Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assisted Reproductive Technology
Assisted Reproductive Technology
Uploaded by
Ananda Sadhukhan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views16 pagesInfertility is defined as the failure to achieve pregnancy after 12 months of unprotected sex. Common causes of female infertility include ovulation disorders, blocked fallopian tubes, uterine anomalies, and fibroids. Common male infertility factors are azoospermia, oligospermia, malformed sperm, and genetic issues. Assisted reproductive technologies (ART) are procedures used to help infertile couples conceive, including in vitro techniques like IVF and ICSI, and in vivo techniques like IUI. IVF involves fertilizing eggs and sperm outside the body then transferring the embryo to the uterus.
Original Description:
ASSISTED REPRODUCTIVE TECHNOLOGY
Original Title
ASSISTED REPRODUCTIVE TECHNOLOGY
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentInfertility is defined as the failure to achieve pregnancy after 12 months of unprotected sex. Common causes of female infertility include ovulation disorders, blocked fallopian tubes, uterine anomalies, and fibroids. Common male infertility factors are azoospermia, oligospermia, malformed sperm, and genetic issues. Assisted reproductive technologies (ART) are procedures used to help infertile couples conceive, including in vitro techniques like IVF and ICSI, and in vivo techniques like IUI. IVF involves fertilizing eggs and sperm outside the body then transferring the embryo to the uterus.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views16 pagesAssisted Reproductive Technology
Assisted Reproductive Technology
Uploaded by
Ananda SadhukhanInfertility is defined as the failure to achieve pregnancy after 12 months of unprotected sex. Common causes of female infertility include ovulation disorders, blocked fallopian tubes, uterine anomalies, and fibroids. Common male infertility factors are azoospermia, oligospermia, malformed sperm, and genetic issues. Assisted reproductive technologies (ART) are procedures used to help infertile couples conceive, including in vitro techniques like IVF and ICSI, and in vivo techniques like IUI. IVF involves fertilizing eggs and sperm outside the body then transferring the embryo to the uterus.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 16
WHAT IS INFERTILITY?
Infertility is a disease of the male or female reproductive system
defined by the failure to achieve a pregnancy after 12 months or more
of regular unprotected sexual intercourse.
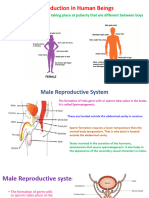
FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
COMMON FEMALE INFERTILITY FACTORS
• Most common ovulation disorder
• Blocked fallopian tubes(can cause when a women has had pelvic
inflammatory diseases or endometriosis)a condition where tissues
are similar to the lining of the womb or uterus started to grow in
other places such as ovaries or fallopian tube).
• Congenital anomalies involving the structure of uterus and uterine
fibroid can be associated with repeat miscarriages.
• Instead of these causes, there also have many other causes of female
infertility.
COMMON MALE INFERTILITY FACTORS
• Most common male infertility factors include azoospermia(no sperm
cells are produced) and oligospermia (few sperm cells are produced).
• Sometimes sperm cells are malformed or they die before they can
reach the egg.
• Also a genetic disease as chromosomal abnormalities causes infertility
in men.
• Diabetes mellitus
• Obesity
• Instead of these causes, there also have many other causes of male
infertility.
What is Assisted Reproductive Technology?
• A collection of procedures, which includes the handling of gamates
and/or embroys outside the body to achieve a pregnancy, is known as
Assisted Reproductive Technology(ART).
• Increases the chance of pregnancy in infertile couples.
• In earlier 19th Century, Infertile couples have two options either to
adopt or be childless.
• But now for past few decades some breakthrough artificial
reproductive techniques are invented.
ART TECHNIQUES
IN VITRO TECHNIQUES IN VIVO TECHNIQUES
• In vitro fertilization(IVF) • Intra uterine insemination(IUI)
• Zygote intra fallopian • Artificial Insemination(AI)
transfer(ZIFT) • Gamete intrafallopian
• Intra uterine transfer(IUT) transfer(GIFT)
• Intra cytoplasmic sperm
injection(ICSI)
• Surrogacy
Invitro Fertilization(IVF)
• Also called as “Test tube baby
techniques”.
• Fertilization outside the body followed by
embryo transfer.
• Ova from the wife/donor female and
sperms from the husband/ donor male
are collected.
• The eggs are combined with sperm for
fertilization in laboratory.
• The fertilization of egg results in the
formation of zygote.
• The Zygote or Early embryos(with up to 8
blastomeres) transferred into the
woman’s uterus for further development.
Zygote Intra Fallopian
Transfer(ZIFT)
• ZIFT is used when there is a blockage in
the fallopian tube which prevents the
fertilization of egg by the sperm.
• Egg is removed from the ovary.
• Fertilization of the egg with sperm is
carried out outside the body(IVF).
• The zygote up to 8 blastomere stage is
transferred to the fallopian tube.
• It continues its natural divisions and
develop further.
Intra Uterine
Transfer(IUT)
Embryo with more than 8 cell blastomere is
inserted into the uterus to complete its
further development.
INTRA CYTOPLASMIC
SPERM INJECTION
• Sometimes the sperm cannot penetrate
the outer layers of ovum for a variety
reasons.
• Thick outer layer(zona pellucida) can be a
cause that a sperm become unable to
penetrate.
• In this type of conditions ICSI can be done
along either IVF to help fertilize the egg.
• A single sperm is injected directly into the
cytoplasm of an ovum under specific
laboratory condition.
Surrogacy
• This is a kind of agreement where a
women agrees to carry a pregnancy for
another person, who will become the
newborn child’s parent after birth.
• Here by the process of IVF, embroys are
created in laboratory and implant into
surrogate mother’s uterus.
Intra Uterine
Insemination
• This is a procedure of treating infertile
men due to low sperm count or
morphologically abnormal sperm.
• Semen is collected either from the
husband or from a healthy donor and
prepared through a specific long process.
• After preparing the sperm, the sperm is
introduced into the uterus through vagina
by catheter after stimulating the ovaries
to produce more ova.
• The motto of IUI technique is to increase
the number of sperm that reach to the
fallopian tubes and subsequently increase
the chance of fertilization.
ARTIFICIAL
INSEMINATION
• In this cases either due to inability of the
male partner to inseminate the female or
due to very low sperm count in the
ejaculates, could be corrected by Artificial
Insemination.
• Collected sperm of husband donor is
introduced into the cervix.
Gamete Intrafallopian
Transfer
• A method for the female who could not
produce egg successfully but can provide
suitable environment for fertilization and
further development.
• Entrance of upper segment of ovaries are
blocked.
• In this, the ovum and sperms are directly
injected into the fallopian tube, where
fertilization produced a blastocyst.
• Blastocyst enter the uterus via normal
route.
• GIFT has 30 % success rate.
THANK YOU
You might also like
- Assited Reproductive TechnologyDocument40 pagesAssited Reproductive TechnologySanthosh.S.U100% (1)
- In Vitro Fertilization - Report - g8Document20 pagesIn Vitro Fertilization - Report - g8Maica GeeNo ratings yet
- Argumentative Essay Final DraftDocument4 pagesArgumentative Essay Final Draftapi-332220891100% (1)
- Ivf PresentationDocument15 pagesIvf Presentationapi-313313875100% (2)
- OB Nursing Ma'Am PacabisDocument16 pagesOB Nursing Ma'Am PacabisArgee AlonsabeNo ratings yet
- Assisted Reproductive TechnologiesDocument19 pagesAssisted Reproductive TechnologiesGURU ROHIIT KNo ratings yet
- Assisted Reproductive Technology by Rosemary C. AgboDocument19 pagesAssisted Reproductive Technology by Rosemary C. AgboRosemaryNo ratings yet
- Ivf ENTER - Final FinalDocument15 pagesIvf ENTER - Final FinalsumanavijitNo ratings yet
- 4 Family Having Difficulty Conceiving A ChildDocument10 pages4 Family Having Difficulty Conceiving A ChildDrex CuritanaNo ratings yet
- Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART) : and ApplicationDocument38 pagesAssisted Reproductive Technology (ART) : and ApplicationPraluki HerliawanNo ratings yet
- Assisted Reproductive TechnologyDocument16 pagesAssisted Reproductive TechnologyQilaNo ratings yet
- Bio Seminar - ARTDocument22 pagesBio Seminar - ARTmanisha.e08No ratings yet
- Chapter:4 Reproductive Health: Assisted Reproductive Technology (Art)Document11 pagesChapter:4 Reproductive Health: Assisted Reproductive Technology (Art)Nikhil BijuNo ratings yet
- Infertility, ART, and The Reproductive SystemDocument5 pagesInfertility, ART, and The Reproductive Systemsomeone4630No ratings yet
- FertilizationDocument108 pagesFertilizationDauda RukaiyaNo ratings yet
- Ivf Clinic at AurangabadDocument7 pagesIvf Clinic at AurangabadSanjay PagareNo ratings yet
- Why and When Do You Need To Go For IVF?Document2 pagesWhy and When Do You Need To Go For IVF?gbrclinicNo ratings yet
- In VitrofertilizationDocument29 pagesIn VitrofertilizationRad RYNo ratings yet
- Assiated Reproductive Technology IpDocument25 pagesAssiated Reproductive Technology IpBharati patil100% (1)
- Test Tube Baby 1Document16 pagesTest Tube Baby 1nitesh.th15005No ratings yet
- Assisted Reproductive TechnologyDocument14 pagesAssisted Reproductive Technologyarchana jainNo ratings yet
- CMC Assisted ReproductionDocument3 pagesCMC Assisted Reproductionmavazbo1508No ratings yet
- In-Vitro Fertilisation: Shruti Samal ROLL NUMBER - 1120096 B.Sc. Life Science Second SemesterDocument20 pagesIn-Vitro Fertilisation: Shruti Samal ROLL NUMBER - 1120096 B.Sc. Life Science Second SemesterSHRUTI SAMALNo ratings yet
- Project Part-21Document87 pagesProject Part-21Bhimasen PradhanNo ratings yet
- Recent Advancements in Infertility Techniques AloneDocument111 pagesRecent Advancements in Infertility Techniques AlonesanthanalakshmiNo ratings yet
- Infertility TreatmentDocument9 pagesInfertility TreatmentNur Farizah ZuhaidiNo ratings yet
- Intrauterine Insemination (IUI)Document21 pagesIntrauterine Insemination (IUI)Chanta MaharjanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document19 pagesChapter 3Shelina Elora LiewNo ratings yet
- UMK Animal Reproduction Semester 2Document40 pagesUMK Animal Reproduction Semester 2Rina Abigail CarterNo ratings yet
- Dr.L.Ananda Kumar M.D (F.M)Document33 pagesDr.L.Ananda Kumar M.D (F.M)viratyuguNo ratings yet
- Artificial InseminationDocument11 pagesArtificial InseminationShrestha NeharikaNo ratings yet
- Reproductive HealthDocument6 pagesReproductive HealthAdesh BhullarNo ratings yet
- Artificial Reproductive TechniqueDocument34 pagesArtificial Reproductive TechniqueBhawna JoshiNo ratings yet
- In Vitro FertilizationDocument4 pagesIn Vitro FertilizationFrances Kaye Sta. CruzNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Investigatory Project....Document8 pagesClass 12 Investigatory Project....shivshankardahayat80No ratings yet
- (L7) - Reproductive Health - Aug 23, 2019 - FridayDocument49 pages(L7) - Reproductive Health - Aug 23, 2019 - Fridaysarthak kedariNo ratings yet
- Explore Your Options With in Vitro FertilizationDocument10 pagesExplore Your Options With in Vitro FertilizationCurrae HospitalNo ratings yet
- Procedure: in Vitro Fertilization (Ivf)Document7 pagesProcedure: in Vitro Fertilization (Ivf)Lovely SarangiNo ratings yet
- Ivf at Rajul Nursing Home, AligarhDocument2 pagesIvf at Rajul Nursing Home, AligarhAnjulaNo ratings yet
- Female InfertilityDocument33 pagesFemale InfertilityKiprotich Titus NgetichNo ratings yet
- Infertility To ShowDocument29 pagesInfertility To ShowRaven Renz OngNo ratings yet
- Assisted Reproductive Technology945Document35 pagesAssisted Reproductive Technology945Praluki HerliawanNo ratings yet
- Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART) : Doaa HegabDocument23 pagesAssisted Reproductive Technologies (ART) : Doaa HegabLinguum100% (1)
- Best Dr. Seng Shay WayDocument8 pagesBest Dr. Seng Shay Wayhar shishNo ratings yet
- Technology PsdaDocument8 pagesTechnology PsdaSHREYANo ratings yet
- Artificial ReproductionDocument9 pagesArtificial ReproductionSagar HanamasagarNo ratings yet
- Micro ManipulationDocument6 pagesMicro ManipulationSai SridharNo ratings yet
- ICSI Treatment at Mantri Hospital, JalnaDocument2 pagesICSI Treatment at Mantri Hospital, JalnaArti MantriNo ratings yet
- Infertility 2023Document5 pagesInfertility 2023Charlette GuadalupeNo ratings yet
- IVF Basic PrinciplesDocument3 pagesIVF Basic PrinciplesreadtometooNo ratings yet
- In Vitro FertilisationDocument5 pagesIn Vitro FertilisationVikram VenugopalNo ratings yet
- INFERTILITYDocument19 pagesINFERTILITYAnu LijuNo ratings yet
- Bio Investigatory ProjectDocument23 pagesBio Investigatory Projectpratim.2006.ghoshNo ratings yet
- Biology Investigatory Project Class 12 - EditedDocument17 pagesBiology Investigatory Project Class 12 - Editedharveylenseena2006No ratings yet
- IVF (In Vitro Fertilization)Document14 pagesIVF (In Vitro Fertilization)alishobi422No ratings yet
- 437563872-Art-Bio-Project-1Document11 pages437563872-Art-Bio-Project-1Aswath SNo ratings yet
- In Vitro Treatment Strategies: Over The Years Charts Have Demonstrated That There HasDocument4 pagesIn Vitro Treatment Strategies: Over The Years Charts Have Demonstrated That There HasBảo Duy Nguyễn HuỳnhNo ratings yet
- Issues On ArtifDocument7 pagesIssues On ArtifRegene SorianoNo ratings yet
- Best IVF Doctor in Delhi and NCRDocument7 pagesBest IVF Doctor in Delhi and NCRDr. Prerna GuptaNo ratings yet
- Embryo Transfer TechnologyDocument55 pagesEmbryo Transfer TechnologyShubham AgrawalNo ratings yet
- WHAT IS INFERTILITY Final - Docx 1Document16 pagesWHAT IS INFERTILITY Final - Docx 1guntamukkalaparinikaNo ratings yet
- How Do Organisms Reproduce Part-IIDocument16 pagesHow Do Organisms Reproduce Part-IIraghavrungtambwaNo ratings yet
- The Role of Son Preference in Reproductive Behaviour in PakistanDocument10 pagesThe Role of Son Preference in Reproductive Behaviour in Pakistanbilal rajputNo ratings yet
- Crazy Condom QuizDocument3 pagesCrazy Condom QuizPaulNo ratings yet
- Laparoscopsic Insemination of Sheep in Republic of Serbia - A.Milovanović, N. Maksimović, T. Barna, M. Lazarević, N. DelićDocument8 pagesLaparoscopsic Insemination of Sheep in Republic of Serbia - A.Milovanović, N. Maksimović, T. Barna, M. Lazarević, N. DelićCk_psihNo ratings yet
- Advantages of ContraceptivesDocument4 pagesAdvantages of ContraceptivesArgel Linard Francisco MabagaNo ratings yet
- Booklet The 8th JAKINUDocument20 pagesBooklet The 8th JAKINUsamuelionardiNo ratings yet
- Human ReproductionDocument20 pagesHuman ReproductionKhibul Lim100% (1)
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument125 pagesIlovepdf MergedinnyNo ratings yet
- Artificial Family Planning MethodsDocument8 pagesArtificial Family Planning MethodsUrielle Reign ArciagaNo ratings yet
- Family Planning MethodDocument105 pagesFamily Planning MethodKailash NagarNo ratings yet
- Infertility Latest 14.02.2010.Document13 pagesInfertility Latest 14.02.2010.brilliantpaulNo ratings yet
- The Challenges of Teenage Pregnants of NamarabarDocument3 pagesThe Challenges of Teenage Pregnants of NamarabarbokanegNo ratings yet
- QuzyDocument13 pagesQuzygnpobsNo ratings yet
- Abortion Access&teen MortherhoodDocument25 pagesAbortion Access&teen MortherhoodPhanita PhakdiNo ratings yet
- Kehamilan EktopikDocument9 pagesKehamilan EktopikEka AfriliaNo ratings yet
- FISIOLOGI HAID-tgs DR NasDocument24 pagesFISIOLOGI HAID-tgs DR NasShandy Suwanto PutraNo ratings yet
- NCM 101 Course OutlineDocument6 pagesNCM 101 Course OutlineToni Angelie CaprechoNo ratings yet
- GO - 102splCL Vesectomy TubectomyDocument3 pagesGO - 102splCL Vesectomy Tubectomyyounusbasha143No ratings yet
- Sterilization and MutilationDocument17 pagesSterilization and Mutilationacha90% (10)
- TijuanaDocument6 pagesTijuanaRoy MarínNo ratings yet
- Methods of Birth ControlDocument22 pagesMethods of Birth ControlDwayne SmithNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan For DemoDocument8 pagesLesson Plan For DemoAriel BadanaNo ratings yet
- Family PlanningDocument31 pagesFamily PlanningCzarina May TumandanNo ratings yet
- Public SpeakingDocument1 pagePublic SpeakingDonna Borres SaysonNo ratings yet
- Laporan SPH 2 Sistem ReproduksiDocument4 pagesLaporan SPH 2 Sistem ReproduksiAghits LailyNo ratings yet
- All India Fertility Ivf Ranking Survey 2017Document1 pageAll India Fertility Ivf Ranking Survey 2017shiv mangoNo ratings yet
- Rumus DemografiDocument23 pagesRumus Demografidannyindrajaya_bpNo ratings yet
- Sales & Distribution Project: Contraceptive Condom DurexDocument32 pagesSales & Distribution Project: Contraceptive Condom DurexManish NeerajNo ratings yet