Professional Documents
Culture Documents
LAS - Trigonometric Identities
LAS - Trigonometric Identities
Uploaded by
JERLYN MACADOCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- About Electricians Guide To Conduit Bending Third Edition PDFDocument186 pagesAbout Electricians Guide To Conduit Bending Third Edition PDFGaudencio BoniceliNo ratings yet
- TOM Project ReportDocument21 pagesTOM Project Reportzachaboi33% (3)
- Full SolutionsDocument446 pagesFull SolutionsMadelyn Oronos100% (1)
- 1934-HOSKINS-Water Pressure in A Tank Caused by A Simulated EarthquakeDocument32 pages1934-HOSKINS-Water Pressure in A Tank Caused by A Simulated EarthquakeEuge Compagnoni100% (1)
- Module 8 Lesson 8 Trigo IdentitiesDocument5 pagesModule 8 Lesson 8 Trigo IdentitiesHilan Gel GulmaticoNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric IdentitiesDocument1 pageTrigonometric IdentitiesCarlos Manuel Rodríguez MartínezNo ratings yet
- Trigo 2Document2 pagesTrigo 2Julie OcolNo ratings yet
- Simplifying and Proving Trig ExpressionsDocument3 pagesSimplifying and Proving Trig ExpressionsAndrea LacdaoNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Function Identities: Quotient Identities Reciprocal IndentitiesDocument1 pageTrigonometry Function Identities: Quotient Identities Reciprocal IndentitiesCuong NguyenNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric IdentitiesDocument7 pagesTrigonometric IdentitiesMarjun PachecoNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Identities WorksheetDocument2 pagesTrigonometric Identities WorksheetYuri SamozvanovNo ratings yet
- Trig IDsDocument2 pagesTrig IDsSarah Mae BautistaNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Identities (Study Sheet)Document1 pageTrigonometric Identities (Study Sheet)Arfred VillaluzNo ratings yet
- Lesson 14 - Trigonometry IIDocument6 pagesLesson 14 - Trigonometry IIAmmar RizwanNo ratings yet
- Graphs of Cosecant, Secant, and CotangentDocument4 pagesGraphs of Cosecant, Secant, and CotangentmussNo ratings yet
- TrigoDocument2 pagesTrigoJulie OcolNo ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument1 pageTrigonometryteachopensourceNo ratings yet
- Verifying Trig EquationsDocument5 pagesVerifying Trig EquationsjulesNo ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument52 pagesTrigonometrychristiantc0000No ratings yet
- Identifying Identities!: Precalculus Quarter 2 - Module 3 (WEEK 5 & 6)Document18 pagesIdentifying Identities!: Precalculus Quarter 2 - Module 3 (WEEK 5 & 6)Toni Angeline MurilloNo ratings yet
- Potongan B InggrisDocument3 pagesPotongan B InggrisD3 TTRandhi Eka PratamaNo ratings yet
- Math 111: Summary of Trigonometric IdentitiesDocument1 pageMath 111: Summary of Trigonometric IdentitiesalyssaNo ratings yet
- Pure Math: Topic: Trigonometric FunctionsDocument8 pagesPure Math: Topic: Trigonometric FunctionsKienNo ratings yet
- Lect6 IdentitiesDocument38 pagesLect6 IdentitiessatyamkumarNo ratings yet
- Prove The Following. Show Complete Solutions.: SolutionDocument4 pagesProve The Following. Show Complete Solutions.: SolutionRaycelyn Joy CaburnayNo ratings yet
- Ch-08 Solution-1328673Document19 pagesCh-08 Solution-1328673umangpadaya0No ratings yet
- Trigonometric and Hyperbolic FunctionsDocument8 pagesTrigonometric and Hyperbolic FunctionsJpricarioNo ratings yet
- H Essential TrigDocument1 pageH Essential TriglilxinNo ratings yet
- Definition of The Trig FunctionsDocument2 pagesDefinition of The Trig FunctionsJulie OcolNo ratings yet
- Set 3Document4 pagesSet 3Gaffar KadirNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Part 1 GroupworkDocument5 pages5.1 Part 1 GroupworkPeytonNo ratings yet
- 117 Midterm ReferenceDocument1 page117 Midterm Referencesissy.he.7No ratings yet
- Trigonometric FormulaeDocument3 pagesTrigonometric FormulaeUnkown BuddyNo ratings yet
- ProductosDocument2 pagesProductosAndres hurtadoNo ratings yet
- Integration Tips For Finding Fourier Series Math 21b, O. KnillDocument2 pagesIntegration Tips For Finding Fourier Series Math 21b, O. KnillNitya SagarNo ratings yet
- Basic Cal IdentitiesDocument1 pageBasic Cal IdentitieslanceandreycafeNo ratings yet
- SMC2 Formula SheetDocument1 pageSMC2 Formula SheetagamdeepNo ratings yet
- Integration FormulaDocument1 pageIntegration Formulagengenko4No ratings yet
- Trigonometric FormulasDocument2 pagesTrigonometric FormulasErik MierasNo ratings yet
- OctaDocument2 pagesOctaFrancis AngtudNo ratings yet
- TrignometryDocument2 pagesTrignometryRohit C DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- 150 Lecture Notes - Section 7.1 Trigonometric Identities: C Marcia Drost, March 10, 2008Document4 pages150 Lecture Notes - Section 7.1 Trigonometric Identities: C Marcia Drost, March 10, 2008Kella OrtegaNo ratings yet
- θ= cosθ sinθ csc θ=1+cot θ θ secθcosθ sinθ: csc = Product to SumDocument2 pagesθ= cosθ sinθ csc θ=1+cot θ θ secθcosθ sinθ: csc = Product to SumIsrael Sapnu Jr.No ratings yet
- Test1 SSCM1023 20192020 1Document2 pagesTest1 SSCM1023 20192020 1Aisyah NadhirahNo ratings yet
- Solution 2Document156 pagesSolution 2Amit SinghNo ratings yet
- Maths - Trigonometric EquationDocument38 pagesMaths - Trigonometric EquationSefat UllahNo ratings yet
- Sheet - 01 - Trigonometric EquationsDocument16 pagesSheet - 01 - Trigonometric Equationsnsphysics11No ratings yet
- 11 - Trigonometric IdentitiesDocument6 pages11 - Trigonometric IdentitiesQwert RNo ratings yet
- MHF4U Sample Formula SheetDocument1 pageMHF4U Sample Formula Sheetututoringunion1No ratings yet
- Pre-Calculus Test On Chapter 5 Analytic Trigonometry Date: - Name: - PeriodDocument3 pagesPre-Calculus Test On Chapter 5 Analytic Trigonometry Date: - Name: - PeriodIshaan VermaNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry: Definition of The Trig FunctionsDocument4 pagesTrigonometry: Definition of The Trig FunctionsJulie OcolNo ratings yet
- π sec x .cos x π: Ejercicio 1Document4 pagesπ sec x .cos x π: Ejercicio 1Jhoan Sebastian Osma PimientoNo ratings yet
- Homework 1 SolutionsDocument4 pagesHomework 1 Solutionsepsilon miranda canoNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Functions of Acute AnglesDocument16 pagesTrigonometric Functions of Acute Anglesbyunbacooon456No ratings yet
- MIT18 03SCF11 Ps5 s21sDocument3 pagesMIT18 03SCF11 Ps5 s21sBild LucaNo ratings yet
- XPL 2.0 Module Exam 18 SolutionsDocument11 pagesXPL 2.0 Module Exam 18 Solutionsjustinakmanoj22No ratings yet
- Math 126: Calculus IiDocument1 pageMath 126: Calculus IinarasimhacharibabuNo ratings yet
- ( Cos Cos : Explanation: We Have, CosDocument10 pages( Cos Cos : Explanation: We Have, CospoodhilNo ratings yet
- (Download PDF) Precalculus 5th Edition Faires Test Bank Full ChapterDocument87 pages(Download PDF) Precalculus 5th Edition Faires Test Bank Full Chapteryoyaplesia100% (7)
- Trigonometric Formulas R3Document3 pagesTrigonometric Formulas R3weird factsNo ratings yet
- Trigo Formula 20-21Document3 pagesTrigo Formula 20-21ForpdfsNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Chapter 4Document7 pagesTrigonometry Chapter 4freda licudNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- LAS AnnuitiesDocument2 pagesLAS AnnuitiesJERLYN MACADONo ratings yet
- LAS ParabolaDocument2 pagesLAS ParabolaJERLYN MACADONo ratings yet
- Conic Section - Problem SolvingDocument1 pageConic Section - Problem SolvingJERLYN MACADONo ratings yet
- GenMath11 - Q1 - Mod8 - Logarithmic Equations and Inequalities - Version 4 FinalDocument24 pagesGenMath11 - Q1 - Mod8 - Logarithmic Equations and Inequalities - Version 4 FinalJERLYN MACADONo ratings yet
- LAS - Stocks and BondsDocument2 pagesLAS - Stocks and BondsJERLYN MACADONo ratings yet
- Binomial Theorem - LASDocument2 pagesBinomial Theorem - LASJERLYN MACADONo ratings yet
- Answersheet Module6Document2 pagesAnswersheet Module6JERLYN MACADONo ratings yet
- EllipseDocument2 pagesEllipseJERLYN MACADONo ratings yet
- Gen - Math - Answersheet (Module 8)Document2 pagesGen - Math - Answersheet (Module 8)JERLYN MACADONo ratings yet
- Learning Worksheet Q2 Module 9Document5 pagesLearning Worksheet Q2 Module 9JERLYN MACADONo ratings yet
- HyperbolaDocument2 pagesHyperbolaJERLYN MACADONo ratings yet
- Learning Worksheet - Q2 - Module 6Document7 pagesLearning Worksheet - Q2 - Module 6JERLYN MACADONo ratings yet
- Learning Worksheet - Q2 - Module 4Document8 pagesLearning Worksheet - Q2 - Module 4JERLYN MACADONo ratings yet
- PRECALCULUS TOS-MidtermDocument2 pagesPRECALCULUS TOS-MidtermJERLYN MACADONo ratings yet
- Learning Worksheet - Q2 - Module 5Document2 pagesLearning Worksheet - Q2 - Module 5JERLYN MACADONo ratings yet
- Precalculus - ANSWERSHEET Q1 M7 8Document2 pagesPrecalculus - ANSWERSHEET Q1 M7 8JERLYN MACADONo ratings yet
- PC Answersheet (Q2 M1-2)Document2 pagesPC Answersheet (Q2 M1-2)JERLYN MACADONo ratings yet
- PC Answersheet (Q2 M6-7)Document3 pagesPC Answersheet (Q2 M6-7)JERLYN MACADONo ratings yet
- m3 Vtu NotesDocument25 pagesm3 Vtu NotesNiranjan Jb0% (1)
- Chapter 5 Trigonometric RatiosDocument22 pagesChapter 5 Trigonometric RatiosHazmin NawiNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Modeling of Biological Processes: Avner Friedman Chiu-Yen KaoDocument152 pagesMathematical Modeling of Biological Processes: Avner Friedman Chiu-Yen KaoSamuel Yufra100% (1)
- Workshop CalculationDocument61 pagesWorkshop CalculationAshwani Dogra80% (5)
- Experiment No 1: Balancing of Single Disturbing Mass at The Same RadiiDocument14 pagesExperiment No 1: Balancing of Single Disturbing Mass at The Same RadiiAhmad AnsariNo ratings yet
- Maths Class XDocument111 pagesMaths Class XPrashant JainNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Identities: Always LearningDocument4 pagesTrigonometric Identities: Always LearningJesus HernandezNo ratings yet
- PeriodogramaDocument7 pagesPeriodograma777666sbmNo ratings yet
- AvkflyfilyfluyfluyfrDocument55 pagesAvkflyfilyfluyfluyfrabcNo ratings yet
- Singapore Chinese Girls' School Preliminary Examination 2008Document5 pagesSingapore Chinese Girls' School Preliminary Examination 2008JASON_INGHAMNo ratings yet
- Maths - Trigonometry - 1st April PDFDocument2 pagesMaths - Trigonometry - 1st April PDFAbhinav RaiNo ratings yet
- 300+ TOP Engineering Mechanics Objective Questions & AnswersDocument24 pages300+ TOP Engineering Mechanics Objective Questions & AnswersramkumarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet On Vector Valued FunctionsDocument6 pagesWorksheet On Vector Valued FunctionsvietboiiNo ratings yet
- Q2 How Can Android-Based Trigonometry Learning Improve The Math Learning ProcessDocument13 pagesQ2 How Can Android-Based Trigonometry Learning Improve The Math Learning ProcessLidra Ety Syahfitri HarahapNo ratings yet
- DIPIETE ETmainDocument89 pagesDIPIETE ETmainVitthal TalawarNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Studies Paper 2 SL MarkschemeDocument22 pagesMathematical Studies Paper 2 SL MarkschemeYash LalaNo ratings yet
- Homework 4Document7 pagesHomework 4Ale Gomez100% (1)
- GHS AP Stat TalkDocument8 pagesGHS AP Stat Talksouvik5000No ratings yet
- 1 Ahmad Dallal - Hybridity, Critical Outlook, New SciencesDocument13 pages1 Ahmad Dallal - Hybridity, Critical Outlook, New SciencesemoizedNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Final ExamDocument6 pagesTrigonometry Final ExamJhunnerpaul SolisNo ratings yet
- CBSE 10th Mathematics Sample Paper 2019 Question PaperDocument6 pagesCBSE 10th Mathematics Sample Paper 2019 Question PapermisostudyNo ratings yet
- RD Sharma InequationDocument150 pagesRD Sharma InequationSandeep Kumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesTrigonometry Lesson Planapi-570462651No ratings yet
- Grade 11Document2 pagesGrade 11Joe Jayson CaletenaNo ratings yet
- Development of A Cell Phone Based Remote Control System: An Effective Switching System For Controlling Home and Office AppliancesDocument7 pagesDevelopment of A Cell Phone Based Remote Control System: An Effective Switching System For Controlling Home and Office AppliancesKosala BandaraNo ratings yet
- Maths AA HL Review SheetDocument26 pagesMaths AA HL Review SheetShreyans JuniwalNo ratings yet
LAS - Trigonometric Identities
LAS - Trigonometric Identities
Uploaded by
JERLYN MACADOOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
LAS - Trigonometric Identities
LAS - Trigonometric Identities
Uploaded by
JERLYN MACADOCopyright:
Available Formats
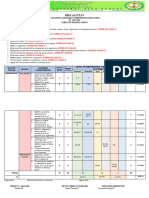
PRECALCULUS Trigonometric identities and its situational problems
Learning Activity Sheet
2nd Quarter-WEEK 4-5
NAME: ___________________________________________ DATE: _______________________
TRACK-STRAND/SECTION: _______________________ CP #: ________________________
Learning Competencies
1. Determine whether an equation is an identity or a conditional equation. STEM_PC11AG-IIe-1
2. Derive the fundamental trigonometric identities. STEM_PC11AG-IIe-2
3. Simplify trigonometric expressions. STEM_PC11AG-IIf-2
KEY CONCEPTS:
Trigonometric principles, identities, and equations are widely employed nowadays in surveying, navigation,
engineering, electrical, optics, music, medicine, criminology, and a variety of other industries.
An identity equation is one that holds true for all values of the variable in the equation's domain. If some values
of the variable in the domain of the equation do not satisfy the equation, it is a conditional equation.
Exercises 1. Identify whether the equation: x 3−2=(x−√ 3
2)( x + √ 2 x+ √ 4) is an identity or a conditional equation.
2 2 3
Solution: It is an identity equation because it involves factoring of the difference of two cubes. The equation will be
satisfied with any value of x.
Exercises 2. Identify whether the equation: sin2 θ=cos2 θ+1is an identity or a conditional equation.
Solution: It is a conditional equation. If equals 𝜃=0, the left side of the equation is 0 and the right side is 2, indicating
that both sides are unequal.
Remember:
For all values of x (domain), an identity equation shows that both sides are equal. On the other hand, a
conditional equation demonstrates that the value of x will satisfy either the left or right sides of the equation, but not both.
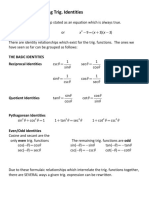
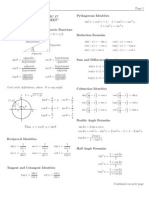
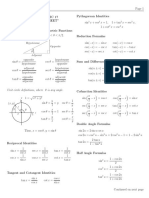
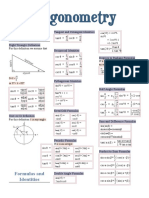
FUNDAMENTAL TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES
An equation containing a trigonometric function or a combination of trigonometric functions that is valid for all
values of the variable for which the functions are defined is known as trigonometric identity.
These identities are verified using the fundamental identities that hold for every value of the angle or real
number, for which the functions involved are defined.
Reciprocal Identities Quotient Identities
1 1 y sinθ
(1) cosθ= secθ= (4) tanθ= =
secθ cosθ x cosθ
1 1 x cosθ
(2) sinθ= cscθ= (5) cotθ= =
cscθ sinθ y sinθ
1 1
(3) tanθ= cotθ =
cotθ tanθ
Pythagorean Identities
(6) cos 2 θ+ sin2 θ=1 2
cos θ=1−sin θ
2
sin θ=1−cos θ
2 2
(7) 1+ tan 2 θ=sec 2 θ 2 2
tan θ=sec θ−1
2 2
1=sec θ−tan θ
(8) cot 2 θ+1=csc 2 θ 2 2
cot θ=csc θ−1
2 2
1=csc θ−cot θ
Even and Odd Identities
Odd Identities: (9) sin (−θ )=−sinθ , csc (−θ )=−cscθ
(10) tan (−θ )=−tanθ , cot (−θ )=−cotθ
Even Identity: (11) cos (−θ )=cosθ , sec (−θ )=secθ
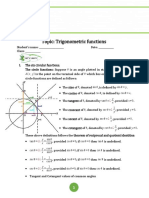
SUM AND DIFFERENCE IDENTITIES
The general addition formulas are used to find the value of a circular function of a sum or difference of two angles
Note: A and B represents angles
Sum and Difference Formulas
(1) cos ( A+ B )=cosAcosB−sinAsinB
The value of a function at A is the same as the value of its cofunction at B. This always happens with complementary angles; in fact, it
is this phenomenon that gives a “cofunction” its name. The “co” stands for “complement”.
Cofunction Identities
sin( π2 −θ )=cosθ ( π2 −θ )=cscθ
sec
cos ( −θ )=sinθ csc ( −θ )=secθ
π π
2 2
tan ( −θ )=cotθ cot ( −θ )=tan
π π
2 2
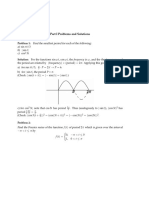
PERFORMANCE TASK
A. Complete the proving pattern.
Expression Explanation/ Reason
cosθ
(1) =1−sinθ Given
secθ +tanθ
cosθ
=1−sinθ
(2) 1 sinθ Apply __________ identity for secθand _______ identity for tanθ
+
cosθ cosθ
cosθ
(3) =1−sinθ Adding the denominator through LCD
¿¿
¿¿
(4) cosθ ∙ Get the ______________ of the denominator
¿¿ =1−sinθ¿
¿¿
(5) =1−sinθ ¿ Simplify
1+ sinθ
2
1−sin θ
(6) =1−sinθ Apply _______________ identity of cos 2 θ
1+ sinθ
(1−sinθ)(¿¿ )
(7) =1−sinθ Factor out 1−sin2 θ
1+ sinθ
(8) ¿¿ =1−sinθ Reduce to lowest term
5 −4
B. Given cosA = and sinB= , find cos ¿ ) if both A and B are in QIV. Write your complete solution in
13 5
another sheet of paper.
RUBRICS FOR CHECKING
CRITERIA SCORES
ACCURACY (COMPLETENESS & CORRECTNESS)
5pts: Show correct answer with accurate and complete solution.
4pts: Show correct answer with accuracy in the process but incomplete solution.
3pts: Show correct answer with incomplete solution.
2pts: Perform a solution but arrive incorrect answer.
1pt: Attempts an answer.
You might also like
- About Electricians Guide To Conduit Bending Third Edition PDFDocument186 pagesAbout Electricians Guide To Conduit Bending Third Edition PDFGaudencio BoniceliNo ratings yet
- TOM Project ReportDocument21 pagesTOM Project Reportzachaboi33% (3)
- Full SolutionsDocument446 pagesFull SolutionsMadelyn Oronos100% (1)
- 1934-HOSKINS-Water Pressure in A Tank Caused by A Simulated EarthquakeDocument32 pages1934-HOSKINS-Water Pressure in A Tank Caused by A Simulated EarthquakeEuge Compagnoni100% (1)
- Module 8 Lesson 8 Trigo IdentitiesDocument5 pagesModule 8 Lesson 8 Trigo IdentitiesHilan Gel GulmaticoNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric IdentitiesDocument1 pageTrigonometric IdentitiesCarlos Manuel Rodríguez MartínezNo ratings yet
- Trigo 2Document2 pagesTrigo 2Julie OcolNo ratings yet
- Simplifying and Proving Trig ExpressionsDocument3 pagesSimplifying and Proving Trig ExpressionsAndrea LacdaoNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Function Identities: Quotient Identities Reciprocal IndentitiesDocument1 pageTrigonometry Function Identities: Quotient Identities Reciprocal IndentitiesCuong NguyenNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric IdentitiesDocument7 pagesTrigonometric IdentitiesMarjun PachecoNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Identities WorksheetDocument2 pagesTrigonometric Identities WorksheetYuri SamozvanovNo ratings yet
- Trig IDsDocument2 pagesTrig IDsSarah Mae BautistaNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Identities (Study Sheet)Document1 pageTrigonometric Identities (Study Sheet)Arfred VillaluzNo ratings yet
- Lesson 14 - Trigonometry IIDocument6 pagesLesson 14 - Trigonometry IIAmmar RizwanNo ratings yet
- Graphs of Cosecant, Secant, and CotangentDocument4 pagesGraphs of Cosecant, Secant, and CotangentmussNo ratings yet
- TrigoDocument2 pagesTrigoJulie OcolNo ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument1 pageTrigonometryteachopensourceNo ratings yet
- Verifying Trig EquationsDocument5 pagesVerifying Trig EquationsjulesNo ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument52 pagesTrigonometrychristiantc0000No ratings yet
- Identifying Identities!: Precalculus Quarter 2 - Module 3 (WEEK 5 & 6)Document18 pagesIdentifying Identities!: Precalculus Quarter 2 - Module 3 (WEEK 5 & 6)Toni Angeline MurilloNo ratings yet
- Potongan B InggrisDocument3 pagesPotongan B InggrisD3 TTRandhi Eka PratamaNo ratings yet
- Math 111: Summary of Trigonometric IdentitiesDocument1 pageMath 111: Summary of Trigonometric IdentitiesalyssaNo ratings yet
- Pure Math: Topic: Trigonometric FunctionsDocument8 pagesPure Math: Topic: Trigonometric FunctionsKienNo ratings yet
- Lect6 IdentitiesDocument38 pagesLect6 IdentitiessatyamkumarNo ratings yet
- Prove The Following. Show Complete Solutions.: SolutionDocument4 pagesProve The Following. Show Complete Solutions.: SolutionRaycelyn Joy CaburnayNo ratings yet
- Ch-08 Solution-1328673Document19 pagesCh-08 Solution-1328673umangpadaya0No ratings yet
- Trigonometric and Hyperbolic FunctionsDocument8 pagesTrigonometric and Hyperbolic FunctionsJpricarioNo ratings yet
- H Essential TrigDocument1 pageH Essential TriglilxinNo ratings yet
- Definition of The Trig FunctionsDocument2 pagesDefinition of The Trig FunctionsJulie OcolNo ratings yet
- Set 3Document4 pagesSet 3Gaffar KadirNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Part 1 GroupworkDocument5 pages5.1 Part 1 GroupworkPeytonNo ratings yet
- 117 Midterm ReferenceDocument1 page117 Midterm Referencesissy.he.7No ratings yet
- Trigonometric FormulaeDocument3 pagesTrigonometric FormulaeUnkown BuddyNo ratings yet
- ProductosDocument2 pagesProductosAndres hurtadoNo ratings yet
- Integration Tips For Finding Fourier Series Math 21b, O. KnillDocument2 pagesIntegration Tips For Finding Fourier Series Math 21b, O. KnillNitya SagarNo ratings yet
- Basic Cal IdentitiesDocument1 pageBasic Cal IdentitieslanceandreycafeNo ratings yet
- SMC2 Formula SheetDocument1 pageSMC2 Formula SheetagamdeepNo ratings yet
- Integration FormulaDocument1 pageIntegration Formulagengenko4No ratings yet
- Trigonometric FormulasDocument2 pagesTrigonometric FormulasErik MierasNo ratings yet
- OctaDocument2 pagesOctaFrancis AngtudNo ratings yet
- TrignometryDocument2 pagesTrignometryRohit C DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- 150 Lecture Notes - Section 7.1 Trigonometric Identities: C Marcia Drost, March 10, 2008Document4 pages150 Lecture Notes - Section 7.1 Trigonometric Identities: C Marcia Drost, March 10, 2008Kella OrtegaNo ratings yet
- θ= cosθ sinθ csc θ=1+cot θ θ secθcosθ sinθ: csc = Product to SumDocument2 pagesθ= cosθ sinθ csc θ=1+cot θ θ secθcosθ sinθ: csc = Product to SumIsrael Sapnu Jr.No ratings yet
- Test1 SSCM1023 20192020 1Document2 pagesTest1 SSCM1023 20192020 1Aisyah NadhirahNo ratings yet
- Solution 2Document156 pagesSolution 2Amit SinghNo ratings yet
- Maths - Trigonometric EquationDocument38 pagesMaths - Trigonometric EquationSefat UllahNo ratings yet
- Sheet - 01 - Trigonometric EquationsDocument16 pagesSheet - 01 - Trigonometric Equationsnsphysics11No ratings yet
- 11 - Trigonometric IdentitiesDocument6 pages11 - Trigonometric IdentitiesQwert RNo ratings yet
- MHF4U Sample Formula SheetDocument1 pageMHF4U Sample Formula Sheetututoringunion1No ratings yet
- Pre-Calculus Test On Chapter 5 Analytic Trigonometry Date: - Name: - PeriodDocument3 pagesPre-Calculus Test On Chapter 5 Analytic Trigonometry Date: - Name: - PeriodIshaan VermaNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry: Definition of The Trig FunctionsDocument4 pagesTrigonometry: Definition of The Trig FunctionsJulie OcolNo ratings yet
- π sec x .cos x π: Ejercicio 1Document4 pagesπ sec x .cos x π: Ejercicio 1Jhoan Sebastian Osma PimientoNo ratings yet
- Homework 1 SolutionsDocument4 pagesHomework 1 Solutionsepsilon miranda canoNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Functions of Acute AnglesDocument16 pagesTrigonometric Functions of Acute Anglesbyunbacooon456No ratings yet
- MIT18 03SCF11 Ps5 s21sDocument3 pagesMIT18 03SCF11 Ps5 s21sBild LucaNo ratings yet
- XPL 2.0 Module Exam 18 SolutionsDocument11 pagesXPL 2.0 Module Exam 18 Solutionsjustinakmanoj22No ratings yet
- Math 126: Calculus IiDocument1 pageMath 126: Calculus IinarasimhacharibabuNo ratings yet
- ( Cos Cos : Explanation: We Have, CosDocument10 pages( Cos Cos : Explanation: We Have, CospoodhilNo ratings yet
- (Download PDF) Precalculus 5th Edition Faires Test Bank Full ChapterDocument87 pages(Download PDF) Precalculus 5th Edition Faires Test Bank Full Chapteryoyaplesia100% (7)
- Trigonometric Formulas R3Document3 pagesTrigonometric Formulas R3weird factsNo ratings yet
- Trigo Formula 20-21Document3 pagesTrigo Formula 20-21ForpdfsNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Chapter 4Document7 pagesTrigonometry Chapter 4freda licudNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- LAS AnnuitiesDocument2 pagesLAS AnnuitiesJERLYN MACADONo ratings yet
- LAS ParabolaDocument2 pagesLAS ParabolaJERLYN MACADONo ratings yet
- Conic Section - Problem SolvingDocument1 pageConic Section - Problem SolvingJERLYN MACADONo ratings yet
- GenMath11 - Q1 - Mod8 - Logarithmic Equations and Inequalities - Version 4 FinalDocument24 pagesGenMath11 - Q1 - Mod8 - Logarithmic Equations and Inequalities - Version 4 FinalJERLYN MACADONo ratings yet
- LAS - Stocks and BondsDocument2 pagesLAS - Stocks and BondsJERLYN MACADONo ratings yet
- Binomial Theorem - LASDocument2 pagesBinomial Theorem - LASJERLYN MACADONo ratings yet
- Answersheet Module6Document2 pagesAnswersheet Module6JERLYN MACADONo ratings yet
- EllipseDocument2 pagesEllipseJERLYN MACADONo ratings yet
- Gen - Math - Answersheet (Module 8)Document2 pagesGen - Math - Answersheet (Module 8)JERLYN MACADONo ratings yet
- Learning Worksheet Q2 Module 9Document5 pagesLearning Worksheet Q2 Module 9JERLYN MACADONo ratings yet
- HyperbolaDocument2 pagesHyperbolaJERLYN MACADONo ratings yet
- Learning Worksheet - Q2 - Module 6Document7 pagesLearning Worksheet - Q2 - Module 6JERLYN MACADONo ratings yet
- Learning Worksheet - Q2 - Module 4Document8 pagesLearning Worksheet - Q2 - Module 4JERLYN MACADONo ratings yet
- PRECALCULUS TOS-MidtermDocument2 pagesPRECALCULUS TOS-MidtermJERLYN MACADONo ratings yet
- Learning Worksheet - Q2 - Module 5Document2 pagesLearning Worksheet - Q2 - Module 5JERLYN MACADONo ratings yet
- Precalculus - ANSWERSHEET Q1 M7 8Document2 pagesPrecalculus - ANSWERSHEET Q1 M7 8JERLYN MACADONo ratings yet
- PC Answersheet (Q2 M1-2)Document2 pagesPC Answersheet (Q2 M1-2)JERLYN MACADONo ratings yet
- PC Answersheet (Q2 M6-7)Document3 pagesPC Answersheet (Q2 M6-7)JERLYN MACADONo ratings yet
- m3 Vtu NotesDocument25 pagesm3 Vtu NotesNiranjan Jb0% (1)
- Chapter 5 Trigonometric RatiosDocument22 pagesChapter 5 Trigonometric RatiosHazmin NawiNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Modeling of Biological Processes: Avner Friedman Chiu-Yen KaoDocument152 pagesMathematical Modeling of Biological Processes: Avner Friedman Chiu-Yen KaoSamuel Yufra100% (1)
- Workshop CalculationDocument61 pagesWorkshop CalculationAshwani Dogra80% (5)
- Experiment No 1: Balancing of Single Disturbing Mass at The Same RadiiDocument14 pagesExperiment No 1: Balancing of Single Disturbing Mass at The Same RadiiAhmad AnsariNo ratings yet
- Maths Class XDocument111 pagesMaths Class XPrashant JainNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Identities: Always LearningDocument4 pagesTrigonometric Identities: Always LearningJesus HernandezNo ratings yet
- PeriodogramaDocument7 pagesPeriodograma777666sbmNo ratings yet
- AvkflyfilyfluyfluyfrDocument55 pagesAvkflyfilyfluyfluyfrabcNo ratings yet
- Singapore Chinese Girls' School Preliminary Examination 2008Document5 pagesSingapore Chinese Girls' School Preliminary Examination 2008JASON_INGHAMNo ratings yet
- Maths - Trigonometry - 1st April PDFDocument2 pagesMaths - Trigonometry - 1st April PDFAbhinav RaiNo ratings yet
- 300+ TOP Engineering Mechanics Objective Questions & AnswersDocument24 pages300+ TOP Engineering Mechanics Objective Questions & AnswersramkumarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet On Vector Valued FunctionsDocument6 pagesWorksheet On Vector Valued FunctionsvietboiiNo ratings yet
- Q2 How Can Android-Based Trigonometry Learning Improve The Math Learning ProcessDocument13 pagesQ2 How Can Android-Based Trigonometry Learning Improve The Math Learning ProcessLidra Ety Syahfitri HarahapNo ratings yet
- DIPIETE ETmainDocument89 pagesDIPIETE ETmainVitthal TalawarNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Studies Paper 2 SL MarkschemeDocument22 pagesMathematical Studies Paper 2 SL MarkschemeYash LalaNo ratings yet
- Homework 4Document7 pagesHomework 4Ale Gomez100% (1)
- GHS AP Stat TalkDocument8 pagesGHS AP Stat Talksouvik5000No ratings yet
- 1 Ahmad Dallal - Hybridity, Critical Outlook, New SciencesDocument13 pages1 Ahmad Dallal - Hybridity, Critical Outlook, New SciencesemoizedNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Final ExamDocument6 pagesTrigonometry Final ExamJhunnerpaul SolisNo ratings yet
- CBSE 10th Mathematics Sample Paper 2019 Question PaperDocument6 pagesCBSE 10th Mathematics Sample Paper 2019 Question PapermisostudyNo ratings yet
- RD Sharma InequationDocument150 pagesRD Sharma InequationSandeep Kumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesTrigonometry Lesson Planapi-570462651No ratings yet
- Grade 11Document2 pagesGrade 11Joe Jayson CaletenaNo ratings yet
- Development of A Cell Phone Based Remote Control System: An Effective Switching System For Controlling Home and Office AppliancesDocument7 pagesDevelopment of A Cell Phone Based Remote Control System: An Effective Switching System For Controlling Home and Office AppliancesKosala BandaraNo ratings yet
- Maths AA HL Review SheetDocument26 pagesMaths AA HL Review SheetShreyans JuniwalNo ratings yet