Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Medsurg 8 Cardiovascular Medications
Medsurg 8 Cardiovascular Medications
Uploaded by
Alaa OmarCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Anaesthesia VaporizersDocument49 pagesAnaesthesia VaporizersAlaa OmarNo ratings yet
- CPT Coding Examples For Common Spine Procedures: CervicalDocument5 pagesCPT Coding Examples For Common Spine Procedures: CervicalKrishna KumarNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Finals ReviewerDocument8 pagesPharmacology Finals ReviewerCherry Lou GuanzingNo ratings yet
- Propranolol, Prophylactic Warfarin, Low Molecular Weight Heparin (LMWH), Furosemide, AntibioticsDocument8 pagesPropranolol, Prophylactic Warfarin, Low Molecular Weight Heparin (LMWH), Furosemide, AntibioticsArlyn MarcelinoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Table 3Document5 pagesDrug Study Table 3Juliet De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Cardio DrugsDocument5 pagesCardio DrugsemranalshaibaniNo ratings yet
- Pharma S02 SBR6 Se02Document18 pagesPharma S02 SBR6 Se02sky vallartaNo ratings yet
- Nitrates andDocument61 pagesNitrates andMrunalini DandamudiNo ratings yet
- L P 4 Blood Pharmacology - Final-2022Document26 pagesL P 4 Blood Pharmacology - Final-2022Zakria Al-HadadNo ratings yet
- Aag Drug StudyDocument7 pagesAag Drug StudyAudrie Allyson GabalesNo ratings yet
- Anti Hypertensive DrugsDocument40 pagesAnti Hypertensive DrugsjawadNo ratings yet
- Dx. StudyDocument3 pagesDx. Studymayumitanaka8042No ratings yet
- SUMMARY Drugs Used in HypertensionDocument11 pagesSUMMARY Drugs Used in HypertensionPAULINE ANGELI DIEGONo ratings yet
- PHARMA R2.1 Antihypertensive AgentsDocument13 pagesPHARMA R2.1 Antihypertensive Agentscharmainemargaret.parreno.medNo ratings yet
- Antiplatelet, Thrombolitik, Antikoagulan, Vasodilator Referat VaskularDocument23 pagesAntiplatelet, Thrombolitik, Antikoagulan, Vasodilator Referat Vaskularmonyet65No ratings yet
- PharmacologyDocument116 pagesPharmacologyDanica Chiara MotiaNo ratings yet
- Systemic HypertensionDocument9 pagesSystemic HypertensionYousef El3alameyNo ratings yet
- DiureticsDocument5 pagesDiureticsUsmanNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Vascular DisordersDocument4 pagesPeripheral Vascular DisordersDawnmurph Dharlene Wag-eNo ratings yet
- Antihypertensive AgentsDocument97 pagesAntihypertensive AgentsL2 - MAKILALA, Zion joy B.No ratings yet
- Vasoactive Drugs in Paediatric Intensive Care-7Document24 pagesVasoactive Drugs in Paediatric Intensive Care-7Alex MacedoNo ratings yet
- Antihypertensive Agents 2ndDocument40 pagesAntihypertensive Agents 2ndalikhan52612No ratings yet
- Anti Coagulants & FibrinolyticsDocument54 pagesAnti Coagulants & FibrinolyticsSunanda mohanNo ratings yet
- AntihipertensiDocument39 pagesAntihipertensiHarri HardiNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Assignment No.02: Submitted By: Submitted To: Nandraj Ma'am Areeba Shafiq Roll No. 1817007Document23 pagesPharmacology Assignment No.02: Submitted By: Submitted To: Nandraj Ma'am Areeba Shafiq Roll No. 1817007Nandraj123100% (1)
- CoagulationDocument3 pagesCoagulationRonica PascuaNo ratings yet
- Hypertension: PharmacotherapyDocument23 pagesHypertension: Pharmacotherapytorr123No ratings yet
- Drug Study 3Document5 pagesDrug Study 3jasper pachingelNo ratings yet
- Drug StudypppDocument42 pagesDrug Studyppp2022106284No ratings yet
- Heart FailureDocument3 pagesHeart FailureDr. Jennie Kim100% (3)
- Overview of HemostasisDocument21 pagesOverview of Hemostasis黄資元100% (1)
- Antihypertensives and Fluid Replacement TherapyDocument31 pagesAntihypertensives and Fluid Replacement TherapyAli Husain HabibNo ratings yet
- Coagulation Related DrugsDocument20 pagesCoagulation Related DrugsshehranNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used in Disorders of Coagulation: Presented by 張獻元Document47 pagesDrugs Used in Disorders of Coagulation: Presented by 張獻元i54096149No ratings yet
- Anti HistaminesDocument5 pagesAnti HistaminesAnkit PandeyNo ratings yet
- TransesDocument5 pagesTransesTintin HonraNo ratings yet
- 2 5377779365079685362Document23 pages2 5377779365079685362ahmaNo ratings yet
- NCM 112 TH (9F)Document11 pagesNCM 112 TH (9F)Justine April YbanezNo ratings yet
- Honors Complete PharmDocument10 pagesHonors Complete Pharmapi-724442716No ratings yet
- BP Regulation Medications ChartDocument5 pagesBP Regulation Medications ChartLovely CervantesNo ratings yet
- Nursing CS Angina-Pectoris-medications 03Document1 pageNursing CS Angina-Pectoris-medications 03Mahdia akterNo ratings yet
- Study On Pharmacology .Document93 pagesStudy On Pharmacology .upbandaraNo ratings yet
- C. Anti-Hypertensive Drugs.Document10 pagesC. Anti-Hypertensive Drugs.Nabeel AsifNo ratings yet
- Drug Treatment of HypertensionDocument36 pagesDrug Treatment of HypertensionAngetile KasangaNo ratings yet
- Ace InhibitorsDocument26 pagesAce InhibitorsDeipa KunwarNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Aids SupplementDocument13 pagesCognitive Aids SupplementKe YuheNo ratings yet
- Drug Study CRF PDFDocument21 pagesDrug Study CRF PDFshiplusNo ratings yet
- Atropine 8-28-22Document1 pageAtropine 8-28-22ladawskiNo ratings yet
- Crisis of Hypertension Revised 1Document57 pagesCrisis of Hypertension Revised 1keenmunir100% (4)
- Drug in EmergencyDocument8 pagesDrug in EmergencySuzana YusofNo ratings yet
- Mixed Acting Adrenergic AgonistDocument27 pagesMixed Acting Adrenergic AgonistqbNo ratings yet
- 312-Rle-Drug StudyDocument4 pages312-Rle-Drug StudyRogelyn PatriarcaNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used in Hypertension: Dr. R. PilvinieneDocument33 pagesDrugs Used in Hypertension: Dr. R. PilvinieneNewteNo ratings yet
- Anticoagulant, Antithrombotic and Anti-Platelet DrugsDocument63 pagesAnticoagulant, Antithrombotic and Anti-Platelet Drugsruchipickle100% (1)
- AntihypertensionDocument17 pagesAntihypertension백지원 (소네트리)No ratings yet
- Antiarrythmics PDFDocument1 pageAntiarrythmics PDFRonica PascuaNo ratings yet
- Antihypertensive Drugs: DR. DR Umi Kalssum MkesDocument58 pagesAntihypertensive Drugs: DR. DR Umi Kalssum MkesadilaalifnugrahaeniNo ratings yet
- CV Drugs ListDocument2 pagesCV Drugs ListAndrew MakariosNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used in Coagulation DisordersDocument11 pagesDrugs Used in Coagulation Disordersshoaib106muhammadNo ratings yet
- UROKINASE (Kinlytic)Document4 pagesUROKINASE (Kinlytic)Mikaela Gabrielle GeraliNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Medications: Vasopressors, Inotropes and Anti-Hypertensives Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Vasopressors, Inotropes and Anti-Hypertensives Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet
- LyL Folleto USA Material Estudiante InteractivoDocument16 pagesLyL Folleto USA Material Estudiante InteractivoAlaa OmarNo ratings yet
- 4burn Injury (4 Files Merged)Document39 pages4burn Injury (4 Files Merged)Alaa OmarNo ratings yet
- The Healing Power of GemstonesDocument47 pagesThe Healing Power of GemstonesAlaa OmarNo ratings yet
- Focused Neurological Assessment From Simple NursingDocument1 pageFocused Neurological Assessment From Simple NursingAlaa OmarNo ratings yet
- Untitled NotebookDocument4 pagesUntitled NotebookAlaa OmarNo ratings yet
- Example of A Work PlanDocument2 pagesExample of A Work PlanAlaa OmarNo ratings yet
- Memory Notebook of Nursing VolDocument170 pagesMemory Notebook of Nursing VolAlaa OmarNo ratings yet
- Hypnotherapy +aromatherapy + Laughter Therapy+ ImmuneDocument131 pagesHypnotherapy +aromatherapy + Laughter Therapy+ ImmuneAlaa OmarNo ratings yet
- Simple Nursing StudyDocument5 pagesSimple Nursing StudyAlaa OmarNo ratings yet
- Ali 2018Document16 pagesAli 2018Alaa OmarNo ratings yet
- Grammar Guide To Spanish PronounsDocument7 pagesGrammar Guide To Spanish PronounsAlaa OmarNo ratings yet
- Drawing TherapyDocument36 pagesDrawing TherapyAlaa OmarNo ratings yet
- Language Tutor Lesson IndexDocument7 pagesLanguage Tutor Lesson IndexAlaa OmarNo ratings yet
- L1 NotesDocument3 pagesL1 NotesAlaa OmarNo ratings yet
- Arterial Blood Gases Modes of Ventilation: Richmond Agitation Sedation ScaleDocument1 pageArterial Blood Gases Modes of Ventilation: Richmond Agitation Sedation ScaleAlaa OmarNo ratings yet
- Air Way Equipment 1Document38 pagesAir Way Equipment 1Alaa OmarNo ratings yet
- L 8storage and Handling of Medical GasDocument25 pagesL 8storage and Handling of Medical GasAlaa OmarNo ratings yet
- Stages of AnesthesiaDocument3 pagesStages of AnesthesiaAlaa OmarNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure - Video, Anatomy, Definition & Function - OsmosisDocument9 pagesHeart Failure - Video, Anatomy, Definition & Function - OsmosisAlaa OmarNo ratings yet
- ACLS Algorithms 2020Document8 pagesACLS Algorithms 2020Alaa OmarNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Exercise AssignmentDocument5 pagesTherapeutic Exercise AssignmentAlaa OmarNo ratings yet
- L4 Infection Control PPE and TBPDocument11 pagesL4 Infection Control PPE and TBPAlaa OmarNo ratings yet
- MedicalDocument958 pagesMedicalAlaa OmarNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument1 pageAssignmentAlaa OmarNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia Machine 5 and Breathing SystemsDocument33 pagesAnesthesia Machine 5 and Breathing SystemsAlaa OmarNo ratings yet
- Neurological Disorders Can Vary Widely in Their EtiologyDocument1 pageNeurological Disorders Can Vary Widely in Their EtiologyAlaa OmarNo ratings yet
- Air Way Equipment 2Document29 pagesAir Way Equipment 2Alaa OmarNo ratings yet
- Equipment of Locoregional Anesthesia 13-14Document44 pagesEquipment of Locoregional Anesthesia 13-14Alaa OmarNo ratings yet
- Invasive Blood PressureDocument5 pagesInvasive Blood PressureAlaa OmarNo ratings yet
- Pujo / UpjoDocument39 pagesPujo / UpjoHafizur RashidNo ratings yet
- OriginsDocument15 pagesOriginsRonilyn Mae AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Alternative Orchiopexy Undescended Testis: Simple Technique ofDocument3 pagesAlternative Orchiopexy Undescended Testis: Simple Technique ofShariq ShaNo ratings yet
- Stroke Pathophysiology Diagnosis and Management 7E 2021 7Th Edition James Grotta Full Chapter PDF ScribdDocument67 pagesStroke Pathophysiology Diagnosis and Management 7E 2021 7Th Edition James Grotta Full Chapter PDF Scribdalissa.leon383100% (7)
- (WHO) Intensive Care Unit (ICU)Document4 pages(WHO) Intensive Care Unit (ICU)desiveronikaNo ratings yet
- Zamboanga Doctors Hospital, Inc., Zamboanga City: Surgical Procedure PerformedDocument1 pageZamboanga Doctors Hospital, Inc., Zamboanga City: Surgical Procedure PerformedJaiton PagayonanNo ratings yet
- UK PhysiciansDocument230 pagesUK PhysiciansPatrickNo ratings yet
- A Case Study of Splenic Hemangiosarcoma in A Bitch and Its Surgical ManagementDocument3 pagesA Case Study of Splenic Hemangiosarcoma in A Bitch and Its Surgical ManagementWira KusumaNo ratings yet
- Kelompok Tindakan Bedah DigestifDocument3 pagesKelompok Tindakan Bedah DigestifSumiadiNo ratings yet
- Genitourinary Radiology ExamDocument9 pagesGenitourinary Radiology ExamNour NoorNo ratings yet
- Ressume With PhotoDocument5 pagesRessume With PhotoAsheervadamma Obul reddypalleNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Assessment BeforeDocument4 pagesDiagnostic Assessment BeforeBinod KumarNo ratings yet
- Intraoperative Desaturation During Thyroidectomy .27Document2 pagesIntraoperative Desaturation During Thyroidectomy .27Annakay HudsonNo ratings yet
- Hernias UltrasoundDocument35 pagesHernias UltrasoundRafa Rodríguez AveigaNo ratings yet
- (Download PDF) Core Topics in Cardiac Anaesthesia 3Rd Edition Andrew Roscoe Editor Online Ebook All Chapter PDFDocument42 pages(Download PDF) Core Topics in Cardiac Anaesthesia 3Rd Edition Andrew Roscoe Editor Online Ebook All Chapter PDFrachel.jones745100% (8)
- Ma. Theresa O. Bermudez 4BSN1/ GroupDocument4 pagesMa. Theresa O. Bermudez 4BSN1/ GroupJenna AbuanNo ratings yet
- Group - 5 Plastic SurgeryDocument2 pagesGroup - 5 Plastic SurgeryKiki AkiraNo ratings yet
- Presentation Myasthenia Gravis and ThymomaDocument12 pagesPresentation Myasthenia Gravis and ThymomaabciximabNo ratings yet
- MRI Protokol Review Adi WS QCDocument150 pagesMRI Protokol Review Adi WS QChadiNo ratings yet
- 12-Giant Cell LesionDocument78 pages12-Giant Cell Lesionفراس الموسويNo ratings yet
- Kelompok 4 - 1B - Temporomandibular JointDocument25 pagesKelompok 4 - 1B - Temporomandibular JointLutfi HanifahNo ratings yet
- 4.2 Binomial DistributionsDocument13 pages4.2 Binomial DistributionssakshiNo ratings yet
- Quality Assurance GuidelinesDocument28 pagesQuality Assurance Guidelinesmonir61No ratings yet
- Ruptur Vesica Urinaria Case ReportDocument2 pagesRuptur Vesica Urinaria Case ReportAinun Jariah FahayNo ratings yet
- Management of Penetrating Eye Injury With Intraocular Foreign BodyDocument5 pagesManagement of Penetrating Eye Injury With Intraocular Foreign BodyChristian FaustNo ratings yet
- July 285Document1 pageJuly 285Akash NiamatNo ratings yet
- Active Surgical Oncology Physician Assistant PA Resume SW Houston TXDocument3 pagesActive Surgical Oncology Physician Assistant PA Resume SW Houston TXRick Whitley100% (1)
- Imperforate Anus and Cloacal MalformationsDocument110 pagesImperforate Anus and Cloacal MalformationsAhmad Abu KushNo ratings yet
- All You Need To Know About Vascular SurgeryDocument33 pagesAll You Need To Know About Vascular SurgeryDr. Vinicius MajdalaniNo ratings yet
Medsurg 8 Cardiovascular Medications
Medsurg 8 Cardiovascular Medications
Uploaded by
Alaa OmarOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Medsurg 8 Cardiovascular Medications
Medsurg 8 Cardiovascular Medications
Uploaded by
Alaa OmarCopyright:
Available Formats
lOMoARcPSD|17042315
NCM 112: MEDSURG ● Hemorrhage - very significant
Week 11: Cardiovascular Medications ● Hematuria (blood in urine)
Clinical Instructor: Ms. Stephanie Minoza ● Epistaxis (nosebleed)
● Ecchymosis (discoloration of skin resulting
PART 1: CARDIOVASCULAR MEDICATIONS in bleeding underneath or bruises)
● Bleeding gums
a. Anticoagulants ● Thrombocytopenia
b. Thrombolytic Medications
c. Antiplatelet Medications
SIDE & ○ If low platelet count gani, there would
d. Positive Inotropic and Cardiotonic Medications ADVERSE be risk for bleeding sa ato px.
e. Cardiac Glycosides EFFECTS ● Hypotension
i. Digoxin ○ Because of hemorrhage, a lot of blood
f. Antihypertensive Medications: Diuretics is coming out from our patient or
i. Thiazide diuretics blood loss which can cause to low
ii. Loop diuretics blood volume → cause hypotension
iii. Osmotic diuretics which eventually leads to shock →
iv. Potassium-retaining (sparing) diuretics
g. Peripherally Acting α-Adrenergic Blockers
leading to low blood pressure and
h. Centrally acting Sympatholytics (Adrenergic Blocker) increase heart rate
COMMON ANTICOAGULANTS
ANTICOAGULANTS 1. Heparin Sodium
2. Enoxaparin or Rivaroxaban
ORAL
3. Warfarin sodium
● Warfarin sodium 4. Dabigatran etexilate
● Dabigatran etexilate mesylate
● Rivaroxaban
1) HEPARIN SODIUM
● Apixaban
● Prevents thrombin from converting
PARENTERAL
fibrinogen to fibrin
LIST OF RX ● Argatroban
○ Fibrin is responsible for blood clot
● Bivalirudin
formation; Heparin prevents fibrin
● Dalteparin
DEFINITION ● Prevents thromboembolism
● Desirubin
● Therapeutic dose does not dissolve clots
● Enoxaparin
but prevents new thrombus formation.
● Fondaparinux
○ Therapeutic dose is different from
● Heparin sodium
therapeutic value
● Prevent the extension and formation of
● Monitor aPTT
clots by inhibiting factors in the clotting
○ Normal aPTT: 30-40 seconds
cascades and decreasing blood
DEFINITION ○ Therapeutic level: 1.5 - 2.5 x normal
coagulability.
value
● Very common for those disorders that have
○ Should be measured q4-6H during the
thrombus formation problems
initial infusion of therapy
● Myocardial infarction ○ If aPTT is too long, doctor may order
● Unstable angina to decrease dosage; if too short,
● Atrial fibrillation doctor may order to increase the
● Deep vein thrombosis dosage
● Pulmonary embolism ● Monitor platelet count
INDICATION ● Presence of mechanical heart valves ○ Anticoagulants can lower down
These disorders has a problem with blood clot platelet count and puts patient at risk
formation/ thrombosis formotion. With the help of INTERVENTI for bleeding
our anticoagulants it will help to decrease blood ONS ● Observe for bleeding gums, bruises,
clot formation and will prevent creating a new nosebleeds, hematuria, hematemesis, occult
clot. blood in the stool, and petechiae
Anticoagulants prolong or increase the time for ● Instruct the client regarding measures to
the blood clots to form and to prevent formation prevent bleeding
of new blood clots.When we give anticoagulants, ● The antidote to heparin is protamine sulfate
the one problem we need to monitor is the ○ Take note in giving heparin through IV
bleeding or hemorrhage. That is why it is C/I to: infusion, we must use an infusion
C/I
● Active bleeding pump to ensure a precise rate of
● Bleeding d/o or blood dyscrasias (disease) delivery and correct dosage.
● Ulcers (cause GI bleeding) ● Inject into the abdomen with ⅝ inch (16-mm)
● Liver and kidney disease or needle (25 to 28 gauge) at 90 degree
● Hemorrhagic brain injuries angle and do not aspirate or rub the injection
● Allopurinol site.
● Cimetidine
● Corticosteroids 2) ENOXAPARIN OR RIVAROXABAN
SUBSTANC ● Green, leafy vegetables and other foods
● Low-molecular-weight heparins
ES TO high in Vitamin K
● Have the same mechanism of action and
AVOID WITH ● Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
use as heparin but are not interchangeable
ANTICOAG ● Oral hypoglycemic agents
with heparin
ULANTS ● Phenytoin
DEFINITION ○ Enoxaparin has a lower incidence of
● Salicylates
bleeding and other complications;
● Sulfonamides
Unlike heparin, it is life-threatening due
● Gingko and ginseng (herbs)
to severe adverse reaction called
Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia
Notes by: Caloocan boy :> #PogiProblems 1
Downloaded by Alaa Omar (alaaomar3002@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|17042315
○Enoxaparin is more preferred for INTERVENTI ● Same as for warfarin, except no routine
long-term use because Heparin cannot ONS monitoring is required.
be used long term, only short-term.
● Administer enoxaparin subcutaneous
injection into the anterolateral or THROMBOLYTIC MEDICATIONS
posterolateral abdominal wall ● Alteplase
● Do not expel air bubble from the prefilled LIST OF RX
● Tenecteplase
syringe or aspirate during injection ● Activate plasminogen to generate plasmin.
○ E.g., Clexane - the syringe has a small ○ Plasmin is the enzyme that dissolves
area in which we should not expel. clots.
○ so makita ni ninyo sa area if you have Note: The role of anticoagulants is to prevent or
the authority to give the medication, ACTION
decrease the blood clot formation, but for
make sure ayaw jud i-expel ang air thrombolytics; meaning there is already clot
INTERVENTI bubble para ang ato ma hatag na rate
ONS formation, so thrombolytics's role is to dissolve
or dose is fixed and precise and do not clots.
aspirate. Also do not aspirate when More on disorders that have blood clot formation
you inject. ● Myocardial infarction
● Rivaroxaban is taken orally, once daily. ● Arterial thrombosis
INDICATION
● Deep vein thrombosis
● Occluded shunts or catheters
● Pulmonary emboli
Same with anticoagulants, contraindicated for
patients who have active bleeding or those
Picture: Clexane conditions at higher risk for bleeding
● Active internal bleeding
3) WARFARIN SODIUM ● History of hemorrhagic stroke
● Suppresses coagulation by acting as an ● Intracranial problems including trauma
antagonist of vitamin K by inhibiting 4 ● Intracranial or intraspinal surgery within the
dependent clotting factors (X, IX, VII, and C/I previous two months
II). ● Thoracic, pelvic, or abdominal surgery within
○ Vitamin K helps in blood clot formation. the previous ten days
DEFINITION Warfarin prevents vitamin K. This is by ● History of hepatic or renal disease
inhibiting the 4 dependent clotting ● Uncontrolled hypertension
factors ● Recent, prolonged cardiopulmonary
● Prolongs clotting time and is monitored by resuscitation
the prothrombin time (PT) and the ● Known allergy to product or its preservatives
international normalized ratio SIDE & ● Bleeding
● Warfarin is used for long term ADVERSE ● Dysrhythmias
anticoagulation to prevent thromboembolic EFFECTS ● Allergic reactions
conditions such as: More on monitoring the bleeding
○ Thrombophlebitis ● Determine aPTT, PT, fibrinogen level,
○ Pulmonary Embolism hematocrit, and platelet count.
INDICATION ● Monitor vital signs.
○ Embolism Formation
● E.g., if our patient is using Heparin and they ● Assess pulses.
are to be discharged the next day, the ● Monitor for bleeding and check all excretions
doctor will discontinue Heparin and will start for occult blood.
Warfarin ● Monitor for neurological changes.
● Monitor PT and INR. ● Monitor for hypotension and tachycardia.
INTERVENTI
NOTE: ○ Signs of shock
ONS
● If patient is on Warfarin: PT & INR ● Avoid injections and venipunctures if possible.
● If patient is on Heparin: Only aPTT is ● Apply direct pressure over a punctuation site
important to monitor, but it does not mean we for 20 to 30 minutes.
should not check other laboratory values ● Handle the client gently when moving
● If Enoxaparin and Rivaroxban: no need to
● Instruct the client to use an electric razor for
monitor the 3 laboratory values
INTERVENTI ● shaving and to brush teeth gently.
Observe for bleeding gums, bruises,
ONS ● Withhold the medication if bleeding develops
nosebleeds, hematuria, hematemesis,
and notify the physician if bleeding occurs.
occult blood in the stool, and petechiae.
● Antidote: Aminocaproic acid
● Instruct the client regarding diet and
measures to prevent bleeding.
○ Diet: avoid food rich in vitamin K such ANTIPLATELET MEDICATIONS
as green leafy vegetables
● The antidote for warfarin is phytonadione Oral
(Vitamin K). ● Acetylsalicylic Acid
● Anagrelide
● Cilostazol
4) DABIGATRAN ETEXILATE
● Clopidogrel
● Works through direct inhibition of thrombin,
preventing the conversion of fibrinogen into LIST OF RX ● Dipyridamole
● Ticlopidine
fibrin and activation of factor XIII.
● Ticagrelor
DEFINITION ○ Factor XIII: stabilize the formation of
blood clots Parenteral
● Use for clot prevention associated with ● Abciximab
nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. ● Eptifibatide
Notes by: Caloocan boy :> #PogiProblems 2
Downloaded by Alaa Omar (alaaomar3002@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|17042315
● Tirofiban 4.
Hepatotoxicity (caused by elevated enzyme
● Inhibit the aggregation (formation) of levels)
platelets in the clotting process, thereby 5. Hypersensitivity (manifested by wheezing,
prolonging the bleeding time. shortness of breath, pruritus, urticaria,
ACTION ○ If bleeding time is prolonged, there clammy skin, and flushing)
would be slow formation of the blood 1. Positive inotropic and cardiotonic
clot so it prevents blood clot medications
formation. 2. For continuous IV infusion, administer with
● It can be used together with the an infusion pump.
anticoagulants. 3. Stop the infusion if the client’s BP drops or
IND ● Prophylaxis of long-term complications dysrhythmias occur
such as MI, coronary revascularization, 4. Monitor the apical pulse and BP
stents and stroke. 5. Monitor for hypersensitivity
● Bleeding disorders 6. Assess lung sounds if there are presence of
C/I INTERVENTI wheezing or crackles
● Hypersensitivity
1. Bruising ONS 7. Monitor for edema
SIDE & 8. Monitor for relief of heart failure
2. Hematuria
ADVERSE 9. Noted by reduction of edema, also
3. Gastrointestinal bleeding
EFFECTS lessening of dyspnea, and fatigue)
4. Tarry stools
1. A blood test may be prescribed 10. Monitor electrolyte and liver enzyme levels,
● To determine the client sensitivity to platelet count, and renal function studies
the medication before beginning the 11. This is because these medications may
administration decrease the potassium level and increase
2. Monitor the vital signs. the liver enzyme level
3. Instruct the client to take medication with 12. Consider a continuous ECG monitoring
food if gastrointestinal upset occurs
4. Monitor bleeding time CARDIAC GLYCOSIDES
5. Instruct the patient to monitor for side
INTERVENTIO
and adverse effects and in the measures DIGOXIN
NS
to prevent bleeding. ● Inhibit the sodium-potassium pump →
● If a patient is receiving increasing intracellular calcium → causes
anticoagulants, thrombolytics,and heart muscle fibers to contract more efficiently
antiplatelets; the primary concern for ● Produce a positive inotropic action →
ACTION
these 3 medications is the bleeding increases the force of myocardial contractions
time, therefore we should monitor ● Produce a negative dromotropic action →
the bleeding in our patient and/or Slows conduction velocity through the
put the patient in/as bleeding atrioventricular (AV) node
precaution. ● Heart failure
● Cardiogenic shock
IND ● Atrial tachycardia
POSITIVE INOTROPIC AND CARDIOTONIC
● Atrial fibrillation
MEDICATIONS
● Atrial flutter
● Stimulates myocardial contractility ● Ventricular dysrhythmias
○ Helps myocardium contract ● Second or third degree heart block
C/I
● Produces a positive inotropic effect ● Renal disease
○ Helps cardiac muscle contract stronger, ● Hypothyroidism
helps cardiac output back to a normal level, DIGOXIN TOXICITY
and increases amount of blood that heart ● If digoxin is used long-term and if there is
can pump out CAUSES overuse of digoxin, digoxin toxicity will
● Aids in the distribution of blood flow to other organs happen
● Helps increase myocardial contractility that would not B = Bradycardia
only improve the cardiac but also the peripheral and A = Anorexia
kidney function in our patient. N = Nausea
● Helps in increasing cardiac output and decreasing the D = Diarrhea
preload, improves blood flow to the periphery and A = Abdominal Pain
kidneys. CLINICAL V = Visual disturbance (yellow or green halos,
EXAMPLES MANIFESTA blurred vision, diplopia, photophobia)
Dobutamine TIONS
● Used for short term management of heart failure Early signs of toxicity:
● Increases myocardial contractility 1. Gastrointestinal Manifestations (anorexia,
Dopamine nausea, vomiting, diarrhea)
● Used as a short term rescue measure 2. Heart rate abnormalities
● Increases myocardial contractility
● Dilates renal blood vessels and increases renal blood flow
3. Visual disturbances
and urine output ● Monitor for toxicity
Milrinone Lactate ○ Remember the mnemonic BANDAV
● Used for short term management of heart failure; may be ● Monitor serum digoxin level, electrolyte
given before heart transplantation levels, and renal function test results
INTERVENTI
IND ● Heart Failure ○ Therapeutic range for digoxin is 0.5 -
ONS
SIDE AND 1. Dysrhythmias 2.0 mg/dl
ADVERSE 2. Hypotension ○ However a level on the low end of
EFFECTS 3. Thrombocytopenia normal, it is preferred in order to avoid
toxicity.
Notes by: Caloocan boy :> #PogiProblems 3
Downloaded by Alaa Omar (alaaomar3002@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|17042315
● Monitor potassium level especially for ● Instruct the client to take the medication in
hypokalemia the morning in order to avoid nocturia and
○ Less than 3.5/L (max) sleep interruption
○ Notify healthcare provider if ● Instruct the client in how to record the BP
hypokalemia occurs. ● Instruct the client to eat foods high in
■ High risk for digoxin toxicity potassium
● Instruct the client to avoid over-the-counter ● Instruct the client in how to take potassium
medications supplements if prescribed
● Monitor the client taking a potassium losing ● Instruct the client to take medication with
diuretic or corticosteroids closely for food in order to avoid GI upset
hypokalemia ● Instruct the client to change positions slowly
● Note that older clients are more sensitive to in order to prevent the orthostatic
digoxin toxicity. hypotension
● Advise the client to eat foods high in ● Instruct the client to use sunscreen when in
potassium such as fresh and dry fruits, fruit direct sunlight because of increased
juices, vegetables and potatoes photosensitivity
● Monitor the apical pulse for 1 full minute ● Instruct the client with diabetes mellitus to
○ Lower than 60 bpm = medication have the blood glucose checked
should be withheld; notify the periodically
physician
○ Teach the client how to measure the LOOP DIURETICS
pulse ● Loop diuretics inhibit sodium and chloride
● Antidote: Digoxin immune Fab is used in reabsorption from the loop of Henle and the
extreme toxicity distal tubule.
○ Focuses more on the sodium and
chloride.
ANTIHYPERTENSIVE MEDICATIONS: DIURETICS ● It has a little effect on the blood glucose
a. Thiazide diuretics level however they cause depletion of water
i. Chlorothiazide ACTION and electrolytes, and also they can increase
ii. Chlorthalidone the uric acid levels and excretion of calcium
iii. Hydrochlorothiazide sa px.
iv. Indapamide
● It can also cause rapid diuresis, so mas
v. Metolazone
b. Loop diuretics paspas ang excretion niya.
c. Osmotic diuretics ○ Faster excretion = decreased vascular
d. Potassium-retaining (sparing) diuretics fluid volume, decreased cardiac output,
and decreased blood pressure
THIAZIDE DIURETICS ● Hypertension - Loop diuretics can
Increases sodium and water excretion by decrease the blood pressure
ACTION inhibiting sodium reabsorption in the distal tubule ● Pulmonary Edema - If there is edema,
of the kidney. there is a lot of fluid inside the body of our
● Hypertension patient. Diuretics can help to excrete those
IND ● Peripheral edema INDICATION excess fluid volume in our patient.
NOT EFFECTIVE FOR IMMEDIATE DIURESIS. ● Hypercalcemia - It can increase the
● Lithium excretion of calcium. So if hypercalcemia
○ It can cause lithium toxicity, since inyong patient, it can help in order to lower
thiazide will excrete the sodium, less the calcium level.
sodium can increase the lithium ● Renal disease
C/I ● Digoxin
levels.
● Digoxin ● Lithium
● Corticosteroids CONTRAIND ● Aminoglycosides
● Hypoglycemic medications ICATION ● Anticoagulants
● Hypercalcemia, hyperglycemia, ● Corticosteroids
hyperuricemia ● Amphotericin B
● Hypokalemia, hyponatremia ● Hypokalemia (low potassium),
SIDE & hyponatremia (low sodium), hypocalcemia
● Hypovolemia
ADVERSE (low calcium), hypomagnesemia (low
● Hypotension
EFFECTS magnesium)
● Rashes
● Photosensitivity ● Thrombocytopenia
SIDE
● Dehydration ● Hyperuricemia
EFFECTS &
● Monitor vital signs ● as mentioned a while ago, loop diuretics
ADVERSE
● Monitor weight can increase the uric acid levels
EFFECTS
○ Very important if the patient has ● Orthostatic hypotension
edema to check if medication is ● Rash
effective in patients with edema. ● Ototoxicity and deafness
INTERVENTI ● Monitor urine output ● Thiamine deficiency
ONS ● Monitor the electrolytes, glucose, calcium. ● Dehydration
Blood urea nitrogen (BUN), creatinine, and ● Same with thiazide diuretics
uric acid levels ● Monitor electrolytes, calcium, magnesium,
● Check peripheral extremities for edema BUN, creatinine, and uric acid levels
INTERVENTI
● Monitor for signs of digoxin or lithium ● Administer IV furosemide slowly over 1 to 2
ONS
toxicity minutes
○ Because hearing loss can occur if it is
injected rapidly.
Notes by: Caloocan boy :> #PogiProblems 4
Downloaded by Alaa Omar (alaaomar3002@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|17042315
● Monitor vital signs
OSMOTIC DIURETICS ● Monitor urine output
LIST OF RX Mannitol ● Monitor for signs and symptoms of
● This kind of diuretic is more common in hyperkalemia
BACKGROU neurological disorders. ○ Such as nausea, diarrhea, abdominal
ND ● This is usually given to px when there is an cramps, tachycardia, which is followed
increased ICP by bradycardia
○ In our ECG we can see there at all
POTASSIUM-RETAINING (SPARING) DIURETICS) peak T waves.
● Amiloride hydrochloride ○ Px can also manifest oliguria =
● Eplerenone meaning low urine output
LIST OF RX INTERVENTI
● Spironolactone ● Monitor for a potassium level greater than 5.0
ONS
● Triamterene mEq/L (5.0 mmol/L)
○ The normal level is 3.5 to 5.0.
● Potassium-retaining (sparing) diuretics
● Instruct the client to avoid foods high in
acts on the distal tube to promote sodium
potassium.
and water excretion but there would be
potassium retention. ● Instruct the client to avoid exposure to direct
- From the word itself, potassium sunlight
ACTION ● Instruct the client to monitor for signs of
retaining or potassium sparing meaning
it will spare the potassium sa body, so hyperkalemia
dli niya iapil ug excrete. Magpabilin ang ● Instruct the client to avoid salt substitutes
potassium sa atong body while the ● Instruct the client to take the medication with
sodium and water kay ipagawas niya. or after meals
● Edema
● Hypertension PERIPHERALLY ACTING α-ADRENERGIC BLOCKERS
● Low Urine Output
● Fluid Retention and Overload ● Ex. Prazosin and Terazosin
● Ascites ● Decrease sympathetic vasoconstriction →
● Diuretic - induced hypokalemia reducing the effects of norepinephrine at
- So both thiazide and loop diuretics peripheral nerve endings → vasolidation
can decrease the electrolytes including and decreased BP
the potassium that is why we have ACTION ○ Norepinephrine is the fight or flight
IND response. It increases the blood
diuretic-induced hypokalemia.
- But the potassium-retaining diuretics pressure and heart rate.
is very different from those two types of ○ If the norepinephrine is reduced, there
diuretics because it allows the will be vasodilation and decreased
potassium to retain. So if the patient blood pressure.
needs to have diuretics but at the same ● Maintain renal blood flow
time, needs to retain the potassium in ● Hypertension
INDICATION
the body, that’s the best time to give ○ This medication will help to vasodilate
S
the Potassium-retaining diuretics. which will improve blood flow and
● Severe kidney or hepatic disease reduce blood pressure of the patient.
● Severe hyperkalemia ● Orthostatic hypotension
○ The goal for this type of diuretic is to ● Reflex tachycardia
retain potassium, but if the potassium ● Sodium and water retention
SIDE &
is severely high, this is not indicated ● Edema
ADVERSE
to the px. ● Weight gain
EFFECTS
○ Normal level of potassium = 3.5-5.0. ● Gastrointestinal disturbances
○ Severe is more than 5.0 = we can’t ● Drowsiness
give this type of diuretic to the px. ● Nasal Congestion
● Diabetes mellitus 1. Monitor vital signs especially blood
C/I pressure
● Lithium
● ACE inhibitors 2. Monitor for fluid retention and edema
● Potassium supplements 3. Instruct the client to change positions
○ Contraindicated because this type of slowly
NSG INT
diuretic is already sparing/retaining 4. Instruct the client in how to monitor the BP
the potassium, so we don’t want to 5. Instruct the client to monitor for edema
have severe hyperkalemia for the px. 6. Instruct the client to decrease salt intake
When taking the medication, it is 7. Instruct the client to avoid OTC
important to advise or px not to take medications
potassium supplements.
● Hyperkalemia CENTRALLY ACTING SYMPATHOLYTICS
● Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea (Adrenergic Blockers)
● Rash ● Stimulate receptors in the central nervous
SIDE & ● Dizziness, weakness system to inhibit vasoconstriction →
ACTION
ADVERSE ● Headache reducing peripheral resistance →
EFFECTS ● Dry mouth vasodilation
● Photosensitivity IND ● Hypertension
● Anemia ● Impaired liver function (because it can
● Thrombocytopenia C/I
cause hepatotoxicity)
SIDE & ● Sodium and water retention
ADVERSE ● Edema
Notes by: Caloocan boy :> #PogiProblems 5
Downloaded by Alaa Omar (alaaomar3002@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|17042315
EFFECTS ● Drowsiness, dizziness ● Instruct the client not to discontinue
● Dry mouth medications
● Hypotension ○ Because rebound HPN can occur
● Bradycardia ● Instruct the client not to take over-the-counter
● Impotence medications.
● Depression ● Instruct the client in how to take BP.
1. Monitor vital signs ● Inform the client that the taste of food may be
2. Instruct the client not to discontinue diminished
medication because abrupt withdrawal can ○ Occurs during the first month of the
NSG INT therapy
cause severe rebound hypertension
3. Monitor liver function tests because this ● Instruct the client to report adverse effects to
can cause severe hepatotoxicity. the physician.
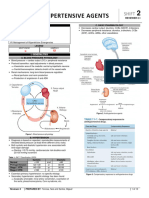
ACE and ARBs NITRATES
● ACE = Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Antianginal Medication or Organic Nitrates
(ACE) Inhibitors ● Produce vasodilation, decrease preload
ACTION
○ ACE inhibitors prevent peripheral and afterload, and reduce myocardial
vasoconstriction by blocking oxygen consumption.
conversion of angiotensin I to ● Hypotension
angiotensin II (AII). ● Increased ICP
● ARBs = Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers C/I ● Severe anemia
○ ARBS prevent peripheral ● Medications for erectile dysfunction
vasoconstriction and secretion of ● Severe renal or hepatic disease
aldosterone and block the binding of 1. Headache
ACTION
AII to type 1 AII receptors. 2. Orthostatic hypotension
○ Role of Angiotensin II: promote SIDE & 3. Dizziness, weakness
vasoconstriction, that is why we ADVERSE 4. Faintness
have ACE and ARBs in order to EFFECTS 5. Flushing or pallor
prevent AII 6. Dry mouth
○ If there is vasoconstriction, it can 7. Reflex tachycardia
increase px BP (which we do not
want since patient is already ROUTES OF ADMINISTRATION
hypertensive and our desired 1. Sublingual Medications
outcome is to lower the BP) 2. Translingual Medications (Spray)
● Hypertension 3. Sustained-Release Medications
IND 4. Transdermal Patch
● Heart failure
5. Topical Ointments
● Potassium supplements
6. Patches and Ointments
● Potassium-retaining (sparing) diuretics
Why? ACE & ARBs can increase SUBLINGUAL MEDICATIONS
C/I a. Monitor vital signs
potassium level which is not desirable.
Immediately stop these if ever currently a. Offer sips of water before giving, because dryness
taking ACE & ARBs. may inhibit medication absorption
b. Instruct the client to place under the tongue and leave
1. Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea until fully dissolved
2. Persistent dry cough (Taking ACE c. Instruct the client not to swallow the medication
inhibitors) d. Instruct the at-home client to take 1 tablet for pain
● Very common complaint and to immediately contact emergency medical
● Instruct px to contact physician services if pain is not relieved; in the hospitalized
● Subsides w/in a few weeks client, 1 tablet is administered every 5 minutes for a
3. Hypotension total of 3 doses
SIDE & e. Inform the client that a stinging or burning sensation
4. Hyperkalemia
ADVERSE may indicate that the tablet is fresh.
5. Tachycardia
EFFECTS f. Instruct the client to store medication in a dark, tightly
6. Headache
7. Dizziness, fatigue closed bottle.
8. Insomnia g. Instruct the client to take acetaminophen for a
9. Hypoglycemic reaction in px w/ diabetes headache.
mellitus
10. Bruising, petechiae, bleeding TRANSLINGUAL MEDICATIONS (SPRAY)
11. Diminished taste (ACE inhibitors) a. Instruct the client to direct the spray against the oral
● Monitor vital signs. mucosa.
● Monitor white blood cells, and protein, b. Instruct the client to avoid inhaling the spray.
albumin. BUN, creatinine, and potassium
levels. SUSTAINED-RELEASE MEDICATIONS
● Monitor for hypoglycemic reactions a. Instruct the client to swallow and not to chew or crush
○ In the client w/ DM the medication.
NSG INT ● If captopril (an ACE inhibitor) is prescribed,
instruct the client to take the medication TRANSDERMAL PATCH
20-60 minutes before a meal. a. Instruct the client to apply the patch to a hairless
○ This is for increased effectiveness of area, using a new patch and different site each day.
the captopril b. Instruct the client to remove the patch after 12 to 14
● Monitor for bruising, petechiae, or bleeding hours, allowing 10 to 12 "patch free" hours each day
with captopril. in order to prevent tolerance.
Notes by: Caloocan boy :> #PogiProblems 6
Downloaded by Alaa Omar (alaaomar3002@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|17042315
● Migraine headaches
TRANSDERMAL PATCH ● Prevention of Myocardial infarction
a. Instruct the client to remove the ointment on the skin ● Glaucoma
from the previous dose. ● Asthma
b. Instruct the client to squeeze a ribbon of ointment of ● Bradycardia
the prescribed length onto the applicator or ● Heart failure
dose-measuring paper. ● Severe renal or hepatic disease
c. Instruct the client to spread the ointment over a 2.5- ● Hyperthyroidism
by 3.5-inch (6.5 by 9 cm) area and cover with plastic ● Stroke
wrap, using the chest, back, abdomen, upper arm, or ● Diabetes Mellitus
anterior thigh. C/I
○ Can cause hypoglycemia
d. Instruct the client to rotate sites and to avoid touching ● Antihypertensive medication
the ointment when applying. ○ This medication can decrease the BP;
if an antihypertensive medication is
PATCHES AND OINTMENTS given together with beta adrenergic
a. Wear gloves when applying the patches and blockers, severe hypotension may
ointments to our patients. occur
b. Do not apply on the chest in the area of ● Bradycardia
defibrillator-cardioverter pad placement. ● Bronchospasm
○ This is because skin burns can result if the ○ tightening or narrowing of airway
pads need to be placed. ● Hypotension
● Weakness, fatigue
REMEMBER! If nitroglycerin tablets are used by the patient, ● Nausea, vomiting
we need to check the expiration date on the medication SIDE &
● Dizziness
bottle. ADVERSE
● Hyperglycemia
Not only for us nurses, but it is also important to instruct our EFFECTS
● Agranulocytosis
patient to check the medication bottle for the expiration date. ○ Severe reduction in the white blood
This is because expiration may occur within six months of cells, specifically the granulocytes
obtaining the medication and then the tablets will not relieve ● Behavioral or psychotic response
the chest pain if they're already expired. ● Depression
● Nightmares
● Monitor vital signs (especially BP)
PART 2: CARDIOVASCULAR MEDICATIONS ● Withhold the medication if the pulse or BP is
a. β-Adrenergic Blockers not within the prescribed parameters.
b. Calcium Channel Blockers ○ A decrease of PR and BP
c. Peripheral vasodilators ● Monitor For signs of heart failure or
d. Direct-acting Arterial Vasodilators worsening heart failure
e. Miscellaneous Vasodilators ● Assess for respiratory distress and for signs
● Nesiritide of wheezing and dyspnea.
f. Antidysrhythmic Medications
● Instruct the client to report dizziness,
g. Adrenergic Agonists
● Dobutamine lightheadedness, or nasal congestion.
● Dopamine ● Instruct the client not to stop the medication.
● Epinephrine ○ Because there will be rebound
● Norepinephrine hypertension, rebound tachycardia or
INTERVENT
anginal attack.
IONS
β-ADRENERGIC BLOCKERS ● Advise the client taking insulin that
●
Inhibit response to β-adrenergic B-adrenergic blocker can mask early signs of
stimulation, thus decreasing cardiac output. hypoglycemia.
If there would be decreased cardiac output, ○ Such as tachycardia and nervousness
there would also be decreased blood ● Instruct the client in taking insulin to monitor
pressure. the blood glucose level.
DEFINITION ● Instruct the client in how to take pulse and BP
● They block the release of catecholamines,
epinephrine, and norepinephrine. These ● Instruct the client to change positions slowly
can decrease heart rate & blood pressure, ○ To prevent the orthostatic hypotension
the workload of the heart, and the oxygen ● Instruct the client to avoid over-the-counter
demands. medications
Nonselective (Blockβ1 and β2) ○ especially the cold medications and
● Carvedilol nasal decongestants
● Labetalol
● Nadolol CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS
● Pindolol ● Amlodipine
● Propranolol ● Clevidipine
● Sotalol ● Diltiazem
LIST OF RX ● Felodipine
Cardioselective (Block β1)
● Acebutolol ● Isradipine
LIST OF RX
● Atenolol ● Nicardipin
● Betaxolol ● Nifedipine
● Bisoprolol ● Nimodipine
● Esmolol ● Nisoldipine
● metoprolol ● Verapamil
● Angina ● Decrease cardiac contractility and the
INDICATION ● Dysrhythmias ACTION workload of the heart, thus decreasing the
● Hypertension need for oxygen
Notes by: Caloocan boy :> #PogiProblems 7
Downloaded by Alaa Omar (alaaomar3002@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|17042315
○ A negative inotropic effect ● Monitor for orthostatic hypotension and
○ It helps by relaxing the smooth muscle tachycardia
● Promote vasodilation of the coronary and ● Monitor for signs of inadequate blood
peripheral vessels flow to the extremities such as pallor,
○ This medication can also decrease the feeling cold, and pain
blood pressure of the patient. ● Instruct the client that it may take up to
● Angina 3 months for a desired therapeutic
INDICATION ● Dysrhythmias response
● Hypertension ● Advise the client not to smoke this is
● Heart Failure because smoking can increase the
C/I ● Bradycardia vasospasm so ma wa ang purpose sa
● Atrioventricular Block or AV Block atong tambal if ever man ghani ni
● Bradycardia smoke si patient
● Hypotension ● Instruct the client to avoid aspirin or
● Reflex tachycardia as a result of aspirin-like compounds unless
hypotension approved by the PHCP.
SIDE AND ● Headache ● Instruct the client to take the medication
ADVERSE ● Dizziness, Lightheadedness with meals if gastrointestinal
EFFECTS ● Fatigue disturbances occur.
● Peripheral Edema ● Instruct the client to avoid alcohol. It
● Constipation may cause hypotensive reaction
● Flushing of Skin ● Encourage the client to change the
● Changes in liver and kidney function position slowly to avoid orthostatic
1. Monitor vital signs hypotension.
● Especially the BP and HR
2. Monitor for signs of heart failure DIRECT-ACTING ARTERIAL VASODILATORS
● This is because this medication can ● Diazoxide
cause peripheral edema which is one ● Fenoldopam
of the manifestations of heart failure LIST OF RX ● Hydralazine
3. Monitor liver enzyme levels ● Nitroglycerin
● Since it can cause changes to the liver ● Sodium nitroprusside
function and the kidney function as ● Relaxes the smooth muscles of the blood
well vessels, mainly the arteries, causing
INTERVENTI
4. Monitor kidney function tests vasodilation
ONS
5. Instruct the client not to discontinue the ○ So if there is vasodilation, the blood
medication pressure will drop
6. Instruct the client in how to take the pulse ○ The bad side here is that the sodium
7. Instruct the client to notify the PHCP and water will be retained in the body
(physician) if dizziness or fainting occurs ○ So if this happens, it will cause
ACTION
8. Instruct the client not to crush or chew peripheral edema, so this is the most
sustained-release tablets. common side effect that we should
● If the medication is in a monitor
sustained-release form, it is not ○ If there is peripheral edema, the doctor
advisable to crush the tablet. may prescribe diuretics for that in order
to decrease the edema
PERIPHERAL VASODILATORS ● Promotes an increase in blood flow to the
● Decrease peripheral resistance by exerting a direct brain and kidneys
action on the arteries or on the arteries and the veins ● Hypertension
INDICATION
● Increase blood flow to the extremities ● Acute hypertensive emergencies
○ That’s why it is used for peripheral vascular ● Hypotension
disorders of venous and arterial vessels ● Reflex tachycardia (caused by vasodilation
○ Decreased peripheral resistance > Peripheral and a drop in BP)
Vasodilation > Increased blood flow to that ● Palpitations
periphery ● Edema
α-Adrenergic Calcium Channel Hemorheological SIDE AND ● Dizziness
Blockers Blockers ADVERSE ● Headache
● Diltiazem ● Pentoxifylline EFFECTS ● Nasal Congestion
● Doxazosin ● Gastrointestinal bleeding
● Nifedipine (increases
● Prazosin ● Neurological symptoms
● Nimodipine microcirculation &
● Terazosin ● Confusion
● Verapamil tissue perfusion)
● Peripheral vascular disorders ● Sodium nitroprusside -> cyanide toxicity
● Raynaud’s disease and thiocyanate toxicity can occur.
INDICATIONS 1. Monitor vital signs, especially BP
● Decrease some symptoms of cerebral
vascular insufficiency 2. Sodium nitroprusside
● Lightheadedness, dizziness a. Monitor cyanide and thiocyanate
● Orthostatic hypotension levels.
SIDE AND INTERVENTI b. Protect from light because the
● Tachycardia
ADVERSE ONS medication decompresses.
● Palpitations
EFFECTS c. When administering, the solution must
● Flushing
● Gastrointestinal distress be covered by a dark bag provided by
● Monitor vital signs, especially the BP the manufacturer and is stable for 24
INTERVENTIONS hours.
and the HR.
Notes by: Caloocan boy :> #PogiProblems 8
Downloaded by Alaa Omar (alaaomar3002@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|17042315
d. Discard if the medication is bright red, ○ We must also
green, or blue; since sodium monitor ECG for
nitroprusside is originally colorless in clients receiving
nature. Amiodarone
3. Instruct patients that they can position hydrochloride
slowly when rising from a lying position to a because it may
sitting or standing position. prolong the QT
interval of the
MISCELLANEOUS VASODILATORS patient that could
NESIRITIDE lead to Torsade de
● Recombinant version of human B-type natriuretic peptide pointes.
that vasodilates arteries and veins. INTERVENTIONS
● Used for treatment of decompensated heart failure. 1. Monitor heart rate, respiratory rate, and BP
● Hypotension 2. Monitor electrocardiogram
SIDE AND 3. Provide continuous cardiac monitoring
● Confusion
ADVERSE 4. Maintain therapeutic serum medication levels
● Dizziness
EFFECTS 5. Before administering lidocaine, always check the vial
● Dysrhythmias
● Administer by continuous IV infusion via label
infusion device 6. Do not administer antidysrhythmics with food
INTERVENTI 7. Mexiletine may be administered with food or antacids
● Monitor BP, cardiac rhythm, urine output,
ONS ● in order to reduce GI distress.
and body weight.
● Monitor for signs of resolving heart failure. 8. Always administer IV antidysrhythmics via an infusion
pump.
● This is because in order to deliver the precise or
ANTIDYSRHYTHMIC MEDICATIONS
accurate dose to the patient,
● Suppress dysrhythmias by inhibiting abnormal pathways
9. Monitor for signs of fluid retention.
of electrical conduction through the heart
● Retention means nagpabilin sa body sa patient. So if
○ Class I antidysrhythmics: sodium channel
there is a lot of fluid na nagpabilin sa body sa
blockers
patient, expected na naay weight gain, peripheral
○ Class II: Beta blockers
edema, or shortness of breath
○ Class III: potassium channel blockers
10. Advise the client to limit fluid and salt intake to minimize
○ Class IV: calcium channel blockers
fluid retention.
Class I Class II Class III Class IV Others ● As mentioned, if daghan fluid ang nabilin sa body
CLASS IA: ● Acebutolol ● Amiodarone ● Verapamil ● Adenos
sa patient, we don’t want to increase our fluid
● Disopyramide ● Esmolol ● Dofetilide ● Diltiazem ine
● Procainamide ● Propranolol ● Ibutilide ● Digoxin intake, including salt, since wherever sodium goes,
● Quinidine ● Metoprolol ● Sotalol water will follow.
sulfate ● Atenolol 11. Monitor respiratory, thyroid, and neurological functions
12. Instruct the client to change positions slowly
CLASS IB: 13. Instruct the client taking amiodarone to use sunscreen
● Lidocaine and protective clothing
● Mexiletine 14. Encourage the client to increase fiber intake
hydrochloride
● Phenytoin
CLASS IC: ADRENERGIC AGONISTS
● Flecainide
acetate DOBUTAMINE
● Propafenone
hydrochloride
● Increases myocardial force and cardiac output through
stimulation of β-receptors
SIDE EFFECTS AND ADVERSE EFFECTS
○ Very opposite to beta-adrenergic blockers because
Class I Class II
the beta-adrenergic blockers block the stimulation
● Dizziness of our beta-receptors. But for our adrenergic
● Hypotension
● Fatigue agonists, they promote or stimulate the
● Heart failure
● Hypotension beta-receptors so opposite sad iyang effect ani sa
● Worsened or new
● Bradycardia atoang beta-adrenergic blockers
dysrhythmias
● Heart Failure ○ They increase cardiac output
● Nausea
● Dysrhythmias ● Used in clients with heart failure and for clients
● Vomiting
● Heart block undergoing cardiopulmonary bypass surgery
● Diarrhea
● Bronchospasm
● Gastrointestinal distress
DOPAMINE
Class III Class IV
● Increases BP and cardiac output through positive
● Hypotension ● Dizziness
inotropic action and increases renal blood flow through
● Bradycardia ● Hypotension
● Nausea, Vomiting ● Bradycardia its action on α- and β-receptors
● Amiodarone ● Edema ● Used to treat mild kidney failure that is caused by low
hydrochloride – ● Constipation cardiac output
pulmonary fibrosis,
photosensitivity, bluish EPINEPHRINE
skin discoloration, ● Used for cardiac stimulation in cardiac arrest
corneal deposits, ● Used for bronchodilation in asthma or allergic reactions
peripheral neuropathy, ● Produces mydriasis
tremor, poor coordination, ○ Mydriasis means dilation of the pupil
abnormal gait, and
hypothyroidism
Notes by: Caloocan boy :> #PogiProblems 9
Downloaded by Alaa Omar (alaaomar3002@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|17042315
● Produces local vasoconstriction when combined with
local anesthetics and prolongs anesthetic action by
decreasing the blood flow to the side.
NOREPINEPHRINE
● Stimulates the heart in cardiac arrest
● Vasoconstricts and increases the BP in hypotension and
shock
REMEMBER: If there is vasodilation, there is a drop in
the blood pressure or decrease in blood pressure.
If there is vasoconstriction, there is an increase in the
blood pressure.
Side and 1. Dysrhythmias
Adverse 2. Tachycardia
Effects 3. Angina
4. Restlessness
5. Urgency or urinary incontinence
Interventions 1. Monitor vital signs especially the blood
pressure.
2. Monitor lung sounds.
3. Monitor urinary output.
4. Monitor electrocardiogram (ECG).
5. Administer the medication through a
large vein.
“MAMA THANK YOU VERY MUCH YOU KNOW THAT
I LOVE CHICKEN NUGGETS!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!”
#WeWillSeetheScattered
Notes by: Caloocan boy :> #PogiProblems 10
Downloaded by Alaa Omar (alaaomar3002@gmail.com)
You might also like
- Anaesthesia VaporizersDocument49 pagesAnaesthesia VaporizersAlaa OmarNo ratings yet
- CPT Coding Examples For Common Spine Procedures: CervicalDocument5 pagesCPT Coding Examples For Common Spine Procedures: CervicalKrishna KumarNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Finals ReviewerDocument8 pagesPharmacology Finals ReviewerCherry Lou GuanzingNo ratings yet
- Propranolol, Prophylactic Warfarin, Low Molecular Weight Heparin (LMWH), Furosemide, AntibioticsDocument8 pagesPropranolol, Prophylactic Warfarin, Low Molecular Weight Heparin (LMWH), Furosemide, AntibioticsArlyn MarcelinoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Table 3Document5 pagesDrug Study Table 3Juliet De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Cardio DrugsDocument5 pagesCardio DrugsemranalshaibaniNo ratings yet
- Pharma S02 SBR6 Se02Document18 pagesPharma S02 SBR6 Se02sky vallartaNo ratings yet
- Nitrates andDocument61 pagesNitrates andMrunalini DandamudiNo ratings yet
- L P 4 Blood Pharmacology - Final-2022Document26 pagesL P 4 Blood Pharmacology - Final-2022Zakria Al-HadadNo ratings yet
- Aag Drug StudyDocument7 pagesAag Drug StudyAudrie Allyson GabalesNo ratings yet
- Anti Hypertensive DrugsDocument40 pagesAnti Hypertensive DrugsjawadNo ratings yet
- Dx. StudyDocument3 pagesDx. Studymayumitanaka8042No ratings yet
- SUMMARY Drugs Used in HypertensionDocument11 pagesSUMMARY Drugs Used in HypertensionPAULINE ANGELI DIEGONo ratings yet
- PHARMA R2.1 Antihypertensive AgentsDocument13 pagesPHARMA R2.1 Antihypertensive Agentscharmainemargaret.parreno.medNo ratings yet
- Antiplatelet, Thrombolitik, Antikoagulan, Vasodilator Referat VaskularDocument23 pagesAntiplatelet, Thrombolitik, Antikoagulan, Vasodilator Referat Vaskularmonyet65No ratings yet
- PharmacologyDocument116 pagesPharmacologyDanica Chiara MotiaNo ratings yet
- Systemic HypertensionDocument9 pagesSystemic HypertensionYousef El3alameyNo ratings yet
- DiureticsDocument5 pagesDiureticsUsmanNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Vascular DisordersDocument4 pagesPeripheral Vascular DisordersDawnmurph Dharlene Wag-eNo ratings yet
- Antihypertensive AgentsDocument97 pagesAntihypertensive AgentsL2 - MAKILALA, Zion joy B.No ratings yet
- Vasoactive Drugs in Paediatric Intensive Care-7Document24 pagesVasoactive Drugs in Paediatric Intensive Care-7Alex MacedoNo ratings yet
- Antihypertensive Agents 2ndDocument40 pagesAntihypertensive Agents 2ndalikhan52612No ratings yet
- Anti Coagulants & FibrinolyticsDocument54 pagesAnti Coagulants & FibrinolyticsSunanda mohanNo ratings yet
- AntihipertensiDocument39 pagesAntihipertensiHarri HardiNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Assignment No.02: Submitted By: Submitted To: Nandraj Ma'am Areeba Shafiq Roll No. 1817007Document23 pagesPharmacology Assignment No.02: Submitted By: Submitted To: Nandraj Ma'am Areeba Shafiq Roll No. 1817007Nandraj123100% (1)
- CoagulationDocument3 pagesCoagulationRonica PascuaNo ratings yet
- Hypertension: PharmacotherapyDocument23 pagesHypertension: Pharmacotherapytorr123No ratings yet
- Drug Study 3Document5 pagesDrug Study 3jasper pachingelNo ratings yet
- Drug StudypppDocument42 pagesDrug Studyppp2022106284No ratings yet
- Heart FailureDocument3 pagesHeart FailureDr. Jennie Kim100% (3)
- Overview of HemostasisDocument21 pagesOverview of Hemostasis黄資元100% (1)
- Antihypertensives and Fluid Replacement TherapyDocument31 pagesAntihypertensives and Fluid Replacement TherapyAli Husain HabibNo ratings yet
- Coagulation Related DrugsDocument20 pagesCoagulation Related DrugsshehranNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used in Disorders of Coagulation: Presented by 張獻元Document47 pagesDrugs Used in Disorders of Coagulation: Presented by 張獻元i54096149No ratings yet
- Anti HistaminesDocument5 pagesAnti HistaminesAnkit PandeyNo ratings yet
- TransesDocument5 pagesTransesTintin HonraNo ratings yet
- 2 5377779365079685362Document23 pages2 5377779365079685362ahmaNo ratings yet
- NCM 112 TH (9F)Document11 pagesNCM 112 TH (9F)Justine April YbanezNo ratings yet
- Honors Complete PharmDocument10 pagesHonors Complete Pharmapi-724442716No ratings yet
- BP Regulation Medications ChartDocument5 pagesBP Regulation Medications ChartLovely CervantesNo ratings yet
- Nursing CS Angina-Pectoris-medications 03Document1 pageNursing CS Angina-Pectoris-medications 03Mahdia akterNo ratings yet
- Study On Pharmacology .Document93 pagesStudy On Pharmacology .upbandaraNo ratings yet
- C. Anti-Hypertensive Drugs.Document10 pagesC. Anti-Hypertensive Drugs.Nabeel AsifNo ratings yet
- Drug Treatment of HypertensionDocument36 pagesDrug Treatment of HypertensionAngetile KasangaNo ratings yet
- Ace InhibitorsDocument26 pagesAce InhibitorsDeipa KunwarNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Aids SupplementDocument13 pagesCognitive Aids SupplementKe YuheNo ratings yet
- Drug Study CRF PDFDocument21 pagesDrug Study CRF PDFshiplusNo ratings yet
- Atropine 8-28-22Document1 pageAtropine 8-28-22ladawskiNo ratings yet
- Crisis of Hypertension Revised 1Document57 pagesCrisis of Hypertension Revised 1keenmunir100% (4)
- Drug in EmergencyDocument8 pagesDrug in EmergencySuzana YusofNo ratings yet
- Mixed Acting Adrenergic AgonistDocument27 pagesMixed Acting Adrenergic AgonistqbNo ratings yet
- 312-Rle-Drug StudyDocument4 pages312-Rle-Drug StudyRogelyn PatriarcaNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used in Hypertension: Dr. R. PilvinieneDocument33 pagesDrugs Used in Hypertension: Dr. R. PilvinieneNewteNo ratings yet
- Anticoagulant, Antithrombotic and Anti-Platelet DrugsDocument63 pagesAnticoagulant, Antithrombotic and Anti-Platelet Drugsruchipickle100% (1)
- AntihypertensionDocument17 pagesAntihypertension백지원 (소네트리)No ratings yet
- Antiarrythmics PDFDocument1 pageAntiarrythmics PDFRonica PascuaNo ratings yet
- Antihypertensive Drugs: DR. DR Umi Kalssum MkesDocument58 pagesAntihypertensive Drugs: DR. DR Umi Kalssum MkesadilaalifnugrahaeniNo ratings yet
- CV Drugs ListDocument2 pagesCV Drugs ListAndrew MakariosNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used in Coagulation DisordersDocument11 pagesDrugs Used in Coagulation Disordersshoaib106muhammadNo ratings yet
- UROKINASE (Kinlytic)Document4 pagesUROKINASE (Kinlytic)Mikaela Gabrielle GeraliNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Medications: Vasopressors, Inotropes and Anti-Hypertensives Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Vasopressors, Inotropes and Anti-Hypertensives Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet
- LyL Folleto USA Material Estudiante InteractivoDocument16 pagesLyL Folleto USA Material Estudiante InteractivoAlaa OmarNo ratings yet
- 4burn Injury (4 Files Merged)Document39 pages4burn Injury (4 Files Merged)Alaa OmarNo ratings yet
- The Healing Power of GemstonesDocument47 pagesThe Healing Power of GemstonesAlaa OmarNo ratings yet
- Focused Neurological Assessment From Simple NursingDocument1 pageFocused Neurological Assessment From Simple NursingAlaa OmarNo ratings yet
- Untitled NotebookDocument4 pagesUntitled NotebookAlaa OmarNo ratings yet
- Example of A Work PlanDocument2 pagesExample of A Work PlanAlaa OmarNo ratings yet
- Memory Notebook of Nursing VolDocument170 pagesMemory Notebook of Nursing VolAlaa OmarNo ratings yet
- Hypnotherapy +aromatherapy + Laughter Therapy+ ImmuneDocument131 pagesHypnotherapy +aromatherapy + Laughter Therapy+ ImmuneAlaa OmarNo ratings yet
- Simple Nursing StudyDocument5 pagesSimple Nursing StudyAlaa OmarNo ratings yet
- Ali 2018Document16 pagesAli 2018Alaa OmarNo ratings yet
- Grammar Guide To Spanish PronounsDocument7 pagesGrammar Guide To Spanish PronounsAlaa OmarNo ratings yet
- Drawing TherapyDocument36 pagesDrawing TherapyAlaa OmarNo ratings yet
- Language Tutor Lesson IndexDocument7 pagesLanguage Tutor Lesson IndexAlaa OmarNo ratings yet
- L1 NotesDocument3 pagesL1 NotesAlaa OmarNo ratings yet
- Arterial Blood Gases Modes of Ventilation: Richmond Agitation Sedation ScaleDocument1 pageArterial Blood Gases Modes of Ventilation: Richmond Agitation Sedation ScaleAlaa OmarNo ratings yet
- Air Way Equipment 1Document38 pagesAir Way Equipment 1Alaa OmarNo ratings yet
- L 8storage and Handling of Medical GasDocument25 pagesL 8storage and Handling of Medical GasAlaa OmarNo ratings yet
- Stages of AnesthesiaDocument3 pagesStages of AnesthesiaAlaa OmarNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure - Video, Anatomy, Definition & Function - OsmosisDocument9 pagesHeart Failure - Video, Anatomy, Definition & Function - OsmosisAlaa OmarNo ratings yet
- ACLS Algorithms 2020Document8 pagesACLS Algorithms 2020Alaa OmarNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Exercise AssignmentDocument5 pagesTherapeutic Exercise AssignmentAlaa OmarNo ratings yet
- L4 Infection Control PPE and TBPDocument11 pagesL4 Infection Control PPE and TBPAlaa OmarNo ratings yet
- MedicalDocument958 pagesMedicalAlaa OmarNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument1 pageAssignmentAlaa OmarNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia Machine 5 and Breathing SystemsDocument33 pagesAnesthesia Machine 5 and Breathing SystemsAlaa OmarNo ratings yet
- Neurological Disorders Can Vary Widely in Their EtiologyDocument1 pageNeurological Disorders Can Vary Widely in Their EtiologyAlaa OmarNo ratings yet
- Air Way Equipment 2Document29 pagesAir Way Equipment 2Alaa OmarNo ratings yet
- Equipment of Locoregional Anesthesia 13-14Document44 pagesEquipment of Locoregional Anesthesia 13-14Alaa OmarNo ratings yet
- Invasive Blood PressureDocument5 pagesInvasive Blood PressureAlaa OmarNo ratings yet
- Pujo / UpjoDocument39 pagesPujo / UpjoHafizur RashidNo ratings yet
- OriginsDocument15 pagesOriginsRonilyn Mae AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Alternative Orchiopexy Undescended Testis: Simple Technique ofDocument3 pagesAlternative Orchiopexy Undescended Testis: Simple Technique ofShariq ShaNo ratings yet
- Stroke Pathophysiology Diagnosis and Management 7E 2021 7Th Edition James Grotta Full Chapter PDF ScribdDocument67 pagesStroke Pathophysiology Diagnosis and Management 7E 2021 7Th Edition James Grotta Full Chapter PDF Scribdalissa.leon383100% (7)
- (WHO) Intensive Care Unit (ICU)Document4 pages(WHO) Intensive Care Unit (ICU)desiveronikaNo ratings yet
- Zamboanga Doctors Hospital, Inc., Zamboanga City: Surgical Procedure PerformedDocument1 pageZamboanga Doctors Hospital, Inc., Zamboanga City: Surgical Procedure PerformedJaiton PagayonanNo ratings yet
- UK PhysiciansDocument230 pagesUK PhysiciansPatrickNo ratings yet
- A Case Study of Splenic Hemangiosarcoma in A Bitch and Its Surgical ManagementDocument3 pagesA Case Study of Splenic Hemangiosarcoma in A Bitch and Its Surgical ManagementWira KusumaNo ratings yet
- Kelompok Tindakan Bedah DigestifDocument3 pagesKelompok Tindakan Bedah DigestifSumiadiNo ratings yet
- Genitourinary Radiology ExamDocument9 pagesGenitourinary Radiology ExamNour NoorNo ratings yet
- Ressume With PhotoDocument5 pagesRessume With PhotoAsheervadamma Obul reddypalleNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Assessment BeforeDocument4 pagesDiagnostic Assessment BeforeBinod KumarNo ratings yet
- Intraoperative Desaturation During Thyroidectomy .27Document2 pagesIntraoperative Desaturation During Thyroidectomy .27Annakay HudsonNo ratings yet
- Hernias UltrasoundDocument35 pagesHernias UltrasoundRafa Rodríguez AveigaNo ratings yet
- (Download PDF) Core Topics in Cardiac Anaesthesia 3Rd Edition Andrew Roscoe Editor Online Ebook All Chapter PDFDocument42 pages(Download PDF) Core Topics in Cardiac Anaesthesia 3Rd Edition Andrew Roscoe Editor Online Ebook All Chapter PDFrachel.jones745100% (8)
- Ma. Theresa O. Bermudez 4BSN1/ GroupDocument4 pagesMa. Theresa O. Bermudez 4BSN1/ GroupJenna AbuanNo ratings yet
- Group - 5 Plastic SurgeryDocument2 pagesGroup - 5 Plastic SurgeryKiki AkiraNo ratings yet
- Presentation Myasthenia Gravis and ThymomaDocument12 pagesPresentation Myasthenia Gravis and ThymomaabciximabNo ratings yet
- MRI Protokol Review Adi WS QCDocument150 pagesMRI Protokol Review Adi WS QChadiNo ratings yet
- 12-Giant Cell LesionDocument78 pages12-Giant Cell Lesionفراس الموسويNo ratings yet
- Kelompok 4 - 1B - Temporomandibular JointDocument25 pagesKelompok 4 - 1B - Temporomandibular JointLutfi HanifahNo ratings yet
- 4.2 Binomial DistributionsDocument13 pages4.2 Binomial DistributionssakshiNo ratings yet
- Quality Assurance GuidelinesDocument28 pagesQuality Assurance Guidelinesmonir61No ratings yet
- Ruptur Vesica Urinaria Case ReportDocument2 pagesRuptur Vesica Urinaria Case ReportAinun Jariah FahayNo ratings yet
- Management of Penetrating Eye Injury With Intraocular Foreign BodyDocument5 pagesManagement of Penetrating Eye Injury With Intraocular Foreign BodyChristian FaustNo ratings yet
- July 285Document1 pageJuly 285Akash NiamatNo ratings yet
- Active Surgical Oncology Physician Assistant PA Resume SW Houston TXDocument3 pagesActive Surgical Oncology Physician Assistant PA Resume SW Houston TXRick Whitley100% (1)
- Imperforate Anus and Cloacal MalformationsDocument110 pagesImperforate Anus and Cloacal MalformationsAhmad Abu KushNo ratings yet
- All You Need To Know About Vascular SurgeryDocument33 pagesAll You Need To Know About Vascular SurgeryDr. Vinicius MajdalaniNo ratings yet