Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 viewsFunda5 - Asepsis
Funda5 - Asepsis
Uploaded by
bondadluiThis document discusses fundamentals of nursing asepsis. It defines key terms like resident flora, infection, disease, and virulence. It describes the chain of infection and types of microorganisms that cause infections. It also discusses the different types of infections like local vs. systemic. The document outlines nonspecific body defenses against infection. It discusses diagnosing risk for infection and examples of risk factors. Finally, it identifies the 5 moments for proper hand hygiene in nursing care.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Evidence Plan: Competency Standard: Carpentry Nc2 Unit of Competency: Ways in Which Evidence Will Be CollectedDocument5 pagesEvidence Plan: Competency Standard: Carpentry Nc2 Unit of Competency: Ways in Which Evidence Will Be CollectedBhem Boy100% (1)
- Annexure A Price Schedule STSDocument188 pagesAnnexure A Price Schedule STSRuslan Ibragimov100% (1)
- Communicable Disease Nursing Ca1 July 2018 5 PDFDocument461 pagesCommunicable Disease Nursing Ca1 July 2018 5 PDFJordz Placi100% (3)
- Principles of Asepsis and Sterile TechniquesDocument4 pagesPrinciples of Asepsis and Sterile Techniquesjgcriste93% (14)
- Welding ConsumablesDocument20 pagesWelding ConsumablesThillaivananNo ratings yet
- Retail ProjectDocument114 pagesRetail ProjectSowjanya KunareddyNo ratings yet
- FUNDA SLE - AsepsisDocument8 pagesFUNDA SLE - Asepsisprincessdiane.agripaNo ratings yet
- Infection CompreDocument4 pagesInfection CompreaccachuelaNo ratings yet
- Communicable DiseasesDocument19 pagesCommunicable Diseasesriamanabat100% (5)
- Communicable Dse Nursing Discussion Continuation JKMDocument56 pagesCommunicable Dse Nursing Discussion Continuation JKMKyla Ysabelle PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Lec5 MP Bacteria and DiseaseDocument51 pagesLec5 MP Bacteria and DiseasePriya ManobalNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Nursing Practice - MidtermDocument24 pagesFundamentals of Nursing Practice - MidtermShene Claire VigillaNo ratings yet
- Communicable DiseaseDocument41 pagesCommunicable DiseaseMrz AlzNo ratings yet
- Micro LEC - Principles of Disease and EpidemiologyDocument14 pagesMicro LEC - Principles of Disease and EpidemiologykapeNo ratings yet
- Preventing InfectionDocument56 pagesPreventing InfectionSol Angelika G. SuropiaNo ratings yet
- Asepsis ReviewerDocument2 pagesAsepsis ReviewerveetshinNo ratings yet
- Infectious Diseases 2Document30 pagesInfectious Diseases 2Hunter BravoNo ratings yet
- MICROPARA - MidtermDocument4 pagesMICROPARA - MidtermclaribelNo ratings yet
- COMMUNICABLE-DISEASE-NURSING-DAY1.pdf - PDF ExpertDocument24 pagesCOMMUNICABLE-DISEASE-NURSING-DAY1.pdf - PDF ExpertFrances Sofia DuranNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Infection and Transmission of Disease: PresentationDocument29 pagesMechanism of Infection and Transmission of Disease: PresentationSuryakant SonwaniNo ratings yet
- Microbio 06 Host Microbe InteractionsDocument41 pagesMicrobio 06 Host Microbe InteractionsArissa Jamelia Lofranco AldeanoNo ratings yet
- 4 - Host Microbe Interaction - 5nov2021Document50 pages4 - Host Microbe Interaction - 5nov2021haiqalfariq07No ratings yet
- Wound Infection Part 1,2Document23 pagesWound Infection Part 1,2Noura RihanNo ratings yet
- Communicable Disease Nursing Ca1 July 2018 5Document461 pagesCommunicable Disease Nursing Ca1 July 2018 5Jordz PlaciNo ratings yet
- NCMA 113 Week 2 AsepsisDocument28 pagesNCMA 113 Week 2 AsepsisLunaNo ratings yet
- AsepsisDocument4 pagesAsepsisJared Elazegui EncioNo ratings yet
- Module - Basic Infection ControlDocument7 pagesModule - Basic Infection ControlJerald FernandezNo ratings yet
- Funda MidtermDocument21 pagesFunda MidtermTrisha ApalisNo ratings yet
- 1 BASIC INFECTION CONTROL HandwashingDocument4 pages1 BASIC INFECTION CONTROL HandwashingLiane BartolomeNo ratings yet
- Host-Parasite Relationship: Yuyun Kusnaningrum Pembimbing DR - Dewi Retnoningsih, SPMKDocument38 pagesHost-Parasite Relationship: Yuyun Kusnaningrum Pembimbing DR - Dewi Retnoningsih, SPMKBagus Ramanto SaputraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Infection Control LecDocument45 pagesChapter 2 Infection Control LecRhea CarinoNo ratings yet
- Asepsis Funda LabDocument2 pagesAsepsis Funda LabdaclangiaNo ratings yet
- Infectious DiseasesDocument4 pagesInfectious DiseasesLily BettyNo ratings yet
- IPC Orientation 2023 IntensiveDocument155 pagesIPC Orientation 2023 Intensivealfio malinaoNo ratings yet
- Communicable Disease ReviewerDocument18 pagesCommunicable Disease ReviewerMicah Jonah Elicaño100% (1)
- Famorca Et Al. 2013. Nursing Care of The CommunityDocument36 pagesFamorca Et Al. 2013. Nursing Care of The CommunityKate SantosNo ratings yet
- Disease & Immunity PDFDocument48 pagesDisease & Immunity PDFS-20127 PADMASHIRI REDDY A/P NADARAJAHNo ratings yet
- CD Respiratory 1Document8 pagesCD Respiratory 1gwen manalonNo ratings yet
- Mekanisme Penyakit InfeksiDocument35 pagesMekanisme Penyakit InfeksiNur FaidahNo ratings yet
- NCM 213 RLE - Principles of Asepsis - 230919 - 123039Document5 pagesNCM 213 RLE - Principles of Asepsis - 230919 - 123039Seungwoo ParkNo ratings yet
- Biological WeaponsDocument43 pagesBiological WeaponsYasmina BadrNo ratings yet
- CHN1 Chapter 12 17 FInalDocument64 pagesCHN1 Chapter 12 17 FInalGALPAO MELISSANo ratings yet
- Rle - Asepsis and Infection ControlDocument36 pagesRle - Asepsis and Infection ControlAngelyn SalimbajonNo ratings yet
- NOTES P6 Pathogenesis and Normal Flora - Student'sDocument42 pagesNOTES P6 Pathogenesis and Normal Flora - Student'sRIZZIE CVNo ratings yet
- AsepsisDocument7 pagesAsepsisAdriane VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Principle of Prevention To Infectious DiseaseDocument37 pagesPrinciple of Prevention To Infectious DiseaseSheryl ElitaNo ratings yet
- Infectious Disease Study NotesDocument56 pagesInfectious Disease Study NotesPierre BenardNo ratings yet
- Opportunistic Mycoses: Infections Due To Fungi of Low Virulence in Patients Who Are Immunologically CompromisedDocument117 pagesOpportunistic Mycoses: Infections Due To Fungi of Low Virulence in Patients Who Are Immunologically Compromisedblue_blooded23No ratings yet
- Week 4. Infection Control Fall 22-23Document40 pagesWeek 4. Infection Control Fall 22-23aisha.hadid31No ratings yet
- Host Pathogen Interaction FinalDocument37 pagesHost Pathogen Interaction FinalSrijan BhattaraiNo ratings yet
- Host Pathogen Interaction FinalDocument37 pagesHost Pathogen Interaction FinalSrijan BhattaraiNo ratings yet
- FundamentalDocument3 pagesFundamentalMarianne june JamilaNo ratings yet
- Definition of TerminologiesDocument9 pagesDefinition of TerminologiestheonlinegeekhubNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Nursing (Midterm Topic 3)Document7 pagesFundamentals of Nursing (Midterm Topic 3)Manuel, Precious Marie B.No ratings yet
- #3.1 FUNDA - Asepsis& InfectionDocument10 pages#3.1 FUNDA - Asepsis& InfectionBritthaney BuladacoNo ratings yet
- Transmission of Infection, The Compromised Host and EpidemiologyDocument53 pagesTransmission of Infection, The Compromised Host and Epidemiologymopper7No ratings yet
- InfectionDocument51 pagesInfectionMASCULINE DEACONNo ratings yet
- Funda NotesDocument4 pagesFunda Notesloviamae.belizarNo ratings yet
- Interaction Between Microbe and HostDocument21 pagesInteraction Between Microbe and HostGil Platon SorianoNo ratings yet
- Foundations in Microbiology: Microbe-Human Interactions: Infection and Disease TalaroDocument46 pagesFoundations in Microbiology: Microbe-Human Interactions: Infection and Disease TalaroOdurNo ratings yet
- Lezon 1Document2 pagesLezon 1Idk UlitNo ratings yet
- NOTES CD Lecture Generic 2022Document182 pagesNOTES CD Lecture Generic 2022Meryville JacildoNo ratings yet
- Clinical Laboratory of San Bernardino, IncDocument40 pagesClinical Laboratory of San Bernardino, Inckharberson1613No ratings yet
- MATERIALS KD. 3.2. Presentation ExpressionsDocument3 pagesMATERIALS KD. 3.2. Presentation ExpressionsBayu Aji SaputraNo ratings yet
- Pinelands National ReserveDocument2 pagesPinelands National ReservesallyNo ratings yet
- L4Tnm-Psa: Product ClassificationDocument4 pagesL4Tnm-Psa: Product Classificationhassan329No ratings yet
- 02 Kinematics VectorsDocument16 pages02 Kinematics VectorsAnna HansenNo ratings yet
- Analog Communication Model ExamDocument20 pagesAnalog Communication Model ExamwalternampimadomNo ratings yet
- Recognition and Extinction of StatesDocument4 pagesRecognition and Extinction of StatesCristy C. BangayanNo ratings yet
- UGWT Lecture 1 To 6Document83 pagesUGWT Lecture 1 To 6Meesam AliNo ratings yet
- Reduced Graphene Oxide Filled Cellulose Films For Flexible Temperature SensorDocument8 pagesReduced Graphene Oxide Filled Cellulose Films For Flexible Temperature SensorMicu CristiNo ratings yet
- Ethylene Dichloride (Edc) / Vinyl Chloride Monomer (VCM) : Customer Process BrochureDocument4 pagesEthylene Dichloride (Edc) / Vinyl Chloride Monomer (VCM) : Customer Process Brochurerkapoor584199No ratings yet
- Campbell Systematic Reviews - 2011 - Morton - Youth Empowerment Programs For Improving Self Efficacy and Self Esteem ofDocument81 pagesCampbell Systematic Reviews - 2011 - Morton - Youth Empowerment Programs For Improving Self Efficacy and Self Esteem ofAndra ComanNo ratings yet
- Bad For Democracy How The Presidency Undermines The Power of The PeopleDocument272 pagesBad For Democracy How The Presidency Undermines The Power of The PeoplePaulNo ratings yet
- Coping Strategies, Optimism, and Life SatisfactionDocument12 pagesCoping Strategies, Optimism, and Life SatisfactionNurulAtiqahAbRajiNo ratings yet
- Assessment 1 IMINT Exercise BRAVODocument6 pagesAssessment 1 IMINT Exercise BRAVOYousef Al HashemiNo ratings yet
- Catalogo Fleximark InglesDocument52 pagesCatalogo Fleximark InglesFrancisco ArauzNo ratings yet
- Requirements Analysis - SPMDocument11 pagesRequirements Analysis - SPMantonyNo ratings yet
- LIC Exp Date: AetnaDocument66 pagesLIC Exp Date: AetnaTrudyNo ratings yet
- Silvia Rey Resume OkDocument3 pagesSilvia Rey Resume Okapi-489656705No ratings yet
- Heredity and EvolutionDocument5 pagesHeredity and EvolutionRahul Ecka100% (3)
- Curriculum Vitae: Pramod - Junior CAM EngineerDocument4 pagesCurriculum Vitae: Pramod - Junior CAM EngineerpramodNo ratings yet
- CPT & Suctioning Rle ExamDocument2 pagesCPT & Suctioning Rle ExamJojo JustoNo ratings yet
- Bharat Heavy Electricals LimitedDocument4 pagesBharat Heavy Electricals LimitedkmbkrisNo ratings yet
- FirstSpear Commercial CatalogDocument23 pagesFirstSpear Commercial CatalogsolsysNo ratings yet
- Cockateil Pairing DetailsDocument4 pagesCockateil Pairing DetailsWaseem UllahNo ratings yet
- Mini WorkshopDocument27 pagesMini Workshopapi-548854218No ratings yet
Funda5 - Asepsis
Funda5 - Asepsis
Uploaded by
bondadlui0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesThis document discusses fundamentals of nursing asepsis. It defines key terms like resident flora, infection, disease, and virulence. It describes the chain of infection and types of microorganisms that cause infections. It also discusses the different types of infections like local vs. systemic. The document outlines nonspecific body defenses against infection. It discusses diagnosing risk for infection and examples of risk factors. Finally, it identifies the 5 moments for proper hand hygiene in nursing care.
Original Description:
Original Title
FUNDA5_ ASEPSIS.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses fundamentals of nursing asepsis. It defines key terms like resident flora, infection, disease, and virulence. It describes the chain of infection and types of microorganisms that cause infections. It also discusses the different types of infections like local vs. systemic. The document outlines nonspecific body defenses against infection. It discusses diagnosing risk for infection and examples of risk factors. Finally, it identifies the 5 moments for proper hand hygiene in nursing care.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesFunda5 - Asepsis
Funda5 - Asepsis
Uploaded by
bondadluiThis document discusses fundamentals of nursing asepsis. It defines key terms like resident flora, infection, disease, and virulence. It describes the chain of infection and types of microorganisms that cause infections. It also discusses the different types of infections like local vs. systemic. The document outlines nonspecific body defenses against infection. It discusses diagnosing risk for infection and examples of risk factors. Finally, it identifies the 5 moments for proper hand hygiene in nursing care.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
FUNDAMENTALS OF NURSING
ASEPSIS
● Exogenous - from hospital environment,
INTRODUCTION
personnel
● Resident flora - collective vegetation in an area
● Infection - growth of microorganisms in body
THE CHAIN OF INFECTION
tissue where they are not usually found
● Disease - detectable alteration in normal tissue
function
● Virulence (strength) - ability of a microorganism to
produce disease
● Communicable disease - transferable to individual
by direct or indirect contact
● Pathogenicity - ability to produce disease;
opportunistic pathogen
● Asepsis - freedom from disease-causing
organisms
● Medical asepsis
○ All practices intended to confine a specific
microorganism to a specific area
○ Limits number, growth, and transmission
of microorganisms
○ Objects referred to as clean or dirty
(soiled, contaminated)
● Surgical asepsis (sterile technique)
○ Practices that keep area or object free of all
microorganisms
○ Practices that destroy all microorganisms
and spores
○ Used for all procedures involving sterile
areas of the body
● Sepsis is the state of infection.
TYPES OF MICROORGANISMS THAT METHOD OF TRANSMISSION
CAUSE INFECTIONS
● Direct transmission
● Bacteria - most common ● Indirect transmission
● Viruses - primarily consist of nucleic acid ○ Vehicle-borne - any substance
● Fungi - yeasts and molds ○ Vector-borne - animal or insect
● Parasites - live on other living organisms ○ Airborne transmission - droplet nuclei
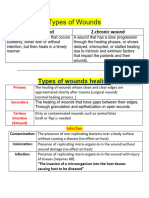
TYPES OF INFECTIONS BODY DEFENSES AGAINST INFECTION
● Colonization of resident flora not infection
● Invasion to unprotected area is infection.
NONSPECIFIC DEFENSES
● Local infection
○ Limited to a specific body part
● Systemic infection - spreads and damages different ● Inflammatory response
body parts ○ Inflammation - local, nonspecific
● Bacteremia - microorganisms in the blood defensive response of the tissues to
● Septicemia - systemic infection resulting from injurious or infectious agent
bacteremia
● Acute infections - appear suddenly or last a short
period of time
● Chronic infections
○ May occur slowly over a long period
○ May lasts months or years
NOSOCOMIAL AND HEALTH
CARE-ASSOCIATED INFECTIONS
● Nosocomial - infections that originate in the
hospital
● Endogenous - from clients themselves
LUIS BRYSON BONDAD 1
FUNDA5: ASEPSIS
NURSING MANAGEMENT
DIAGNOSING
● Risk for Infection
○ State in which an individual is at increased
risk for being invaded by pathogenic
microorganisms
● Risk factors
○ Inadequate primary defenses
○ Inadequate secondary defenses
● Examples
○ Potential Complication of Infection: Fever
○ Imbalanced Nutrition: Less than Body
Requirements
○ Acute Pain
○ Impaired Social Interaction or Social
Isolation
○ Anxiety
5 MOMENTS FOR HAND HYGIENE
1. Before touching a patient
2. Before clean/aseptic procedure
3. After body fluid exposure risk
4. After touching a patient
5. After touching patient surrounding
LUIS BRYSON BONDAD 2
You might also like
- Evidence Plan: Competency Standard: Carpentry Nc2 Unit of Competency: Ways in Which Evidence Will Be CollectedDocument5 pagesEvidence Plan: Competency Standard: Carpentry Nc2 Unit of Competency: Ways in Which Evidence Will Be CollectedBhem Boy100% (1)
- Annexure A Price Schedule STSDocument188 pagesAnnexure A Price Schedule STSRuslan Ibragimov100% (1)
- Communicable Disease Nursing Ca1 July 2018 5 PDFDocument461 pagesCommunicable Disease Nursing Ca1 July 2018 5 PDFJordz Placi100% (3)
- Principles of Asepsis and Sterile TechniquesDocument4 pagesPrinciples of Asepsis and Sterile Techniquesjgcriste93% (14)
- Welding ConsumablesDocument20 pagesWelding ConsumablesThillaivananNo ratings yet
- Retail ProjectDocument114 pagesRetail ProjectSowjanya KunareddyNo ratings yet
- FUNDA SLE - AsepsisDocument8 pagesFUNDA SLE - Asepsisprincessdiane.agripaNo ratings yet
- Infection CompreDocument4 pagesInfection CompreaccachuelaNo ratings yet
- Communicable DiseasesDocument19 pagesCommunicable Diseasesriamanabat100% (5)
- Communicable Dse Nursing Discussion Continuation JKMDocument56 pagesCommunicable Dse Nursing Discussion Continuation JKMKyla Ysabelle PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Lec5 MP Bacteria and DiseaseDocument51 pagesLec5 MP Bacteria and DiseasePriya ManobalNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Nursing Practice - MidtermDocument24 pagesFundamentals of Nursing Practice - MidtermShene Claire VigillaNo ratings yet
- Communicable DiseaseDocument41 pagesCommunicable DiseaseMrz AlzNo ratings yet
- Micro LEC - Principles of Disease and EpidemiologyDocument14 pagesMicro LEC - Principles of Disease and EpidemiologykapeNo ratings yet
- Preventing InfectionDocument56 pagesPreventing InfectionSol Angelika G. SuropiaNo ratings yet
- Asepsis ReviewerDocument2 pagesAsepsis ReviewerveetshinNo ratings yet
- Infectious Diseases 2Document30 pagesInfectious Diseases 2Hunter BravoNo ratings yet
- MICROPARA - MidtermDocument4 pagesMICROPARA - MidtermclaribelNo ratings yet
- COMMUNICABLE-DISEASE-NURSING-DAY1.pdf - PDF ExpertDocument24 pagesCOMMUNICABLE-DISEASE-NURSING-DAY1.pdf - PDF ExpertFrances Sofia DuranNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Infection and Transmission of Disease: PresentationDocument29 pagesMechanism of Infection and Transmission of Disease: PresentationSuryakant SonwaniNo ratings yet
- Microbio 06 Host Microbe InteractionsDocument41 pagesMicrobio 06 Host Microbe InteractionsArissa Jamelia Lofranco AldeanoNo ratings yet
- 4 - Host Microbe Interaction - 5nov2021Document50 pages4 - Host Microbe Interaction - 5nov2021haiqalfariq07No ratings yet
- Wound Infection Part 1,2Document23 pagesWound Infection Part 1,2Noura RihanNo ratings yet
- Communicable Disease Nursing Ca1 July 2018 5Document461 pagesCommunicable Disease Nursing Ca1 July 2018 5Jordz PlaciNo ratings yet
- NCMA 113 Week 2 AsepsisDocument28 pagesNCMA 113 Week 2 AsepsisLunaNo ratings yet
- AsepsisDocument4 pagesAsepsisJared Elazegui EncioNo ratings yet
- Module - Basic Infection ControlDocument7 pagesModule - Basic Infection ControlJerald FernandezNo ratings yet
- Funda MidtermDocument21 pagesFunda MidtermTrisha ApalisNo ratings yet
- 1 BASIC INFECTION CONTROL HandwashingDocument4 pages1 BASIC INFECTION CONTROL HandwashingLiane BartolomeNo ratings yet
- Host-Parasite Relationship: Yuyun Kusnaningrum Pembimbing DR - Dewi Retnoningsih, SPMKDocument38 pagesHost-Parasite Relationship: Yuyun Kusnaningrum Pembimbing DR - Dewi Retnoningsih, SPMKBagus Ramanto SaputraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Infection Control LecDocument45 pagesChapter 2 Infection Control LecRhea CarinoNo ratings yet
- Asepsis Funda LabDocument2 pagesAsepsis Funda LabdaclangiaNo ratings yet
- Infectious DiseasesDocument4 pagesInfectious DiseasesLily BettyNo ratings yet
- IPC Orientation 2023 IntensiveDocument155 pagesIPC Orientation 2023 Intensivealfio malinaoNo ratings yet
- Communicable Disease ReviewerDocument18 pagesCommunicable Disease ReviewerMicah Jonah Elicaño100% (1)
- Famorca Et Al. 2013. Nursing Care of The CommunityDocument36 pagesFamorca Et Al. 2013. Nursing Care of The CommunityKate SantosNo ratings yet
- Disease & Immunity PDFDocument48 pagesDisease & Immunity PDFS-20127 PADMASHIRI REDDY A/P NADARAJAHNo ratings yet
- CD Respiratory 1Document8 pagesCD Respiratory 1gwen manalonNo ratings yet
- Mekanisme Penyakit InfeksiDocument35 pagesMekanisme Penyakit InfeksiNur FaidahNo ratings yet
- NCM 213 RLE - Principles of Asepsis - 230919 - 123039Document5 pagesNCM 213 RLE - Principles of Asepsis - 230919 - 123039Seungwoo ParkNo ratings yet
- Biological WeaponsDocument43 pagesBiological WeaponsYasmina BadrNo ratings yet
- CHN1 Chapter 12 17 FInalDocument64 pagesCHN1 Chapter 12 17 FInalGALPAO MELISSANo ratings yet
- Rle - Asepsis and Infection ControlDocument36 pagesRle - Asepsis and Infection ControlAngelyn SalimbajonNo ratings yet
- NOTES P6 Pathogenesis and Normal Flora - Student'sDocument42 pagesNOTES P6 Pathogenesis and Normal Flora - Student'sRIZZIE CVNo ratings yet
- AsepsisDocument7 pagesAsepsisAdriane VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Principle of Prevention To Infectious DiseaseDocument37 pagesPrinciple of Prevention To Infectious DiseaseSheryl ElitaNo ratings yet
- Infectious Disease Study NotesDocument56 pagesInfectious Disease Study NotesPierre BenardNo ratings yet
- Opportunistic Mycoses: Infections Due To Fungi of Low Virulence in Patients Who Are Immunologically CompromisedDocument117 pagesOpportunistic Mycoses: Infections Due To Fungi of Low Virulence in Patients Who Are Immunologically Compromisedblue_blooded23No ratings yet
- Week 4. Infection Control Fall 22-23Document40 pagesWeek 4. Infection Control Fall 22-23aisha.hadid31No ratings yet
- Host Pathogen Interaction FinalDocument37 pagesHost Pathogen Interaction FinalSrijan BhattaraiNo ratings yet
- Host Pathogen Interaction FinalDocument37 pagesHost Pathogen Interaction FinalSrijan BhattaraiNo ratings yet
- FundamentalDocument3 pagesFundamentalMarianne june JamilaNo ratings yet
- Definition of TerminologiesDocument9 pagesDefinition of TerminologiestheonlinegeekhubNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Nursing (Midterm Topic 3)Document7 pagesFundamentals of Nursing (Midterm Topic 3)Manuel, Precious Marie B.No ratings yet
- #3.1 FUNDA - Asepsis& InfectionDocument10 pages#3.1 FUNDA - Asepsis& InfectionBritthaney BuladacoNo ratings yet
- Transmission of Infection, The Compromised Host and EpidemiologyDocument53 pagesTransmission of Infection, The Compromised Host and Epidemiologymopper7No ratings yet
- InfectionDocument51 pagesInfectionMASCULINE DEACONNo ratings yet
- Funda NotesDocument4 pagesFunda Notesloviamae.belizarNo ratings yet
- Interaction Between Microbe and HostDocument21 pagesInteraction Between Microbe and HostGil Platon SorianoNo ratings yet
- Foundations in Microbiology: Microbe-Human Interactions: Infection and Disease TalaroDocument46 pagesFoundations in Microbiology: Microbe-Human Interactions: Infection and Disease TalaroOdurNo ratings yet
- Lezon 1Document2 pagesLezon 1Idk UlitNo ratings yet
- NOTES CD Lecture Generic 2022Document182 pagesNOTES CD Lecture Generic 2022Meryville JacildoNo ratings yet
- Clinical Laboratory of San Bernardino, IncDocument40 pagesClinical Laboratory of San Bernardino, Inckharberson1613No ratings yet
- MATERIALS KD. 3.2. Presentation ExpressionsDocument3 pagesMATERIALS KD. 3.2. Presentation ExpressionsBayu Aji SaputraNo ratings yet
- Pinelands National ReserveDocument2 pagesPinelands National ReservesallyNo ratings yet
- L4Tnm-Psa: Product ClassificationDocument4 pagesL4Tnm-Psa: Product Classificationhassan329No ratings yet
- 02 Kinematics VectorsDocument16 pages02 Kinematics VectorsAnna HansenNo ratings yet
- Analog Communication Model ExamDocument20 pagesAnalog Communication Model ExamwalternampimadomNo ratings yet
- Recognition and Extinction of StatesDocument4 pagesRecognition and Extinction of StatesCristy C. BangayanNo ratings yet
- UGWT Lecture 1 To 6Document83 pagesUGWT Lecture 1 To 6Meesam AliNo ratings yet
- Reduced Graphene Oxide Filled Cellulose Films For Flexible Temperature SensorDocument8 pagesReduced Graphene Oxide Filled Cellulose Films For Flexible Temperature SensorMicu CristiNo ratings yet
- Ethylene Dichloride (Edc) / Vinyl Chloride Monomer (VCM) : Customer Process BrochureDocument4 pagesEthylene Dichloride (Edc) / Vinyl Chloride Monomer (VCM) : Customer Process Brochurerkapoor584199No ratings yet
- Campbell Systematic Reviews - 2011 - Morton - Youth Empowerment Programs For Improving Self Efficacy and Self Esteem ofDocument81 pagesCampbell Systematic Reviews - 2011 - Morton - Youth Empowerment Programs For Improving Self Efficacy and Self Esteem ofAndra ComanNo ratings yet
- Bad For Democracy How The Presidency Undermines The Power of The PeopleDocument272 pagesBad For Democracy How The Presidency Undermines The Power of The PeoplePaulNo ratings yet
- Coping Strategies, Optimism, and Life SatisfactionDocument12 pagesCoping Strategies, Optimism, and Life SatisfactionNurulAtiqahAbRajiNo ratings yet
- Assessment 1 IMINT Exercise BRAVODocument6 pagesAssessment 1 IMINT Exercise BRAVOYousef Al HashemiNo ratings yet
- Catalogo Fleximark InglesDocument52 pagesCatalogo Fleximark InglesFrancisco ArauzNo ratings yet
- Requirements Analysis - SPMDocument11 pagesRequirements Analysis - SPMantonyNo ratings yet
- LIC Exp Date: AetnaDocument66 pagesLIC Exp Date: AetnaTrudyNo ratings yet
- Silvia Rey Resume OkDocument3 pagesSilvia Rey Resume Okapi-489656705No ratings yet
- Heredity and EvolutionDocument5 pagesHeredity and EvolutionRahul Ecka100% (3)
- Curriculum Vitae: Pramod - Junior CAM EngineerDocument4 pagesCurriculum Vitae: Pramod - Junior CAM EngineerpramodNo ratings yet
- CPT & Suctioning Rle ExamDocument2 pagesCPT & Suctioning Rle ExamJojo JustoNo ratings yet
- Bharat Heavy Electricals LimitedDocument4 pagesBharat Heavy Electricals LimitedkmbkrisNo ratings yet
- FirstSpear Commercial CatalogDocument23 pagesFirstSpear Commercial CatalogsolsysNo ratings yet
- Cockateil Pairing DetailsDocument4 pagesCockateil Pairing DetailsWaseem UllahNo ratings yet
- Mini WorkshopDocument27 pagesMini Workshopapi-548854218No ratings yet