Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chemistry Q2
Chemistry Q2
Uploaded by
Kristel Anne Magaru-Macauggal-Lugo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views3 pagesThis document discusses various concepts in chemistry including dilution, colligative properties, vaporization, vapor pressure, boiling point elevation, and freezing point depression. It defines key terms and formulas. Dilution is the process of adding more solvent to lower a solution's concentration. Colligative properties depend only on the number of solute particles and not their nature. Vaporization is the phase change from liquid to gas, occurring through evaporation below the boiling point or boiling at the boiling point. The vapor pressure of a solution is lowered compared to the pure solvent, increasing the boiling point and decreasing the freezing point.
Original Description:
ESSAY
Original Title
CHEMISTRY-Q2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses various concepts in chemistry including dilution, colligative properties, vaporization, vapor pressure, boiling point elevation, and freezing point depression. It defines key terms and formulas. Dilution is the process of adding more solvent to lower a solution's concentration. Colligative properties depend only on the number of solute particles and not their nature. Vaporization is the phase change from liquid to gas, occurring through evaporation below the boiling point or boiling at the boiling point. The vapor pressure of a solution is lowered compared to the pure solvent, increasing the boiling point and decreasing the freezing point.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views3 pagesChemistry Q2
Chemistry Q2
Uploaded by
Kristel Anne Magaru-Macauggal-LugoThis document discusses various concepts in chemistry including dilution, colligative properties, vaporization, vapor pressure, boiling point elevation, and freezing point depression. It defines key terms and formulas. Dilution is the process of adding more solvent to lower a solution's concentration. Colligative properties depend only on the number of solute particles and not their nature. Vaporization is the phase change from liquid to gas, occurring through evaporation below the boiling point or boiling at the boiling point. The vapor pressure of a solution is lowered compared to the pure solvent, increasing the boiling point and decreasing the freezing point.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
CHEMISTRY
LECTURE / PPT AND HANDOUT BASE
DILUTION Colligative Properties
The process in which more solvent is
added to a solution in order to lower its Depend only on the relative amounts of
concentration. solute and solvent of a solution.
Types of solution according to concentration Depend only pn the number of solute
1. Dilute Solution particles in solution and not on the
nature of the solute particles.
Contains a relatively small amount of
solute. Types of solutions according to electrical
conductivity
2. Concentrated Solution 1. Electrolyte
Contains a relatively large amount of Solution that conducts electricity.
solute.
2. Non-electrolyte
FORMULA
Solution that does not conduct
C1V1=C2V2
electricity.
Where:
Colligative properties of Non- Electrolyte
C1 - Concentration of the concentrated stock Solution
solution. Vapor-Pressure Reduction
C2 - Concentration of the diluted stock Boiling Point Elevation
solution.
Freezing Point Depression
V1 - Volume of the concentrated stock
Osmotic Pressure
solution.
VAPORIZATION
V2 - Volume of the diluted stock solution.
Gas vs Vapor
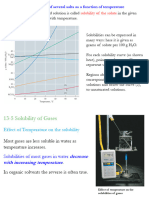
HENRY’S LAW
Gas
William Henry (1774-1836) English
Chemist A substance that is normally In the
gaseous state at ordinary temperatures
The solubility of a gas in a liquid is
and pressure.
directly proportional to the partial
pressure of the gas above the solution. Vapor
FORMULA A substance that is the gaseous form of
C = kP any substance that is liquid or a solid at
normal temperatures and pressures.
Where:
Vaporization
C - Molar concentration of the gas in the
solution phase Phase transition where a substance
changes its phase from liquid to gas.
k - Henry’s Law Constant
VAPORIZATION
P - Partial pressure of the gas over the
solution (Evaporation vs. Boiling)
COLLIGATIVE PROPERTIES OF Evaporation
SOLUTIONS
Colligative Properties of Non- Vaporization of a liquid below its
Electrolyte Solution boiling point.
Colligative Properties of Electrolyte Takes place at the surface of the liquid.
Solution
CHEMISTRY
LECTURE / PPT AND HANDOUT BASE
Occurs when the liquid particles at the Psol’n = Xsolvent Psolvent
surface of the liquid have enough KE
to overcome the attractive forces and
escape into the atmosphere.
* Bubbles cannot form since the vapor
pressure is less than atmospheric pressure.
Boiling
Vaporization of a liquid at its boiling
point.
Takes place beneath the surface of the
liquid.
Occurs when the gas particles (bubbles)
have great pressure to resist the
pressure of the surrounding water.
VAPOR PRESSURE
The pressure exhibited by vapor
present above a liquid surface.
The pressure exerted when the
molecules leave the surface at the same
rate as they return.
The Effect of Vapor Pressure Reduction
or Boiling Point Elevation
The temperature at which the vapor
pressure equate the external
atmospheric pressure.
The presence of the nonvolatile solute
lowers the vapor pressure of the
The lowering of the vapor pressure of solution.
the liquid solvent in a solution.
The lower the vapor pressure the higher
the boiling point since more heat is
applied.
Defines as the boiling point of the
solution (Tb Solution) minus the boiling
point of the pure solvent (Tb Solvent).
Tb = Tb Solution - Tb Solvent
Raoult’s Law Tb = Kbm
The vapor pressure of the solution,
Psol'n is equal to the product of the APPLICATIONS OF BOILING POINT
mole fraction of the solvent, Xsolvent, ELEVATION
and the vapor pressure of the pure
solvent, Psolvent 1. Engine Coolant
CHEMISTRY
LECTURE / PPT AND HANDOUT BASE
2. Cooking
3. Sugar refining
FREEZING POINT DEPRESSION
The freezing point of a substance is
identical ti its melting point.
They only differ in the direction from
which the people change is approached.
The temperature at which the substance
freezes.
(similarity with the boiling point) the
vapor pressure of the solution also
affects the boiling freezing point.
The pressure of the nonvolatile solute
lowers the vapor pressure of the
solution and causes it to freeze at
lower temperature.
= Tf Solvent - Tf Solution
= Kfm
T
APPLICATIONS OF BOILING POINT
ELEVATION
1. Engine Coolant
2. Dirty Ice cream
3. Icy roads
4. Vodka
You might also like
- CH 6 2nd SolutionDocument130 pagesCH 6 2nd SolutionDiego Hernán Moreno González100% (1)
- Advanced Pharmaceutical analysisFrom EverandAdvanced Pharmaceutical analysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Fundamentals of Thermodynamics Solutions ch08Document207 pagesFundamentals of Thermodynamics Solutions ch08Cierré No'Middlename Jones86% (7)
- Properties of Gasoline and Fuel Gases: de La Salle UniversityDocument10 pagesProperties of Gasoline and Fuel Gases: de La Salle UniversityNazario Emil LintagNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry2 - Lesson2Document2 pagesGeneral Chemistry2 - Lesson2Ronalda GuevarraNo ratings yet
- Meeting 6-7Document30 pagesMeeting 6-7Aldo FirmansyahNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Lecture 5Document17 pagesModule 1 Lecture 5Amirs AmjadNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 5 - Module 1Document17 pagesLecture - 5 - Module 1Zaira Eliz GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Colligative Properties of Solution (3rd Week)Document41 pagesColligative Properties of Solution (3rd Week)SomeThingNo ratings yet
- Mod 3.2 Colligative, Tonicity and Mod 4 Solubility (PDF - Io)Document62 pagesMod 3.2 Colligative, Tonicity and Mod 4 Solubility (PDF - Io)Charles DapitoNo ratings yet
- SOLUTIONSDocument57 pagesSOLUTIONSTanvi KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem Rev Pre Fi (2nd Sem)Document6 pagesGen Chem Rev Pre Fi (2nd Sem)Caeyla NhinaNo ratings yet
- 1 Lecture Note Chem 2 ColligativeDocument2 pages1 Lecture Note Chem 2 ColligativeMarjorie BrondoNo ratings yet
- Hukum RoultDocument25 pagesHukum RoultZaqiya zahwa alifaNo ratings yet
- Chem LeeDocument3 pagesChem LeeLee Alvin MagyayaNo ratings yet
- 13.2 Colligative Properties of SolutionsDocument11 pages13.2 Colligative Properties of SolutionsOmar AlwaerNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Notes Ch02 Solutions UnlockedDocument5 pages12 Chemistry Notes Ch02 Solutions UnlockedcdrthsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 .Solutions: Short Questions With AnswerDocument6 pagesChapter 9 .Solutions: Short Questions With AnswerMuhammad ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Solutions: Roult's LawDocument2 pagesSolutions: Roult's LawSsNo ratings yet
- Colligative Properties of SolutionsDocument66 pagesColligative Properties of Solutionspalitpa moreNo ratings yet
- Solution - in - One - Page (1) .Doc - 20240222 - 235427 - 0000Document4 pagesSolution - in - One - Page (1) .Doc - 20240222 - 235427 - 0000Naaz ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Solutions G Colligative PropDocument14 pagesSolutions G Colligative PropHusnul YaqinNo ratings yet
- 9.solubility and Partition PhenomenaDocument44 pages9.solubility and Partition Phenomena劉育維No ratings yet
- 4 Colligativeproperties 180825211533Document88 pages4 Colligativeproperties 180825211533Rmon ianNo ratings yet
- Chemistry InvestigatoryDocument16 pagesChemistry InvestigatorySai NandhaNo ratings yet
- Solution in One PageDocument2 pagesSolution in One Pageraiprisha06No ratings yet
- Colligative Properties of Solutions ReviewerDocument4 pagesColligative Properties of Solutions ReviewerPrecious Lara MangobaNo ratings yet
- As NotesDocument95 pagesAs NotesJude JosephNo ratings yet
- 4 Colligative Properties of SolutionsDocument84 pages4 Colligative Properties of SolutionsujargohandiNo ratings yet
- 5) 2020 - SolutionsDocument10 pages5) 2020 - SolutionsFaizan AnsariNo ratings yet
- Colligative PropertyDocument26 pagesColligative PropertyKshama SharmaNo ratings yet
- 1.9 Colligative Properties of SolutionsDocument9 pages1.9 Colligative Properties of Solutionsfikerdereje697No ratings yet
- Colligative Properties of SolutionsDocument8 pagesColligative Properties of SolutionspieNo ratings yet
- GenChem2 3rdsem EndTerm ReviewerDocument4 pagesGenChem2 3rdsem EndTerm ReviewerJames Andre DionedaNo ratings yet
- Henrys Law Coll PropDocument26 pagesHenrys Law Coll PropCindelle Mariae GomiegaNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument5 pagesChemistryLevi AckermanNo ratings yet
- Lec21607 +#+# (# (#?Document24 pagesLec21607 +#+# (# (#?Rylle PongaseNo ratings yet
- Raoult's Law123Document25 pagesRaoult's Law123Abdur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Random Notes Class 12 ChemistryDocument87 pagesRandom Notes Class 12 Chemistryankitajamatia06No ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Lecture-2Document10 pagesChapter 13 Lecture-2Çetin UzişNo ratings yet
- 01 - Liquid Solution Theory - PMDDocument19 pages01 - Liquid Solution Theory - PMDSumant KumarNo ratings yet
- Week 6 Gen ChemDocument29 pagesWeek 6 Gen ChemPaolo Joacquin FaenagNo ratings yet
- NEET UG Chemistry Solutions PDFDocument31 pagesNEET UG Chemistry Solutions PDFAlexa Siddhi0% (1)
- Colligative PropertiesDocument41 pagesColligative PropertiesJoshua SagunNo ratings yet
- X-Ray Diffraction Document (1) (4) - 1Document9 pagesX-Ray Diffraction Document (1) (4) - 1MEEZAN TVNo ratings yet
- 1. Solution - XII-1Document53 pages1. Solution - XII-1karanchinna987No ratings yet
- Solution NotesDocument8 pagesSolution NotesAnmolNo ratings yet
- Solution (Part 2)Document24 pagesSolution (Part 2)saptarshi senNo ratings yet
- Solution: STR Ycl AssesDocument40 pagesSolution: STR Ycl AssesArka DeyNo ratings yet
- M4 Colligative PropertiesDocument46 pagesM4 Colligative Propertiesicebear1333No ratings yet
- Chapter-02 SolutionDocument13 pagesChapter-02 Solutionshrey4602No ratings yet
- เอกสารประกอบรายวิชา pc205 ครั้งที่ 5 solutionDocument57 pagesเอกสารประกอบรายวิชา pc205 ครั้งที่ 5 solutionVeliyana Londong AlloNo ratings yet
- Lesson Presentation ChemistryDocument42 pagesLesson Presentation ChemistryTchr Ezra ChangNo ratings yet
- Solutions NotesDocument34 pagesSolutions NotesAneesh RenuNo ratings yet
- Learning Objectives: Colligative PropertiesDocument9 pagesLearning Objectives: Colligative PropertiesBea Dacillo Bautista100% (3)
- ColligativeDocument24 pagesColligativeHarry WinstonNo ratings yet
- Measuring SolutionsDocument49 pagesMeasuring Solutions23122005trangxinhNo ratings yet
- Freezing Point Depression With Lab QuestDocument12 pagesFreezing Point Depression With Lab QuestiiiNo ratings yet
- 3-SCH 403 Colagative PropertiesDocument25 pages3-SCH 403 Colagative PropertiesAnn KiamaNo ratings yet
- SolutionsDocument31 pagesSolutionsmayashankarjha100% (1)
- Class 12 chemistry-Solutions-AnswersDocument11 pagesClass 12 chemistry-Solutions-AnswersexcellinchemistryNo ratings yet
- Solutios, Solutions of Non Electrolyte - 2019-2020Document80 pagesSolutios, Solutions of Non Electrolyte - 2019-2020hazo hazNo ratings yet
- Ch.1 (Fluid)Document97 pagesCh.1 (Fluid)Ziad ElnagarNo ratings yet
- Material Safety Data Sheet Setseal B - Liquid: 1: Product and Company IdentificationDocument4 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet Setseal B - Liquid: 1: Product and Company Identificationhussam jumahNo ratings yet
- Hexane Polymerisation: Data SheetDocument3 pagesHexane Polymerisation: Data SheetHamid Vahedi LarijaniNo ratings yet
- Active Ingredients in Pain RelieverDocument13 pagesActive Ingredients in Pain RelieverkatrinaarnaizNo ratings yet
- Evaporation Vs Boiling - Google SearchDocument1 pageEvaporation Vs Boiling - Google SearchFionaNo ratings yet
- Us3629997 PDFDocument5 pagesUs3629997 PDFDellaNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics: Multiple Choice Questions inDocument19 pagesThermodynamics: Multiple Choice Questions inJevan CalaqueNo ratings yet
- Home Prs Msds V en PursueDisinfectantCleanerDocument9 pagesHome Prs Msds V en PursueDisinfectantCleanerMadhavan HarshNo ratings yet
- Tarea 4 TermodinamicaDocument3 pagesTarea 4 TermodinamicaMario GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Unit 2: An Overview of Chemical Process TechnologyDocument39 pagesUnit 2: An Overview of Chemical Process TechnologyChuah Chong YangNo ratings yet
- MSDS - Formic Acid 85 - PCNT - Usa-12322Document11 pagesMSDS - Formic Acid 85 - PCNT - Usa-12322Tahir NizamNo ratings yet
- Identifying Matter: Physical PropertiesDocument1 pageIdentifying Matter: Physical PropertiesbecaNo ratings yet
- CHE Thermodynamics Competency Exam 2013 - 20141 EditedDocument7 pagesCHE Thermodynamics Competency Exam 2013 - 20141 EditedWinsletJoyDauagNo ratings yet
- 1st Puc Physics Chapter11-Thermal Properties of Matter Notes by U N SwamyDocument13 pages1st Puc Physics Chapter11-Thermal Properties of Matter Notes by U N Swamyashwinikumari b100% (1)
- Tutorial 2Document2 pagesTutorial 2FaiqNo ratings yet
- Angelus Shoe Polish CoDocument35 pagesAngelus Shoe Polish Coتلاش منزلNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ExercisesDocument42 pagesChemistry ExercisesdanielitoNo ratings yet
- SDS Hazard Communication Safety Data Sheet According To Regulation (EC) No. 1272/2008 (CLP)Document17 pagesSDS Hazard Communication Safety Data Sheet According To Regulation (EC) No. 1272/2008 (CLP)Gita KodonganNo ratings yet
- 11 Thermal Properties of MatterDocument8 pages11 Thermal Properties of MatterGIENo ratings yet
- Jove Science Education 5700 Fractional DistillationDocument7 pagesJove Science Education 5700 Fractional DistillationAndriana Kusuma Pertiwi0% (1)
- DistillationDocument89 pagesDistillationjokish33% (3)
- CHEM 31 - Laboratory ManualDocument74 pagesCHEM 31 - Laboratory ManualJulianne AromboNo ratings yet
- Utilization of Coconut Fiber WasteDocument7 pagesUtilization of Coconut Fiber WasteIr. Zainuddin Ginting, M.T Teknik KimiaNo ratings yet
- Thermometer Exp 1Document11 pagesThermometer Exp 1hayder alaliNo ratings yet
- DistillationDocument62 pagesDistillationKenil JaganiNo ratings yet
- Formal Report - Experiment 5Document5 pagesFormal Report - Experiment 5Vanessa ValdezNo ratings yet
- Consequence Modeling Using AlohaDocument40 pagesConsequence Modeling Using AlohaNageswar MakalaNo ratings yet