Lec NotesDocument2 pagesQQ MS Lec NotesBellie ArroyoNo ratings yet
- Mass SpectrometryDocument11 pagesMass SpectrometryShigri TahirNo ratings yet
- Atomic Mass SpectrosDocument40 pagesAtomic Mass Spectrosjohnpaul varonaNo ratings yet
- Atomic SpectrosDocument23 pagesAtomic SpectrosJean Kimberly AgnoNo ratings yet
- 3 MassSpectrometry - PPSXDocument13 pages3 MassSpectrometry - PPSXZebBrahviNo ratings yet
- Mass SpectrometryDocument15 pagesMass SpectrometryMeghan Norico Cristuta100% (1)
- Practical Lab - Finals PDFDocument8 pagesPractical Lab - Finals PDFSarmad HussainNo ratings yet
- Mass Spectrometry: I GAA SeptiariDocument31 pagesMass Spectrometry: I GAA SeptiariGung AriNo ratings yet
- Mass Spectroscopy - (Group 13) 5th Sem, Sec-ADocument18 pagesMass Spectroscopy - (Group 13) 5th Sem, Sec-AAhsham AliNo ratings yet
- Fluorometry NotesDocument5 pagesFluorometry NotesHayna RoseNo ratings yet
- Mass Spectrometry (MS) - Principle, Working, Instrumentation, Steps, ApplicationsDocument4 pagesMass Spectrometry (MS) - Principle, Working, Instrumentation, Steps, ApplicationsHà Anh Minh LêNo ratings yet
- 5 - Mass SpectrosDocument58 pages5 - Mass Spectrosamany mohamedNo ratings yet
- Mass SpectrometryDocument4 pagesMass SpectrometryCarlton GrantNo ratings yet
- GP Presentation - Mass SpectrometryDocument19 pagesGP Presentation - Mass SpectrometryAmity BiotechNo ratings yet
- Interference ConcepsDocument3 pagesInterference Concepsjesusoziel santiagogaonaNo ratings yet
- Spectral Methods. Absorption Spectroscopic MethodsDocument14 pagesSpectral Methods. Absorption Spectroscopic MethodsKenan SeneliyevNo ratings yet
- Mass SpectrometryDocument2 pagesMass SpectrometryAathifa ThowfeekNo ratings yet
- For Students - Mass AnalysersDocument27 pagesFor Students - Mass AnalysersArijit Dutta 210075698No ratings yet
- Forensic Science Mass Spectrometry (Principle, Applications and Sample Treatment)Document21 pagesForensic Science Mass Spectrometry (Principle, Applications and Sample Treatment)aniebiet essienpgsNo ratings yet
- What Is SpectrosDocument26 pagesWhat Is SpectrosMelvin Pogi138No ratings yet
- Neutron DetectorDocument10 pagesNeutron DetectorMalik MaazNo ratings yet
- DevicesDocument14 pagesDevicesBelal FatahNo ratings yet
- What Is SpectrosDocument17 pagesWhat Is SpectrosmahirNo ratings yet
- Analytical Technique Used Particulate RadiationDocument8 pagesAnalytical Technique Used Particulate Radiationمحمد الملطاويNo ratings yet
- 01 Atomic StructureDocument49 pages01 Atomic StructurePranav PrasadNo ratings yet
- Mass Spectrometry CompleteDocument155 pagesMass Spectrometry CompleteKamran AlamNo ratings yet
- Principles of Mass SpectrometryDocument23 pagesPrinciples of Mass SpectrometryFatma ZorluNo ratings yet
- Principles of Mass SpectrometryDocument23 pagesPrinciples of Mass SpectrometryFatma Zorlu100% (2)
- Mass Spectrometry and Physical ChemistryDocument20 pagesMass Spectrometry and Physical ChemistryMahmood Mohammed AliNo ratings yet
- Mass Relationship in Chemical Reaction - Atomic MassDocument5 pagesMass Relationship in Chemical Reaction - Atomic MassLovely RamNo ratings yet
- Basic Concept of Instrument Analysis PDFDocument4 pagesBasic Concept of Instrument Analysis PDF1910 65 Vrushali PotdarNo ratings yet
- Analytical Chemistry: Precipitate - Turn The Soluble Substance Into An Insoluble SubstanceDocument7 pagesAnalytical Chemistry: Precipitate - Turn The Soluble Substance Into An Insoluble SubstanceSamantha Jesi Shania EstradaNo ratings yet
- InstrumentsDocument4 pagesInstrumentsP PrabhuNo ratings yet
- Aqa 7404 7405 TN Mass SpectrometryDocument9 pagesAqa 7404 7405 TN Mass SpectrometryAadithNo ratings yet
- Mass Spectrometry: Submitted To: Rani MansuriDocument49 pagesMass Spectrometry: Submitted To: Rani Mansuriamitaggarwal78No ratings yet
- 4101 A Study Material 1 (Mass Spectrometry)Document13 pages4101 A Study Material 1 (Mass Spectrometry)GuRi JassalNo ratings yet
- Mass SpectrometryDocument30 pagesMass Spectrometryfatema100% (1)
- OrbitalDocument2 pagesOrbitaladam millerNo ratings yet
- Mass Spectrometry PPT by KusumDocument23 pagesMass Spectrometry PPT by KusumKusum AhlawatNo ratings yet
- Materi 9. Mass SpectrometryDocument122 pagesMateri 9. Mass Spectrometryinal9474No ratings yet
- Mass SpecDocument22 pagesMass SpecSivam AnandNo ratings yet
- Flame PhotometerDocument14 pagesFlame PhotometerbobNo ratings yet
- Iub Pha404 Autumn 2022 Ms BasicDocument52 pagesIub Pha404 Autumn 2022 Ms BasicTanvir FahimNo ratings yet
- Analytical Presentation Sem 2Document17 pagesAnalytical Presentation Sem 2MSc Part 2 OraganicNo ratings yet
- Atomic SpectrosDocument13 pagesAtomic SpectrosRalph Rezin MooreNo ratings yet
- Spectroscopic Identification of Organic Compounds: TOPIC - 11.3Document15 pagesSpectroscopic Identification of Organic Compounds: TOPIC - 11.3Jes AnthonyNo ratings yet
- Photometry: Science, Sensitivity, and Its Connection to AstronomyFrom EverandPhotometry: Science, Sensitivity, and Its Connection to AstronomyNo ratings yet
- 1.4 Composition of MixturesDocument1 page1.4 Composition of MixturesHilary KNo ratings yet
- 1.6 Nucleic AcidsDocument1 page1.6 Nucleic AcidsHilary KNo ratings yet
- 1.2 - Elements of LifeDocument1 page1.2 - Elements of LifeHilary KNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Settling The ChesapeakeDocument2 pages2.3 Settling The ChesapeakeHilary KNo ratings yet
- 2.2 The Coming of The EnglishDocument2 pages2.2 The Coming of The EnglishHilary KNo ratings yet