Professional Documents
Culture Documents
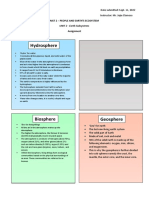
Hazardous Earth A3 Sheet Climate
Hazardous Earth A3 Sheet Climate
Uploaded by
kabiki7750Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hazardous Earth A3 Sheet Climate
Hazardous Earth A3 Sheet Climate
Uploaded by
kabiki7750Copyright:
Available Formats
Unit 1: Topic 1a Hazardous Earth—Climate Change
How does the worlds climate system function? What are the natural causes of climate change? What is the Greenhouse Effect?
What is Global/Atmospheric Circulation? Weather changes from minute to minute, climate is the average weather taken over 30 There are a number of greenhouse gases, methane, nitrous oxide but the one most associ-
The atmosphere is constantly moving - transferring heat around the earth in a global years. In historical times temperatures have varied as much as 1.5°C each side of the aver- ated with human activity is carbon dioxide. Recent changes in CO2 are a result of burning
circulation system. There are three types of circulation cells that make up this circula- age due to natural causes. fossil fuels such as gas, coal and above all oil.
tion pattern. Throughout history the earths temperatures has changed many times both increasing and 1. Greenhouse gases retain heat
The earth receives its energy from the decreasing. There are many reasons for these changes: from the Sun that would otherwise
sun which passes through the atmos- be reflected from Earth back into
phere and heats up the ground directly. space. Without them the planet
This warms the air above the ground, would be too cold to support life.
the warm air rises and transfers heat 2. Solar energy passes through the
into the atmosphere which creates low atmosphere without having any real
pressure. It then cools, travels north impact on it.
and south where it sinks back towards 3. About half of it is absorbed by the
the earth. Rising air cannot hold as Earth, the rest is reflected back by
much moisture that’s why there is more clouds or the ground, absorbed by
precipitation on the equator. As the the clouds or upper atmosphere or
cooler, drier air sinks (30°N/S line of simply scattered back to space.
latitude) it creates high pressure with 4. The other half absorbed by the
clear skies, little precipitation and arid ground is radiated back into the atmosphere and some is trapped by greenhouse gases.
(dry) conditions. How are human activities causing climate change?
The earth receives most radiation on the equator where it is hottest compared to the What is the ‘Enhanced’ Greenhouse
poles where it is the coldest. The Effect?– human activities have in-
equator receives most radiation be- Orbital Changes: creased the amount of CO2 and have
cause the suns rays hit the surface at (Milankovitch cycles) reduced the environment ability to
a right angle. At the poles the angle is Changes in how the absorb it. Since the industrial revolu-
much lower which means they have earth orbits the sun. tion levels of greenhouse gases have
to heat up a much larger area. These cycles are called risen. The developed world are re-
Winds are caused when air moves the Milankovitch cy- sponsible for the majority of this in-
from high to low pressure but be- cles and happen every crease as a result of the following:
cause the earth rotates as the air 100,000 years. The - energy supply which burns coal, gas
moves above the surface, the earth earths orbit changes and oil. US and China majority coal
rotates below it and the winds follow from being circular to (39% CO2)
a curved path. This is called the corio- elliptical (more egg shaped) and this changes the amount of solar energy the earth surface - 90% of journeys use transport which burns oil (29% CO2)
lis effect. In the northern hemi- receives. - manufacturing industry uses energy and produces waste (17% CO2)
sphere the winds are deflected to the Solar Output: (sunspot activity) The suns energy output is not always constant, the most Other greenhouse gases have different origins:
right and in the southern hemisphere to common of these are sunspots, these are darker areas on the sun surface with greater - Nitrous oxide is produced by jet engines, fertilisers and sewage farms.
the left. amounts of solar activity. Sunspots come and go usually every 11 years, the more sunspots - Methane from grazing cows (200 litres of gas per day). Cattle numbers have doubled in
Jet streams also impact on air move- the higher the temperature on earth. last 50years.
ment and they are mainly on the bound- Volcanic Activity: Major volcanic events lead to reduced temperatures as the volcano - Deforestation by humans leads to an increase in CO2 emissions as these are carbon stores
erupts large amounts of ash into the atmosphere. This blocks out solar radiation and reduces and without them this reduces the ability of the earth to absorb CO2.
the amount of suns energy reaching the earths surface and therefore reducing the tempera- What are the possible consequences of climate change?
ture. Asteroid Sea level changes
Collisions: Can lead to small periods of cooling due to the ash/dust particles put into the at- The most obvious impact of climate change is and rising temperatures is rising sea levels.
mosphere following the collision with earths surface. As with volcanic activity these also Sea levels have risen by around 200mm since 1870. This is due to two main reasons:
block out or absorb solar radiation. - As temperatures rise, water expands causing sea volume to increase.
What evidence is there of natural climate change? - Melting ice caps and glaciers, most is held in Greenland and Antarctica
aries of the main circulation cells changing We know about climate change in the past because of: There could be a
the weather for different places. - Tree rings. Growth rings are wider indicating warmer wetter conditions. rise in sea levels by
Oceanic currents also transfer heat around - Ice cores from Greenland and Antarctica indicating levels of CO2 from when the ice was 300mm to 1000mm
the earth. Surface ocean currents are driven formed. depending on how
by the movement of air across them, where- - Historical sources, dairies, paintings, farming/yield records, we look at global
as deep ocean currents are determined by warming. Melting
ice can unlock
colder salty water near the greenhouse gases
Arctic and Antarctic sinking such as Methane
pulling warmer water into that have been
them from lower latitudes. locked away for
centuries, increas-
ing the greenhouse
effect further.
You might also like
- 6 What Factors Affect ClimateDocument6 pages6 What Factors Affect ClimateSandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- CH 9Document9 pagesCH 9anil.gelra5140No ratings yet
- Kegy 208Document9 pagesKegy 208nandanpancholi2000No ratings yet
- Class 11 Chap 8Document9 pagesClass 11 Chap 8Vishal Deep SarangalNo ratings yet
- S R, H B T: Olar Adiation EAT Alance AND EmperatureDocument9 pagesS R, H B T: Olar Adiation EAT Alance AND EmperatureLaila KhattakNo ratings yet
- Hurricanes. These Storms Have GreatDocument3 pagesHurricanes. These Storms Have GreatarkelNo ratings yet
- Science 9 - ClimateDocument3 pagesScience 9 - ClimateJOSHUA CABIGAYANNo ratings yet
- Climate Change PPTDocument30 pagesClimate Change PPTjoseph birung100% (2)
- Climate Topic 2Document11 pagesClimate Topic 2auroracerianiNo ratings yet
- Student Copy Session 9 GR 7A ESDocument2 pagesStudent Copy Session 9 GR 7A ESMeme 2020No ratings yet
- Pointers: Layers of The Earth's AtmosphereDocument4 pagesPointers: Layers of The Earth's AtmosphereMorTech JulietStore BatahoyNo ratings yet
- THE EARTH, Man and His EnvironmentDocument4 pagesTHE EARTH, Man and His Environmentlodelyn caguilloNo ratings yet
- Weather - Geography Form 1 Notes.: Daily Atmospheric Conditions of A Place at A Particular TimeDocument22 pagesWeather - Geography Form 1 Notes.: Daily Atmospheric Conditions of A Place at A Particular Timemakarcyber42No ratings yet
- NAPULI, H WrittenReportDocument2 pagesNAPULI, H WrittenReportHaina NapuliNo ratings yet
- Teacher Background: Earth'S Atmosphere: Layers of The AtmosphereDocument7 pagesTeacher Background: Earth'S Atmosphere: Layers of The AtmosphereIndhumathiNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 9: Solar Radiation, Heat Balance and TemperatureDocument4 pagesChapter - 9: Solar Radiation, Heat Balance and TemperatureJagatraj SahuNo ratings yet
- TBI Earths Radiative Heat BudgetDocument5 pagesTBI Earths Radiative Heat Budgetcoderb1010No ratings yet
- Causes of Aridity, and Geography of The World S DesertsDocument10 pagesCauses of Aridity, and Geography of The World S DesertsSATYABRAT ROUTNo ratings yet
- Climate and Biosphere: Dynamic PartnersDocument5 pagesClimate and Biosphere: Dynamic PartnerskryspoNo ratings yet
- Earths Climate Past and Future 3rd Edition Ruddiman Solutions ManualDocument3 pagesEarths Climate Past and Future 3rd Edition Ruddiman Solutions Manualjessicaramseymxpqrcbgjt100% (11)
- Insolation and Heat Balance of The EarthDocument10 pagesInsolation and Heat Balance of The EarthDevraj H SNo ratings yet
- Biophysical Environments: The AtmosphereDocument5 pagesBiophysical Environments: The AtmosphereAnanya UppalNo ratings yet
- Climate Change and Its Effects - Who's Taking Charge?Document104 pagesClimate Change and Its Effects - Who's Taking Charge?RAYMOND BRIAN TORRESNo ratings yet
- Greenhouse Effect: An Effect in The Atmosphere As A Result of The Presence of Greenhouse GasesDocument2 pagesGreenhouse Effect: An Effect in The Atmosphere As A Result of The Presence of Greenhouse GasesWen You ChanNo ratings yet
- Module 5Document4 pagesModule 5Jacqueline OrtegaNo ratings yet
- PG SEM 2-Mod-206-Factors Affecting The Global Atmospheric CirculationDocument3 pagesPG SEM 2-Mod-206-Factors Affecting The Global Atmospheric CirculationEVA JOSEPHINE CASTORNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Natural Causes of Climate ChangeDocument4 pagesLesson 3 - Natural Causes of Climate Changesalehalmasroori7No ratings yet
- Science - Greenhouse EffectDocument1 pageScience - Greenhouse Effectathena sarrah torresNo ratings yet
- Solar Insolation by Dr. Pranab KR DasDocument5 pagesSolar Insolation by Dr. Pranab KR DasPranab Kr DasNo ratings yet
- Climate Change Grade 9 - NeptuneDocument3 pagesClimate Change Grade 9 - NeptuneClyde PabilonaNo ratings yet
- MST2 U2a1 Gabrino SDocument1 pageMST2 U2a1 Gabrino Sjuicely gabrinoNo ratings yet
- KO ClimateChangeDocument3 pagesKO ClimateChangeEmmanuel RichardNo ratings yet
- The Earths Energy BalanceDocument14 pagesThe Earths Energy BalanceMohau MailaNo ratings yet
- 2 Climate Change BasicsDocument8 pages2 Climate Change BasicsBardhyll GashiNo ratings yet
- MeteorologyDocument30 pagesMeteorologyZaria WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science - Atmosphere1Document61 pagesEnvironmental Science - Atmosphere1whether913No ratings yet
- O Level Geography Notes Physical NotesDocument157 pagesO Level Geography Notes Physical NotesBrendon T100% (3)
- Group 4 - Structured Assignment Theoretical 7Document10 pagesGroup 4 - Structured Assignment Theoretical 7Tavia BrinleyNo ratings yet
- Inter-Tropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ)Document8 pagesInter-Tropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ)Jamhur JamhurNo ratings yet
- Inter-Tropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ)Document8 pagesInter-Tropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ)Jamhur JamhurNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7: Weather Hazards: Learning Outcomes Essential QuestionsDocument25 pagesChapter 7: Weather Hazards: Learning Outcomes Essential Questionsapi-270268482No ratings yet
- 10 Climate Change Revision OrganiserDocument5 pages10 Climate Change Revision OrganiserAarush GuptaNo ratings yet
- Kids Guide To Climate ChangeDocument2 pagesKids Guide To Climate ChangeEmad AlinyNo ratings yet
- PlanetEnergyBal PrintVersionDocument8 pagesPlanetEnergyBal PrintVersionMahesh MNo ratings yet
- CH 10Document18 pagesCH 10Quinn ShyamNo ratings yet
- Sir Des Physical GeoDocument7 pagesSir Des Physical GeoATE MHELLNo ratings yet
- Science 7 Module 15.1Document17 pagesScience 7 Module 15.1ryfreelance10No ratings yet
- Insolation & TemperatureDocument6 pagesInsolation & TemperatureAswin ANo ratings yet
- METEOROLGYDocument8 pagesMETEOROLGYRina MorenoNo ratings yet
- Science Q4 Worksheet Week3Document4 pagesScience Q4 Worksheet Week3JEMIMA BERNARDONo ratings yet
- Module 3Document6 pagesModule 3CTGPH 2021No ratings yet
- Lutgens Cap 2 PDFDocument31 pagesLutgens Cap 2 PDFgabriel andres cifuentes baqueroNo ratings yet
- Climate Change Pabilona Chito Grade 9 - NeptuneDocument2 pagesClimate Change Pabilona Chito Grade 9 - NeptuneKalæ DöNo ratings yet
- My Science JournalDocument60 pagesMy Science JournalZamzam ShubberNo ratings yet
- Ak HWDocument4 pagesAk HWakbarshahbasaratNo ratings yet
- Earth Processes Atmosphere NotesDocument6 pagesEarth Processes Atmosphere NotesMuhammad SabeehNo ratings yet
- Meteorology Chapter 7 Flashcards - QuizletDocument4 pagesMeteorology Chapter 7 Flashcards - QuizletvalmikisatishNo ratings yet
- Earth Heat Budget SystemDocument19 pagesEarth Heat Budget SystemHuma r.no:7 Bs zoology VllNo ratings yet
- Questions and Answers about: Planet EarthFrom EverandQuestions and Answers about: Planet EarthRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- A Giant Shield : A Study of the Atmosphere - Weather Books for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksFrom EverandA Giant Shield : A Study of the Atmosphere - Weather Books for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksNo ratings yet
- Heat and Work DemoDocument39 pagesHeat and Work DemoGerald E BaculnaNo ratings yet
- Lahan PadiDocument23 pagesLahan PadiSimon32 TooNo ratings yet
- Rural Water SupplyDocument24 pagesRural Water SupplyRiJade Bibiano100% (1)
- 7 Environmental Problems That Are Worse Than We ThoughtDocument6 pages7 Environmental Problems That Are Worse Than We ThoughtHelen ShcholokovaNo ratings yet
- Dampak Degradasi Lingkungan Pesisir Terhadap Kondisi Ekonomi Nelayan: Studi Kasus Desa Takisung, Desa Kuala Tambangan, Desa TabanioDocument7 pagesDampak Degradasi Lingkungan Pesisir Terhadap Kondisi Ekonomi Nelayan: Studi Kasus Desa Takisung, Desa Kuala Tambangan, Desa Tabanioibnu njNo ratings yet
- 12.0 Ecosystem Ecology Recap: 12.1 Energy Flow and Chemical CyclingDocument5 pages12.0 Ecosystem Ecology Recap: 12.1 Energy Flow and Chemical CyclingOtiosse MyosotisNo ratings yet
- Type A Caption For Your PhotoDocument2 pagesType A Caption For Your Photoapi-280797972No ratings yet
- Proposal of Go Green 2020Document10 pagesProposal of Go Green 2020baharin bin mohd tahirNo ratings yet
- Coastline Change Detection of Trinidad and Tobago 1994 - 2014 - IMADocument117 pagesCoastline Change Detection of Trinidad and Tobago 1994 - 2014 - IMANikia GoodingNo ratings yet
- Basic Information - : (Lecturer and Researcher)Document3 pagesBasic Information - : (Lecturer and Researcher)habtamu tamiru100% (1)
- Lesson 3 Disaster Awareness Preparedness and Management Part 2 September 18, 2021Document16 pagesLesson 3 Disaster Awareness Preparedness and Management Part 2 September 18, 2021Lanz Sedrick PascuaNo ratings yet
- Report CBD Aquifer LahoreDocument92 pagesReport CBD Aquifer LahoreDawood MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Sahara Desert Lesson For Elementary by SlidesgoDocument8 pagesSahara Desert Lesson For Elementary by SlidesgoM MINNAARNo ratings yet
- Disaster Resilient Construction of Water Spouts in Kathmandu Valley of NepalDocument12 pagesDisaster Resilient Construction of Water Spouts in Kathmandu Valley of NepalPushkar MathemaNo ratings yet
- Waters of KosovoDocument40 pagesWaters of Kosovorimi7alNo ratings yet
- ELGE Letter About Kalamazoo River Sediment BuildupDocument2 pagesELGE Letter About Kalamazoo River Sediment BuildupWWMTNo ratings yet
- Climatic Factor For Design of BuildingDocument66 pagesClimatic Factor For Design of Buildingarchitectneha614No ratings yet
- Summative Test On VolcanoesDocument11 pagesSummative Test On VolcanoesGeminiana MacalindongNo ratings yet
- Case Study TemplatesDocument10 pagesCase Study Templatessydneycarter873No ratings yet
- Irrigation Water Quality: Muhammad Arshad and Aamir ShakoorDocument16 pagesIrrigation Water Quality: Muhammad Arshad and Aamir ShakoorStephen SanjayaNo ratings yet
- 5 - Q3 SciDocument21 pages5 - Q3 Scimaximo meridaNo ratings yet
- Answer Script For Bangladesh Studies 2 Topic 4Document4 pagesAnswer Script For Bangladesh Studies 2 Topic 4Inaaya ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- PsychrometryDocument31 pagesPsychrometryshrutiNo ratings yet
- Beaufort ScaleDocument3 pagesBeaufort Scalerioabigail_389944433No ratings yet
- Heat Index Chart: by Temperature (F) and Relative Humidity (%)Document1 pageHeat Index Chart: by Temperature (F) and Relative Humidity (%)Olga KardashNo ratings yet
- Cfe 1 - Cabrera - Treeparenting - Bsit1cDocument2 pagesCfe 1 - Cabrera - Treeparenting - Bsit1cNikolai CabreraNo ratings yet
- A Horse With No NameDocument3 pagesA Horse With No NameInma Nada MásNo ratings yet
- Hydrology - Basic ConceptsDocument14 pagesHydrology - Basic ConceptsEngr.Hamid Ismail CheemaNo ratings yet
- Layout of Typical Pump Fed FarmDocument4 pagesLayout of Typical Pump Fed FarmAtul SinghNo ratings yet
- 08 WS BiogeochemicalCyclesColoringQuestions 1Document2 pages08 WS BiogeochemicalCyclesColoringQuestions 1Maricel CapiliNo ratings yet